CBSE Class 10 Maths Notes Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Pdf free download is part of Class 10 Maths Notes for Quick Revision. Here we have given NCERT Class 10 Maths Notes Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry. According to new CBSE Exam Pattern, MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths Carries 20 Marks.
CBSE Class 10 Maths Notes Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry
- Position of a point P in the Cartesian plane with respect to co-ordinate axes is represented by the ordered pair (x, y).
- Trigonometry is the science of relationships between the sides and angles of a right-angled triangle.
- Trigonometric Ratios: Ratios of sides of right triangle are called trigonometric ratios.
Consider triangle ABC right-angled at B. These ratios are always defined with respect to acute angle ‘A’ or angle ‘C. - If one of the trigonometric ratios of an acute angle is known, the remaining trigonometric ratios of an angle can be easily determined.
- How to identify sides: Identify the angle with respect to which the t-ratios have to be calculated. Sides are always labelled with respect to the ‘θ’ being considered.
Let us look at both cases:
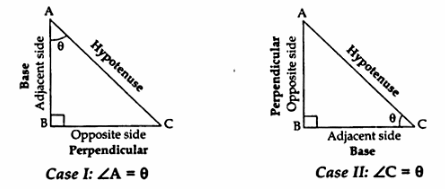
In a right triangle ABC, right-angled at B. Once we have identified the sides, we can define six t-Ratios with respect to the sides.
| case I | case II |
| (i) sine A = \(\frac { perpendicular }{ hypotenuse } =\frac { BC }{ AC } \) | (i) sine C = \(\frac { perpendicular }{ hypotenuse } =\frac { AB }{ AC } \) |
| (ii) cosine A = \(\frac { base }{ hypotenuse } =\frac { AB }{ AC } \) | (ii) cosine C = \(\frac { base }{ hypotenuse } =\frac { BC }{ AC } \) |
| (iii) tangent A = \(\frac { perpendicular }{ base } =\frac { BC }{ AB } \) | (iii) tangent C = \(\frac { perpendicular }{ base } =\frac { AB }{ BC } \) |
| (iv) cosecant A = \(\frac { hypotenuse }{ perpendicular } =\frac { AC }{ BC } \) | (iv) cosecant C = \(\frac { hypotenuse }{ perpendicular } =\frac { AC }{ AB } \) |
| (v) secant A = \(\frac { hypotenuse }{ base } =\frac { AC }{ AB } \) | (v) secant C = \(\frac { hypotenuse }{ base } =\frac { AC }{ BC } \) |
| (v) cotangent A = \(\frac { base }{ perpendicular } =\frac { AB }{ BC } \) | (v) cotangent C = \(\frac { base }{ perpendicular } =\frac { BC }{ AB } \) |
Note from above six relationships:
cosecant A = \(\frac { 1 }{ sinA }\), secant A = \(\frac { 1 }{ cosineA }\), cotangent A = \(\frac { 1 }{ tanA }\),
However, it is very tedious to write full forms of t-ratios, therefore the abbreviated notations are:
sine A is sin A
cosine A is cos A
tangent A is tan A
cosecant A is cosec A
secant A is sec A
cotangent A is cot A
TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES
An equation involving trigonometric ratio of angle(s) is called a trigonometric identity, if it is true for all values of the angles involved. These are:
tan θ = \(\frac { sin\theta }{ cos\theta } \)
cot θ = \(\frac { cos\theta }{ sin\theta } \)
- sin² θ + cos² θ = 1 ⇒ sin² θ = 1 – cos² θ ⇒ cos² θ = 1 – sin² θ
- cosec² θ – cot² θ = 1 ⇒ cosec² θ = 1 + cot² θ ⇒ cot² θ = cosec² θ – 1
- sec² θ – tan² θ = 1 ⇒ sec² θ = 1 + tan² θ ⇒ tan² θ = sec² θ – 1
- sin θ cosec θ = 1 ⇒ cos θ sec θ = 1 ⇒ tan θ cot θ = 1
ALERT:
A t-ratio only depends upon the angle ‘θ’ and stays the same for same angle of different sized right triangles.
Value of t-ratios of specified angles:
| ∠A | 0° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 90° |
| sin A | 0 | \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) | \(\frac { 1 }{ \sqrt { 2 } } \) | \(\frac { \sqrt { 3 } }{ 2 } \) | 1 |
| cos A | 1 | \(\frac { \sqrt { 3 } }{ 2 } \) | \(\frac { 1 }{ \sqrt { 2 } } \) | \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) | 0 |
| tan A | 0 | \(\frac { 1 }{ \sqrt { 3 } } \) | 1 | √3 | not defined |
| cosec A | not defined | 2 | √2 | \(\frac { 2 }{ \sqrt { 3 } } \) | 1 |
| sec A | 1 | \(\frac { 2 }{ \sqrt { 3 } } \) | √2 | 2 | not defined |
| cot A | not defined | √3 | 1 | \(\frac { 1 }{ \sqrt { 3 } } \) | 0 |
The value of sin θ and cos θ can never exceed 1 (one) as opposite side is 1. Adjacent side can never be greater than hypotenuse since hypotenuse is the longest side in a right-angled ∆.
‘t-RATIOS’ OF COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES
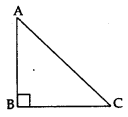
If ∆ABC is a right-angled triangle, right-angled at B, then
∠A + ∠C = 90° [∵ ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180° angle-sum-property]
or ∠C = (90° – ∠A)
Thus, ∠A and ∠C are known as complementary angles and are related by the following relationships:
sin (90° -A) = cos A; cosec (90° – A) = sec A
cos (90° – A) = sin A; sec (90° – A) = cosec A
tan (90° – A) = cot A; cot (90° – A) = tan A
Class 10 Maths Notes
- Chapter 1 Real Numbers Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 2 Polynomials Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 3 Pair of Linear equations in Two Variables Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 6 Triangles Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 10 Circles Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 11 Constructions Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 12 Areas related to Circles Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 14 Statistics Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 15 Probability Class 10 Notes