NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials : Metals and Non-Metals are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials : Metals and Non-Metals.
NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials : Metals and Non-Metals
Multiple Choice Questions
Question. 1 Which of the following is not a metal?
(a) Copper (b) Sulphur (c) Aluminium (d) Iron
Answer. (b) Copper, aluminium and iron are metals but sulphur is not a metal.
Question. 2 The substance that will be flattened on beating with a hammer is
(a) crystal of iodine (b) lump of sulphur
(c) piece of coal 4 (d) zinc granule
Answer. (d) Metals can be beaten into thin sheets (or flattened) with a hammer. Non-metals break into small pieces when hammered. So, zinc granule will be flattened on beating with a hammer.
Question. 3 Boojho has learnt that non-metals on beating with a hammer are generally broken into pieces. Which of the following is non-metal?
(a) Iron nail (b) Aluminium wire
(c) Copper plate (d) Piece of coal
Answer. (d) Piece of coal is a non-metal which broke into small pieces when hammered.
Question. 4 Materials which can be drawn into wires are called ductile. Which of the • following is not a ductile material?
(a) Silver (b) Copper (c) Sulphur (d) Aluminium
Answer. (c) Ductility is a characteristic property of metals. Sulphur is a non-metal, so it is not
ductile. When stretched, sulphur break into pieces and do not form wires.
Question. 5 Metals are generally hard. Which of the following metals is an exception ! and can be cut with a knife?
(a) Iron (b) Sodium (c) Gold (d) Magnesium
Answer. (b) Metals are generally hard. This means that most of the metals cannot be cut easily. But sodium metal is soft and can be easily cut with a knife.
Question. 6 Metals are generally solid. Which of the following metals is in the liquid state at room temperature?
(a) Mercury (b) Silver (c) Aluminium (d) Sodium
Answer. (a) Mercury metal is in the liquid state at room temperature.
Question. 7 Metals generally react with dilute acids to produce hydrogen gas. Which one of the following metals does not react with dilute hydrochloric acid? (a) Magnesium (b) Aluminium (c) Iron (d) Copper
Answer. (d) The less reactive metals like copper, silver and gold do not react with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce hydrogen gas.
Question. 8 Which of the following reacts with cold water vigorously?
(a) Carbon (b) Sodium (c) Magnesium (d) Sulphur
Answer. (b) The vigour (or intensity) of reaction of a metal with water depends on its chemical reactivity. Sodium is a very reactive metal, so it reacts violently even with cold water.
Question. 9 The metal which produces hydrogen gas on reaction with dilute hydrochloric acid as well as sodium hydroxide solution is (a) copper (b) iron (c) aluminium (d) sodium
Answer. (c) Aluminium reacts with hydrochloric acid as well as sodium hydroxide solution to produce hydrogen gas.
Question. 10 Which of the following non-metals reacts and catches fire on exposure to air?(a) Phosphorus (b) Nitrogen » (c) Sulphur (d) Hydrogen
Answer. (a) Phosphorus is a non-metal which reacts and catches fire on exposure to air.
Question. 11 Generally metallic oxides are basic and non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature. Solution of which of the following oxides in water will change the colour of blue litmus to red?
(a) Sulphur dioxide (b) Iron oxide
(c) Magnesium oxide (d) Copper oxide
Answer. (a) Sulphur is a non-metal and it forms an acidic oxide, i.e. sulphur dioxide (S02) which turns blue litmus red.
Question. 12 Which of the following property is not responsible for copper to be used as electrical conduction wires?
(a) Ductility (b) Colour
(c) Good conductor of electricity (d) It is solid
Answer. (b) Colour of the copper metal is not responsible for copper to be used as electrical conduction wires.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. 13 Name two soft metals which can be cut with a knife.
Answer. Metals which can easily cut with a knife
(i) Sodium (ii) Potassium
These are soft metals.
Question. 14 Which non-metal is essential for our life and all living beings inhale it during breathing?
Answer. Oxygen is a non-metal which is used by plants and animals (including human beings) for breathing. Thus, oxygen (non-metal) is essential for maintaining our life.
Question. 15 Name two majorTion:metals which are present in fertilisers and enhance the growth of plants.
Answer. Two major non-metals which are present in fertilisers and enhance the growth of plants are: .
(i) Nitrogen (ii) Phosphorus
Question. 16 Which non-metal is used to disinfect water?
Answer. Chlorine which is a non-metal, is used in water purification plants because chlorine has ‘ the ability to kill germs.
Question. 17 A purple coloured non-metal forms a brown solution in alcohol which is applied on wounds as an antiseptic. Name the non-metal.
Answer. Iodine is a non-metal which*.is used to make purple-coloured solution called tincture iodine which is applied on cuts and wounds as an antiseptic.
Question. 18 Zinc sulphate forms a colourless solution in water. Will you observe any colour on adding copper turning in it?
Answer. There is no colour change on adding copper turning in zinc sulphate solution because copper is less reactive than zinc and it cannot displace zinc from its salt solution. So, displacement reaction does not take place.
Question. 19 Why are bells made of metals?
Answer. Metals have sonorous property. Ringing sound produce by metals is known as sonorous. So, the bells are made of metals. .
Question. 20 Which liquid metal is used for making thermometers?
Answer. Mercury metal is used for making thermometers.
Question. 21 Which of the following metals can displace the other two metals from their salt solutions? Zinc, iron, copper
Answer. Zinc is most reactive among three metals and copper is least-reactive metal. Reactivity of iron is in between zinc and copper. So, zinc metal can displace the other two metals from their salt solutions.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. 22 Paheli bought a statue made up of copper. To her surprise, it acquired a dull green coating after a couple of months. Explain the reason.
Answer. When a copper statue (or copper vessel) is exposed to moist air for long, it acquires a dull green coating. The green material is a mixture of copper hydroxide [Cu(OH)z] and copper carbonate (CuC03) formed due to the reaction of copper with moist air. The following is the reaction.
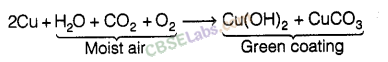
The green coating is commonly known as ‘basic copper carbonate’ and the formation of green coating on copper objects show the corrosion of copper.
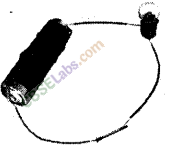
Question. 23 In the given figure, you find that the bulb glows when an iron nail is placed between two ends of wire. Complete the following sentences on the basis of this fact.
(a) is a metal. (b) Metals are good of electricity.
Answer. (a) Iron (b) conductors
Question. 24 If in figure given above, iron nail is replaced by a wooden stick, will the bulb glow or not? Justify your answer.
Answer. No, the bulb will not glow. It is because wood is a non-conductor of electricity.
Question. 25 Paheli prepared a blue coloured solution of copper sulphate in beaker A and placed an iron nail in it. Boojho prepared a yellowish green solution of ferrous sulphate in beaker B and placed a copper wire in it. What changes will they observe in the two beakers after an hour?
Answer. In beaker A1, a reddish brown layer of copper will deposit on the iron nail and blue coloured solution of copper sulphate will become yellowish green due to the formation of iron sulphate. This is because iron is more reactive than copper and it displaces copper from its salt solution (copper sulphate solution). In beaker B1, no change is observed because copper being less reactive does not displace iron (more reactive) from ferrous sulphate solution.
Question. 26 A doctor prescribed a tablet to a patient suffering from iron deficiency. The tablet does not look like iron. Explain.
Answer. Iron is a metal but the tablet is not made up of iron metal. It is made up of a salt of iron. So, it does not look like iron.
Question. 27 Match the Column A with Column B.
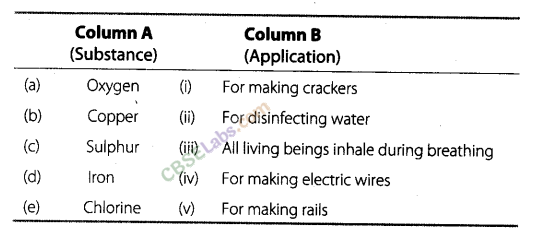
Answer. The correct matching is as given :
(a)—(iii), (b)—(iv), (c)—(i), (d)—(v), (e)-(ii)
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. 28 State whether the following statement are True/False.
- The property of metals by virtue of which they can be drawn into wires is called ductility.
- Metals are good conductors of electricity but poor conductor of heat.
- Articles made up of metals produce ringing sound when struck hard.
- Oxides of non-metals and metals are acidic in nature.
- A less reactive metal displaces a more reactive metal from its salt solution in water.
Answer.
- True
- False, metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
- True, because metals are sonorous.
- False, oxides of non-metals are acidic in nature and oxides of metals are basic in nature.
- False, a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its salt solution in water.
Question. 29 Iron is more reactive than copper. Can you write an activity to show this?
Answer. Take about 50 mL of water in a beaker and dissolve 5 g of copper sulphate in it to obtain copper sulphate solution (which is blue in colour). Put a clean iron nail in this solution and keep the beaker undisturbed for some time.
We will find that the blue colour of copper sulphate solution starts fading gradually and the iron nail gets covered with a red-brown layer of copper metal. It is because iron is more reactive than copper, so it displaces copper metal from its solution of copper sulphate.
It is the copper metal set free from its compound which forms a red-brown layer on the surface of iron nail. This shows that iron is more reactive than copper.
![]()
Question. 30 Fill in the blanks to complete the following paragraph.The name of the product formed in the reaction of sulphur and is sulphur dioxide gas. When sulphur dioxide is dissolved in sulphurous acid is formed. The sulphurous acid turns litmus paper to Generally, oxides of are acidic in nature. After completing the paragraph, write two questions which you can raise on the basis of this information.
Answer. Oxygen, water, blue, red, non-metals.
Questions may be :
- Which gas is formed when sulphur reacts with oxygen?
- What is the nature of oxides of non-metals?
Question. 31 Find out the names of three metals and three non-metals from the box given as figure.

Answer.

Metals Iron, copper, aluminium Non-metals Sulphur, carbon, oxygen
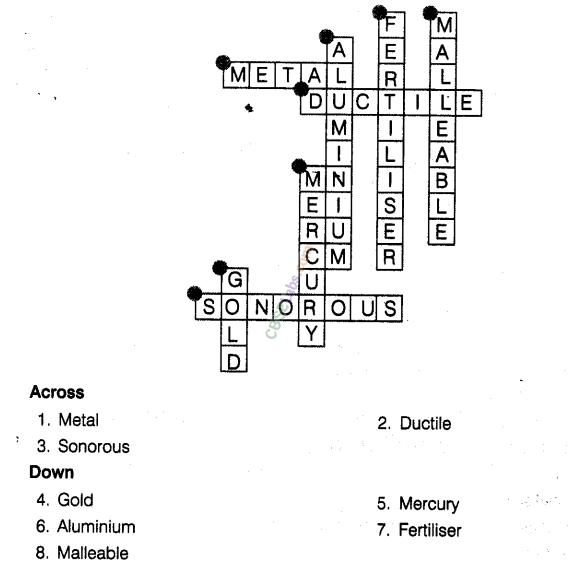
Question. 32 Complete the crossword given in figure with the help of the clues.
Across
1. Which is generally hard, ductile, malleable and sonorous.
2. A metal is called so, it can be drawn into wires.
3. Metal bells are used because of this property.
Down
4. A metal generally used for making jewellery.
5. A metal which -is liquid at room temperature.
6. A metal which reacts with acid as f well as base to form hydrogen gas.
7. Substances used to enhance the growth of plants.
8. Property by virtue of which metals can be beaten into thin sheets.
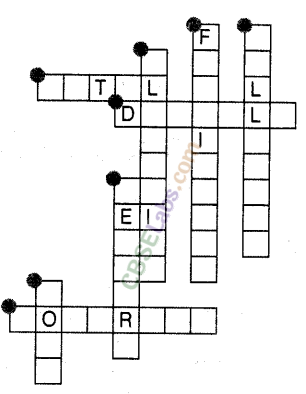
Answer.
NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials : Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 12 Friction
- Chapter 13 Sound
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
NCERT Exemplar SolutionsNCERT Exemplar MathsNCERT Exemplar Science
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials : Metals and Non-Metals help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials : Metals and Non-Metals, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.