Nature’s Treasures NCERT Class 6th Science Chapter 4 Question Answer
Nature’s Treasures Class 6 Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What will happen if the Sun is not visible for a few days? (Page 216)
1. We may have to depend on artificial lighting during day time also.
2. ______________
3. ______________
Answer:
2. With no sunlight, photosynthesis would stop, but that would only kill some of the plants—there are some larger trees that can survive for decades without it.
3. There will be no natural light and heat hence stopping many natural phenomenons like evaporation, transpiration, condensation etc.
Question 2.
What are the consequences of cutting a large forest area? Make a presentation or do a role play, or write a story or a poem that shows what could happen if we continue to cut down trees in our forests. (Page 217)
Answer:
The loss of trees and other vegetation can cause climate change, desertification, soil erosion, flooding, increased greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, and a lot of problems for humans
Presentation/Play/Story or Poem: Do it yourself.
![]()
Let Us Enhance Our Learning (Pages 227-229)
Question 1.
Fig. 11.9 shows items related to natural resources. Match them with their jumbled up names. Make another table and write the names of these resources. Classify these resources as renewable or non-renewable.

Natural resources
Answer:
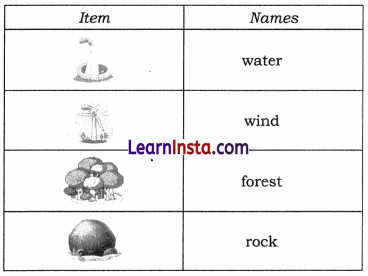
| Resource | Category |
| Water | Renewable resource |
| Wind | Renewable resource |
| Forest | Renewable resource |
| Rock | Non-renewable resource |
Question 2.
State whether the following statements are True [T] or False [F]. If False, correct them.
(i) Nature has all the resources to meet human needs. [ ]
(ii) Machines are a resource found in nature. [ ]
(iii) Natural gas is a non-renewable resource. [ ]
(iv) Air is a renewable resource. [ ]
Answer:
(i) Nature has all the resources to meet human needs. [True]
(ii) Machines are a resource found in nature, [False]
Corrected statement: Machines are human-made resources.
(iii) Natural gas is a non-renewable resource. [True]
(iv) Air is a renewable resource. [True]
Question 3.
Fill in the blank using the most appropriate option-
(i) A fuel that is commonly used in two wheelers like scooters or bikes is-
(a) Kerosene
(b) Petrol
(c) Diesel
(d) LPG
Answer:
(b) Petrol
(ii) An example of a renewable resource is-
(a) Coal
(b) Water
(c) Natural gas
(d) Petrol
Answer:
(b) Water
![]()
Question 4.
Classify the following as renewable or non-renewable resources— coal, natural gas, forests and minerals.
Answer:
| Renewable | Non-renewable |
| – | Coal |
| – | Natural gas |
| Forests | – |
| – | Minerals |
Question 5.
Why do we say that petroleum is a non-renewable resource?
Answer:
Petroleum takes millions of years to form. It is found in limited quantities and once used, it gets exhausted. It cannot be produced or replenished within a reasonable period of time. Hence, petroleum is called non-renewable resource.
Question 6.
It is difficult to regrow forests. Justify this statement.
Answer:
It is difficult to regrow forests because forests take many years, even decades, to grow back fully. Trees and plants need a lot of time to reach their full size. The soil in areas where forests have been cut down or damaged might not be good for growing new trees. It may need special care to become healthy enough for growing new plants.
Question 7.
Make a list of five daily activities in which you use natural resources. Suggest ways by which you can reduce their use.
Answer:
(i) Water: We use water for drinking, washing, cooking and maintaining proper hygiene. We can save water at home by minimising its wastage.
(ii) Diesel: Diesel is used as a fuel in heavy motor vehicles such as buses, trucks, tractors and diesel train engines. We should use electric vehicles.
(iii) Petrol: Petrol is used as a fuel in light motor vehicle such as cars, motorcycles and scooters etc. We should use electric vehicles.
![]()
(iv) Natural Gas: It is used as a domestic and industrial fuel. We should use alternative sources of energy.
(v) Water: It is used in homes for drinking, cooking food, washing utensils, cleaning flour, brushing teeth, washing clothes, flushing toilets and watering plants. We can save water by minimising its wastage.
Question 8.
List four activities that are possible due’to the presence of air.
Answer:
Four activities that are possible due to presence of air
(i) Breathing
(ii) Generating electricity through wind turbines
(iii) Transportation through aeroplanes.
(iv) Flying kites
Question 9.
How can you contribute towards enhancing the green cover of your locality? Make a list of actions to be taken.
Answer:
- I can contribute towards enhancing the green cover of my locality by adopting following practices:
- I can plant more and more trees and help clean up parks, playgrounds, and other green areas by picking up litter.
- I can take care of the plants and trees growing in or around my locality.
- I can encourage the people in my locality to plant more trees by informing them about the importance of growing trees.
![]()
Question 10.
In the given illustration, we see that food is being cooked. Answer the following questions-

(i) What type of energy is being used for cooking?
(ii) Name one benefit and one drawback of using this type of energy for cooking.
Answer:
(i) Solar energy
(ii) One benefit of solar energy for cooking is that it is a renewable energy source and does not cause air pollution and global warming, so it is environment friendly.
Whereas, one drawback of using solar energy for cooking is that it cannot be used during a cloudy days or night as it requires sunlight to cook food. So, solar energy is not very convenient and reliable, specially during cloudy days and nights.
Question 11.
Cutting down trees on a large scale imports the quality of the soil. Why do you think it is so?
Answer:
Cutting down trees on a large scale impacts the quality of soil. Soil erosion is caused when the trees are cut down on a large scale then the top soil gets exposed and becomes loose because there are no roots to bond soil and no cover to soften the effect of falling rain. Blowing wind and flowing water can then carry away this loose soil easily causing soil erosion.
Question 12.
Explain two ways in which human activities pollute the air. Propose one action which can help in reducing air pollution.
Answer:
(i) Deforestation reduces the number of trees that can abdorb carbon dioxide, increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases.
(ii) Burning fossil fuels in vehicles and factories releases harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide and sulphur dioxide into the air.
Action to reduce air pollution: Promote the use of public transport and electric vehicles to decrease the number of fossil fuel-powered vehicles on the road.
![]()
Question 13.
A family uses solarpanels to generate electricity, a gas stove to cook food and a windmill for pumping waterfrom a well. What would happen if there were no sunlight for a week?
Answer:
This family uses solar energy to generate electricity. If there were no sunlight for a week, electricity generation will stop.
Question 14.
Fill up the blanks using the following terms(fossil fuels, forest, air, petroleum, coal, water and non-renewable resources)

Answer:

Question 15.
There is an increasing demand of trees to meet the requirements of industries and for housing. Therefore trees are being cut. Is it justified? Discuss and prepare a brief report.
Answer:
It is not justified to cut trees to meet the requirements of industries and for housing. If the trees disappear
- The temperature on the earth will increase.
- Animals may migrate due to shortage of food
- Soil will not hold water during rains resulting in floods.
- Valuable products such as timber will not be available.
- Lesser scale cutting of trees would lead to lesser rainfall, increased air pollution and soil erosion.
Question 16.
Propose a plan to use less water in your school. What steps would you take to make this plan happen and how would it help the environment?
Answer:
Plan to Use Less Water
- Use grey water for gardening purposes.
- Implement a rainwater harvesting system.
- Install water-efficient faucets and toilets.
Steps to Implement the Plan
- Monitor water usage regularly and set reduction targets.
- Encourage student-led initiatives for water conservation.
- Collaborate with local authorities and experts to install water saving devices.
Environmental Benefits
- Promotes sustainability and responsible water usage within the community.
- Decreases the energy used in water treatment and distribution.
![]()
Activities
Activity 11.3:
Let us Find Out (Page 212)
Fill the Column II and Column III in following table.

Answer:
Table: Wastage of water in your daily activities
| Column I | Column II | Column III | |
| Activity | How is water wasted? | Suggest ways to reduce wastage of water. | |
| 1. Hand washing | Washing your hands or face with the water running uses about 4 litres of water which cause wastage of water. | Turning the water off saves 3 litres, using only 1 litre each time you wash up, saves water. | |
| 2. Washing clothes | Clothes are bleached, dyed with hard chemicals in water makes the leftover chemical filled which causes the water wastage. | Skipping the extra use and re- rise of towels can reduce the wastage of water. | |
| 3. Washing utensils | When washing dishes by hand, the water run while rinsing can cause water wastage. | Fill the sink with soap and water and block the faucet, this will reduce water wastage. | |
| 4. Taking shower | Taking shower for longer duration can cause water wastage. | Taking shower for limited time- period reduce water wastage. | |
| 5. Cooking | Washing vegetables and fruits for cooking in excessive amount cause water wastage. | Steaming the vegetables and fruits reduce the wastage of water. | |
| 6. Gardening | Over watering not only cause water wastage but also harm the garden. | Using of drip irrigation method can reduce the water wastage. | |
| 7. Brushing teeth | Keeping the tap opened while brushing teeth cause water wastage. | Turn off the tap while brushing teeth reduce the water wastage. |
Activity 11.6:
Let us make a list of natural resources used (Page 225)
Make a list of activities you do in your daily life and write down the natural resources that were used directly or indirectly for each activity. In Table, some items are already filled in. Using them as a guide, fill the remaining blank rows.

Answer:
Natural Resource Used
| Activity | Natural Resource |
| 1. Washing clothes | Water |
| 2. Making clay toys | Soil |
| 3. Collecting firewood | Wood |
| 4. Making kites | Resilient Bamboo |
| 5. Having breakfast | Water |
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection
Topics and Sub Topics in Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 11 | Light, Shadows and Reflections |
| 11.1 | Transparent, opaque and translucent objects |
| 11.2 | What exactly are shadows? |
| 11.3 | A pinhole camera |
| 11.4 | Mirrors and reflections |
1. Rearrange the boxes given below to make a sentence that helps us understand opaque objects.
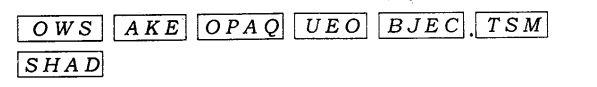
Ans:
![]()
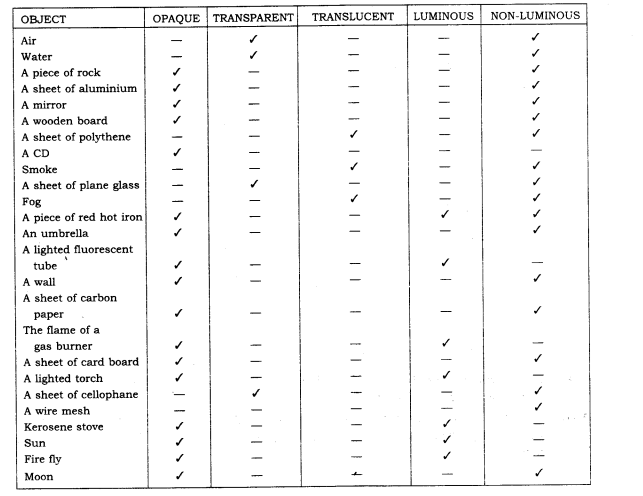
2. Classify the objects or materials given below as opaque, transparent or translucent and luminous or non-luminous:
Air, water, a piece of rock, a sheet of aluminium, a mirror, a wooden board, a sheet of polythene, a CD, smoke, a sheet of plane glass, fog, a piece of red hot iron, an umbrella, a lighted fluorescent tube, a wall, a sheet of carbon paper, the fame of a gas burner, a sheet of cardboard, a lighted torch, a sheet of cellophane, a wire mesh, kerosene stove, sun, firefly, moon.
Ans:
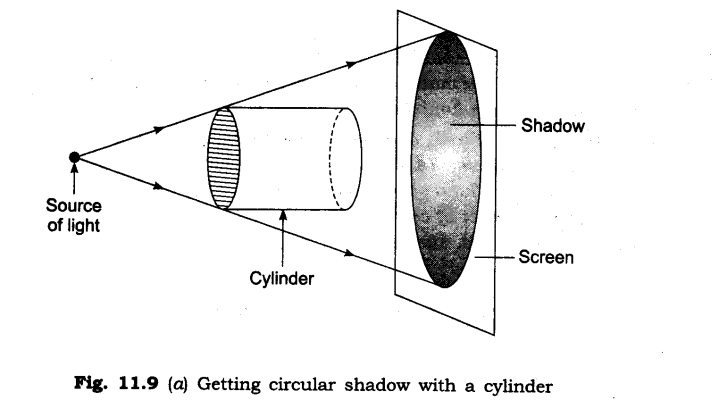
3. Can you think of creating a shape that would give a circular shadow if held in one way and a rectangular shadow if held in another way?
Ans: Yes, there are many things which give a circular shadow if held in one way and a rectangular shadow if held in another way. For example: a cylinder, a circular disc etc.
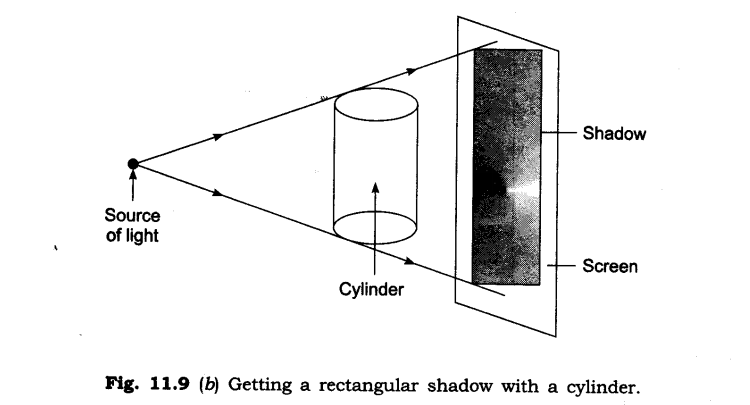
4. In a completely dark room, if you hold up a mirror in front of you, will you see a reflection of yourself in the mirror?
Ans: No, in a completely dark room no image will be formed because there is no light in the room so no reflection of light takes place and no image will be formed.
Class 6 Science Chapter 11 VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Whether the moon is luminous or non-luminous body?
Ans: Moon is non-luminous body.
2. What is umbra?
Ans: Umbra is the dark region behind object facing light which does not receive light at all.
3. How does a light ray travel?
Ans: Light ray travels in a straight line.
4. Give one natural source of light.
Ans: Sun is a natural source of light.
5. What is shadow?
Ans: Shadow is the dark space behind an opaque object where light does not reach.
6. What is penumbra?
Ans: The less darker shadow formed penumbra.on the periphery of dark shadow is called penumbra.
Class 6 Science Chapter 11 SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. State difference between a luminous and a non-luminous body.
Ans: The bodies which emit light are called luminous bodies. Example: sun, stars, burning candle etc.
The bodies which does not emit light are called non-luminous bodies. Example: moon, earth, blackboard.
2. Why is the moon not considered as a luminous body?
Ans: Moon is non-luminous body because it shines by reflecting the sunlight falling on it.
3. What is an incandescent body? Give example.
Ans: The bodies which emit light when heated to a very high temperature are called incandescent bodies. Example: electric bulb.
4. When does a shadow form?
Ans: Shadow is formed when light does not reach behind the opaque object kept in the path of light
5. Draw a diagram to illustrate the formation of umbra and penumbra.
Ans:
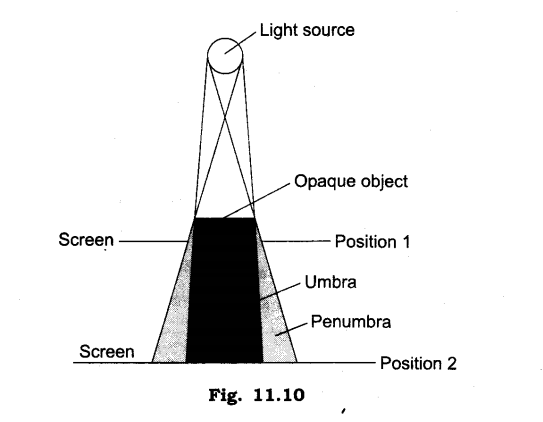
6. What are the essential conditions for the formation of shadow?
Ans:
(1) There should be an opaque material.
(2) There should be a source of light and screen.
The object must be placed in the path of light. Then shadow is formed on the screen.
7. Define reflection of light.
Ans: When light rays after striking the smooth and shiny surface return to same medium, this phenomenon is called reflection of light.
8. Write difference between shadow and image.
Ans:

9. How will you convert a glass sheet into a translucent sheet?
Ans: There are following two methods to convert glass sheet into a translucent sheet:
(i) By smearing a thin layer of oil on glass sheet.
(ii) By covering a side of sheet by butter paper.
10. What is shadow? How does the colour of an opaque object affects the colour of the shadow?
Ans: A dark outline or patch formed by an opaque object that blocks light coming from a source of light is called shadow. The colour of an opaque object does not affect the colour of the shadow.
11. Write the differences between umbra and penumbra.
Ans:
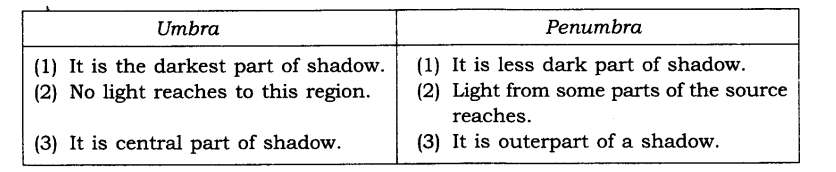
12. What do we need in order to see a shadow?
Ans: We need: (i) A source of light (ii) a screen (in) an opaque object.
13. What do you mean by scattering of light?
Ans: When a beam of light falls on a rough surface it is turned back in different directions. It is called scattering of light.
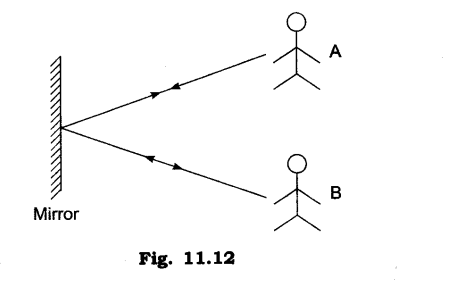
14. A and B are facing the mirror and standing in such a way that A can see B and B can see A. Explain this phenomenon.
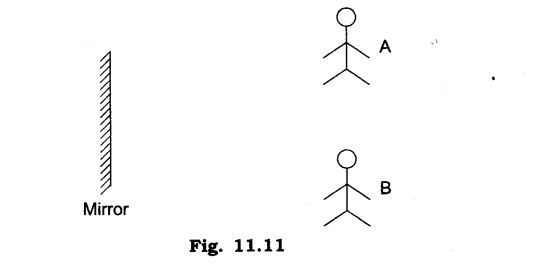
Ans: The light rays from A falls on the mirror and gets reflected and reaches B, the light from B falls on the mirror and reflects to reach A. The path of light is just reversed as shown.
15. ‘X’ is 20 cm away from the mirror. If he moves few steps closer to the mirror what will happen to the image
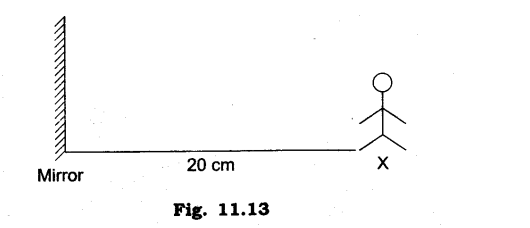
Ans: The size of the image will be same as the size of the object.
16.Write the mirror image of ‘SMART’?
Ans: THAM8
17. Have you ever seen an ambulance? It is written in the form of mirror image on vehicles. Explain why it is done so and give the mirror image of AMBULANCE.
Ans: The mirror image of AMBULANACE is aovt/yuaMA.
It is written so on the vehicles for the people to see in their rear view mirrors, read it correctly and immediately give way to the vehicle as it carries patients who need urgent medication.
18. You have to cost the shadow of your pencil on the wall with the help of candle in a dark room. How can you obtain the shadow of same size, small size and big size of the same pencil?
Ans: (a)The shadow of the pencil will be small when the pencil is taken close to the wall and away from the candle.
(b)The shadow will be big in size when the pencil is taken closer to the candle.
(c)To get the same sized shadow as the pencil is, adjust the distance between the wall, pencil and candle at equal distances.
Class 6 Science Chapter 11 LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What is reflection of light? Explain reflection of light with the help of an activity.
Ans: When light rays fall on a highly polished (e.g. mirror) smooth surface and return to the same medium, it is called reflection of light.
Activity to show reflection of light: This activity should be done at night or in a dark room. Ask your friend to hold a mirror in his hand at one corner of the room. Stand at another comer with a torch in your hand. Cover the glass of torch with your fingers and switch it on. There should be small gap between your fingers. Direct the beam of torch-light on to the mirror that your friend is holding. Adjust the direction of torch so that patch of light falls on your friend standing in the room. This activity shows the reflection of light also that light travels in straight line.
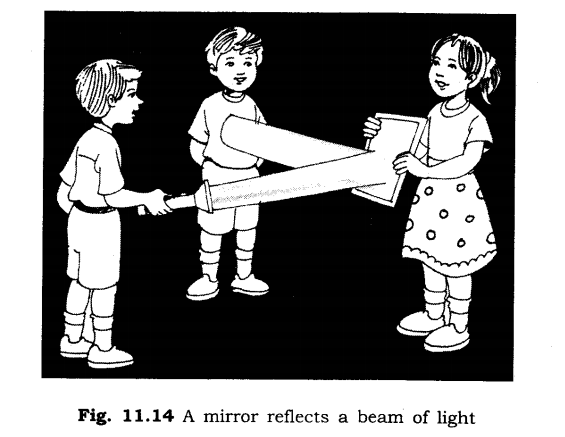
2. Explain the manner in which light travels with the help of an activity.
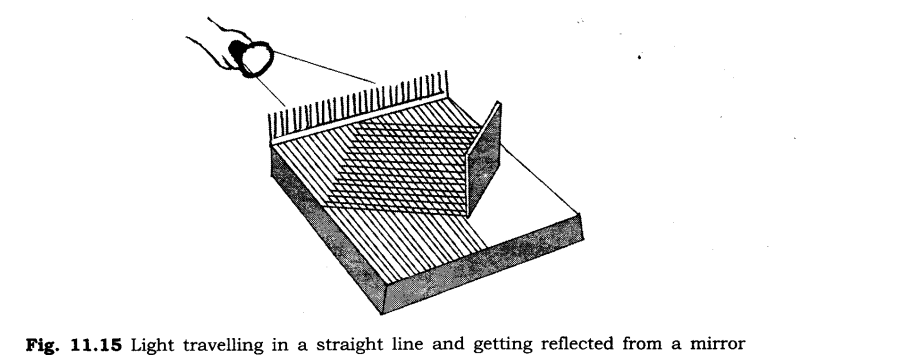
Ans: Take a comb and fix it on one side of a thermacol sheet. Fix a mirror on the other side as shown in figure. Spread a dark coloured sheet of paper between the mirror and the comb. Send a beam of light from a torch through the comb. You get a pattern of light similar to that shown in figure. This activity explains the manner in which light travels and gets reflected from a mirror.
3. Explain that light has the property of rectilinear propagation.
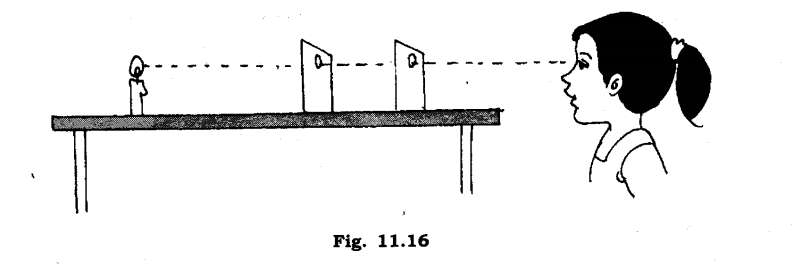
Ans: We take three pieces of cardboard. Place them one on the top of one another and make a hole in the middle of each cardboard by using a thick nail. Erect these cards up on the table at a short distance away from each other. Take a candle which is of the same height as the holes in the cards. Light the candle and place it in front of the cards. We see that the light of candle is visible only when the holes on cards lie in a straight line. If we disturb them the light of candle disappears. This experiment shows that light propagates in a straight line.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science – All Chapters
- Chapter 1 The Wonderful World of Science
- Chapter 2 Diversity in the Living World
- Chapter 3 Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body
- Chapter 4 Exploring Magnets
- Chapter 5 Measurement of Length and Motion
- Chapter 6 Materials Around Us
- Chapter 7 Temperature and its Measurement
- Chapter 8 A Journey through States of Water
- Chapter 9 Methods of Separation in Everyday Life
- Chapter 10 Living Creatures: Exploring their Characteristics
- Chapter 11 Nature’s Treasures
- Chapter 12 Beyond Earth