NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Water are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 14 Water.
NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 14 Water
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following activity does not involve use of water?
(a) Washing clothes
(b) Bathing
(c) Cleaning utensils
(d) Drying wet clothes
Solution:
(d): Washing, bathing and cleaning utensils are the activities which require the use of water whereas in drying wet clothes, water gets converted into vapour form.
Question 2.
In which of the following activities will you use minimum amount of water?
(a) Bathing
(b) Brushing teeth
(c) Washing clothes
(d) Mopping a room
Solution:
(b) Bathing, washing clothes and mopping a room will require a large amount of water. The minimum amount of water will be required for brushing teeth.
Question 3.
The quantity of water required to produce one page of your book is
(a) one bucket
(b) ten buckets
(c) two glasses
(d) few drops.
Solution:
(c) Almost two glasses of water are required to make one sheet of paper.
Question 4.
Water in our tap comes from a
(a) river
(b) lake
(c) well
(d) river, lake or well.
Solution:
(d) Water in our tap comes from rivers, lakes or wells. Before supplying the water through tap, it is routed through water treatment plants. The water drawn from these sources is fit for consumption.
Question 5.
In which of the following case evaporation of water will be slowest?
(a) A tray of water kept in sunlight.
(b) A kettle of water kept on a burner.
(c) A glass of water kept in a room.
(d) A bucket of water kept on rooftop.
Solution:
(c) Evaporation is affected by temperature. When temperature increases, evaporation also increases. Room temperature is the lowest temperature as compared to the temperatures of sunlight, burner and rooftop. So, a glass of water kept in a room has slowest water evaporation.
Question 6.
Transpiration is a process in which plants
(a) receive water from soil
(b) absorb water vapour from air
(c) prepare food from water
(d) release water vapour.
Solution:
(d) The loss of water in the vapour form from the exposed parts of a plant (mainly leaves) is called transpiration. The loss of water due to transpiration is quite high.
Question 7.
Clouds are
(a) tiny drops of water floating in air
(b) mixture of dust and water vapour
(c) particles of water vapour
(d) rain drops in air.
Solution:
(a) At sufficient heights water vapour present in air condenses to form tiny droplets of water floating in air which appear to us as clouds. Later these tiny water droplets come together to form larger sized water drops and become so heavy that they begin to fall in the form of rain.
Question 8.
Wells are fed by
(a) pond water
(b) lake water
(c) rain water
(d) groundwater.
Solution:
(d) Rainwater fills up lakes, ponds, rivers and other water bodies. A part of the rainwater gets absorbed by the ground. Some of it is brought back to air by evaporation and transpiration. The rest seeps into the ground and becomes available as groundwater. Wells are fed by this ground water.
Question 9.
Floods cause extensive damage to
(a) crops
(b) property and human life
(c) domestic animals
(d) all of the above.
Solution:
(d) Heavy rains lead to rise in the level of water in rivers, lakes and ponds. This water then spreads over large area causing floods. The crop fields, forests, villages and cities get submerged under water. In our country, floods cause extensive damage to crops, domestic animals, property and human life.
Question 10.
“Catch water where it falls” is the basic idea behind
(a) recycling of water
(b) making dams to store water
(c) rainwater harvesting
(d) condensation of water vapour.
Solution:
(c) One way of increasing the availability of water is to collect rainwater and store it for later use. Collecting rainwater in this way is called rainwater harvesting.
Two techniques of rainwater harvesting are
(i) Rooftop rainwater harvesting – In this system the rainwater is collected from the rooftop to a storage tank, through pipes. This water may contain soil from the roof and needs filtering before it is used. Instead of collecting rainwater in the tank, the pipes can go directly into a pit in the ground. This then seeps into the soil to recharge or refill the groundwater.
(ii) Another option is to allow water to go into the ground directly from the roadside drains that collects rainwater.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 11.
Look at Fig. 14.1.

Write down activities shown in this figure in which water is being used.
Solution:
The activities shown in the given figure in which water is being used are :
(i) Bathing
(ii) Washing clothes.
Question 12.
Write any two activities which require more than a bucket of water.
Solution:
The two activities which require more than a bucket of water are :
(i) Washing ten clothes or more.
(ii) Irrigating a crop field.
Question 13.
Write any two activities which require less than one bucket of water.
Solution:
The two activities which require less than one bucket of water are :
(i) Brushing teeth
(ii) Washing a handkerchief.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 14.
Why do wet clothes placed on a clothes line get dry after some time? Explain.
Solution:
On exposing to heat, water present in wet clothes gets converted into water vapour due to evaporation and as a result clothes get dry after some time.
Question 15.
Water kept in sunlight gets heat from sun and is evaporated. But how does water kept under the shade of a tree also get evaporated? Explain.
Solution:
Air around us gets heated from sunlight. This warm air provides heat for evaporation of water kept under the shade of a tree.
Question 16.
How do the areas covered with concrete affect the availability of groundwater?
Solution:
Areas covered with concrete reduce the seepage of rainwater into the ground, thus reducing the availability of groundwater.
Question 17.
Why is there a need for conserving water? Give two reasons.
Solution:
There is a need for conserving water because :
(i) The demand for water is increasing day – by – day, with rise in population but amount of water available for use is very limited.
(ii) The level of groundwater is decreasing drastically which would lead to extreme water scarcity in near future.
Question 18.
Fill in the blanks selecting words from, the following list.
snow, rain, clouds, vapour, evaporation, transpiration.
Water, as ______ goes into atmosphere by the processes of _____ and _____ and forms ____ ,which on condensation fall in the form
of ____ and _____ .
Solution:
vapour, evaporation, transpiration, clouds,, snow, rain
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 19.
Most of the water that falls on the land as rain and snow, sooner or later goes back to a sea or an ocean. Explain how it happens?
Solution:
Most of the water that falls on the land as rain flows into the rivers and streams and finally into the sea. This is called surface run off. Some of it seeps through and becomes available to us as groundwater. The groundwater is pumped out for domestic, irrigation and industrial use, which eventually goes into rivers and finally into the seas or oceans. In the similar way, the water that falls on the land as snow melts during summers and flows into the rivers and streams, from there it goes into the sea or oceans.
Thus, most of the water that falls on the land as rain or snow, sooner or later goes back to a sea or an ocean.
Question 20.
Draw a diagram to show how sea water reaches a lake or pond.
Solution:
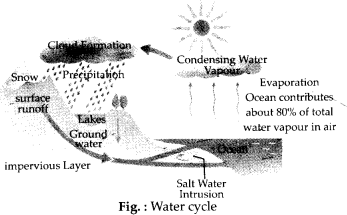
Question 21.
Dissolve two spoons of common salt in half a cup of water. Now if you want to get the salt back, what will you do?
Solution:
To get the salt back, we have to remove water from the solution. Water can be removed from the salt solution by heating it on a stove or keeping it in the sun in a plate for few hours for evaporation. Evaporation is a slow conversion of water into its vapour state. Once the water gets evaporated, we get the salt back.
Question 22.
Explain the process of rooftop rainwater harvesting with the help of a suitable diagram.
Solution:
Rooftop rainwater harvesting – is a method of rainwater harvesting in which the rainwater is collected from the rooftop to a storage tank, through pipes. This water may contain soil from the roof and need filtering before it is used. Instead of collecting rainwater in the tank, the pipes can go directly into a pit in the ground. This then seeps into the soil to recharge or refill the groundwater.
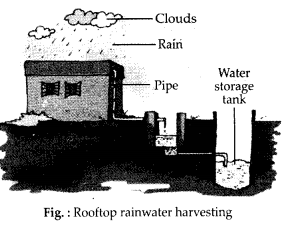
NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions
- Chapter 1 Food: Where Does It Come From?
- Chapter 2 Components of Food
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 Sorting Materials into Groups
- Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
- Chapter 6 Changes around Us
- Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants
- Chapter 8 Body Movements
- Chapter 9 The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings
- Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
- Chapter 11 Light, Shadows and Reflections
- Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
- Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
- Chapter 14 Water
- Chapter 15 Air Around Us
- Chapter 16 Garbage In, Garbage Out
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Water will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 14 Water, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.