NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Chapter 6 Changes around Us are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 6 Changes around Us.
NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 6 Changes around Us
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Pick the change that can be reversed from the following.
(a) Cutting of trees
(b) Melting of ghee
(c) Burning of candle
(d) Blooming of flower
Solution:
(b): The molten ghee can be frozen again hence this change can be reversed. Cutting of trees, burning of candle and blooming of flower cannot be reversed.
Question 2.
Which of the following change cannot be reversed?
(a) Hardening of cement
(b) Freezing of ice cream
(c) Opening a door
(d) Melting of chocolate
Solution:
(a): Hardening of cement is irreversible because once hardened it cannot come back to its original shape.
Question 3.
An iron ring is heated. Which of the following statement about it is incorrect?
(a) The ring expands.
(b) The ring almost comes to the same size on cooling.
(c) The change in this case is reversed.
(d) The ring changes its shape and the change cannot be reversed.
Solution:
(d) : The ring expands on heating and comes back to its original size on cooling. The change is reversible.
Question 4.
While lighting a candle, Paheli observed the following changes.
(i)Wax was melting
(ii)Candle was burning
(iii)Size of the candle was reducing
(iv)Melted wax was getting solidified. of the above, the changes that can be reversed are
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Solution:
(d): Molten wax solidifies and the solid wax can be again melted. Hence melting of wax and its solidification are reversible changes.
Question 5.
Salt can be separated from its solution (salt dissolved in water), because
(a) mixing of salt in water is a change that can be reversed by heating and melting of salt
(b) mixing of salt in water is a change that cannot be reversed
(c) mixing of salt in water is a permanent ‘ change
(d) mixing of salt in water is a change that can be reversed by evaporation.
Solution:
(d): Salt can be separated from its water solution by evaporating the water. Hence mixing of salt in water is a reversible change.
Question 6.
Rolling of chapati and baking of chapati are the changes that
(a) can be reversed
(b) cannot be reversed
(c) can be reversed and cannot be reversed, respectively
(d) cannot be reversed and can be reversed, respectively.
Solution:
(c) : Rolling of chapati is a physical reversible change because there is no change in the properties of kneaded flour. Once the chapati is baked it cannot be reversed.
Question 7.
Iron rim is made slightly smaller than the wooden wheel. The rim is usually heated before fixing into the wooden wheel, because on heating the iron rim
(a) expands and fits onto the wooden wheel
(b) contracts and fits onto the wooden wheel
(c) no change in the size takes place
(d) expands first, then on cooling contracts and fits onto the wooden wheel.
Solution:
(d) : The smaller iron rim expands on heating fits into the wooden wheel and on cooling contracts to fit into the wooden wheel tightly hence does not come out.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 8.
Look at figure 6.1 which shows three situations
(a) a burning candle
(b) an extinguished candle
(c) melting wax.
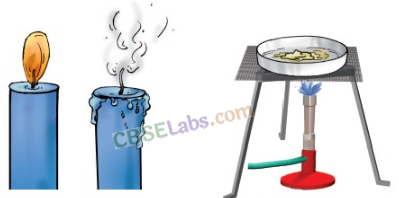
Which of these shows a reversible change and why?
Solution:
Melting of wax in the figure (c) is a reversible change because the molten wax can be solidified again.
Question 9.
A piece of iron is heated till it becomes red-hot. it then becomes soft and is beaten to a desired shape. What kind of changes are observed in this process-reversible or irreversible?
Solution:
A piece of iron on heating can be beaten into desired shape. It is a reversible change because the object of desired shape can be again heated and beated to give the original shape.
Question 10.
Paheli had bought a new bottle of pickle from the market. She tried to open the metal cap to taste it but could not do so. She then took a bowl of hot water and immersed the upper end of the bottle in it for five minutes. She could easily open the bottle now. Can you give the reason for this?
Solution:
On immersing in hot water, the metal cap expands in size hence it can be removed easily.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 11.
Can we reverse the following changes? If yes, suggest the name of the method.
(a) Water into water vapour
(b) Water vapour into water
(c) Ice into water
(d) Curd into milk.
Solution:
(a) Water into water vapour – Yes, by condensation water vapour can be converted to water.
(b) Water vapour into water – Yes, water can be converted to water vapour by evaporation.
(c) Ice into water – Yes, water can be converted to ice by freezing.
(d) Curd into milk is an irreversible process.
Question 12.
Which of the following changes cannot be reversed?
(a) Blowing of a balloon
(b) Folding a paper to make a toy aeroplane
(c) Rolling a ball of dough to make roti
(d) Baking cake in an oven
(e) Drying a wet cloth
(f) Making biogas from cow dung
(g) Burning of a candle
Solution:
(a) Blowing of a ballon
(b) Folding a paper to make a toy aeroplane
(c) Rolling a ball of dough to make roti
(d) Baking of a cake is irreversible.
(e) Drying a wet cloth
(f) Making biogas from cow dung is irreversible.
(g) Burning of a candle is irreversible.
Question 13.
Boojho’s sister broke a white dove, a symbol of peace, made of Plaster of Paris (POP). Boojho tried to reconstruct the toy by making a powder of the broken pieces and then making a paste by mixing water. Will he be successful in his effort? Justify your answer.
Solution:
Boojho will not be successful because making of toy from Plaster of Paris (POP) is an irreversible change. Once the Plaster of Paris is mixed with water and dried it cannot regain its properties.
Question 14.
Tearing of paper is said to be a change that cannot be reversed. What about paper recycling?
Solution:
Recycling of paper cannot be classified as a reversible change because the quality, colour and texture of the paper changes on recycling and we get a different type of paper not the original one.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 15.
(b) Change which occurs on heating but cannot be reversed.
(c) Change which occurs on cooling but can be reversed.
(d) Change which occurs on mixing two substances, but can be reversed.
(e) Change which occurs on mixing two substances, but cannot be reversed.
Solution:
(a) Heating of an iron rod
(b) Baking of chapati
(f) Formation of ice from water
(d) Formation of salt solution
(e) Mixing of cement with water
Question 16.
A potter working on his wheel shaped a lump of clay into a pot. He then baked the pot in an oven. Do these two acts lead to the same kind of changes or different? Give your opinion and justify your answer.
Solution:
The two acts lead to the different kind of changes. Shaping of pot on a wheel is a physical, reversible change while baking the pot in an oven is an irreversible change.
Question 17.
Conversion of ice into water and water into ice is an example of change which can be reversed. Give four more examples where you can say that the changes can be reversed.
Solution:
Examples of reversible changes
(i) Melting of wax
(ii) Folding of a paper
(iii) Inflating a tyre or balloon
(iv) Knitting of a sweater
Question 18.
Change of a bud into a flower is a change which cannot be reversed. Give four more such example.
Solution:
Examples of irreversible changes
(i) Milk into curd
(ii) Burning of wood
(iii) Ripening of fruits
(iv) Digestion of food
Question 19.
Paheli mixed flour and water and (i) made a dough, (ii) rolled the dough to make a chapati, (iii) baked the chapati on a pan, (iv) dried the chapati and ground it in a grinder to make powder. Identify the changes (i) to (iv) as the changes that can be reversed or that cannot be reversed.
Solution:
(i) Making of dough from flour and water is irreversible change.
(ii) Rolling the dough to make a chapati is reversible change.
(iii) Baking the rolled chapati on a pan is irreversible change.
(iv) Grinding of dried chapati in a grinder is irreversible change.
Question 20.
lt was Paheli’s birthday, her brother Simba was helping her to decorate the house for the birthday party and their parents were also busy making other arrangements. Following were the activities going on at Paheli’s home:
(i) Simba blew balloons and put them on the wall.
(ii) Some of the balloons got burst.
(iii) Paheli cut colourful strips of paper and put them on the wall with the help of tape.
(iv) She also made some flowers by origami (paper folding) to decorate the house.
(v) Her father made dough balls.
(vi) Mother rolled the dough balls to make puries.
(vii) Mother heated oil in a pan.
(viii) Father fried the puries in hot oil.
Identify the activities at Paheli’s home as those that can be reversed and those which cannot be reversed.
Solution:
Activities (i), (iv), (v), (vi) and (vii) can be reversed and rest cannot be reversed.
NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions
- Chapter 1 Food: Where Does It Come From?
- Chapter 2 Components of Food
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 Sorting Materials into Groups
- Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
- Chapter 6 Changes around Us
- Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants
- Chapter 8 Body Movements
- Chapter 9 The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings
- Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
- Chapter 11 Light, Shadows and Reflections
- Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
- Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
- Chapter 14 Water
- Chapter 15 Air Around Us
- Chapter 16 Garbage In, Garbage Out
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Chapter 6 Changes around Us will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 6 Changes around Us, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.