Beyond Earth NCERT Class 6th Science Chapter 12 Question Answer
Beyond Earth Class 6 Questions and Answers
Let Us Enhance Our Learning (Pages 249-251)
Question 1.
Match the column:
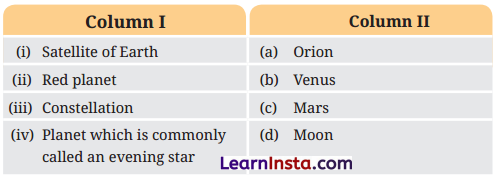
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Satellite of Earth | (d) Moon |
| (ii) Red planet | (c) Mars |
| (iii) Constellation | (a) Orion |
| (iv) Planet which is commonly called an evening star | (b) Venus |
Question 2.
(i) Solve the following riddle:
My first alphabet is the MAN but not in CAN.
My second alphabet is in ACE also in FAN.
My third alphabet is the RAT and not in CAT.
My fourth alphabet is in SUN but not in FUN.
Answer:
MARS
(ii) Make two similar riddles by your self.
Answer:
(a) My first alphabet is in VAN but not in PAN
My second alphabet is in EARTH and also in HEAVEN
My third alphabet is in ONE and not in TWO
My fourth alphabet is in SUN and also in FUN
My last alphabet is in STAR but not in RADAR
I am a planet that moves around the Sun.
Answer: VENUS
(b) My first alphabet is in EAT but not in BAT
My second alphabet is in FAT and also in SAT
My third alphabet is in RAT and not in MAT
My fourth alphabet is in TEN and also in NET
My fifth alphabet is in HAT but not in PAT.
I am a planet that moves round the Sun.
Answer: EARTH
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the following is not a member of our solar system?
(i) Sirius
(ii) Comets
(iii) Asteroids
(iv) Pluto
Answer:
(i) Sirius
Question 4.
Which of the following is not a planet of the Sun?
(i) Jupiter
(ii) Pluto
(iii) Neptune
(iv) Saturn
Answer:
(ii) Pluto
Question 5.
Which is the brighter star, the Pole star or sirius?
Answer:
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky.
Question 6.
An artist’s representation of the solar system is given in the figure. Is the order of the planets correct? If not, write the correct order in the boxes in the figure.

Answer:
The correct sequence is as follows: 1,3,2,4,5,7,6,8
Question 7.
A portion of night sky with stars is shown in Fig. Look carefully and identify the groups of stars that from the pattern- the Big Dipper and the Little Dipper. Draw lines to connect the stars for these patterns and label the Pole star. You may refer to Fig .12 for help.
Answer:

Question 8.
A portion of the night sky is shown in Figure. Draw lines to connect the stars for Orion and label the star Sirius. You may refer to Fig. 12.3.

Answer:

![]()
Question 9.
You can see stars fading away at dawn and appearing at dusk. During the day we do not see the stars. Explain why.
Answer:
During the day, the Sun’s bright light outshines the stars, making them invisible to our eyes. The atmosphere scatters Sunlight, creating the blue sky and masking the faint light of the stars.
Question 10.
During a clear night try to observe the big depart 3-4 times at an interval of 2-3 hours. Also try to locate the pole star each time. Does the Big Dipper appears to move? Draw a rough sketch. to illustrate this, mentioning the time in each case.
Answer:
The Big Dipper appears to move around the Pole Star due to the rotation of the Earth. Over a few hours, its position changes, making it seem as if it is rotating around the Pole Star.

Question 11.
Think about the night sky and write a poem or a story on it.
Answer:
Today I saw a comet while watching the night sky. I told my grandparents about this episode and to this, they reply it is a messenger of disaster like pandemic or flood.
But these are all myths and superstition, As I learned in my institution.
Appearance of a comet is a natural phenomenon. We have no reason to be afraid of this Grandma.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
Topics and Sub Topics in Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 12 | Electricity and Circuits |
| 12.1 | Electric cell |
| 12.2 | A bulb connected to an electric cell |
| 12.3 | An electric circuit |
| 12.4 | Electric switch |
| 12.5 | Electric conductors and insulators |
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) A device that is used to break an electric circuit is called_______________
(b) An electric cell has___________
Ans:
(a) switch
(b) two
2. Mark ‘True’ or ‘False’ for the following statements:
(a) Electric current can flow through metals.
(b) Instead of metal wires, a jute string can be used to make a circuit.
(c) Electric current can pass through a sheet of thermocol.
Ans:
(a) True
(b) False
(c) False.
3.Explain why the bulb would not glow in the arrangement shown in fig
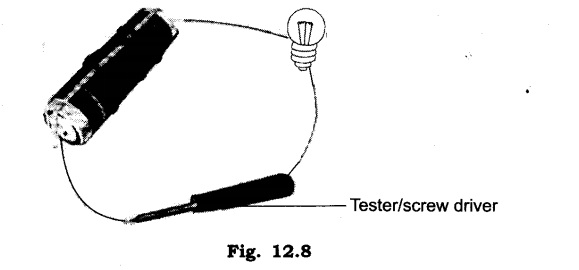
Ans: The bulb would not glow in the arrangement shown in figure because the one end of tester/screw driver is made up of plastic which does not allow the electric current to flow through it.
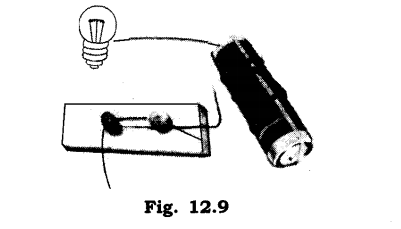
4. Complete the drawing shown in Fig. 12.9 to indicate where the free ends of the two wires should be joined to make the bulb glow.
Ans:
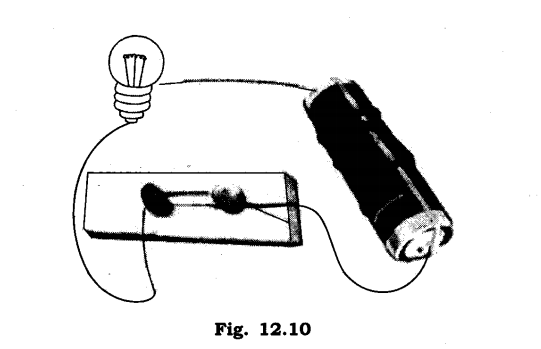
5. What is the purpose of using an electric switch? Name some electrical gadgets that have switches built into them.
Ans: Electric switch is used to make electric circuit open or closed for a particular appliance and hence with the help of a switch we can use an appliance according
6. Would the bulb glow after completing the circuit shown in Fig. 12.9 if instead of safety pin we use an eraser?
Ans: No, since eraser is an insulator so it does not allow the current to pass. Hence the bulb will not glow.
7. Would the bulb glow in the circuit shown in Fig. 12.11.
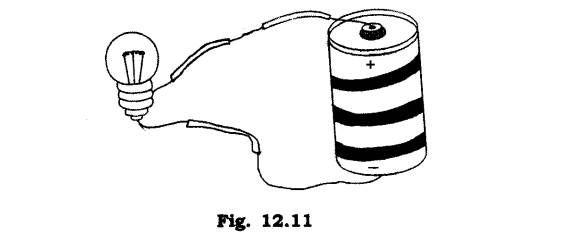
Ans: Yes, the electric circuit is closed so the bulb will glow.
8. Using the“conduction tester” on an object it was found that the bulb begins to glow. Is that object a conductor or an insulator? Explain.
Ans: Yes, if the object is good conductor of electricity then current will pass through conduction tester and the bulb will glow. Hence the object will be a conductor of electricity.
9. Why should an electrician use rubber gloves while repairing an electric switch at your home? Explain.
Ans: Our body is good conductor of electricity and rubber is insulator. During repairing work if the body comes in contact with current carrying wire then there will not be any accident as rubber does not allow the passage of current through it. Hence electrician uses rubber gloves while repairing an electric switch.
10. The handles of the tools like screwdrivers and pliers used by electricians for repair work usually have plastic or rubber covers on them. Can you explain why?
Ans: Plastic or rubber is an insulator which does not allow electric current to pass through it. The handles of the tools like screwdrivers and pliers used by electricians for repair have covering of plastic or rubber so that electric current may not pass through these tools to the body of the electrician to harm him.
Class 6 Science Chapter 12 VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What is the direction of flow of current in a dry cell?
Ans: . The current flows in closed circuit from +ve to -ve terminal of cell.
2. Name the +ve terminal of dry cell.
Ans:. Carbon rod with a metal cap on it.
3. Name the -ve terminal of a dry cell.
Ans: Zinc metal plate.
4. What is dry cell?
Ans: It is a device which converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
5. What is solar cell?
Ans: A device which converts solar energy into electrical energy.
6. What is open circuit?
Ans: An electric circuit in which electrical contact at any point is broken is called open circuit.
7. Write one use of insulators.
Ans: Insulators are used in making switchboard, handles of testers, screw drivers.
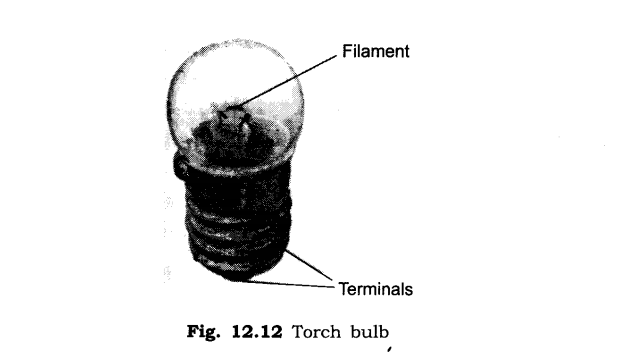
8. What is the name of thin wire in the electric bulb?
Ans: Filament.
Class 6 Science Chapter 12 SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Mention two advantages of a dry cell.
Ans:
1. It converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
2. It is light and small in size.
2. Draw a diagram showing the two terminals of a bulb.
Ans:
3. Draw the circuit diagram for operating a bulb with the help of a dry cell.
Ans:
4. Define conductors and insulators. Give one example of each.
Ans: A conductor is that which easily allows the passage of current through it. Example: Aluminium or any metal.
An insulator is that which does not allow the passage of current through it. Example: Rubber.
5. Identify conductors and insulators from the following:Eraser, paper, matchstick, copper wire, pencil lead, polythene
Ans: Conductors: Copper wire, pencil lead.
Insulator. Eraser, paper, matchstick, polythene.
6. Name the scientist who invented electric cell and the scientist who invented electric bulb.
Ans: Electric cell: Alessandro Volta.
Electric bulb: Thomas Alva Edison.
7. Give one activity to prove that air is an insulator.
Ans: Take an electric circuit, keep the terminals unconnected in the air. The bulb do not glow, as air is an insulator and does not allow the current to flow through it.
8. In any electric circuit, when the switch is on and the current flows through it why do the wire, switches, bulb or devices become hot?
Ans.: This is because electric energy changes into heat energy.
9.The headlights of a car have reflectors behind the bulb. What is the function of reflectors?
Ans: The reflector helps in reflecting the light into a focussed area.
10.If you touch an electric wire carrying current you get a shock, but if on the same wire the birds sit they do not get any shock/current. Explain why?
Ans: When we hold the wire carrying current then the circuit is closed and the current flows from our body and enters earth but the birds sitting on the same wire do not get any current as the circuit is not complete. If the bird touches the earth wire, it will also die due to electric shock.
Class 6 Science Chapter 12 LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1.(1)What is electric circuit?
(2)How many types of electric circuit are there? Define them.
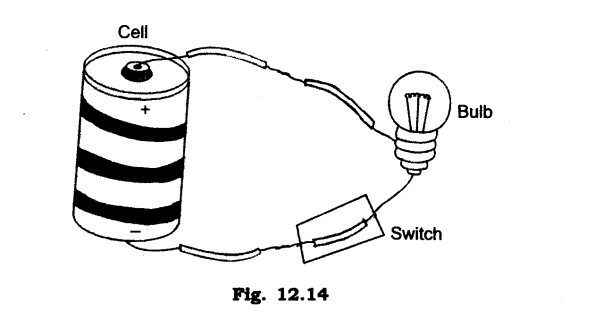
(3)Draw a diagram to show the closed circuit for switch, bulb and dry cell.
Ans:
(1)The diagram that shows the path of electric current is called electric circuit.
(2)There are two types of electric circuit:
(a) Open electric circuit
(b) Closed electric circuit
(a)Open electric circuit: The circuit in which electrical contact at any point is broken is called open electric circuit.
(b)Closed electric circuit: The circuit in which electric current flows from one terminal of a cell or battery to the other is called a closed circuit.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science – All Chapters
- Chapter 1 The Wonderful World of Science
- Chapter 2 Diversity in the Living World
- Chapter 3 Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body
- Chapter 4 Exploring Magnets
- Chapter 5 Measurement of Length and Motion
- Chapter 6 Materials Around Us
- Chapter 7 Temperature and its Measurement
- Chapter 8 A Journey through States of Water
- Chapter 9 Methods of Separation in Everyday Life
- Chapter 10 Living Creatures: Exploring their Characteristics
- Chapter 11 Nature’s Treasures
- Chapter 12 Beyond Earth