NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals.
NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
Question 1.
Given below from (i) to (iv) are some food items.
(i) Boiled and mashed potato
(ii) Glucose solution
(iii) A slice of bread
(iv) Mustard oil
Which of the above will give blue-black colour when tested with iodine?
(a) (i) and(ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Solution:
(b) When iodine is added to starch, it turns blue-black in colour. Potato and bread are rich in starch. Therefore, boiled and mashed potato and a slice of bread turn blue-black in colour when tested with iodine. Glucose solution does not change colour because it is digestive product of starch.
Question 2.
Which of the following pair of teeth differ in structure but are similar in function?
(a) Canines and incisors
(b) Molars and premolars
(c) Incisors and molars
(d) Premolars and canines
Solution:
(b) Our teeth cut, tear and grind the food before we swallow it. There are four types of teeth in our mouth –
- Incisors – These are the front eight teeth, four in upper and four in lower jaw. These are well adapted for cutting and biting of food items.
- Canines – There are four canines, one canine each on either side of each jaw. These teeth are well adapted to hold and tear the food.
- Premolars – There are eight premolars in total, two premolars in each half of the both upper and lower jaws. These are well adapted to crush and grind food.
- Molars – There are twelve molars, three in each half of the both upper and lower jaws. These are well adapted to crush and grind the food.
Question 3.
Read carefully the terms given below. Which of the following sets is the correct combination of organs that do not carry out any digestive functions?
(a) Oesophagus, Large intestine, Rectum
(b) Buccal cavity, Oesophagus, Rectum
(c) Buccal cavity. Oesophagus, Large intestine
(d) Small intestine, Large intestine. Rectum
Solution:
(a) Oesophagus gently pushes food down to the stomach in a wave like action called peristalsis. No digestion takes place in oesophagus.
In large intestine, undigested food enters where water is absorbed from it. No digestion takes place in large intestine.
In rectum, semi-solid residue is stored and is finally thrown out of the body through the anus in the form of faeces. No digestion takes place in rectum.
Question 4.
The swallowed food moves downwards in the alimentary canal because of
(a) force provided by the muscular tongue
(b) the flow of water taken with the food
(c) gravitational pull
(d) the contraction of muscles in the wall of food pipe.
Solution:
(d) The muscles of oesophagus gently push the food down to the stomach in a wave-like action (contractions and relaxations) called peristalsis. Actually, this movement takes place throughout the alimentary canal to push the food forward.
Question 5.
The acid present in the stomach
(a) kills the harmful bacteria that may enter along with the food
(b) protects the stomach lining from harmful substances
(c) digests starch into simpler sugars
(d) makes the medium alkaline.
Solution:
(a) Hydrochloric acid (HCI) present in stomach kills the harmful bacteria that enter stomach along with food and makes the medium in the stomach acidic.
Question 6.
The finger-like outgrowths of Amoeba help to ingest food. However, the finger-like outgrowths of human intestine help to
(a) digest the fatty food substances
(b) make the food soluble
(c) absorb the digested food
(d) absorb the undigested food.
Solution:
(c) Finger-like outgrowths called villi are present in small intestine. They increase the surface area of small intestine for the absorption of digested food.
Question 7.
Read the following statements with reference to the villi of small intestine.
(i) They have very thin walls.
(ii) They have a network of thin and small blood vessels close to the surface.
(iii) They have small pores through which food can easily pass.
(iv) They are finger-like projections.
Identify those statements which enable the villi to absorb digested food.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Solution:
(a) Villi are the numerous, small finger-like projections present in the inner walls of the small intestine. Villi increase the surface area of small intestine for absorption of digested food due to their thin, finger-like shape. Each villus has a network of thin and small blood vessels close to its surface. The food absorbed oh the surface of villus passes into the blood in the capillaries. Villi do not have any pores.
Question 8.
The false feet of Amoeba are used for
(a) movement only
(b) capture of food only
(c) capture of food and movement
(d) exchange of gases only.
Solution:
(c) False feet or pseudopodia of Amoeba are used for both movement and capture of food. Exchange of gases takes place by body wall through diffusion.
Question 9.
The enzymes present in the saliva convert
(a) fats into fatty acids and glycerol
(b) starch into simple sugars
(c) proteins into amino acids
(d) complex sugars into simple sugars.
Solution:
None of these: The fluids secreted by the salivary glands constitute saliva. Saliva is slightly acidic. It contains a digestive enzyme called salivary amylase, which helps in the breakdown of starch (and not any other complex sugar) into simpler sugars (oligosaccharides) and not into simple sugars (monosaccharides).
Question 10.
Cud is the name given to the food of ruminants which is
(a) swallowed and undigested
(b) swallowed and partially digested
(c) properly chewed and partially digested
(d) properly chewed and completely digested.
Solution:
(b)
Question 11.
Choose the correct order of terms that describe the process of nutrition in ruminants.
(a) Swallowing→ partial digestion →chewing of cud→complete digestion
(b) Chewing of cud → swallowing → partial digestion → complete digestion
(c) Chewing of cud → swallowing → mixing with digestive juices → digestion
(d) Swallowing →chewing and mixing → partial digestion → complete digestion
Solution:
(a)
Question 12.
Cellulose-rich food substances are good source of roughage in human beings because
(a) human beings do not have cellulose digesting enzymes
(b) cellulose gets absorbed in the human blood and converts into fibres
(c) the cellulose-digesting bacteria convert cellulose into fibres
(d) cellulose breaks down into smaller components which are egested as roughage.
Solution:
(a) Human beings do not have cellulose-digesting enzymes in their bodies and are therefore unable to digest cellulose. Since it is not digested, it passes down the entire digestive tract from mouth to anus. It acts as roughage, adds bulk to the food and helps the body to easily get rid of undigested food.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 13.
Name the parts of the alimentary canal where
(i) water gets absorbed from undigested food
(ii) digested food gets absorbed
(iii) taste of the food is perceived
(iv) bile juice is produced.
Solution:
(i) Large intestine
(ii) Small intestine
(iii) Tongue
(iv) Liver
Question 14.
Mark the following statements as true or false. If false, write the correct statements.
(a) Tongue is attached to the roof of the mouth cavity at the back.
(b) The large intestine is longer and wider than the small intestine of the human alimentary canal.
(c) Mucus protects the stomach lining from damage.
(d) All heterotrophs have a similar basic process of nutrition.
Solution:
(a) False — Tongue is attached to the floor of the mouth cavity at the back.
(b) False – The large intestine is shorter and wider than the small intestine of the human alimentary canal.
(c) True
(d) True
Question 15.
Choose the odd one out from each group and give reasons.
(i) Liver, salivary gland, starch, gall bladder
(ii) Stomach, liver, pancreas, salivary gland
(iii) Tongue, absorption, taste, swallow
(iv) Oesophagus, small intestine, large intestine, rectum
Solution:
(i) Starch is the odd one out because it is a complex sugar whereas all others i.e., liver, salivary gland and gall bladder are body organs.
(ii) Stomach is the odd one out because in stomach, digestion of food takes place. Liver, pancreas and salivary glands secrete bile, pancreatic juice and saliva respectively but digestion of food does not take place inside these organs.
(iii) Absorption is the odd one out because tongue (organ), taste (sense) and swallow (process) all are associated with mouth while absorption process does not occur in mouth.
(iv) Small intestine is the odd one out because no digestive juices are released by other parts and hence no digestion occurs in other parts.
Question 16.
You were blindfolded and asked to identify the drinks provided in two different glasses. You could identify drink A as lime juice and B as bitter gourd juice. How could you do it inspite of being blindfolded?
Solution:
We are able to identify different tastes with the help of different types of taste buds present in the tongue. Tongue is a fleshy muscular organ that bears a large number of taste buds that detect different tastes of food such as sweet, salty, bitter, sour, etc.
Question 17.
Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
(a) The alimentary canal stretches from_____to _____.
(b) Teeth are rooted in separate _____ in between the_____.
(c) Digestion of food starts in _____ and gets completed in_____.
(d) _____ is the largest gland in the human body.
Solution:
(a) mouth, anus
(b) sockets, gums
(c) buccal cavity, small intestine
(d) Liver
Question 18.
Following statements describe the five steps in animal nutrition. Read each statement and give one word for each statement. Write the terms that describe each process.
(a) Transportation of absorbed food to different parts of body and their utilisation.
(b) Breaking of complex food substances into simpler and soluble substances.
(c) Removal of undigested and unabsorbed solid residues of food from the body.
(d) Taking food into the body.
(e) Transport of digested and soluble food from the intestine to blood vessels.
Solution:
(a) Assimilation
(b) Digestion
(c) Egestion
(d) Ingestion
(e) Absorption
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 19.
Match the animals in column I with their mode of feeling listed in Column II
| Column I Animals |
Column II Mode of feeding |
||
| (a) | House fly | (i) | Biting and chewing |
| (b) | Cockroach | (ii) | Suckling |
| (c) | Mosquito | (iii) | Sponging |
| (d) | Infants | (iv) | Sucking |
Solution:
(a) – (iii)
(b) – (i)
(c) – (iv)
(d) – (ii)
Question 20.
Boojho took some grains of boiled rice in test tube ‘A’ and Paheli took boiled and chewed rice in test tube ‘B’. Both of them poured 1 -2 drops of iodine solution into the test tube and observed the colour change. What colour change would they have observed? Give reasons for your answer.
Solution:
After pouring iodine solution in test tube ‘A’, its colour will change to blue-black due to the presence of starch in boiled rice. In test tube B, colour of iodine will not change because of digestion of starch into sugars by the action of salivary amylase enzyme during chewing.
Question 21.
‘A’ got her gall bladder removed surgically as she was diagnosed with stones in her gall bladder. After the surgery, she faced problems in digestion of certain food items when consumed in bulk. Can you tell which kind of food items would they be and why?
Solution:
The food items would be fats because bile juice which is stored by the gall bladder helps in the digestion of fats. Removal of gall bladder leads to difficulty in digestion of fats.
Question 22.
Match the organs in column I with the words listed in column II.
| Column 1 | Column II | ||
| (a) | Rectum | (i) | Mucus |
| (b) | Gall bladder | (ii) | Villi |
| (c) | Stomach | (iii) | Taste buds |
| (d) | Tongue | (iv) | Faeces |
| (e) | Small intestine | (v) | Bile juice |
Solution:
(a) (iv)
(b) (v)
(c) (i)
(d) (iii)
(e) (ii)
Question 23.
Ruminants such as cows and buffaloes swallow their food hurriedly and then sit restfully and chew their food. Can you reason why?
Solution:
Ruminants are hooved plant eating animals (e.g., cattle, sheep, goat etc.) possess a unique digestive system. Their stomach is divided into four compartments – rumen, reticulum, omasum and abomasum. During grazing, they quickly swallow plenty of grass without much chewing. This is an adaptation by which they need very little time for feeding. The half-chewed food is swallowed and it first goes from mouth to the rumen, the first chamber of the stomach. Here it is acted upon by bacteria and microorganisms. This half-digested food then goes to the second muscular chamber-the reticulum, from where it is sent back to the mouth as cud to be chewed again. After completely chewed, the food is sent to other parts of stomach i.e., abomasum and omasum; and ultimately to intestine for complete digestion and absorption of food.
Question 24.
Boojho and Paheli were eating their food hurriedly so that they could go out and play during the recess. Suddenly, Boojho started coughing violently. Think of the reasons why he was coughing and discuss with your friends.
Solution:
Pharynx is a common passage for both food and air. A cartilaginous flap called epiglottis closes the opening of wind pipe while eating and thus prevents the entry of food into the wind pipe. Sometimes, when one eats hurriedly, talks or laughs while eating, the epiglottis remains open. The food may enter the wind pipe and coughing helps to clear it.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 25.
Fill in the blanks using the words listed below.
[water, front, intestinal, salts, pseudopodia, back, vacuole]
(a) The digestion of all food components is completed by the _____ juice.
(b) Large intestine absorbs_____ and some from the undigested food.
(c) Tongue is attached at the_____ to the floor of the mouth cavity and is free at the
(d) Amoeba pushes out_____ around the food and traps it in a food_____.
Solution:
(a) intestinal
(b) water, salts
(c) back, front
(d) pseudopodia, vacuole
Question 26.
Label the given figure 2.1 as directed in (i) to (iv) and give the name of each type of teeth.
(i) The cutting and biting teeth as ‘A’
(ii) The piercing and tearing teeth as ‘B’
(iii) The grinding and chewing teeth as ‘C’
(iv) The grinding teeth present only in adults as’D’
Solution:
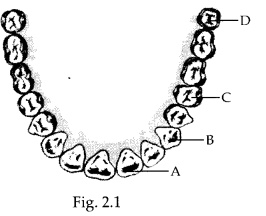
A – Incisors, B – Canines
C – Premolars D – Molars
Question 27.
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow it.
Bile juice is stored in a sac called, gall bladder, located near its organ of secretion, liver. The gall bladder releases the bile juice into the small intestine whenever food reaches there. Though bile juice is devoid of any digestive enzymes, it is required for the digestion of fats. The fats cannot be digested easily because they are insoluble in water and are present as large globules. Bile juice breaks down big fat droplets into smaller droplets. These are then easily digested by the enzymes released from the pancreas.
(a) Which organ secretes the bile juice?
(b) Why is digestion of fats difficult as compared to that of other nutrients?
(c) How does bile juice help in digestion of fat?
(d) Where is the digestion of fat completed?
(e) Does bile juice digest fat completely?
Solution:
(a) Liver secretes the bile juice.
(b) Digestion of fats is difficult because fats are insoluble in water and are present as large globules.
(c) Bile juice breaks down big fat droplets into smaller droplets so that they can be easily digested.
(d) Digestion of fat is completed in small intestine.
(e) No. Bile juice does not contain any enzyme and therefore, it does not digest fat.
Question 28.
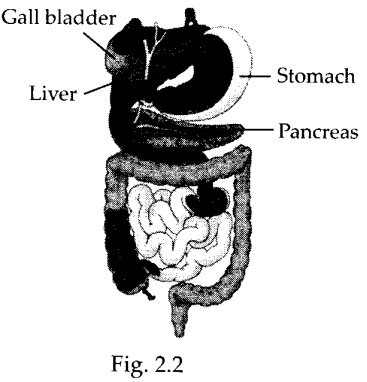
Label the following parts in the figure 2.2 and name them.
(a) The largest gland in our body.
(b) The organ where protein digestion starts.
(c) The organ that releases digestive juice into the small intestine.
(d) The organ where bile juice gets stored.
Solution:
Question 29.
Open your mouth, look into a mirror and try to count the different types of teeth in your mouth. Compare them with figure 2.3 on page 13 of your NCERT textbook. Record your observations in the given table
| Type of teeth | Number of teeth | |
| In my mouth | In the figure | |
| Incisors | ||
| Canines | ||
| Premolars | ||
| Molars | ||
(a) Did you observe any difference in the number of teeth? If yes, could you identify which type of teeth showed the difference?
(b) Compare the number and type of teeth in an adult (say your parents or cousins who have reached the age of 25-30 or more). Note your observation.
Solution:
| Type of teeth | Number of teeth | |
| In my mouth | In the figure | |
| Incisors | 8 | 8 |
| Canines | 4 | 4 |
| Premolars | 8 | 8 |
| Molars | 8 | 12 |
(a) Yes, molar teeth showed the difference in number of teeth.
(b) A child (of class 7) has 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars and 8 molars in his mouth whereas an adult who has reached the age of 25-30 has 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars and last 4 molars are added after the age of 18 years in most human beings.
Question 30.
Solve the crossword given in figure 2.3.
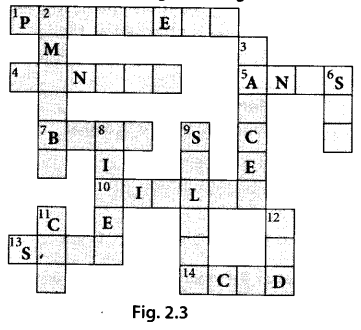
Solution:

NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions
- Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 Heat
- Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes
- Chapter 7 Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Chapter 8 Winds, Storms and Cyclones
- Chapter 9 Soil
- Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
- Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants
- Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants
- Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- Chapter 14 Electric Current and Its Effects
- Chapter 15 Light
- Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource
- Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline
- Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.