NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants.
NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following parts of a plant take part in sexual reproduction?
(i) Flower
(ii) Seed
(iii) Fruit
(iv) Branch
Choose the correct answer from below.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Solution:
Sexual reproduction is the process of development of new organisms through the formation and fusion of gametes. The organs specialised to perform sexual reproduction in flowering plants are flowers. After fertilisation ovary changes into fruit and ovules change into seeds. Seeds produce new plants.
Question 2.
Lila observed that a pond with clear water was covered up with green algae within a week. By which method of reproduction did the algae spread so rapidly?
(a) Budding
(b) Sexual reproduction
(c) Fragmentation
(d) Pollination
Solution:
(c) In fragmentation parent body breaks down into two or more fragments. Each body fragment develops into an organism. Fragmentation is a sexual mode of reproduction and plant body can be fragmented into many parts and each part can develop into new plant so, through this method algae spread rapidly.
Question 3.
Seeds of drumstick and maple are carried to long distances by wind because they possess
(a) winged seeds
(b) large and hairy seeds
(c) long and ridged fruits
(d) spiny seeds.
Solution:
(a) Wings of maple and drumstick seeds help them to fly in air, so they are carried to long distances by wind.
Question 4.
The ‘eye’ of the potato plant is what
(a) the root is to any plant
(b) the bud is to a flower
(c) the bud is to Bryophyllum leaf
(d) the anther is to stamen.
Solution:
(c) Eye of potato is the vegetative bud which arises from nodes of stem tuber and when this bud or eye is placed in soil, it produces new plantlets. Likewise Bryophyllum leaf also has vegetative buds on leaf margins which when placed in soil produce new plantlets.
Question 5.
The ovaries of different flowers may contain
(a) only one ovule
(b) many ovules
(c) one to many ovules
(d) only two ovules.
Solution:
(c) Ovaries of different flowers may have one ovule e.g., wheat, paddy, mango to many ovules, e.g., papaya, watermelon, etc.
Question 6.
Which of the following statements is/are true for sexual reproduction in plants?
(i) Plants are obtained from seeds.
(ii) Two plants are always essential.
(iii) Fertilisation can occur only after pollination.
(iv) Only insects are agents of pollination. Choose from the options given below.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) only
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i)and(iv)
Solution:
(a) It is not necessary to have two plants for sexual reproduction to take place. In self pollinated plants, single plant can perform sexual reproduction.
Besides insects, many other agents carry out pollination i.e., bats, snails, birds, wind, water, etc.
Question 7.
Pollination refers to the
(a) transfer of pollen from anther to ovary
(b) transfer of male gametes from anther to stigma
(c) transfer of pollen from anther to stigma
(d) transfer of pollen from anther to ovule.
Solution:
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is called pollination. Pollen grains are immobile, they cannot move by themselves to reach the stigma. An external agency is required for this.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 8.
Fungus, moss and fern reproduce by a common method of asexual reproduction. Name the method.
Solution:
Fungus, moss and fern reproduce asexually by means of spore formation.
Question 9.
Pick the odd one out from the following on the basis of mode of reproduction and give reason for it.
[Sugarcane, Potato, Rice, Rose]
Solution:
Rice is the odd one out as it reproduces by means of seeds. Sugarcane, potato and rose can reproduce vegetatively by means of their stems.
Question 10.
Boojho had the following parts of a rose plant – a leaf, roots, a branch, a flower, a bud and pollen grains. Which of them can be used to grow a new rose plant?
Solution:
A branch of rose plant can be used to grow a new rose plant. It is because rose can be vegetatively propagated by means of stem cuttings.
Question 11.
Which type of pollination does the figure 12.1 indicate?
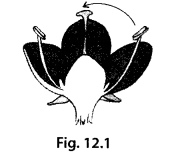
Solution:
The given figure indicates self¬pollination because in this figure pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of the same flower.
Question 12.
One morning as Paheli strolled in her garden she noticed many small plants which were not there a week ago. She wondered where they had come from as nobody had planted them there. Explain the reason for the growth of these plants.
Solution:
The seeds of the plants growing in Paheli s garden may have been brought into the garden by the agency of wind. These seeds on falling on the ground, germinated and developed into new small plants.
Question 13.
In the diagram given in figure 12.2, label the parts marked (a), (b) and (c).
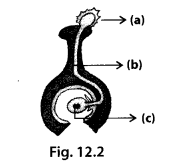
Solution:
In the given diagram (a) is pollen grain, (b) is pollen tube and (c) is zygote.
Question 14.
When you keep food items like bread and fruits outside for a long time especially during the rainy season, you will observe a cottony growth on them.
(a) What is this growth called?
(b) How does the growth take place?
Solution:
(a) It is bread mould, a fungus.
(b) The growth of the fungus takes place by the germination of fungal spores.
Question 15.
Group the seeds given in figure 12.3 (i) to (iii) according to their means of dispersal.
(a) Seed dispersed by wind
(b) Seed dispersed by water
(c) Seed dispersed by animal
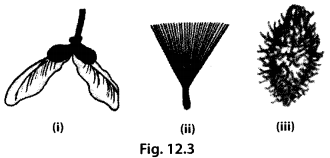
Solution:
(a) (i) and (ii) – seeds dispersed by the agency of wind.
(c) (iii) – seed dispersed by animals
Question 16.
Coconut is a large and heavy fruit. How is it adapted for dispersal by water?
Solution:
Commit fruit has a thick fibrous coat which enables it to float on water.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 17.
In the figure of a flower given in figure 12.4, label the parts whose functions are given below and give their names.
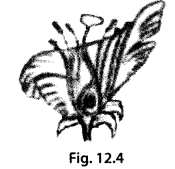
(a) The part which contains pollen grains.
(b) The part where the female gamete is formed.
(c) The female reproductive part where pollen grains germinate.
(d) The colourful part of flower which attracts insects.
Solution:
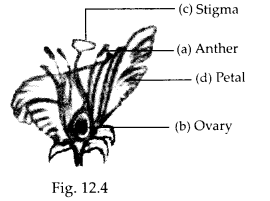
(a) Anther
(b) Ovary
(c) Stigma
(d) Petals
Question 18.
Fill in the blanks with correct terms.
The male and female gametes fuse to form a __(a)__ during the process of __(b)__. This grows into an__(c) __which is enclosed within a seed. After fertilisation the ovules develop into __(d)__ and the ovary develops into a __(e)__.
Solution:
(a) zygote
(b) fertilisation
(c) embryo
(d) seeds
(e) fruit
Question 19.
In the diagram of a bisexual flower, given as figure 12.5 draw the missing part and label the parts marked (a), (b) and (c). Also label the missing part that you draw.
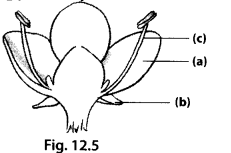
Solution:
The labelled diagram of a bisexual flower along with missing parts (style and stigma) as well as unlabelled part (ovary) is as follows :
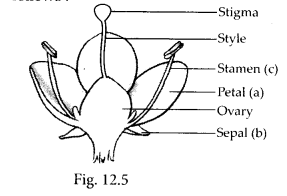
Question 20.
Write how the following seeds are dispersed.
(a) Seeds with wings
(b) Small and light seeds
(c) Seeds with spines/hooks
Solution:
(a) Seeds with wings are dispersed by wind. Wings of the seeds help them to float in air and get carried to long distances, e.g., seeds of maple.
(b) Small and light seeds are dispersed by wind. Small and light seeds are easily blown away by wind and are carried to far off places, e.g., grasses.
(c) Seeds with spines/hooks are dispersed by animals and humans. Spiny or hooked seeds get attached to the bodies of animals or clothes of human beings and are carried to distant places, e.g., Xanthium.
NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions
- Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 Heat
- Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes
- Chapter 7 Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Chapter 8 Winds, Storms and Cyclones
- Chapter 9 Soil
- Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
- Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants
- Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants
- Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- Chapter 14 Electric Current and Its Effects
- Chapter 15 Light
- Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource
- Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline
- Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.