NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants.
NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants
Multiple Choice Question
Question 1.
The muscular tube through which stored urine is passed out of the body is called
(a) kidney
(b) ureter
(c) urethra
(d) urinary bladder.
Solution:
(c) Human excretory system comprises ‘ of a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a urinary bladder, a urethra and urinary opening. Urine passes from the kidneys through two tubes ‘ called ureters into an elastic sac called the urinary bladder. The urinary bladder stores the urine temporarily, which is then excreted i through the urethra.
Question 2.
They are pipe-like, consisting of a group of specialised cells. They transport substances
and form a two-way traffic in plants. Which of the following terms qualify for the features mentioned above?
(a) Xylem tissue
(b) Vascular tissue
(c) Root hair
(d) Phloem tissue
Solution:
(d) Phloem tissue consists of a group of specialised cells. Sieve tubes are elongated tubular conducting channels of phloem through which food is transported. The contents of phloem can move in the upward as well as in the downward direction. Therefore, they form two-way traffic in plants.
Question 3.
The absorption of. nutrients and exchange of respiratory gases between blood and tissues takes place in
(a) veins
(b) arteries
(c) heart
(d) capillaries.
Solution:
(d) Capillaries have thin walls, they pick up carbon dioxide and other wastes from every cell and pass them into the alveoli and kidneys respectively. They also pick up oxygen and digested food from the alveoli and small intestine respectively and pass them to each and every body cell for cellular respiration.
Question 4.
In which of the following parts of human body are sweat glands absent?
(a) Scalp
(b) Armpits
(c) Lips
(d) Palms
Solution:
(c) Lips do not secrete sweat because of the absence of sweat glands.
Question 5.
In a tall tree, which force is responsible for pulling water and minerals from the soil?
(a) Gravitational force
(b) Transportation force
(c) Suction force
(d) Conduction force
Solution:
(c) The root cells absorb water and mineral salts continuously from the soil. The
evaporation of water from the leaf surfaces during the process of transpiration produces a suction force (transpiration pull) that causes the water to move upwards.
Question 6.
Aquatic animals like fish excrete their wastes in gaseous form as
(a) oxygen
(b) hydrogen
(c) ammonia
(d) nitrogen.
Solution:
(c) Most aquatic animals, e.g., bony fish, Hydra, leech, crocodile etc. excrete the waste as ammonia gas, which easily dissolves in water. These animals are referred to as ammonotelic animals and excretion of ammonia is termed as ammonotelism.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 7.
Veins have valves which allow blood to flow only in one direction. Arteries do not have valves. Yet the blood flows in one direction only. Can you explain why?
Solution:
Blood flow in arteries is rapid as the blood in them is under great pressure. Thick elastic walls of arteries are not collapsible and maintain one direction rapid flow.
Question 8.
What is the special feature present in a human heart which does not allow mixing of blood when oxygen-rich and carbon dioxide-rich blood reach the heart?
Solution:
Human heart is four chambered consisting of two atria and two ventricles. The left side of the heart receives oxygen-rich blood whereas the right side of the heart receives carbon dioxide-rich blood. The left and right sides of the heart are completely separated from each other by a muscular septum, which prevents the mixing of oxygen-rich and carbon-dioxide-rich blood.
Question 9.
Name the organ which is located in the chest cavity with its lower tip slightly tilted towards the left.
Solution:
Heart.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 10.
Look at figure 11.1. Draw another figure of the same set-up as would be observed after a few hours.
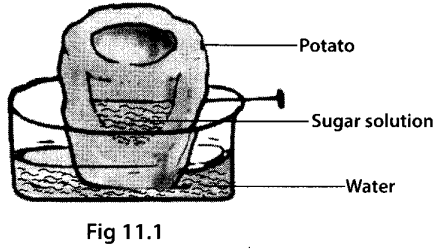
Solution:
After few hours there occurs a rise in the level of sugar solution in potato and fall in the level of water in the beaker, which indicates that the solution has absorbed water from the beaker. The entry of water into the sugar solution occurs by the process of osmosis.
Question 11.
Arrange the following statements in the correct order in which they occur during the formation and removal of urine in human beings.
(a) Ureters carry urine to the urinary bladder.
(b) Wastes dissolved in water are filtered out as urine in the kidneys.
(c) Urine stored in urinary bladder is passed out through the urinary opening at the end of the urethra.
(d) Blood containing useful and harmful substances reaches the kidneys for filtration.
(e) Useful substances are absorbed back into the blood.
Solution:
The correct order of the above given statements is as follows :
(d) Blood containing useful and harmful substances reaches the kidneys for filtration.
(e) Useful substances are absorbed back into the blood.
(b) Wastes dissolved in water are filtered out as urine in the kidneys.
(a) Ureters carry urine to the urinary bladder.
(c) Urine stored in urinary bladder is passed out through the urinary opening at the end of the urethra.
Question 12.
Paheli uprooted a rose plant from the soil. Most of the root tips, with root hair got left behind in the soil. She planted it in a pot with new soil and watered it regularly. Will the plant grow or die? Give reason for your answer.
Solution:
Possible answers are :
Without the root hair, the roots may not be able to absorb water and nutrients from the soil and the plant will die.
The stem of the rose plant may grow new roots and the plant will live.
The rose plant may not be able to survive in a different type of soil.
Question 13.
(a) Name the only artery that carries carbon dioxide-rich blood.
(b) Why is it called an artery if it does not carry oxygen-rich blood?
Solution:
(a) Pulmonary artery
(b) Pulmonary artery does not carry oxygen-rich blood but it carries blood away from the heart like all other arteries. Therefore, it is called an artery.
Question 14.
Boojho’s uncle was hospitalised and put on dialysis after a severe infection in both of his kidneys.
(a) What is dialysis?
(b) When does it become necessary to take such a treatment?
Solution:
(a) Dialysis is the medical process by which the toxic substances are removed from the blood of a person whose kidneys are completely damaged. Artificial kidney is a dialysis machine.
(b) In case a person’s kidney gets damaged due to some infection or injury, dialysis becomes necessary.
Question 15.
Name the process and the organ which helps in removing the following wastes from the body,
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Undigested food
(c) Urine
(d) Sweat
Solution:
| Wastes | Proces | Organ | |
| (a) | Carbon dioxide | Exhalation | Lungs |
| (b) | Undigested food | Egestion | Large intestine and anus |
| (c) | Urine | Excretion | Kidneys |
| Sweat | Perspiration | Sweat |
Question 16.
Observe figure 11.2 and answer the given questions:
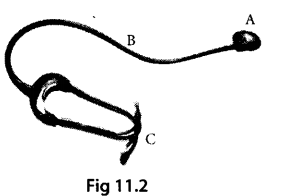
(a) Name the instrument.
(b) Label the parts A, B and C.
Solution:
(a) Stethoscope
(b) A – Chest piece
B – Connecting tube
C – Ear pieces
Question 17.
Paheli noticed water being pulled up by a motor-pump to an overhead tank of a five-storeyed building. She wondered how water moves up to great heights in the tall trees standing next to the building. Can you tell why?
Solution:
If The root cells absorb water and mineral salts from the soil. A continuous upward flow of water from the roots to the top of the plant is maintained due to the suction pull (transpiration pull). This suction pull is created due to continuous loss of water from the leaf surface by the process of transpiration.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 18.
Match the parts of the heart in column I with the direction of flow of blood in column II.
| Column 1 | Column II | ||
| (i) | Right ventricle | (a) | Pushes blood into the pulmonary artery |
| (ii) | Pulmonary veins | (b) | Take deoxygenated blood from the heart to lungs |
| (iii) | Left atrium | (c) | Receives blood from different parts of the body |
| (iv) | Pulmonary arteries | (d) | Bring oxygenated blood from lungs to the heart |
| (v) | Left ventricle | (e) | Pushes blood into the aorta |
| (vi) | Right auricle | (f) | Receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins |
Solution:
(i) (a)
(ii) (d)
(iii) (f)
(iv) (b)
(v) (e)
(vi) (c)
Question 19.
Read the following terms.
| Root hair | Xylem | Urethra |
| Arteries | Kidneys | Veins |
| Atria | Capillaries | Heart |
| Ureter | Phloem | Urinary bladder |
Group the terms on the basis of the categories given below.
(a) Circulatory system of animals.
(b) Excretory system in human.
(c) Transport of substances in plants.
Solution:
(a) Circulatory system of animals – arteries, atria, capillaries, veins, heart
(b) Excretory system in human – ureter, kidneys, urethra, urinary bladder
(c) Transport of substances in plants – root hair, xylem, phloem
Question 20.
Fill in the blanks of the following paragraph using just two words – arteries and veins.
__(a)__ carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to all parts of the body and __(b)__ carry carbon dioxide-rich blood from all parts of the body back to the heart, __(c)__ have thin walls and __(d)__ have thick elastic walls. Blood flows at high pressure in __(e)_ _. Valves are present in __(f)__ which allow blood to flow only towards the heart. __(g)__divide into smaller vessels. These vessels further divide into extremely thin tubes called capillaries. The capillaries join up to form __ (h)__.
Solution:
(a) Arteries
(b) veins
(c) veins
(d) arteries
(e) arteries
(f) veins
(g) arteries
(h) veins
Question 21.
While learning to ride a bicycle Boojho lost his balance and fell. He got bruises on his knees and it started bleeding. However, the bleeding stopped after some time.
(a) Why did the bleeding stop?
(b) What would be the colour of the wounded area and why?
(c) Which type of blood cells are responsible for clotting of blood?
Solution:
(a) Bleeding stops due to coagulation/ clotting of blood.
(b) The colour of wounded area would initially be dark red due to clotting of blood.
(c) Platelets are responsible for clotting of blood.
NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions
- Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 Heat
- Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes
- Chapter 7 Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Chapter 8 Winds, Storms and Cyclones
- Chapter 9 Soil
- Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
- Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants
- Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants
- Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- Chapter 14 Electric Current and Its Effects
- Chapter 15 Light
- Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource
- Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline
- Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.