NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light.
NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Question 1
Part of the eye which controls the entering of light is called
(a) iris (b) cornea
(c) lens (d) retina
Answer.
(a) Iris is a dark muscular structure behind the cornea, which controls the amount of light entering into the eye.
Question 2
We can see a non-luminous object when the light
(a) emitted by the object falls on the eye
(b) is reflected from the object towards our eye
(c) completely passes through the object
(d) gets completely absorbed by the object
Answer.
(b) We can see a non-luminous object (object that does not produce its own light), when light reflected by the object enters our eyes.
Question 3
Light is falling on surfaces S1 S2 and S3 as shown in the figure.
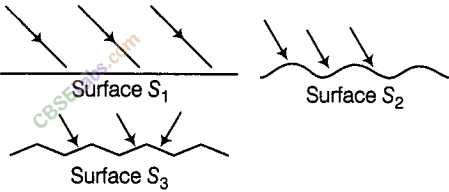
Surfaces on which the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection is/are
(a) Only S1 (b) S1 and S2
(c) S2 and S3 (d) All the three surfaces
Answer.
(d) Laws of reflection are always followed whatever be the surface of the object.
Therefore, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection on ail the three surfaces (S1,S2 and S3).
Question 4
A tiny mirror M is fixed on a piece of cardboard placed on a table. The cardboard is illuminated by light from a bulb. The position of eye with respect to position of bulb is shown in the figure as A, B, C and D. In which position mirror will be visible?
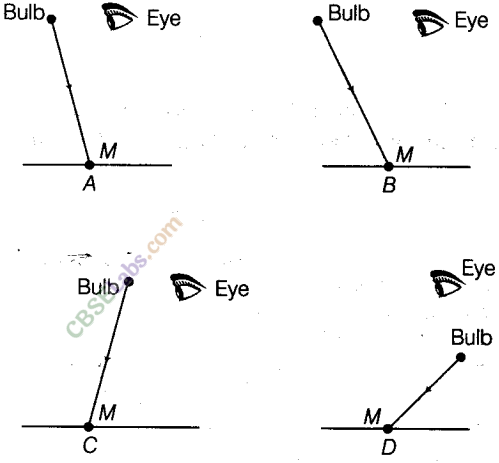
Answer.
(a) Following the laws of reflection of light, in case A, when a ray of light from the bulb strikes the mirror M, it will get reflected back such that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Question 5
A small hole P is made in a piece of cardboard. The hole is illuminated by a torch as shown in the figure. The pencil of light coming out of the hole falls on a mirror.
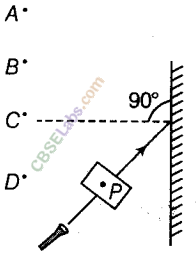
At which point should the eye be placed, so that the hole can be seen?
(a) A (b) B
(c) C (d) D
Answer.
(a) Eye should be placed at A because the hole can be seen only, when the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Question 6
Two mirrors A and B are placed at right angles to each other as shown in the figure.
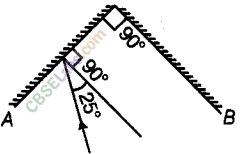
A ray of light incident on mirror A at an angle of 25° falls on mirror B after reflection. The angle of reflection for the ray reflected from mirror B would be
(a) 25° (b) 50°
(c) 65° (d) 115°
Answer.
(c) Angle of reflection for the ray reflected from mirror B will be 65° because figure below shows how reflected ray from mirror A forms incident ray on mirror 6 and then reflected back by an angle of 65°.
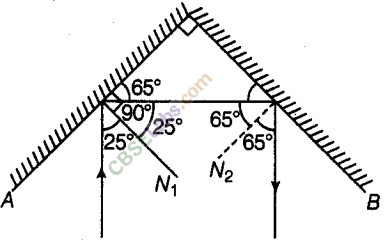
Question 7
Which of the following statements is correct regarding rods and cones in the human eye?
(a) Cones are sensitive to dim light.
(b) Cones are sensitive to bright light
(c) Rods are sensitive to bright light
(d) Rods can sense colour
Answer.
(b) Cones are sensitive to bright light and they sense colour. However, rods are sensitive dim light.
Question 8
In the figure of the human eye, the cornea is represented by the letter.
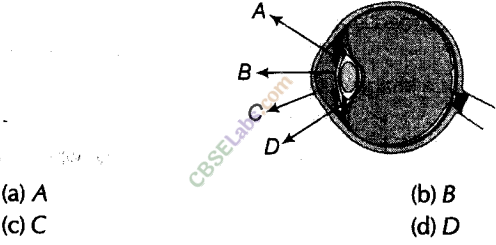
Answer.
(c) The transparent front part of the eye is cornea labelled as C (this is a thin layer).
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 9
Name the part of the eye which gives colour to the eyes.
Answer.
Iris is the part of the eye which gives its distinctive colour.
e.g. If a person is said to have blue eyes, then that actually refers to the blue colour of the iris.
Question 10
Boojho while waving his hand very fast in front of his eyes, observes that his fingers appear blurred. What could be the reason for it?
Answer.
The impression of an image persists for about 1/16th of a second on the retina. This is known as persistence of vision. If still images of a moving object are flashed on the eye at a rate faster than 16 per second, then the eye perceives this object as moving.
So, in case by waving hand very fast in front of eyes, the rate of movement of hand becomes very large (much faster than 16 per second), therefore, the fingers appear blurred.
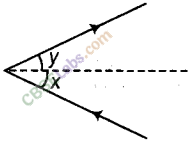
Question 11
How many times is a ray of light reflected by two plane mirrors placed parallel and facing each other?
Answer.
The ray is reflected infinite number of times between the two plane mirrors placed parallel to each other.
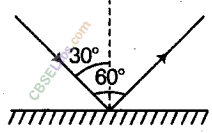
Question 12
The angle between incident ray and reflected ray is 60°. What is the value of angle of incidence? Given that, angle of incidence + angle of reflection = 60°.
Answer.
Since, angle of incidence = angle of reflection. So, angle of incidence = 30°

Question 13
The distance between the object and its image formed by a plane mirror appears to be 24 cm. What is the distance between the mirror and the object?
Answer.
In case of plane mirror, the image formed is at the same distance behind the mirror as the object infront of it.
i.e. object distance from the mirror = image distance from the mirror.
So, distance between the mirror and the object = 12 cm
Question 14
What happens to light when it gets dispersed? Give an example.
Answer.
Light is splitted into its constituent colours, when it gets dispersed, e.g. Rainbow formation is due to the dispersion of white light after passing through water droplets.
Question 15
Draw figure showing the position of the plane mirror. Also, label the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
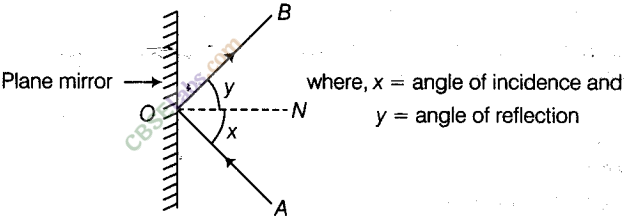
Answer.
Question 16
Look at the figure. Can the image of the child in it be obtained on a screen?

Answer.
The image of the child cannot be obtained on the screen because the image is not real. The images formed by plane mirror are virtual, so these virtual images cannot be seen (or obtain) on the screen.
Question 17
Eyes of the nocturnal birds have large cornea and a large pupil. How does this structure help them?
Answer.
The size of the eyes of nocturnal bird is large. Eyes of the nocturnal birds having large cornea with a wider pupil, can collect more ambient light which help them to see the objects even at night.
Question 18
What kind of lens is there in our eyes? Where does it form the image of an object?
Answer.
Convex lens is present in our eyes, which focuses light on the back of the eye, on a layer called retina. So, it forms the image of an object at retina.
Question 19
Which part of the eye gets affected if someone is suffering from ‘ cataract? How is it treated?
Answer.
In people (particularly old aged) suffering from cataract, the eye lens becomes clouded. Cataract is treated by replacing the opaque lens with a new artificial lens.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 20
Boojho planned an activity to observe an object A through pipes as shown in figure, so that he could see objects which he could not directly see.
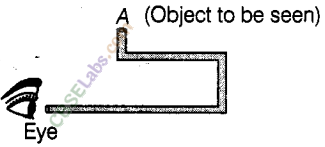
(a) How many mirrors should he use to see the objects?
(b) Indicate the positions of the mirrors in the figure.
(c) What must be the angle with respect to the incident light at which he should place the mirrors?
(d) Indicate the direction of rays in the figure.
(e) If any of the mirrors is removed, will he be able to see the objects?
Answer.
(a) He should use three plane mirrors to see the objects.
(b) Positions of the mirrors are as shown in the figure.
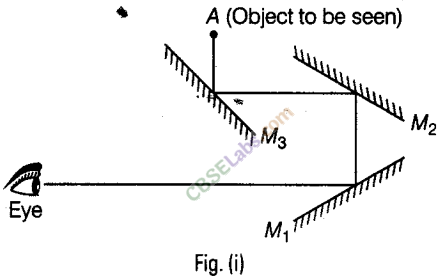
(c) Mirrors should be placed at an angle of 45° with respect to the incident light. So, that the rays can move forward.
(d) Direction of rays is shown in the figure
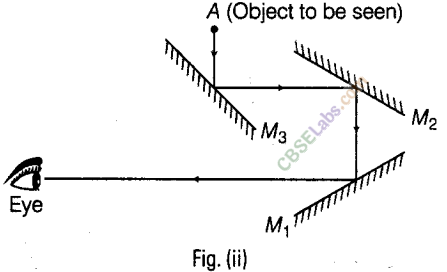
Or
In place of Fig. (i) and Fig. (ii) we may also use this combine figure for answer of Q 20. (b) and (d).
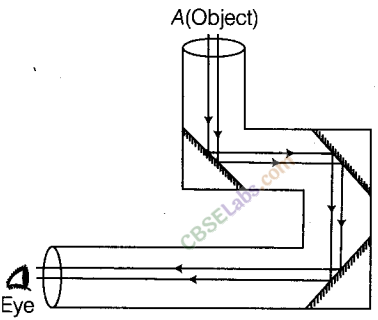
(e) He will not be able to see the objects if any of the mirrors is removed, because he will not get the reflected rays to move forward for further reflection to reach our eyes.
Question 21
There is a mistake in, each of the following ray diagrams given as
Fig. (a), (b), and (c). Make the necessary correction(s).
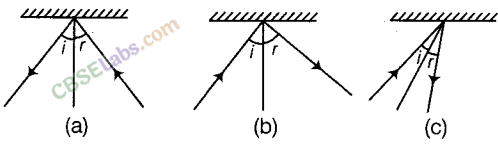
Answer.
The correct diagrams are as given below:
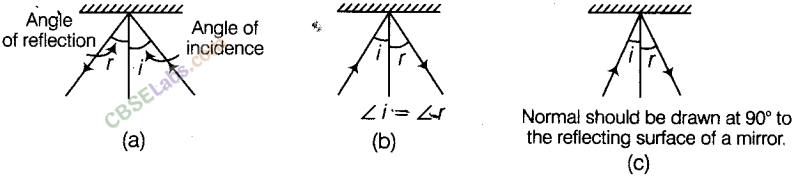
Question 22
Explain the process which enables us to perceive motion in a cartoon film.
Answer.
In a cartoon film, we see the projection of static pictures on the screen in a specific order. Generally, the static pictures are made to move across the eye in a sequence at the rate of 24 pictures per second (faster than 16 per second) giving us the perception of a moving picture. ‘
Question 23
How is the phenomenon of reflection used in making a kaleidoscope. What are the applications of a kaleidoscope?
Answer.
Kaleidoscope is a cylinder with three mirrors containing loose, coloured objects such as beads or pebbles and bits of glass. As the viewer looks into one end, light entering the other end, creates a colourful pattern due to reflection.
It works on the principle of multiple reflection, where several mirrors are placed at an angle (usually 60°) to one another. Typically, these are three rectangular mirrors set at 60° to each other so that they form an equilateral triangle.
The 60° angle creates seven duplicate images of the objects, 5 at 60° and 2 at 90°. As the tube is rotated, the tumbling of the coloured objects present varying colours and patterns.
Its applications are given below:
(i) It is used for decoration purposes, toys, etc.
(ii)Kaleidoscope is also useful for designers and artists to get idea for new patterns to design wallpapers, jwellery and fabrics.
Question 24
Figure shows the word REST written in two ways in front of a mirror.
Show how the word would appear in the mirror.

Answer.
In an image formed by a plane mirror, the left of the object appears on the right and the right appears on the left, i.e. the image formed is laterally inverted, as shown below in the Fig. (A) and (B).
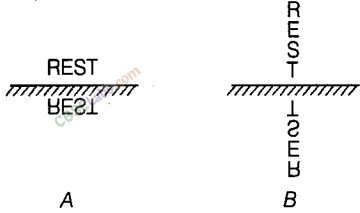
Question 25
Write down the names of parts of the eye in the blank spaces shown in the figure.
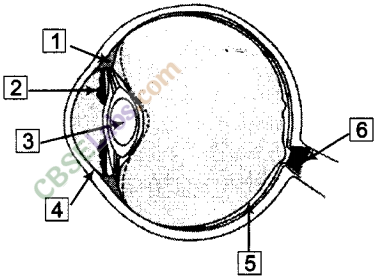
Answer.
The names of the parts of the eye as shown in the figure are:
1.Ciliary muscle
2.Iris
3.Lens
4.Cornea
5.Retina
6.Optic nerve
NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials : Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 12 Friction
- Chapter 13 Sound
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
NCERT Exemplar SolutionsNCERT Exemplar MathsNCERT Exemplar Science
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.