Living Creatures: Exploring their Characteristics NCERT Class 6th Science Chapter 10 Question Answer
Living Creatures: Exploring their Characteristics Class 6 Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How would you now categorise a seed, as living or non¬living? (Page 191)
Answer:
Seed is a living thing. Seed can grow into a plant under right conditions.
Question 2.
How can the life cycle of a mosquito be disrupted? (Page 197)
Answer:
Larvicides (a substance used to kill larvae) target larvae in the breeding habitat before they can mature into adult mosquitoes and disperse. Larvicide treatment of breeding habitats helps reduce the adult mosquito population in nearby areas.
Liquid larvicide products are applied directly to water using backpack sprayers and truck or aircraft-mounted sprayers. Tablet, pellet, granular, and briquet formulations of larvicides are also applied by mosquito controllers to breeding areas.
![]()
Let Us Enhance Our Learning (Page 203 – 204)
Question 1.
List the similarities and differences in life cycles of plants and animals. __
Answer:
Similarities:
- Life cycles of both, plants and animals, begin with an initial stage which is followed by several stages of its growth and development and finally death.
- In life cycle of both, the process of reproduction maintains the continuity of its kind.
Differences:
| Life Cycle of Plants | Life Cycle of Animals |
| 1. A plant’s life cycle starts with seed germination. | 1. An animal’s life cycle begins with a new bom. |
| 2. Germination is followed by flowering and seed production. | 2. New bom animals grow to become adult animals. |
| 3. Seeds produced during their life cycle germinate into new plants. | 3. The process of reproduction does not involve formation of seeds. |
Question 2.
The table given below shows some data. Study the data and try to find out examples appropriate for the conditions given in the second and third columns. If you think that an example for any of the conditions given below is not possible, explain why.

Answer:

Question 3.
You have learnt that different conditions are required for seed germination. How can we use this knowledge for proper storage of grains and pulses?
Answer:
To ensure proper storage of grains and pulses and prevent germination:
- Keep Dry: Ensure grains and pulses are kept in a dry environment to prevent moisture from initiating germination.
- Cool Storage: Store in a cool place to slow down any biological processes.
- Airtight Containers: Use airtight containers to limit exposure to air, which is necessary for germination.
Question 4.
You have learnt that a tail is present in a tadpole but it disappears as it grows into a frog. What is the advantage of having a tail in the tadpole stage?
Answer:
- The tail in the tadpole stage of a frog provides
- Swimming Ability: It helps the tadpole swim efficiently in water to find food and escape predators.
- Balance and Stability: Assist in maintaining balance while moving in water.
![]()
Question 5.
Charan says that a wooden log is non-living as it cannot move. Charu counters it by saying that it is living because it is made of wood obtained from trees. Give your arguments in favour or against the two statements given by Charan and Cham.
Answer:
Argument in favour of “wooden log is non-living thing’:
- Wooden log cannot move, respire or grow.
- It does not respond to any stftnulus.
Argument in favour of “wooden log is living thing’:
- Wooden log is obtained from trees which are living things.
Question 6.
What are the similarities and distinguishing features in the life cycles of a mosquito and a frog?
Answer:
The similarities in the life cycles of a mosquito and a frog are as follows
(i) Both undergo transformation with distinct life stages.
(ii) Both lives start as eggs.
The distinguishing features in the life cycles of a mosquito and a frog are as follows
(i) Life cycle of mosquitoes – egg, larva, pupa, adult.
Life cycle of frog- egg, tadpole, froglet, adult.
(ii) Mosquitoes are entirely terrestrial in adult stages, while frogs can live both on land and in water (amphibians)
Question 7.
A plant is provided with all the conditions suitable for its growth (Fig.8). Draw what you expect to see in the shoot and the root of the plant after one week. Write down the reasons.
Answer:
The roots grow downwards in the soil in search of water. Shoot bends upwards from where the light is coming. The plant shoots bend towards sunlight because the leaves need sunlight to make food. In this case, the stimus is sunlight.
![]()
Question 8.
Tara and Vijay set up the experiment shown in the picture (Fig. 9.). What do you think they want to find out? How will they know if they are correct?

Answer:
They want to find out, how cactus plant is adopted to live in desert. The cactus plants have long roots to absorb water from a larger area. The cactus plants have modified their leaves in the form of thin spines to reduce the loss of water through transpiration.
Question 9.
Design an experiment to check if temperature has an effect on seed germination
Answer:
AIM: Experiment to Check the Effect of Temperature on Seed Germination
Materials: Identical pots, soil, seeds, thermometers, and different tem¬perature-controlled environments (e.g., refrigerator, room temperature, heated environment).
Procedure
(i) Fill each pot with the same type of soil.
(ii) Plant seeds in each pot.
(iii) Place each pot in a different environment with controlled temperatures (e.g., cold, room temperature, warm). For example, keep one pot outside in balcony to get sunlight. Put another in shade in the room. Keep the third one in basement or at coldest part of the house.
(iv) Water each pot equally.
(v) Record the number of seeds germinated in each environment daily for two weeks.
Observation: Measure and compare the rate of germination and growth in different temperatures.
Conclusion: Determine the optimal temperature for seed germination based on observations.
![]()
Activities
Activity 10.2 (Page 188)
When a seed turns into a sprout, it is said to have germinated. Predict whether the seeds in each pot will germinate. Record your predictions for each pot kept under different conditions in Table.

Answer:
Table: Effect of certain conditions on seed germination

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
Topics and Sub Topics in Class 6 Science Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 10 | Motion and Measurement of Distances |
| 10.1 | Story of transport |
| 10.2 | How wide is this desk? |
| 10.3 | Some measurements |
| 10.4 | Standard Units of Measurements |
| 10.5 | Correct Measurement of Length |
| 10.6 | Measuring the length of a curved line |
| 10.7 | Moving things around us |
| 10.8 | Types of motion |
1. Give two examples each of modes of transport used on land, water and air.
Ans:
(i) Land—Bus, truck, train.
(ii) Water—Ship, boat.
(iii) Air—Aeroplane, Helicopter.
2. Fill in the blanks:
(i) One metre is___________
(ii) Five kilometre is___________
(iii) Motion of a child on a swing is_____________ .
(iv) Motion of the needle of a sewing machine is_______________ .
(v) Motion of wheel of a bicycle is_____________ .
Ans:
(i) 100
(ii) 5000
(iii) periodic (oscillatory) motion
(iv) periodic oscillatory (v) circular.
3. Why can a pace or a footstep not be used as a standard unit of length?
Ans: Because a pace or a footstep of each and every person is not equal.
4. Arrange the following lengths in their increasing magnitude :
1 metre, 1 centimetre, 1 kilometre, 1 millimetre.
Ans: Ascending order of length:
1 millimetre < 1 centimetre < 1 metre < 1 kilometre
5. The height of a person is 1.65 m. Express it in cm and mm.
Ans:
(a) 1.65 m, as one metre = 100 cm
= 1.65 x 100 cm = 165 cm
(b)65 x 100 x 10 mm = 1650 mm.
6. The distance between Radha’s home and her school is 3250 ,m. Express this distance in km.
Ans:
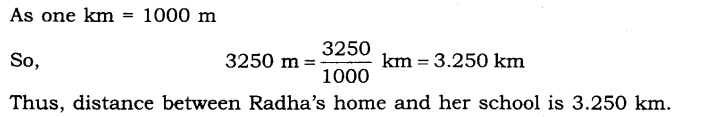
7. While measuring the length of a knitting needle, the reading of the scale at one end is 3.0 cm and at the other end is 33.1 cm. What is the length of the needle?
Ans: Length of the needle = 33.1 cm – 3.0 cm = 30.1 cm.
8. Write the similarities and differences between the motion of a bicycle and a ceiling fan that has been switched on.
Ans:
(i) Similarity: Both the wheel of a bicycle and a ceiling fan exhibit motion on a fixed axis.
(ii) Dissimilarity: Bicycle moves forward thus executes rectilinear motion but fan does not show such motion.
9. Why could you not use an elastic measuring tape to measure distance? What would be some of the problems you would meet in telling someone about a distance you measured with an elastic tape?
Ans: An elastic measuring tape gives incorrect length of the distance between two points.
Reasons:
(i) The length of the elastic tape varies and depends upon the force by which it is stretched.
(ii) Measurement would vary between 2 or 3 readings even when measured by the same person and by the same elastic tape.
(iii) Measurement would also vary if different persons measure the same distance.
10. Give two examples of periodic motion.
Ans:
(i) Oscillations of a pendulum.
(ii) Motion of swing/motion of earth round the sun.
Class 6 Science Chapter 10 VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Are senses reliable for accurate measurement?
Ans: Our senses are not reliable for accurate measurement.
2. Why can hand span and arm length not be used as standard units of length?
Ans: because these vary from person to person.
3. How many centimetres are there in 1 m?
Ans: 100 cm.
4. Name the measuring device which can be used for measuring the girth of a tree.
Ans: Measuring tape.
5. Give one example of linear motion.
Ans: Motion of stone falling from a certain height.
6. Give an example of circular motion.
Ans: Motion of arms of watch.
7. Name the types of motion in which a body moves along a straight path
Ans: Rectilinear or linear motion.
8.Find the length and breadth of given rectangle in mm and cm.
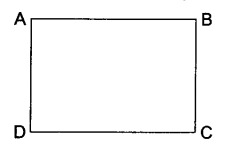
Ans: Using measuring scale (15 cm scale), Length AB = 3 cm and breadth BC = 2 cm.
AB = 3 x 10 = 30 mm
BC = 2 x 10 = 20 mm.
9.Give the unit for measuring the following:
(a) Distance between Delhi and Jaipur.
(b) Thickness of a coin.
(c) Length of your eraser.
(d) Length of your shoe lace.
Ans:
(a) Kilometre
(b) Millimetre
(c) Centimetre
(d) Centimetre
10. Name the device used to measure the following:
(a) Size of your shoulder.
(b) Size of your wrist.
(c) Your height.
(d) Your weight.
(e) Cloth for curtain.
(f) Circumference of round table.
Ans:
(a) Measuring tape
(b) Measuring tape
(c) Measuring tape
(d) Weighing balance
(e) Metre scale or measuring tape
(f) A long thread or measuring tape.
Class 6 Science Chapter 10 SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. State two precautions to be observed while measuring length with the help of a metre scale.
Ans: Two precautions are:
(i) The initial point of distance must coincide with the zero reading of metre scale.
(ii) The eye should be kept in line with the point of measurement.
2. Define rest and motion.
Ans: The objects which do not change their positions with time are said to be at rest. The objects which change their positions with time are said to be in motion.
3. Define the term standard unit.
Ans: The unit that could be used everywhere as a basic unit of measurement is called a standard unit.
4. How can a measured length be expressed?
Ans: Each measurement has:
(i) A number describing the numerical value.
(ii) The unit in which that quantity is measured.
5. Give one example each of the following types of motion:
(a) Linear
(b) Translation
(c) Circular
(d) Periodic.
Ans:
Types of motion Example
(a) Linear motion of stone falling
(b) Translatory buses
(c) Circular ceiling fan
(d) Periodic pendulum of clock
Class 6 Science Chapter 10 LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Why do we need standard unit for measurement?
Ans: We need standard unit for measurement to make our judgement more reliable and accurate. For proper dealing, measurement should be same for everybody. Thus there should be uniformity in measurement. For the sake of uniformity we need a common set of units of measurement, which are called standard units. Nowadays SI units are used in science and technology almost universally.
2. What type of motion do the following objects have?
(a) the galloping of a horse
(b) the needle of a sewing machine
(c) the movements of a mosquito
(d) the blades of an electric fan
(e) the smoke from a lighted dhoopbatti
(f) wheels of moving car.
Ans:
(a) The galloping of a horse: Linear motion.
(b) The needle of a sewing machine: Periodic motion.
(c) Movement of a mosquito: Random motion.
(d) Blade of an electric fan: Circular motion.
(e) The smoke from a lighted dhoopbatti: Random motion.
(f) Wheels of moving car: Linear motion and Rotational motion.
3. Give two examples for each of the following motions:
(i) Linear motion
(ii) Spinning motion
(iii) Oscillatory motion
(iv) Periodic motion
(v) Vibrational motion
(vi) Circular motion
(vii) Random motion
Ans:
(i) Linear motion: (a) Rolling of ball on ground, (b) Moving of bicycle on road,
(ii) Spinning motion: (a) Rotating fan, (b) Wheel of sewing machine.
(iii) Oscillatory motion: (a) Pendulum of clock, (b) Motion of a child on a swing,
(iv) Periodic motion: (a) Pendulum of clock, (b) Motion of a swing, heartbeat.
(v) Vibrational motion: (a) String of a guitar, (b) Surface of drums.
(vi) Circular motion: (a) Rotation of fan, (b) Bicycle wheel.
(vii) Random motion: (a) Motion of football players, (b) Movement of mosquito.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science – All Chapters
- Chapter 1 The Wonderful World of Science
- Chapter 2 Diversity in the Living World
- Chapter 3 Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body
- Chapter 4 Exploring Magnets
- Chapter 5 Measurement of Length and Motion
- Chapter 6 Materials Around Us
- Chapter 7 Temperature and its Measurement
- Chapter 8 A Journey through States of Water
- Chapter 9 Methods of Separation in Everyday Life
- Chapter 10 Living Creatures: Exploring their Characteristics
- Chapter 11 Nature’s Treasures
- Chapter 12 Beyond Earth