NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants.
NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Organisms which prepare food for themselves using simple naturally available raw materials are referred to as
(a) heterotrophs
(b) autotrophs
(c) parasites
(d) saprophytes.
Solution:
(b) Autotrophs are those organisms which are able to prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis, e.g., green plants. Photosynthesis (Gk photos – light, synthesis) is an enzyme regulated anabolic process of manufacturing of organic compounds inside the chlorophyll containing cells from carbon dioxide and water with the help of sunlight as a source of energy.
Question 2.
In the absence of which of the following, will photosynthesis not occur in leaves?
(a) Guard cells
(b) Chlorophyll
(c) Vacuole
(d) Space between cells
Solution:
(b) Chlorophyll is the green photosynthetic pigment, which is present in the cells of green leaves. It traps solar energy. This energy is then used to synthesise food from Co2 and water by the process of photosynthesis.
Question 3.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
(i) All green plants can prepare their own food.
(ii) Most animals are autotrophs.
(iii) Carbon dioxide is not required for photosynthesis.
(iv) Oxygen is liberated during photosynthesis.
Choose the correct answer from the options below.
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) only
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (ii)
Solution:
(a) Animals cannot manufacture their own food so they are heterotrophs, not autotrophs.
Carbon dioxide is a raw material for photosynthesis. In the process of photosynthesis, plants manufacture organic compounds, inside the chlorophyll containing cells from carbon dioxide and water with the help of solar energy. So, Co2 is essential for photosynthesis.
Question 4.
Pitcher plant traps insects because it
(a) is a heterotroph
(b) grows in soils which lack in nitrogen
(c) does not have chlorophyll
(d) has a digestive system like human beings.
Solution:
(b) Pitcher plant (Nepenthes) is an insectivorous plant. It grows in the soils that are usually nitrogen-deficient. It is capable of photosynthesising and manufactures its carbohydrate food. But in order to obtain its nitrogen nutrition it traps and digests insects.
Question 5.
The term that is used for the mode of nutrition in yeast, mushroom and bread mould is
(a) autotrophic
(b) insectivorous
(c) saprophytic
(d) parasitic.
Solution:
(c) Bread mould, yeast and mushroom are all fungi that derive their food from non¬living organic matter. They secrete digestive juices on organic matter which aid in its extracellular digestion and convert it into soluble form. Then they absorb this simplified soluble form of food through their body. This method of getting nutrients in the form of simple soluble form (liquid) is known as saprophytic nutrition.
Question 6.
When we observe the lower surface of a leaf through a magnifying lens we see numerous small openings. Which of the following is the term given to such openings?
(a) Stomata
(b) Lamina
(c) Midrib
(d) Veins
Solution:
(a) Lamina is the green expanded part of the leaf with veins and veinlets. Midrib is middle prominent vein. Veins provide rigidity to leaf and act as channels for transport of water, minerals and food materials. Stomata are the minute pores usually located on the underside of the leaves and take part in exchange of gases (02 and C02) during photosynthesis and respiration. They are surrounded by guard cells.
Question 7.
Two organisms are good friends and live together. One provides shelter, water and nutrients while the other prepares and provides food. Such an association of organisms is termed as
(a) saprophyte
(b) parasite
(c) autotroph
(d) symbiosis.
Solution:
(d) Symbiosis is a special association where two different organisms live together and are mutually benefited. E.g., lichen is a symbiotic association between algae and fungus where fungal partner provides water, minerals and shelter to algal partner and algal partner provides nutrition (food) to fungal partner.
Question 8.
Which of the foliowing raw materials is available in the air for photosynthesis?
(a) Oxygen
(b) Carbon dioxide
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Hydrogen
Solution:
(b) Carbon dioxide is the raw material for photosynthesis which is present in air. Photosynthesis is an enzyme regulated anabolic process of manufacture of organic compounds inside the chlorophyll containing cells from carbon dioxide and water with the help of sunlight as a source of energy.
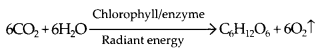
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 9.
Potato and ginger are both underground parts that store food. Where is the food prepared in these plants?
Solution:
In potato and ginger plants, leaves are above ground whereas underground stems store the reserve food material. The leaves prepare food through photosynthesis and transport it to the underground parts for storage.
Question 10.
Photosynthesis requires chlorophyll, and a few other raw materials. Add the missing raw materials to the list given below:
Water, minerals, __ (a)___,___(b)___
Solution:
(a) Sunlight energy
(b) Carbon dioxide
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 11.
A goat eats away all the leaves of a small plant (balsam). However, in a few days, new leaves could be seen sprouting in the plant again. How did the plant survive without leaves?
Solution:
Balsam is a small herbaceous plant. It has green stems which can carry out photosynthesis. Hence, even in the absence of leaves balsam plant could survive due to its photosynthesising stems.
Question 12.
Unscramble the following to form terms related to modes of nutrition.
(i) RASPAEIT
(ii) ROPEHYTSAP
(iii) TOROPHAUT
(iv) SIBIOMSYS
Solution:
(i) Parasite
(ii) Saprophyte
(iii) Autotroph
(iv) Symbiosis
Question 13.
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plant growth. But farmers who cultivate pulse crops like green gram, bengal gram, black gram, etc. do not apply nitrogenous fertilisers during cultivation. Why?
Solution:
Pulse crops like green gram, bengal gram, black gram etc., are the leguminous crops which have symbiotic association with Rhizobium bacteria. Rhizobium converts the atmospheric nitrogen into a soluble form (nitrogen fixation) in the soil. Plants absorb this soluble form of nitrogen from the soil. Thus, growing of leguminous crops helps to enrich soil with nitrogen and there is no need to apply nitrogenous fertilisers to the leguminous crops.
Question 14.
Wheat dough if left in the open, after few days, starts to emit a foul smell and becomes unfit for use. Give reason.
Solution:
Carbohydrate in wheat dough encourages growth of yeast and other saprophytic fungi which breakdown carbohydrates and emit a foul smell.
Question 15.
Sunlight, chlorophyll, carbon dioxide, water and minerals are raw materials essential for photosynthesis. Do you know where they are available? Fill in the blanks with the appropriate raw ipaterials.
(a) Available in the plant: _______
(b) Available in the soil : ________
(c) Available in the air: _________
(d) Available during day: ________
Solution:
(a) Chlorophy II
(b) Water, minerals
(c) Carbon dioxide
(d) Sunlight
Question 16.
Observe the diagram given as figure 1.1 and label the following terms given in the box.
[Stomatal opening, Guard cell]
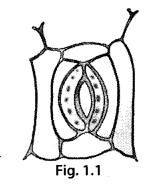
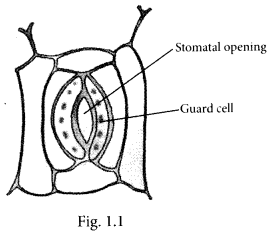
Solution:
The labelled diagram is as follows:
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 17.
Match the organisms given in column I with their mode of nutrition given in column II.
| Column 1 | Column II | ||
| (a) | Mango tree | (i) | Insectivorous plant |
| (b) | Mushroom | (ii) | Heterotroph |
| (c) | Pitcher plant | (iii) | Autotroph |
| (d) | Cuscuta | (iv) | Saprophyte |
| (e) | Elephant | (v) | Parasitic |
Solution:
(a) (iii)
(b) (iv)
(c) (i)
(d) (v)
(e) (ii)
Question 18.
Wild animals like tiger, wolf, lion and leopard do not eat plants. Does this mean that they can survive without plants? Can you provide a suitable explanation?
Solution:
Wild animals like tiger, wolf, lion and leopard do not eat plants. They are carnivorous i.e., they hunt and eat animals which can be herbivorous or carnivorous. Herbivorous animals obtain their food directly from plants i.e., they eat plants or plant products. If there are no plants, herbivorous animals will not survive and thus carnivorous animals feeding on them will also not survive. It implies that all the animals depend on plants directly or indirectly for food.
Question 19.
Fill in the blanks of the paragraph given below with the words provided in the box.
[ Chlorophyll, Energy, Food, Carbon dioxide. Water, Photosynthesis]
(Note: A word can be used more than once)
Leaves have a green pigment called ____(a)_____ which captures _____(b) _____ from sunlight. This ______(c)________ is used in the process of _____(d)_____ and along with other raw materials like ______ (e) _____ and ____ (f) ______ synthesises ______.
Solution:
(a) chlorophyll
(b) energy
(c) energy
(d) photosynthesis
(e) carbon dioxide
(f) water
(g) food
Question 20.
Spot as many organisms as possible in the puzzle given as figure 1.2 by encircling them as shown. Write the names on a sheet of paper and categorise them into autotrophs and heterotrophs. Classify the heterotrophs into herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and saprophytes.

Solution:
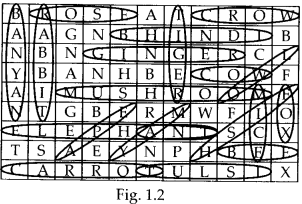
Autotrophs – rose, mango, bhindi, carrot, banyan, tulsi, ginger, yam
Heterotrophs – elephant, ant, yeast, tiger, mushroom, fox, mice, owl, cow, crow, rabbit, bee, fish, ape
Herbivores – elephant, cow, rabbit, bee
Carnivores – tiger
Omnivores – ant, mice, owl, crow, fox, ape
Saprophytes – mushroom, yeast
Note: Fish can be herbivore, carnivore or omnivore depending on the species.
Question 21.
Can you give me a name?
Solve each of the following riddles by writing the name of the organism and its mode of nutrition. One riddle is solved to help you.
(a) I am tall but I cannot move. I am green and can prepare my own food. Tree, autotroph
(b) I live in water; people keep me in an aquarium and feed me. _______ , _________
(c) I am small and I can fly. I disturb your sleep, bite you and suck your blood which is my food. _______ , _________
(d) I am white and soft. I grow well in the rainy seasons. Children pluck me from the ground and admire me. I absorb nutrients from decomposed dead parts of plants and animals in the soil. _______ , _________
Solution:
(b) Fish, heterotroph
(c) Mosquito, parasite
(d) Mushroom, saprophyte
NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions
- Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 Heat
- Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes
- Chapter 7 Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Chapter 8 Winds, Storms and Cyclones
- Chapter 9 Soil
- Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
- Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants
- Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants
- Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- Chapter 14 Electric Current and Its Effects
- Chapter 15 Light
- Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource
- Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline
- Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.