NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 16 Probability are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 16 Probability.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 16 Probability
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. If the letters of the word ALGORITHM are arranged at random in a row what is the probability the letters GOR must remain together as a unit?
Sol: We have word ALGORITHM Number of letters = 9
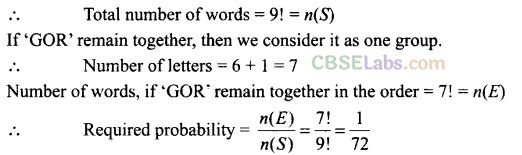
Q2. Six new employees, two of whom are married to each other, are to be assigned six desks that are lined up in a row. If the assignment of employees to desks is made randomly, what is the probability that the married couple will have nonadjacent desks?
Sol: Six employees can be arranged in 6! ways.
n(S) = 6!
Two adjacent desks for married couple can be selected in 5 ways viz.,(l, 2), (2, 3), (3,4), (4, 5), (5,6).
This couple can be arranged in the two desks in 2! ways.
Other four persons can be arranged in 4! ways.
So, number of ways in which married couple occupy adjacent desks
= 5×2! x4! =2×5!
So, number of ways in which married couple occupy non-adjacent desks = 6! – 2 x 5! = 4 x 5! = n(E)
![]()
Q3. Suppose an integer from 1 through 1000 is chosen at random, find the probability that the integer is a multiple of 2 or a multiple of 9.
Sol: We have integers 1,2, 3,…1000
We have integers 1,2, 3,…1000
n(S) = 1000
Number of integers which are multiple of 2 = 500 Let the number of integers which are multiple of 9 be n.
nth term = 999 => 9 + (n -1)9 = 999
=> 9 + 9n – 9 = 999
=> n = 111
From 1 to 1000, the number of multiples of 9 is 111.
The multiple of 2 and 9 both are 18, 36,…, 990.
Let m be the number of terms in above series.
.’. mth term = 990
=> 18 + (m- 1)18 = 990
=> 18+18m-18 = 990
=> m = 55
Number of multiples of 2 or 9 = 500 +111-55 = 556 = n(E)
![]()
Q4. An experiment consists of rolling a die until a 2 appears.
(i) How many elements of the sample space correspond to the event that the 2 appears on the Ath roll of the die?
(ii) How many elements of the sample space correspond to the event that the 2 appears not later than the Ath roll of the die?
Sol: Number of outcomes when die is thrown is ‘6’.
(i) If 2 appears on the Ath roll of the die.
So, first (k -1) roll have 5 outcomes each and Kth roll results 2
Number of outcomes = 5k-1
(ii) If we consider that 2 appears not later than K th roll of the die, then 2 comes before Ath roll.
If 2 appears in first roll, number of ways = 1 If 2 appears in second roll, number of ways
= 5 x 1 (as first roll does not result in 2)
If 2 appears in third roll, number of ways
= 5 x 5 x 1 (as first two rolls do not result in 2)
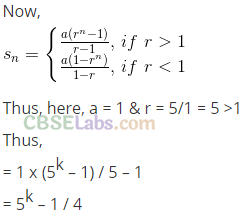
Similarly if 2 appears in (k – l)th roll, number of ways = [5x5x5… (k- 1) times] x 1 = 5k-1 Possible outcomes if 2 appears before kth roll = 1 +5 + 52 + 53+ … +5k-l
Q5. A die is loaded in such a way that each odd number is twice as likely to occur as each even number. Find P(G), where G is the event that a number greater than 3 occurs on a single roll of the die.
Sol: If is given that 2 x Probability of even number = Probability of odd
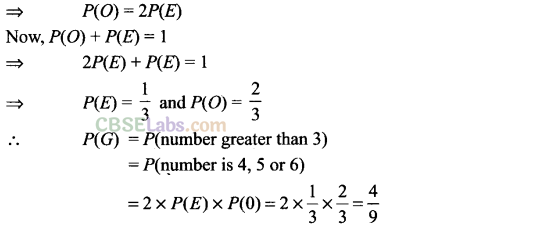
Q6. In a large metropolitan area, the probabilities are .87, .36, .30 that a family (randomly chosen for a sample survey) owns a colour television set, a black and white television set, or both kinds of sets. What is the probability that a family owns either anyone or both kinds of sets?
Sol: Let C be the even that family own colour television set and B be the event that family owns a black and white television set It is given that,
P(C) = 0.87, P{B) = 0.36 and P(C∩B) = 0.30 We have to find probability that a family owns either anyone or both kind of sets i.e., P(B ∪ C)
Now, P(B∪C) = P(B) + P(C)-P(C∩ B)
= 0.87 + 0.36-0.30= 0.93
Q7. If A and B are mutually exclusive events, P(A) =35 and P(B) = 0.45, find
(a) P(A’)
(b) P(B’)
(c) P(A∪ B)
(d) P(A∩ B)
(e) P(A∪ B’)
(f) P(A’∩B’)
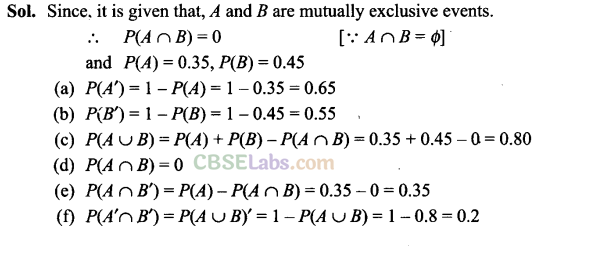
Q8. A team of medical students doing their internship have to assist during surgeries at a city hospital. The probabilities of surgeries rated as very complex, complex, routine, simple or very simple are respectively, 0.15,0.20, 0.31, 0.26, .08. Find the probabilities that a particular surgery will be rated
(a) complex or very complex;
(b) neither very complex nor very simple;
(c) routine or complex
(d) routine or simple

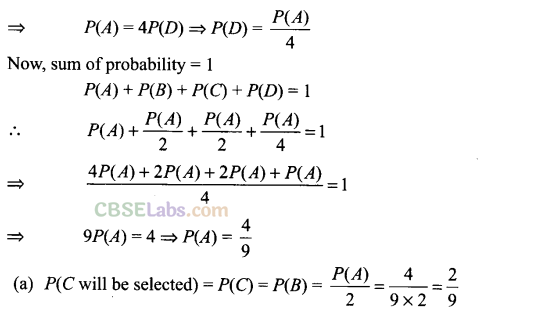
Q9. Four candidates A, B, C, ZJhave applied for the assignment to coach a school cricket team. If A is twice as likely to be selected as B, and B and C are given about the same chance of being selected, while C is twice as likely to be selected as D, what are the probabilities that
(a) C will be selected? (b) A will not be selected?
Sol: It is given that A is twice as likely to be selected as B.
P(A) = 2P(B)
B and C are given about the same chance of being selected.
P(B) = P(C)
C is twice as likely to be selected as D.
P(C) = 2 P(D)
![]()
Q10. One of the four persons John, Rita, Aslam or Gurpreet will be promoted next month. Consequently the sample space consists of four elementary outcomes S = {John promoted, Rita promoted, Aslam promoted, Gurpreet promoted}. You are told that the chances of John’s promotion is same as that of Gurpreet, Rita’s chances of promotion are twice as likely as Johns. Aslam’s chances are four times that of John.
(a) Determine
P(John promoted)
P(Rita promoted)
P(Aslam promoted)
P(Gurpreet promoted)
(b) If A = {John promoted or Gurpreet promoted}, find P(A).
Sol: Let Event: J = John promoted
R = Rita promoted
A = Aslam promoted
G = Gurpreet promoted
Given sample space, S = {John promoted, Rita promoted, Aslam promoted, Gurpreet promoted}
i.e. S={J,R,A,G)
It is given that, chances of John’s promotion is same as that of Gurpreet.
P(J) = P(G)
Rita’s chances of promotion are twice as likely as John.
P(R) = 2P(J)
And Aslam’s chances of promotion are four times that of John.
P(A) = 4P(J)
Now, P(J) + P(R) + P(A) + P(G) = 1 => P(J) + 2P(J) + 4P(J) + P(J) = 1
=> 8P(J) = 1
P(J) = 1/8

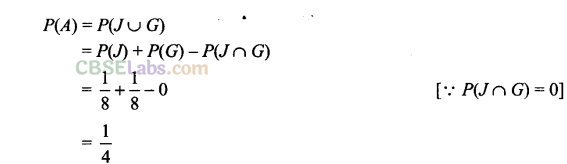
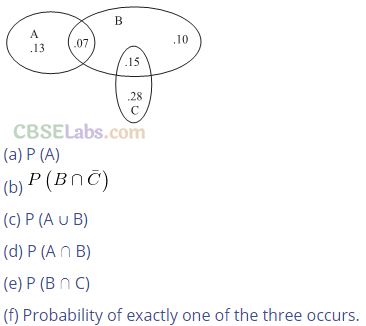
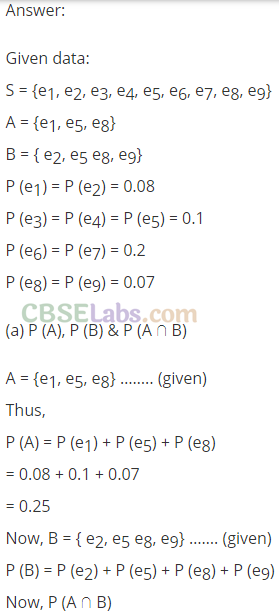
Q11. The accompanying Venn diagram shows three events, A, B, and C, and also the probabilities of the various intersections (for instance, P(A∩B) = .07).


Q12. One urn contains two black balls (labelled Bx and B2) and one white ball. A second urn contains one black ball and two white balls (labelled W1 and W2). Suppose the following experiment is performed. One of the two urns is chosen at random. Next a ball is randomly chosen from the urn. Then a second ball is chosen at random from the same urn without replacing the first ball.
(a) Write the sample space showing all possible outcomes
(b) What is the probability that two black balls are chosen?
(c) What is the probability that two balls of opposite colour are chosen?
Sol:It is given that one of the two urn is chosen, then a ball is randomly chosen
from the urn, then a second ball is chosen at random from the same urn without replacing the first ball.
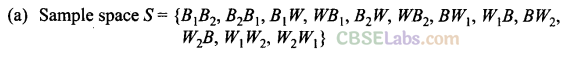

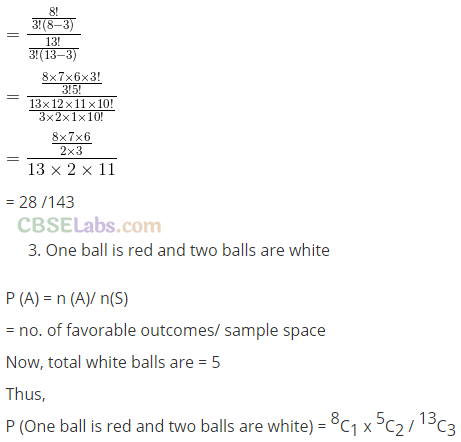
Q13. A bag contains 8 red and 5 white balls. Three balls are drawn at random. Find the Probability that
(a) All the three balls are white
(b) All the three balls are red
(c) One ball is red and two balls are white
Sol:


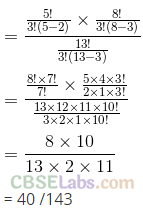



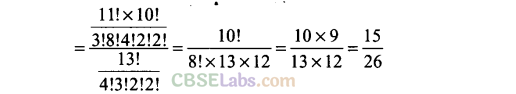
Q15. A card is drawn from a deck of 52 cards. Find the probability of getting a king or a heart or a red card.
Sol: Number of cards = 52 .-. n(S) = 52
4 king + 13 heart + 26 red – 13 – 2 = 28 = n{E)
.’. Required probability = 28/52 = 7/13


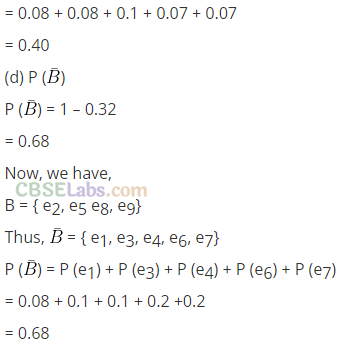
Q17. Determine the probability p, for each of the following events.
(a) An odd number appears in a single toss of a fair die.
(b) At least one head appears in two tosses of a fair coin.
(c) The sum of 6 appears in a single toss of a pair of fair dice.
Sol: (a) When a die is thrown the possible outcomes are
S = {1, 2, 3,4, 5, 6} out of which 1, 3, 5 are odd,

Objective type Questions
Q18. In a non-leap year, the probability of having 53 Tuesdays or 53 Wednesdays is


Q19. Three numbers are chosen from 1 to 20. Find the probability that they are not consecutive
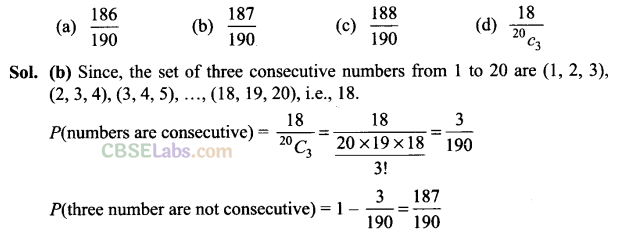
Q20. While shuffling a pack of 52 playing cards, 2 are accidentally dropped. Find the probability that the missing cards to be of different colours

Q21. Seven persons are to be seated in a row. The probability that two particular persons sit next to each other is

Q22. Without repetition of the numbers, four digit numbers are formed with the numbers 0, 2, 3, 5. The probability of such a number divisible by 5 is

Q23. If A and B are mutually exclusive events, then

Q24. If P(A ∪B) = P(A n B) for any two events A and B, then
(a) P(A) = P(B) (b) P (A) > P (B)
(c) P(A ) < P(B) (d) none of these
Sol: (a) We have, P(A ∪ B) = P(A n B)
P(A) + P(B) – P(A ∩ B) = P(A ∩ B)
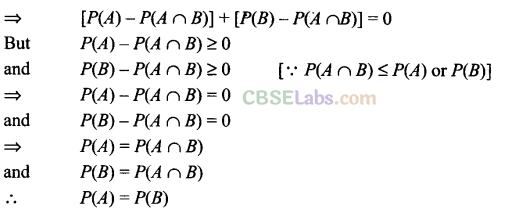
Q25. If 6 boys and 6 girls sit in a row at random. The probability that all the girls sit together is

Q26. A single letter is selected at random from the word ‘PROBABILITY’. The probability that it is a vowel is

Q27. If the probabilities for A to fail in an examination is 0.2 and that for B is 0.3, then the probability that either A or B fails is


Q29. If M and N are any two events, tlie probability that at least one of them occurs is .
(a) P(M) + P(N) – 2 P(M ∩N)
(b) P(M) + P(N) – P(M ∩ N)
(c) P(M) + P(N) + P(M ∩ N)
(d) P(M) + P(N) + 2P(M∩N)
Sol: (B) If M and N are any two events.
.-. P(M ∪N) = P(M) + P(N) – P(M ∩ N) .
True/False Type Questions
Q30. The probability that a person visiting a zoo will see the giraffe is 0.72, the probability that he will see the bears is 0.84 and the probability that he will see both is 0.52.
Sol: False
P(to see giraffe or bear) = P (giraffe) + P (bear) – P(giraffe and bear)
=0.72 + 0.84-0.52= 1.04
which is not possible.
Q31. The probability that a student will pass his examination is 0.73, the probability of the student getting a compartment is 0.13, and the probability that the student will either pass or get compartment is 0.96.
Sol: False
Let A = Student will pass examination
B = Student will getting compartment
P(A) = 0.73, P(B) = 0.13 and P(A or B) = 0.96
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) = 0.73 + 0.13 = 0.86
But P(A or B) = 0.96
Hence, given statement is false.
Q32.The probabilities that a typist will make 0, 1,2, 3, 4, 5 or more mistakes in typing a report are, respectively, 0.12, 0.25, 0.36, 0.14, 0.08, 0.11.
Sol: False
Sum of these probabilities must be equal to 1.
P(0) + P( 1) + P( 2) + P(3) + P{ 4) + P(5)
= 0.12 + 0.25+0.36 + 0.14 + 0.08 + 0.11 = 1.06 which is greater than 1,
So, it is false statement.
Q33. If A and B are two candidates seeking admission in an engineering College. The probability that A is selected is .5 and the probability that both A and B are selected is at most .3. Is it possible that the probability of B getting selected is 0.7?
Sol. False
Given that, P(A ) = 0.5, P(A ∩B)< 0.3
Now, P(A) x P(B) ≤ 0.3
=>0.5 x P(B) ≤0.3
=> P(B) ≤0.6
Hence, it is false statement
Q34. The probability of intersection of two events A and B is always less than or equal to those favourable to the event
Sol: True
We know that A ∩ B ⊂ A
P(A ∩ B) ≤ P(A)
Hence, it is a true statement.
Q35. The probability of an occurrence of event A is .7 and that of the occurrence of event B is .3 and the probability of occurrence of both is .4.
Sol: False
A ∩B⊆ A, B
P(A ∩B) ≤ P(A), P(B)
But given that P(B) = 0.3 and P(A ∩B) = 0.4, which is not possible.
Q36. The sum of probabilities of two students getting distinction in their final examinations is 1.2.
Sol: True
Probability of each student getting distinction in their final examination is less than or equal to 1, sum of the probabilities of two may be 1.2.
Hence, it is true statement.
Fill in the Blanks Type Questions
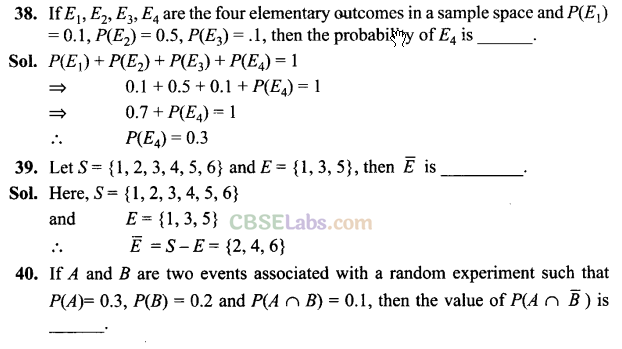
Q37. The probability that the home team will win an upcoming football game is 0.77, the probability that it will tie the game is 0.08, and the probability that it will lose the game is ______.
Sol: P(losing) = 1 – (0.77 + 0.08) = 0.15

NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Solutions
- Chapter 1 Sets
- Chapter 2 Relations and Functions
- Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
- Chapter 4 Principle of Mathematical Induction
- Chapter 5 Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 6 Linear Inequalities
- Chapter 7 Permutations and Combinations
- Chapter 8 Binomial Theorem
- Chapter 9 Sequence and Series
- Chapter 10 Straight Lines
- Chapter 11 Conic Sections
- Chapter 12 Introduction to Three-Dimensional Geometry
- Chapter 13 Limits and Derivatives
- Chapter 14 Mathematical Reasoning
- Chapter 15 Statistics
- Chapter 16 Probability
NCERT Exemplar ProblemsMathsPhysicsChemistryBiology
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 16 Probability help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 16 Probability, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.