NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Playing with Numbers are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Playing with Numbers.
NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Playing with Numbers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question. 1 Generalised form of a four-digit number abdc is
(a) 1000a + 100b + 10c + d (b) 1000a + 100c + 10b + d
(c) 1000a + 100b + 10d + c (d) a x b x c x d
Solution. (c) In generalised form, we express a number as the sum of the products of its digits with their respective place values.
abdc is written in generalised form as 1000a + 100b + 10d + c.
i.e. abdc = 1000a + 100b + 10d + c
Question. 2 Generalised form of a two-digit number xy is
(a)x + y (b)10x + y (c)10x-y (d)10y+x
Solution. (b) In generalised form, xy can be written as the sum of the products of its digits with their respective place values, i.e.xy = 10x+ y
Question. 3 The usual form of 1000a + 10b + c is
(a) abc (b) abc0 (c) a0be (d) ab0c
Solution. (c) Given expanded (or generalised) form of a number is 1000a + 10b + c. Then, we have to find its usual form.
We can write it as 1000 x a + 100 x 0 + 10 x b + c
i.e. a0bc, which is the usual form.
Question. 4 Let abc be a three-digit number. Then, abc – cba is not divisible by
(a) 9 (b) 11 (c) 18 (d) 33
Solution. (c) Given, abc is a three-digit number.
Then, abc = 100a + 10b + c
and cba = 100c + 10b + a
abc -eba = (100a + 10b + c)- (100c + 10b + a)
= 100a – a + 10b – 10b + c -100=
= 99a – 99c = 99 (a -c)
= abc-cba is divisible by 99.
=> abc – cba is divisible by 9,11,33, but it is not divisible by 18.
Question. 5 The sum of all the numbers formed by the digits x, y and z of the number xyz is divisible by (a) 11 (b) 33 (c) 37 (d) 74
Solution. (c) We have, xyz + yzx + zxy
= (100x + 10y + z) + (100y + 10 z+ x) + (100z+ 10x + y) …(i)
= 100x + 10x + x + 10y + 100y + y + z+ 100z+ 10Z
= 111x + 111y + 111z = 111 (x + y + z)
= 3 x 37 x (x + y + z)
Hence, Eq. (i) is divisible by 37, but not divisible by 11,33 and 74.
Question. 6 A four-digit number aabb is divisible by 55. Then, possible value(s) of b is/are
(a) 0 and 2 (b) 2 and 5 (c) 0 and 5 (d) 7
Solution. (c) It is given that, aabb is divisible by 55. Then, it is also divisible by 5.
Now, if a number is divisible by 5, then its unit digit is either 0 or 5.
Hence, the possible values of b are 0 and 5.
Question. 7 Let abc be a three-digit number. Then, abc + bca + cab is not divisible by
(a) a + b + c (b) 3 (c) 37 (d) 9
Solution. (d) We know that, the sum of three-digit numbers taken in cyclic order can be written as 111 (a + b + c).
i.e. abc + pea + cab = 3 x 37 x (a + b + c)
Hence, the sum is divisible by 3, 37 and (a + b + c) but not divisible by 9.
Question. 8 A four-digit number 4ob5 is divisible by 55. Then, the value of b-a is
(a) 0 (b) 1 (0 4 (d) 5
Solution. (b) Given, a four-digit number 4ab5 is divisible by 55. Then, it is also divisible by 11.
The difference of sum of its digits in odd places and sum of its digits in even places is either 0 or multiple of 11.
i.e. (4 + b) – (a + 5) is 0 or a multiple of 11, if 4 + b — a — 5 = 0 => b-a = 1
Question. 9 If abc is a three-digit number, then number abc -a-b-c is divisible by
(a) 9 (b) 90 (c)10 (d) 11
Solution. (d) We have, abc= 100a + 10b+c
.-. abc – a – b-c = (100a + 10b + c)-a – b-c = 100a – a + 10b – b = 99a + 9b = 9(11a + b)
Hence, the given number abc – a – b-c is divisible by 9.
Question. 10 A six-digit number is formed by repeating a three-digit number. For example, 256256, 678678 etc. Any number of this form is divisible by (a) 7 only (b) 11 only (c) 13 only (d) 1001
Solution.
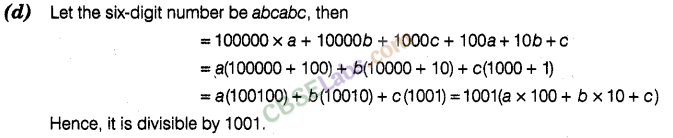
Question. 11 If the sum of digits of a number is divisible by three, then the number is always divisible by (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 6 (d) 9
Solution. (b) We know that, if sum of digits of a number is divisible by three, then the number must be divisible by 3, i.e. the remainder obtained by dividing the number by 3 is same as the remainder obtained by dividing the sum of its digits by 3.
Question. 12 If x +y + z = 6 and z is an odd digit, then the three-digit number xyz is
(a) an odd multiple of 3 (b) an odd multiple of 6
(c) an even multiple of 3 (d) an even multiple of 9
Solution. (a) We have, x + y+ z= 6 and z is an odd digit. Since, sum of the digits is divisible by 3, it will also be divisible by 2 and 3 but unit digit is odd, so it is divisible by 3 only.Hence, the number is an odd multiple of 3.
Question. 13 If 5A + 53 = 65, then the values of A and B is
(a) A = 2,8 = 3 (b) A = 3,8 = 2 (c)A = 2,8 = 1 (d)A=1,8 = 2
Solution.

Question. 14 If A3 + 8B = 150, then the value of A + B is
(a) 13 (b) 12 (c) 17 (d) 15
Solution. (a) We have, A3+ 8B = 150
Here, 3 + B = 0, so 3 + B is a two-digit number whose unit’s digit is zero.
.-. 3+B = 10=>B = 7
: Now, considering ten’s column, A+ 8 + 1 = 15
= A + 9 = 15
=> A = 6
Hence, A+B=6+7 = 13
Question. 15 If 5A x A = 399, then the value of A is
(a) 3 (b) 6 (c) 7 (d) 9
Solution. (c) We have, 5A x A = 399
Here, A x A= 9 i.e. A x A is the number 9 or a number whose unit’s digit is 9. Thus, the number whose product with itself produces a two-digit number having its unit’s digit as 9 is 7.
i.e. A x A = 49 => A=7
Now, 5 x A + 4 = 39
=> 5 x 7+4 = 39
So, A satisfies the product.
Hence, the value of A is 7.
Question. 16 If 6A x B = > 488, then the value of A-B is
(a)-2 (b) 2 (c) -3 (d) 3
Solution. (c) Given, 6A x B = A86
Let us assume, A = 1 and S = 3 Then, LHS = 61 x 3 = 183 and RHS = 183 Thus, our assumption is true.
A-6 = 1-3=-2
Question. 17 Which of the following numbers is divisible by 99?
(a) 913462 (b) 114345 (c) 135792 (d) 3572406
Solution. (b) Given a number is divisible by 99.
Now, going through the options, we observe that the number (b) is divisible by 9 and 11 both as the sum of digits of the number is divisible by 9 and sum of digits at odd places = sum of digits at even places.
Fill in the Blanks
In questions 18 to 33, fill in the blanks to make the statements true.
Question. 18 3134673 is divisible by 3 and————-.
Solution. 9
3134673 is divisible by 3 and 9 as sum of the digits, 3+1+3+4+6+7 + 3 = 27 is divisible by both 3 and 9.
Question. 19 20 x 3 is a multiple of 3, if the digit x is——–or——— or————.
Solution. 1,4,7
We know that, if a number is a multiple of 3, then the sum of its digits is again a multiple of 3, i.e. 2+0+x+3 is a multiple of 3.
x + 5 = 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15 But, x is a digit of the number 20 x 3.
x can take values 0, 1,2, 3,……..9.
=> x + 5 = 6 or 9 or 12
Hence, x = 1 or4 or 7
Question. 20 3 x 5 is divisible by 9, if the digit x is————.
Solution. 1
Since, the number 3 x 5 is divisible by 9, then the sum of its digits is also divisible by 9. i.e. 3 + x + 5 is divisible by 9.
=>x + 8 can take values 9,18, 27,…
But x is a digit of the number 3 x 5, so x = 1.
Question. 21 The sum of a two-digit number and the number obtained by reversing the digits is always divisible by———–.
Solution. 11
Let ab be any two-digit number, then the number obtained by reversing its digits is ba.
Now, ab + ba = (10a + b) + (10b + a) = 11a + 11b = 11(a + b)
Hence, ab + ba is always divisible by 11 and (a + b).
Question. 22 The difference of two-digit number and the number obtained by reversing its digits is always divisible by ———-.
Solution. 9
Let ab be any two-digit number, then we have
ab – ba = (10a + b)- (10b + a)
= 9a – 9b = 9(a – b)
Hence, ab – ba is always divisible by 9 and (a – b).
Question. 23 The difference of three-digit number and the number obtained by putting the digits in reverse order is always divisible by 9 and——-.
Solution. 11
Let abc be a three-digit number, then we have
abc -cba = (100a + 10b + c)- (100c + 10b+ a) ; = (100a – a) + (c – 10Cc)
= 99a – 99c = 99(a -c)
= 9 x 11 x (a – c)
Hence, abc – cba is always divisible by 9,11 and (a – c).
Question. 24

Solution.

Question. 25

Solution.

Question. 26
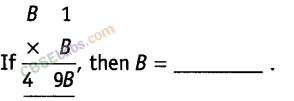
Solution.

Question. 27 1 x 35 is divisible by 9, if x =———.
Solution.

Question. 28 A four-digit number abed is divisible by 11, if d + b =———–or————-.
Solution. a + c,12(a + c)
We know that, a number is divisible by 11, if the difference between the sum of digits at odd places and the sum of its digits at even places is either 0 or a multiple of 11.
Hence, abcd is divisible by 11, if (d + b)- (a + c) = 0,11,22, 33,…
=> d + b = a + c or d + b = 12(a + c)
Question. 29 A number is divisible by 11, if the differences between the sum of digits at its odd places and that of digits at the even places is either 0 or divisible by ————-.
Solution. 11
By test of divisibility by 1,1, we know that, a number is divisible by 11, if the sum of digits at odd places and even places are equal or differ by a number, which is divisible by 11.
Question. 30 If o three-digit number abc is divisible by 11, then——–is either 0 or multiple of 11.
Solution. (a+c)-b
Since, abc is divisible by 11, the difference of sum of its digits at odd places and that of even places is either zero or multiple of 11, i.e. (a + c) – b is either zero or multiple of 11.
Question. 31 If A x 3 = lA then A =————.
Solution.

Question. 32 If B x B = AB, then either A = 2, B = 5 or A =———- B =———-.
Solution.

Question. 33 If the digit 1 is placed after a two-digit number whose ten’s is t and one’s digit is u, the new number is———–.
Solution. tu1
Given, a two-digit number whose ones digit isu in and tens digit isu. If the digit 1 is placed after this number, then the next number will be tu1.
True/False
In questions 34 to 44, state whether the given statements are True or False.
Question. 34 A two-digit number ab is always divisible by 2, if b is an even number.
Solution. True
By the test of divisibility by 2, we know that a number is divisible by 2, if its unit’s digit is even.
Question. 35 A three-digit number abc is divisible by 5, if c is an even number.
Solution. False
By the test of divisibility by 5, we know that if a number is divisible by 5, then its one’s digit will be either 0 or 5, i.e. the numbers ending with the digits 0 or 5 are divisible by 5.
Question. 36 A four-digit mmbeFabcd is divisible by 4, if ab is divisible by 4.
Solution. False
As we know that, if a number is divisible by 4, then the number formed by its digits in unit’s and ten’s place is divisible by 4.
Question. 37 A three-digit number abc is divisible by 6, if c is an even number and a + b + c is a multiple of 3.
Solution. True
If a number is divisible by 6, then it is divisible by both 2 and 3. Since, abc is divisible by 6, it is also divisible by 2 and 3. Therefore, c is an even number and the sum of digits is divisible by 3, i.e. multiple of 3.
Question. 38 Number of the form 3N + 2 will leave remainder 2 when divided by 3.
Solution. True
Let x = 3N + 2. Then, it can be written as.
x = (a multiple of 3) + 2
i.e. x is a number which is 2 more than a multiple of 3
i.e. x is a number, which when divided by 3, leaves the remainder 2.
Question. 39 Number 7N+1 will leave remainder 1 when divided by 7.
Solution. True
Given, a number of the form 7N + 1 = x (say)
Here, we observe that * is a number which is one more than a multiple of 7. i.e. when x is divided by 7, it leaves the remainder 1.
Question. 40 If a number a is divisible by b, then it must be divisible by each factor of b.
Solution. True
Given, a is divisible by b.
Let b = p1•p2, where p1 and p2 are primes.
Since, a is divisible by b, a is a multiple of b
i.e. a = mb
=> a = m.p1.p2
or a=cp2=dp1, where c = mp1, d = mp2
=>a is a multiple of p1 as well as p2.
Hence, a is divisible by each factor b.
Question. 41 If AB x 4 = 192, then A + 6 = 7.
Solution.

Question. 42 If AB + 7C = 102, where \(B\neq 0\), \(C\neq 0\), then A + B + C = 14.
Solution.

If B= C = 1, lf8 = 5,C=7, A = 2 and A +B+C=2 + 5+ 7 = 14
Question. 43 If 213 x 27 is divisible by 9, then the value of x is 0.
Solution. False
Given, 213 x 27 is divisible by 9, so sum of its digits is also divisible by 9.
i.e. 2 1 + 3 + x + 2 + 7 — 0, 9,18, 27, 36,…
=> x+ 15= 0,9,18,27,36,…
=> x + 15 = 18 [x is a digit of a number]
=> x= 3
Question. 44 In N + 5 leaves remainder 3 and \(N\div 2\) leaves remainder 0, then \(N\div 10\) leaves remainder 4.
Solution.


Question. 45 Find the least value that must be given to number a, so that the number 91876a2 is divisible by 8.
Solution. Given, 91876a2 is divisible by 8.
Since, we know that, if a number is divisible by 8, then the number formed by last 3 digits is divisible by 8.
So, 6a2 is divisible by 8.
Here, a can take values from 0 to 9.
For a = 0, 602 is not divisible by 8.
For a = 1, 612, which is not divisible by 8.
For a = 3, 632 is divisible by 8.
Hence, the minimum value of a is 3 to make 91876a2 divisible by 8.
Question. 46

Solution.
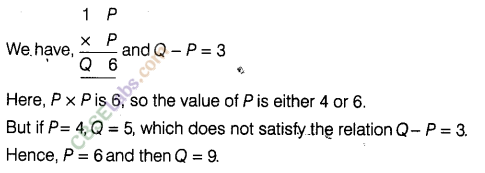
Question. 47 If 1AB + CCA = 697 and there is no carry-over in addition, find the value of A + B + C.
Solution.

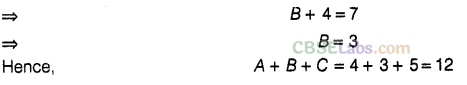
Question. 48 A five-digit number AABAA is divisible by 33. Write all the numbers of this form.
Solution. Given, a number of the form AABAA is divisible by 33. Then, it is also divisible by 3 and
11, as if a number a is divisible by b, then it is also divisible by each factor of b.
Since, AABAA is divisible by 3, sum its digits is also divisible by 3. i.e. 4 + 4 + 8 + A + .4 = 0,3, 6,9…
or 4/4 + 8 = 0, 3, 6 9,… …(i)
From Eq. (i), we have
Further, the given number is also divisible by 11, therefore (2/4 + 8) – 2A = 0,11,22,…
B=Q 11,22,…
8 = 0 [v8 is a digit of the given number]
4/4 = 12or 24 or 36 A= 3, 6 9
Hence, the required numbers are 33033, 66066 and 99099.
In questions 49 to 60, find the value of the letters in each of the following questions.
Question. 49

Solution.

Question. 50

Solution.
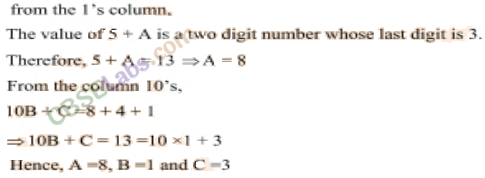
Question. 51
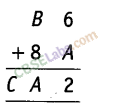
Solution.

Question. 52

Solution.

Question. 53

Solution.

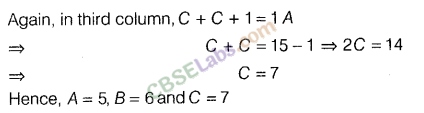
Question. 54

Solution.

Question. 55
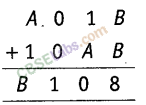
Solution.

Question. 56
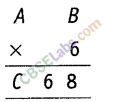
Solution.

Question. 57

Solution.

Question. 58
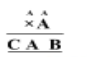
Solution.

Question. 59
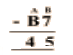
Solution.
![]()
Question. 60

Solution.

Question. 61 If \(27\div A\)= 33, then find the value of A
Solution. We observe that, 4 x 3 can never be a single digit number 2, so 4 x 3 must be a two-digit number, whose ten’s digit is 2 and unit’s digit is the number less than or equal to 4. Therefore, the value of 4 can be 9, as the values of 4 from 1 to 8 do not fit.
Question. 62 212 x 5 is a multiple of 3 and 11. Find the value of x.
Solution. Since, 212 x 5 is a multiple of 3,
2 +1 + 2 +x+5 = 0, 3, 6,9,12,15,18,
=> 10 + x = 0, 3, 6,………..
=> x =2, 5, 8 …(i)
Again, 212×5 is a multiple of 11, (2 + 2 + 5) — (1 + x) = 0,11,22, 33
=> 8 – x = 0,11,22,…
=> x = 8 …(ii)
From Eqs. (i) and (ii), we have ‘
x = 8
Question. 63 Find the value of k, where 31K2 is divisible by 6.
Solution. Given, 31k2 is divisible by 6. Then, it is also divisible by 2 and 3 both.
Now, 31K2 is divisible by 3, sum of its digits is a multiple of 3.
i.e. 3+ 1 + k + 2 = 0, 3, 6, 9,12,…
=> k+ 6 = 0, 3,6, 9,12
=> k = 0 or 3, 6, 9
Question. 64 1y3y6is divisible by 11. Find the value of y.
Solution. It is given that, 1y3y6 is divisible by 11.
Then, we have (1 + 3 + 6) – (y + y) = 0,11,22,…
=> 10-2y= 0,11,22,…
=> 10-2y = 0 [other values give a negative number]
=> 2y = 10
=> y= 5
Question. 65 756x is a multiple of 11, find the value of x.
Solution. We are given that, 756x is a multiple of 11. Then, we have to find the value of x.
Since, 756x is divisible by 11, then (7 + 6) – (5 + x) is a multiple of 11,
i.e. 8-x = 0,11,22,…
=> 8- x = 0
=> x = 8
Question. 66 A three-digits number 203 is added to the number 326 to give a three-digits number 5b9 Which is divisible by 9. Find the value of b – a.
Solution.

Question. 67 Let E = 3, B = 7 and A = 4. Find the other digits in the sum

Solution.
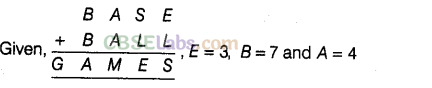

Question. 68 Let D = 3, L = 7 and A = 8. Find the other digits in the sum
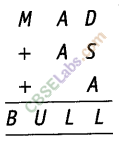
Solution. In the first column, we have
3 + S + 8, which is definitely a two digits number whose unit’s digit is 7.
S must be 6.
Now, in second column, 2A +1 = 16+1 = 7 [1 is carry forward]
In third column, M + 1 is a 2 digit number, therefore M must be 9.
Then, M + 1 = 9+ 1 = 10 6 = 1, U = 0
Hence, S = 6, M = 9, 6 = 1 and U = 0
Question. 69 If from a two-digit number, we subtract the number formed by reversing its digits then the result so obtained is a perfect cube. How many such numbers are possible? Write all of them.
Solution. Let ab be any two-digit number. Then, the digit formed by reversing it digits is ba.
Now, ab-ba = (10a+b)-(10b +a)
=(10a-a)+(b-10b)
= 9a – 9b = 9(a – b)
Further, since ab-ba is a perfect cube and is a multiple of 9.
.-.The possible value of a – b is 3.
i.e. a = b + 3
Here, b can take value from 0 to 6.
Hence, possible numbers are as follow.
For b = 0, a = 3, i.e. 30
For b = 1, a = 4, i.e. 41
For b =2, a = 5, i.e. 52
For b = 3, a = 6, i.e. 63
For b = 4, a = 7, i.e. 74
For b = 5,a = 8, i.e. 85
For b = 6, a = 9, i.e. 96
Question. 70 Work out the following multiplication.

Use the result to answer the following questions.
(a) What will be 12345679 x 45?
(b) What will be 12345679 x 63?
(c) By what number should 12345679 be multiplied to get 888888888?
(d) By what number should 12345679 be multiplied to get 999999999?
Solution.

Question. 71 Find the value of the letters in each of the following.

Solution.

Question. 72 If 148101B095 is divisible by 33, find the value of B.
Solution. Given that the number 148101S095 is divisible by 33, therefore it is also divisible by 3 and 11 both.
Now, the number is divisible by 3, its sum of digits is a multiple of 3. i.e. 1 + 4+ 8+1 + 0+1 + B+ 0+ 9+ 5 is a multiple of 3.
29 + B = 0, 3, 6,9,…
=> B=1,4,7 …(i)
Also, given number is divisible by 11, therefore
(1+ 8 + 0+ B + 9)-(4 + 1+ 1+ 0 + 5)=0, 11,22, …
=> (18 + B) -11 = 0,11,22
B+ 7 = 0,11,22
=> B+7 = 11 => B = 4 …(ii)
From Eqs. (i) and (ii), we have B = 4
Question. 73 If 123123A4 is divisible by 11, find the value of A.
Solution. Given, 12312344 is divisible by 11, then we have (1 + 3 + 2 + 4) – (2 + 1 + 3 + 4) is a multiple of 11.
i.e. (6+ 4)-10 =0,11,22,,..
=> A-4 = 0,11,22,…
=> A-4 = 0 [A is a digit of the given number]
=> A = 4
Question. 74 If 56 x 32y is divisible by 18, find the least value of y.
Solution. It is given that, the number 56 x 32y is divisible by 18. Then, it is also divisible by each factor of 18.
Thus, it is divisible by 2 as well as 3.
Now, the number is divisible by-2, its unit’s digit must be an even number that is 0, 2,4, 6, Therefore, the least value of y is 0.
Again, the number is divisible by 3 also, sum of its digits is a multiple of 3. i.e. 5 + 6 + x + 3 + 2 + y is a multiple of 3
=> 16 + x + y = 0, 3, 6, 9,…
=> 16+ x = 18
=>x = 2, which is the least value of x.
NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Solutions
- Chapter 1 Rational Numbers
- Chapter 2 Data Handling
- Chapter 3 Square-Square Root and Cube-Cube Root
- Chapter 4 Linear Equations in One Variable
- Chapter 5 Understanding Quadrilaterals and Practical Geometry
- Chapter 6 Visualising Solid Shapes
- Chapter 7 Algebraic Expressions, Identities and Factorisation
- Chapter 8 Exponents and Powers
- Chapter 9 Comparing Quantities
- Chapter 10 Direct and Inverse Proportion
- Chapter 11 Mensuration
- Chapter 12 Introduction to Graphs
- Chapter 13 Playing with Numbers
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Playing with Numbers help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 13 Playing with Numbers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.