NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 7 Algebraic Expressions, Identities and Factorisations are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 7 Algebraic Expressions, Identities and Factorisation.
NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 7 Algebraic Expressions, Identities and Factorisation
Multiple Choice Questions
Question. 1 The product of a monomial and a binomial is a
(a) monomial (b) binomial
(c) trinomial (d) None of these
Solution. (b) Monomial consists of only single term and binomial contains two terms. So, the multiplication of a binomial by a monomial will always produce a binomial, whose first term is the product of monomial and the binomial’s first term and second term is the product of monomial and the binomial’s second term.
Question. 2 In a polynomial, the exponents of the variables are always (a)’integers (b) positive integers (c) non-negative integers (d) non-positive integers
Solution. (c) In a polynomial, the exponents of the variables are either positive integers or 0. Constant term C can be written as C x°. We do not consider the expressions as a polynomial which consist of the variables having negative/fractional exponent.
Question. 3 Which of the following is correct?
(a) \({{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+2ab-{{b}^{2}}\) (b) \({{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-2ab+{{b}^{2}}\)
(c) \({{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}\) (d) \({{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+2ab-{{b}^{2}}\)
Solution.

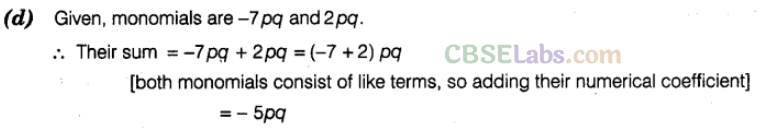
Question. 4 The sum of -7pq and 2pq is
(a) -9pq (b) 9pq
(c) 5pq (d) -5pq
Solution.
Question. 5 If we subtract \(-3{ x }^{ 2 }{ y }^{ 2 }\) from \({ x }^{ 2 }{ y }^{ 2 }\), then we get

Solution.
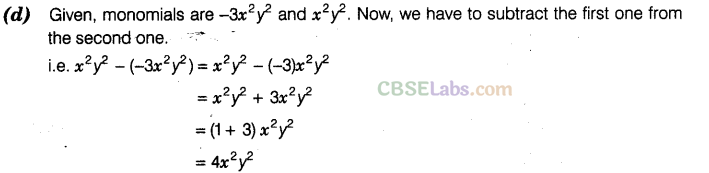
Question. 6 Like term as \(4{ m }^{ 3 }{ n }^{ 2 }\) is
(a)\(4{ m }^{ 2 }{ n }^{ 2 }\) (b) \(-6{ m }^{ 3 }{ n }^{ 2 }\)
(c) \(6p{ m }^{ 3 }{ n }^{ 2 }\) (d) \(4{ m }^{ 3 }{ n }\)
Solution. (b) We know that, the like terms contain the same literal factor. So, the like term as \(4{ m }^{ 3 }{ n }^{ 2 }\) , is \(-6{ m }^{ 3 }{ n }^{ 2 }\), as it contains the same literal factor \({ m }^{ 3 }{ n }^{ 2 }\).
Question. 7 Which of the following is a binomial?

Solution.

Question. 8 Sum of a – b + ab, b + c – bc and c – a – ac is

Solution.
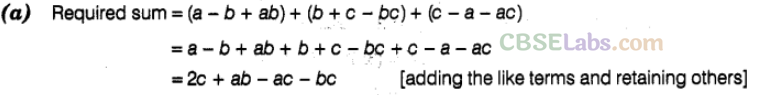
Question. 9 Product of the monomials 4p, -7\({ q }^{ 3 }\), -7pq is

Solution.
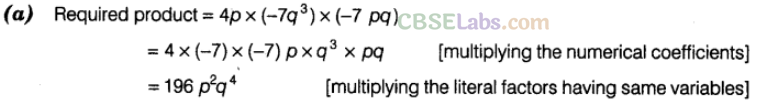
Question. 10 Area of a rectangle with length 4ab and breadth 6\({ b }^{ 2 }\) is

Solution.
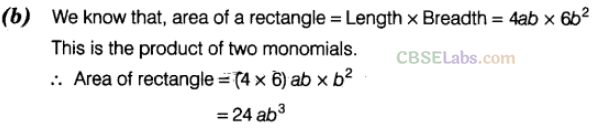
Question. 11 Volume of a rectangular box (cuboid) with length = 2ab, breadth = 3ac and height = 2ac is

Solution.
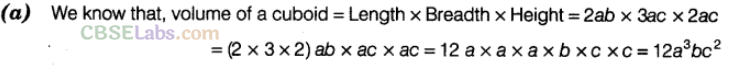
Question. 12 Product of 6\({ a }^{ 2 }\) -7b + 5ab and 2ab is

Solution.
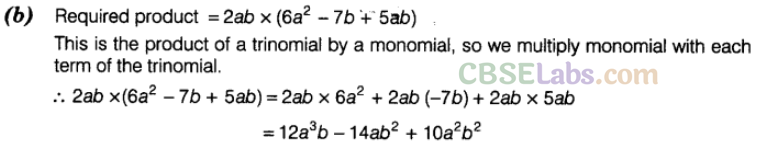
Question. 13 Square of 3x – 4y is
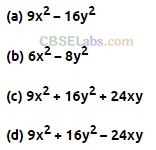
Solution.
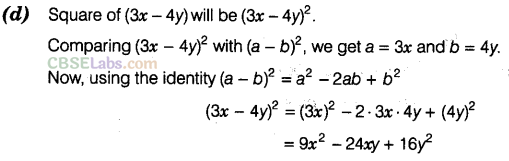
Question. 14 Which of the following are like terms?
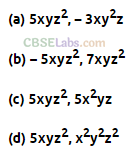
Solution.

Question. 15 Coefficient of y in the term of \({ -y }^{ 3 }\) is
(a)-1 (b)-3 (c)\({ -1 }^{ 3 }\) (d)\({ 1 }^{ 3 }\)
Solution.

Question. 16 \({ a }^{ 2 }-{ b }^{ 2 }\) is equal to
![]()
Solution.
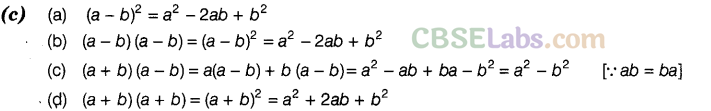
Question. 17 Common factor Of 17abc, 34a\({ b }^{ 2 }\), 51\({ a }^{ 2 }\)b is
(a)17abc (b)17ab (c)17ac (d)17\({ a }^{ 2 }\)\({ b }^{ 2 }\)c
Solution.
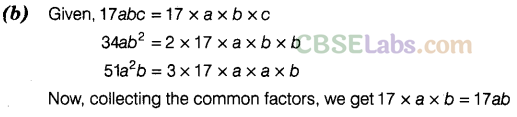
Question. 18 Square of 9x – 7xy is
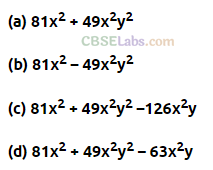
Solution.

Question. 19 Factorised form of 23xy – 46x + 54y -108 is

Solution.
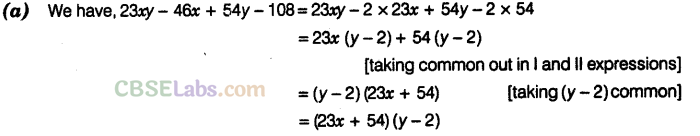
Question. 20 Factorised form of \({ r }^{ 2 }\)-10r + 21 is
(a)(r-1)(r-4) (b)(r-7)(r-3) (c)(r-7)(r+3) (d)(r+7)(r+3)
Solution.

Question. 21 Factorised form of \({ p }^{ 2 }\) – 17p – 38 is
(a) (p -19)(p + 2) (b) (p -19) (p – 2) (c) (p +19) (p + 2) (d) (p + 19) (p – 2)
Solution.

Question. 22 On dividing 57 \({ p }^{ 2 }\) qr by 114pq, we get
![]()
Solution.
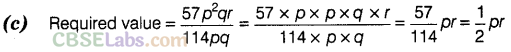
Question. 23 On dividing p(4\({ p }^{ 2 }\) – 16) by 4p (p – 2), we get
(a) 2p + 4 (b) 2p – 4 (c) p + 2 (d) p – 2
Solution.
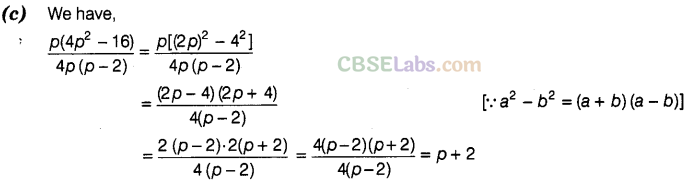
Question. 24 The common factor of 3ab and 2cd is
(a) 1 (b) -1 (c) a (d) c
Solution. (a) We have, monomials 3ab and 2cd Now, 3ab = 3xaxb 2cd =2 x c x d
Observing the monomials, we see that, there is no common factor (neither numerical nor literal) between them except 1.
Question. 25 An irreducible factor of24\({ x }^{ 2 }\)\({ y }^{ 2 }\) is
(a)\({ a }^{ 2 }\) (b)\({ y }^{ 2 }\) (c)x (d)24x
Solution. (c) A factor is said to be irreducible, if it cannot be factorised further.
We have, 24\({ x }^{ 2 }\)\({ y }^{ 2 }\) =2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x x x x x y x y Hence, an irreducible factor of 24\({ x }^{ 2 }\)\({ y }^{ 2 }\) is x.
Question. 26 Number of factors of \({{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}\) is
(a) 4 (b) 3 (c) 2 (d) 1
Solution. (c) We can write \({{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}\) as, (a + b) (a + b) and this cannot be factorised further.
Hence, number of factors of \({{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}\) is 2.
Question. 27 The factorised form of 3x – 24 is
(a) 3x x 24 (b)3 (x – 8) (c)24(x – 3) (d)3(x-12)
Solution. (b) We have,
3x – 24 = 3 x x – 3 x 8= 3 (x – 8) [taking 3 as common]
Question. 28 The factors of \({ x }^{ 2 }\) – 4 are
(a) (x – 2), (x – 2) (b) (x + 2), (x – 2)
(c) (x + 2), (x + 2) (d) (x – 4), (x – 4)
Solution.
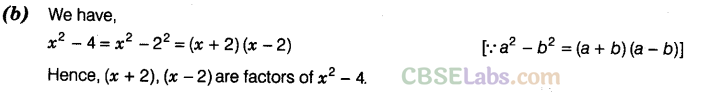
Question. 29 The value of \((-27{ x }^{ 2 }y)\div (-9xy)\) is
(a)3xy (b)-3xy (c)-3x (d)3x
Solution.
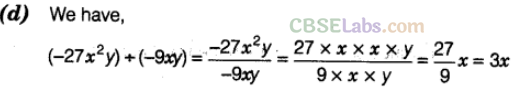
Question. 30 The value of \((2{ x }^{ 2 }+4)\div (2)\) is
![]()
Solution.

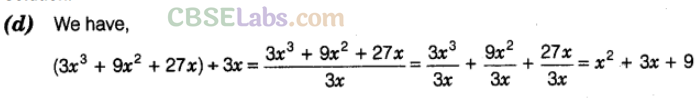
Question. 31 The value of \((3{ x }^{ 3 }+9{ x }^{ 2 }+27x)\div 3x\) is

Solution.
Question. 32 The value of \({{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}+{{(a-b)}^{2}}\) is

Solution.
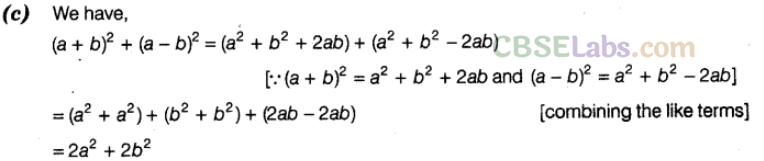
Question. 33 The value of \({{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}-{{(a-b)}^{2}}\) is
![]()
Solution.
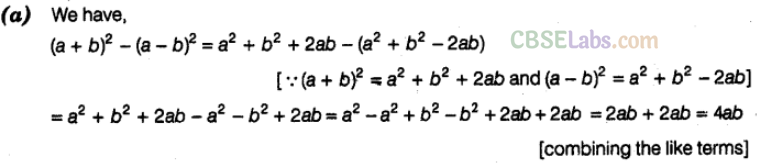
Fill in the Blanks
In questions 34 to 58, fill in the blanks to make the statements true.
Question. 34 The product of two terms with like signs is a term.
Solution. Positive
If both the like terms are either positive or negative, then the resultant term will always be positive.
Question. 35 The product of two terms with unlike signs is a term.
Solution. Negative
As the product of a positive term and a negative term is always negative.
Question. 36 a (b + c) = a x ——– + a x ———-
Solution. b,c
we have , a(b+c)=a x b + a x c [using left distributive law]
Question. 37 (a-b) ————- =\( { a }^{ 2 }-2ab+{ b }^{ 2 }\)
Solution.
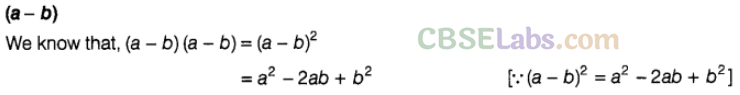
Question. 38 \({ a }^{ 2 }-{ b }^{ 2 }\)=(a+b)—————-
Solution.
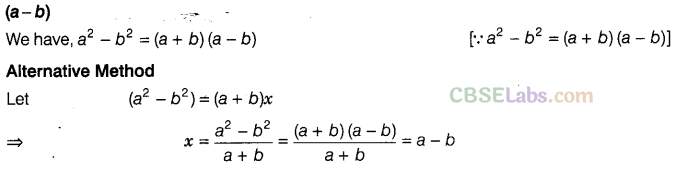
Question. 39 \({{(a-b)}^{2}}\)+—————-=\({ a }^{ 2 }-{ b }^{ 2 }\)
Solution.
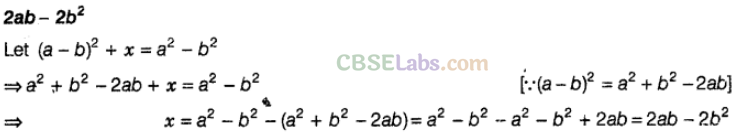
Question. 40 \({{(a+b)}^{2}}\)-2ab=————- + ———–.
Solution.

Question. 41 (x+a)(x+b)=\({ x }^{ 2 }\) + (a+b) x + ———–.
Solution.
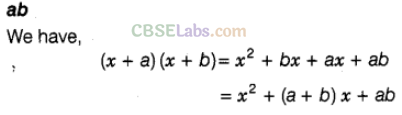
Question. 42 The product of two polynomials is a ————–.
Solution. Polynomial
As the product of two polynomials is again a polynomial.
Question. 43 Common factor of ax2 + bx is——————.
Solution.

Question. 44 Factorised form of 18mn + 10mnp is —————–.
Solution.
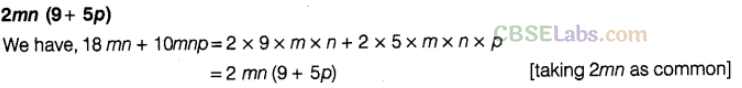
Question. 45 Factorised form of 4\({ y }^{ 2 }\) – 12y + 9 is———– .
Solution.
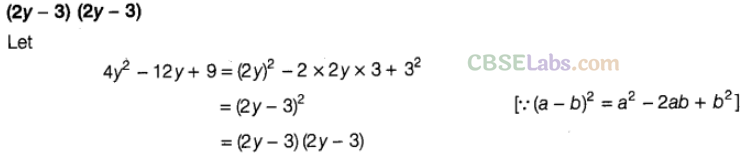
Question. 46 \(38{ x }^{ 2 }{ y }^{ 2 }z\div 19x{ y }^{ 2 }\) is equal to———–.
Solution.
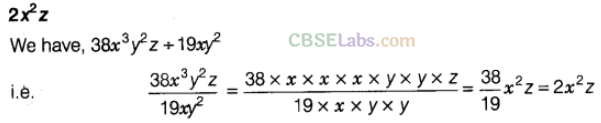
Question. 47 Volume of a rectangular box with length 2x, breadth 3y and height 4z is ——.
Solution. 24 xyz
We know that, the volume of a rectangular box,
V = Length x Breadth x Height = 2x x 3y x 4z = (2 x 3 x 4) xyz = 24 xyz
Question. 48 \( 6{ 7 }^{ 2 }-3{ 7 }^{ 2 }\) =(67 -37) x ———–=————.
Solution.

Question. 49 \( { 103 }^{ 2 }-{ 102 }^{ 2 }\)=————- x (103-102)=————–.
Solution.

Question. 50 Area of a rectangular plot with sides 4\({ y }^{ 2 }\) and 3\({ y }^{ 2 }\) is————–.
Solution.
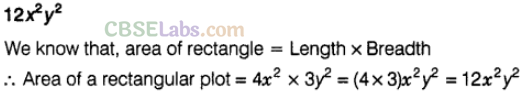
Question. 51 Volume of a rectangular box with l = b = h = 2x is ———-.
Solution.

Question. 52 The numerical coefficient in -37abc is————–.
Solution. -37
The constant term (with their sign) involved in term of an algebraic expression is called the numerical coefficient of that term.
Question. 53 Number of terms in the expression \({ a }^{ 2 }\) and + bc x d is –.
Solution.

Question. 54 The sum of areas of two squares with sides 4o and 4b is————-.
Solution.

Question. 55 The common factor method of factorisation for a polynomial is based on————-property.
Solution.Distributive
In this method, we regroup the terms in such a way, so that each term in the group contains a common literal or number or both.
Question. 56 The side of the square of area 9\({ y }^{ 2 }\) is————.
Solution.

Question. 57 On simplification, \(\frac { 3x+3 }{ 3 }\) =————.
Solution.
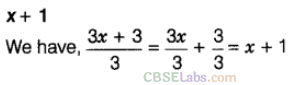
Question. 58 The factorisation of 2x + 4y is————-.
Solution. 2 (x + 2y)
We have, 2x + 4y = 2x + 2 x 2y = 2 (x + 2y)
True/False
In questions 59 to 80, state whether the statements are True or False
Question. 59 \({{(a+b)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}\).
Solution.
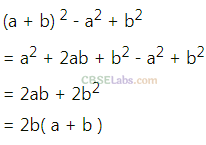
Question. 60 \({{(a-b)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}\).
Solution.
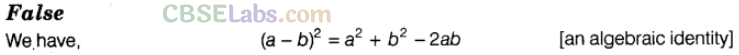
Question. 61 (a+b) (a-b)=\({{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}\)
Solution.
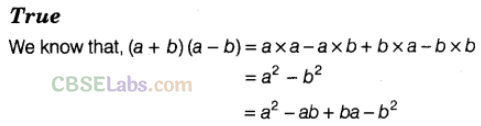
Question. 62 The product of two negative terms is a negative term.
Solution.False
Since, the product of two negative terms is always a positive term, i.e. (-) x (-) = (+).
Question. 63 The product of one negative and one positive term is a negative term.
Solution.True
When we multiply a negative term by a positive term, the resultant will be a negative term, i-e. (-) x (+) = (-).
Question. 64 The numerical coefficient of the term -6\({ x }^{ 2 }{ y }^{ 2 }\) is -6.
Solution. True
Since, the constant term (i.e. a number) present in the expression -6\({ x }^{ 2 }{ y }^{ 2 }\) is -6.
Question. 65 \({ p }^{ 2 }\)q+\({ q }^{ 2 }\)r+\({ r }^{ 2 }\)q is a binomial.
Solution. False
Since, the given expression contains three unlike terms, so it is a trinomial.
Question. 66 The factors of \({ a }^{ 2 }\) – 2ab + \({ b }^{ 2 }\)are (a + b) and (a + b).
Solution.
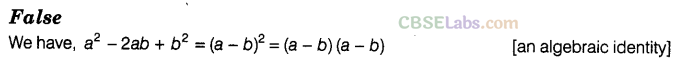
Question. 67 h is a factor of \(2\pi (h+r)\).
Solution.
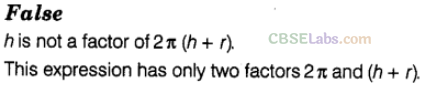
Question. 68 Some of the factors of \(\frac { { n }^{ 2 } }{ 2 } +\frac { n }{ 2 }\) are \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } n\) and (n+1).
Solution.

Question. 69 An equation is true for all values of its variables.
Solution. False
As equation is true only for some values of its variables, e.g. 2x – 4= 0 is true, only for x =2.
Question. 70 \({ x }^{ 2 }\) + (a+b)x +ab =(a+b)(x +ab)
Solution.
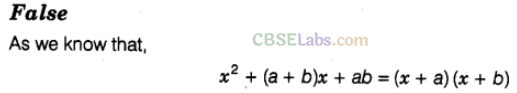
Question. 71 Common factors of \(11p{ q }^{ 2 },121{ p }^{ 2 }{ q }^{ 3 },1331{ p }^{ 2 }q\) is \(11{ p }^{ 2 }{ q }^{ 2 }\)
Solution.
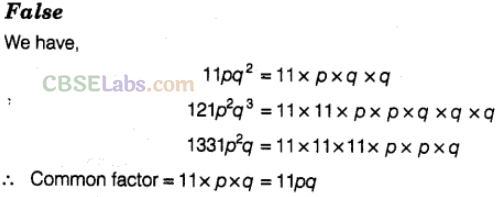
Question. 72 Common factors of 12 \(11{ a }^{ 2 }{ b }^{ 2 }\) +4a\({ b }^{ 2 }\) -32 is 4.
Solution.
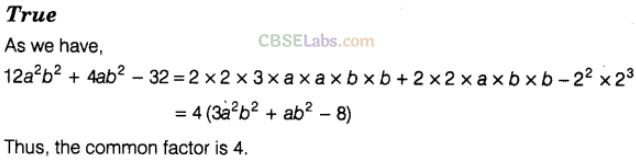
Question. 73 Factorisation of -3\({ a }^{ 2 }\)+3ab+3ac is 3a (-a-b-c).
Solution.
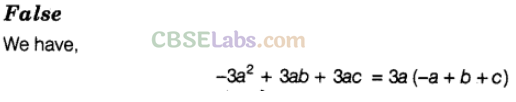
Question. 74 Factorised form of \({ p }^{ 2 }\)+30p+216 is (p+18) (p-12).
Solution.

Question. 75 The difference of the squares of two consecutive numbers is their sum.
Solution.

Question. 76 abc + bca + cab is a monomial.
Solution. True
The given expression seems to be a trinomial but it is not as it contains three like terms which can be added to form a monomial, i.e. abc + abc + abc = 3abc
Question. 77 On dividing \(\frac { p }{ 3 }\) by \(\frac { 3 }{ p }\) ,the quotient is 9
Solution.

Question. 78 The value of p for 5\({ 1 }^{ 2 }\)-4\({ 9 }^{ 2 }\)=100 p is 2.
Solution.

Question. 79 \((9x-51)\div 9\) is x-51.
Solution.
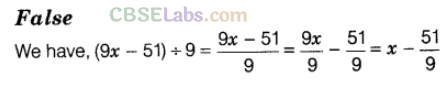
Question. 80 The value of (a+1) (a-1)(\({ a }^{ 2 }\) +1) is \({ a }^{ 4 }\)-1.
Solution.
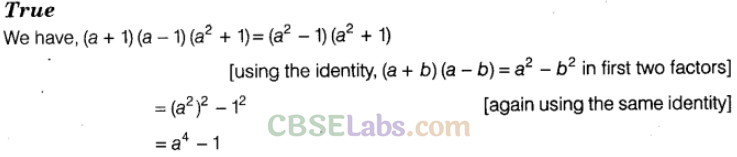
Question. 81 Add:
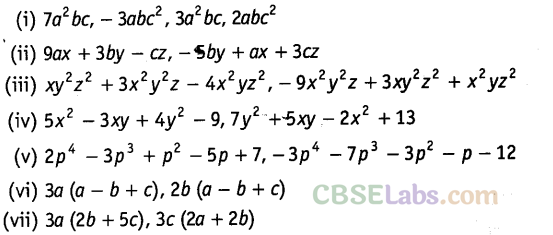
Solution.


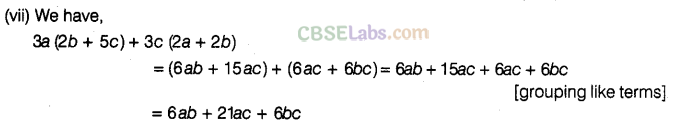
Question. 82 Subtract
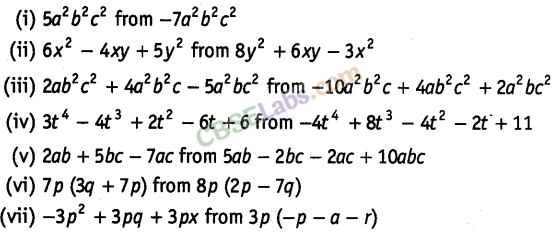
Solution.
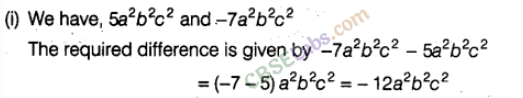


Question. 83 Multiply the following:

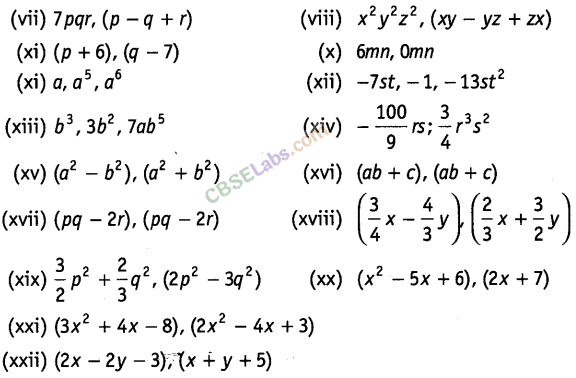
Solution.

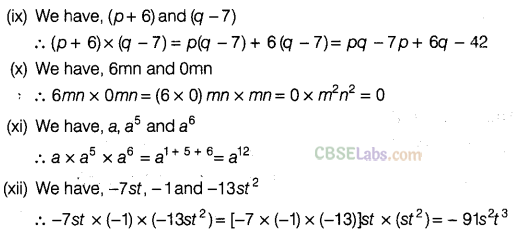
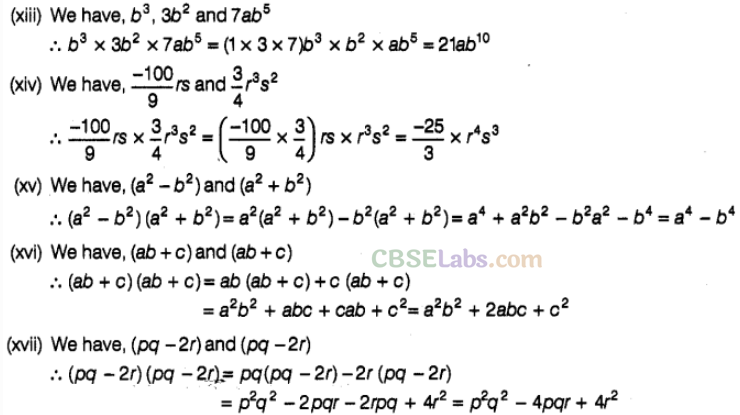
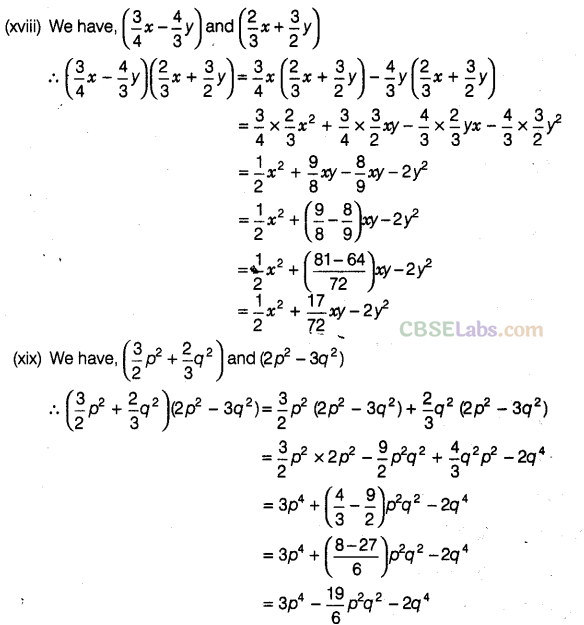
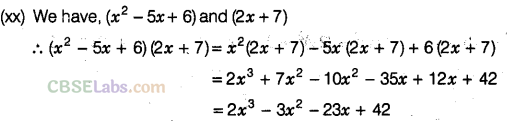

Question. 84 Simplify

Solution.
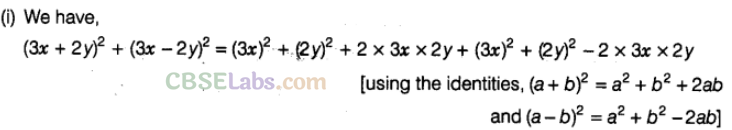

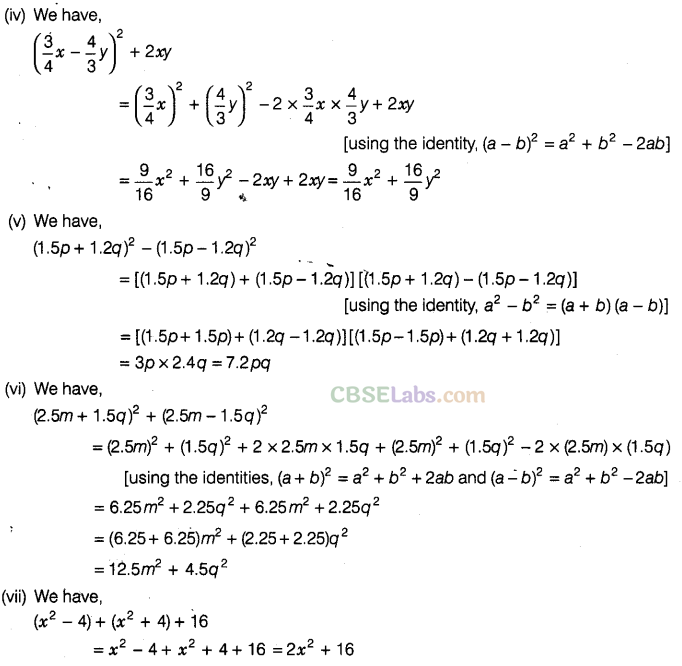

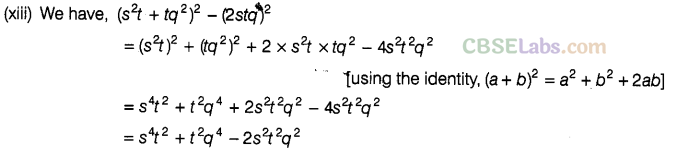
Question. 85 Expand the following, using suitable identities.
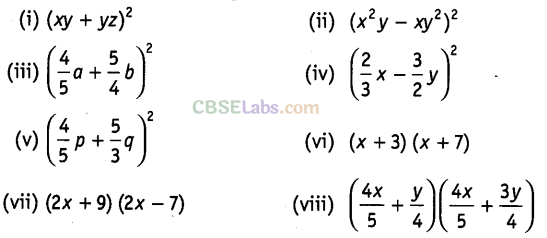
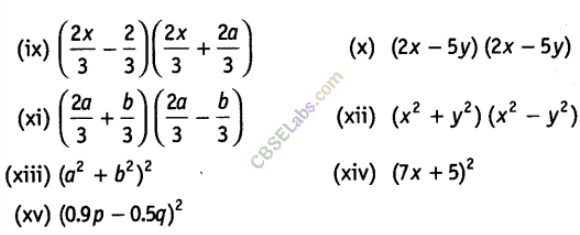
Solution.
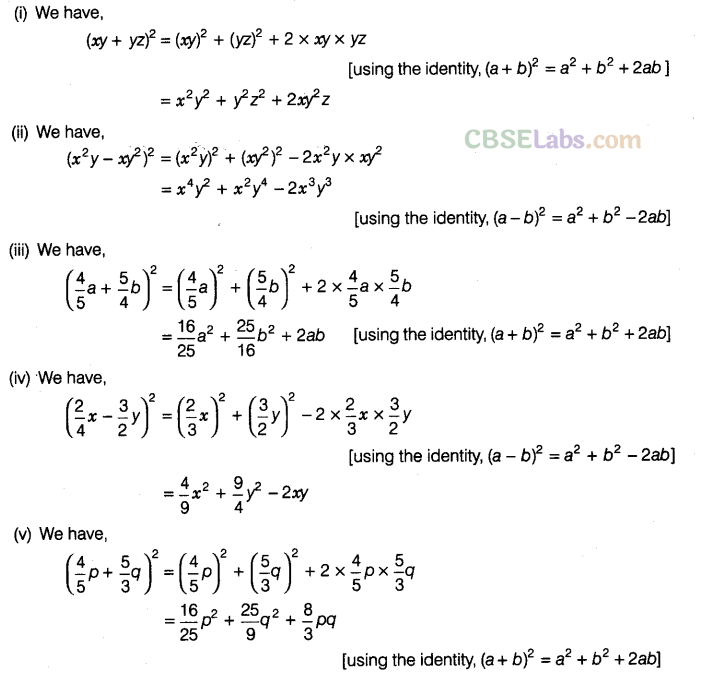
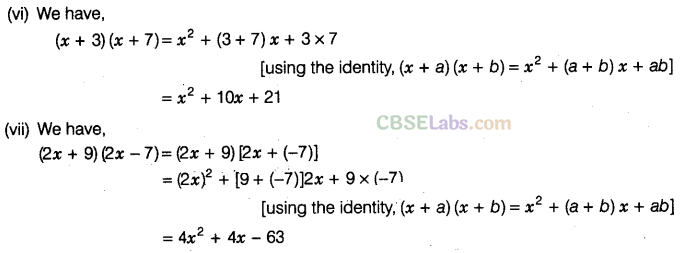

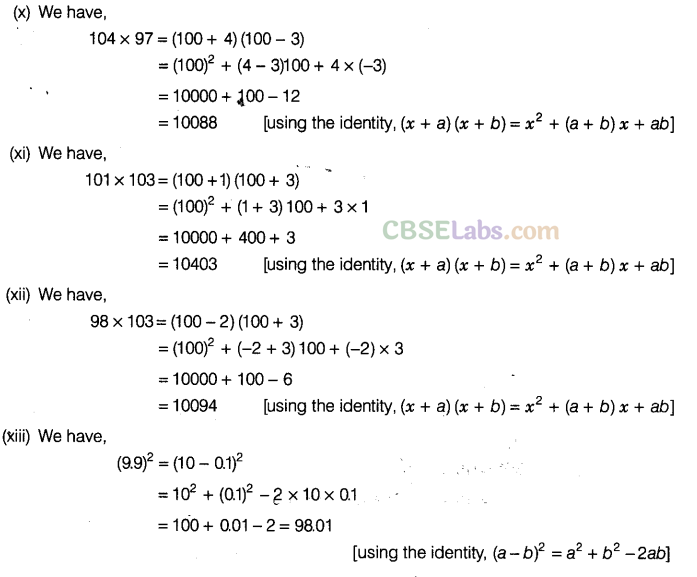
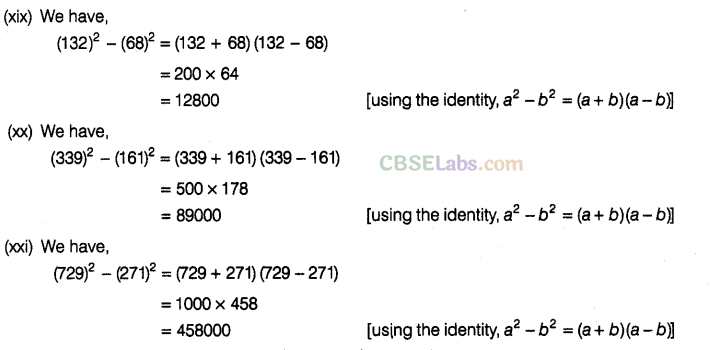
Question. 86 Using suitable identities, evaluate the following:
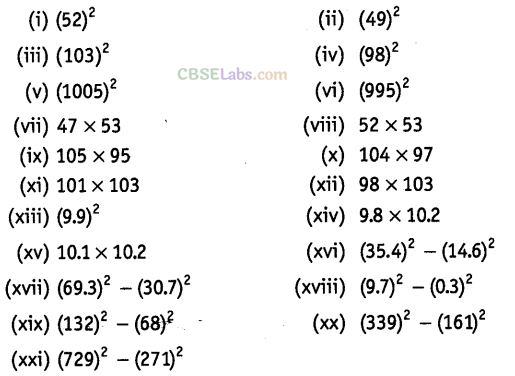
Solution.


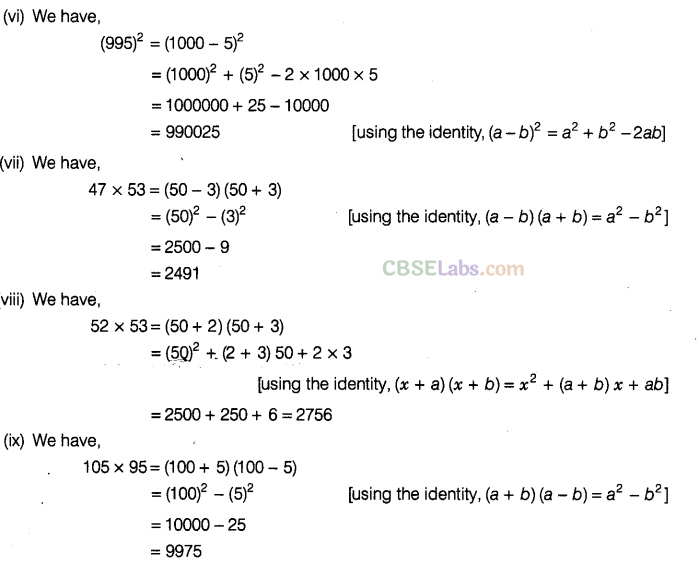

Question. 87 Write the greatest common factor in each of the following terms.


Solution.
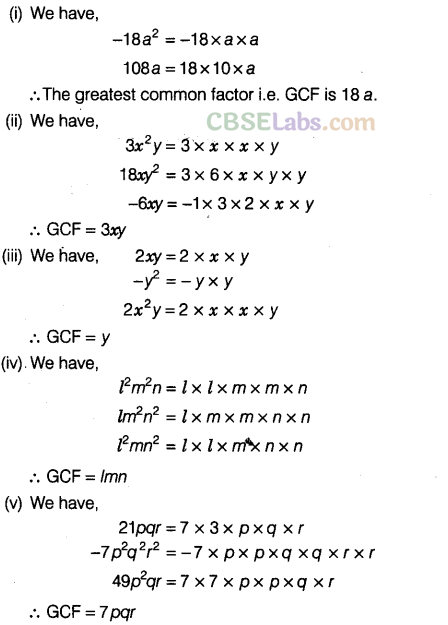


Question. 88 Factorise the following expressions.
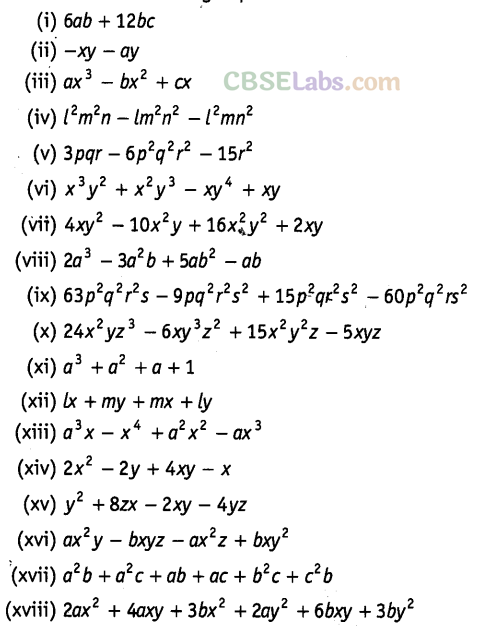
Solution.
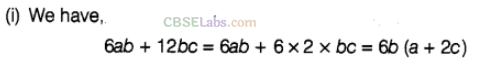

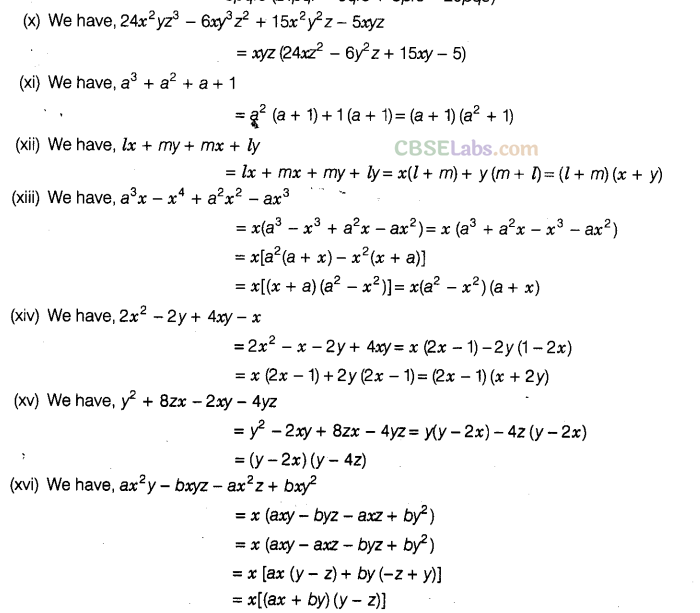
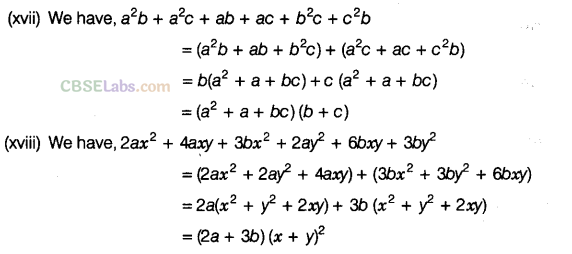
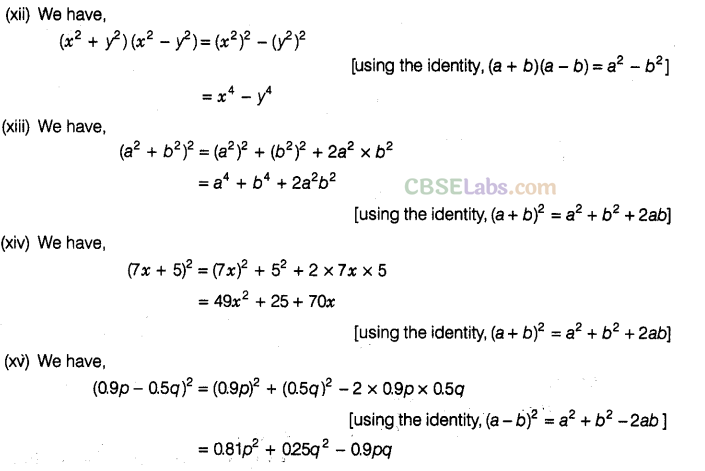
Question. 89Factorise the following, using the identity,\({{a}^{2}}+2ab+{{b}^{2}}={{(a+b)}^{2}}\)
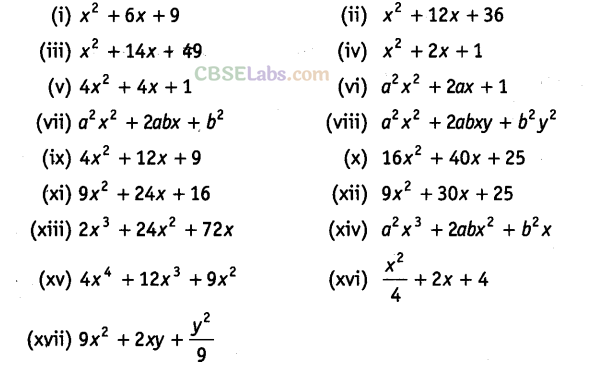
Solution.
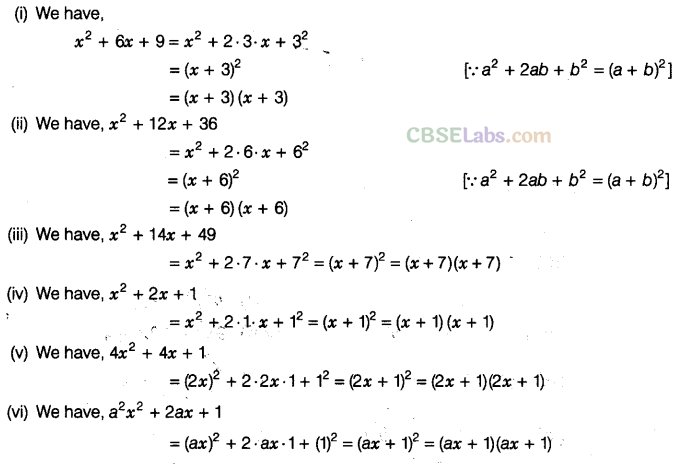
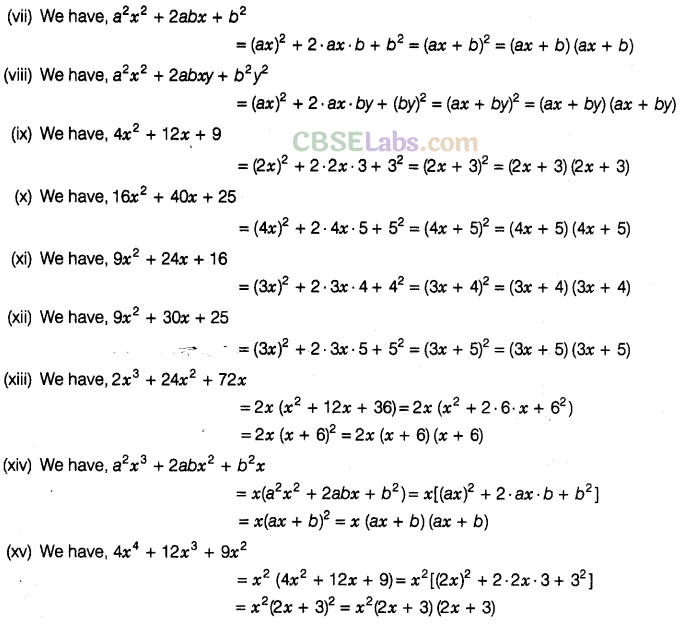
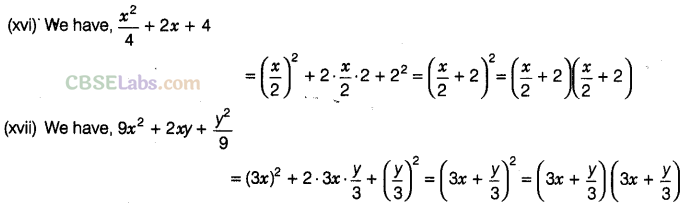
Question. 90 Factorise the following, using the identity,\({{a}^{2}}-2ab+{{b}^{2}}={{(a-b)}^{2}}\)
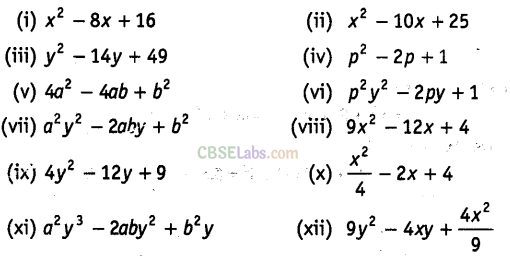
Solution.


Question. 91 Factorise the following
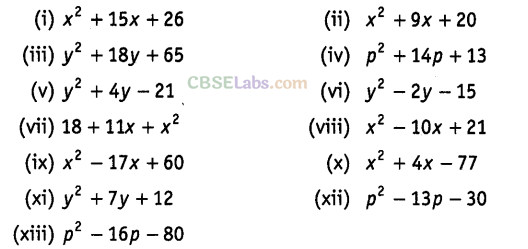
Solution.
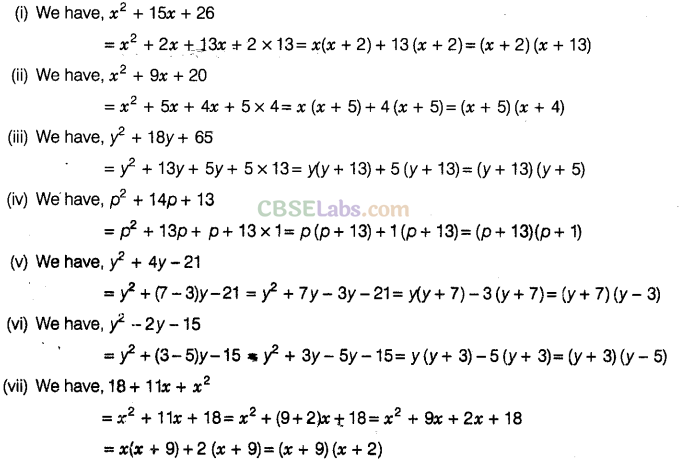
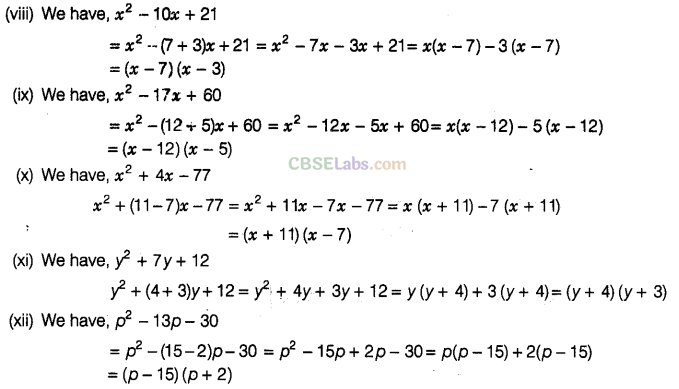
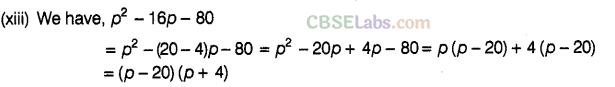
Question. 92 Factorise the following using the identity ,\({{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}\)=(a+b)(a-b).
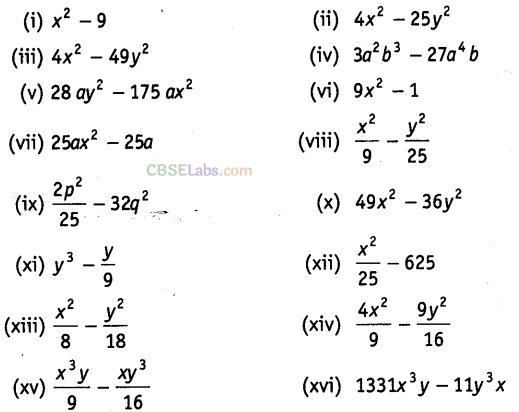
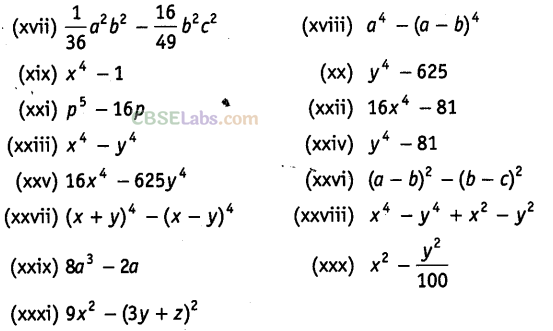
Solution.
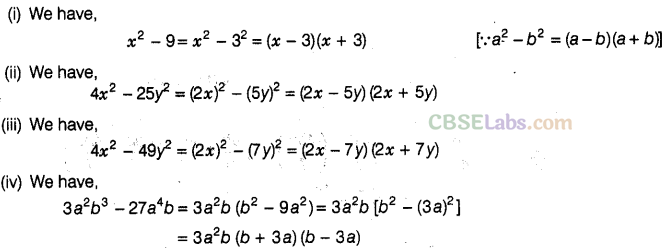
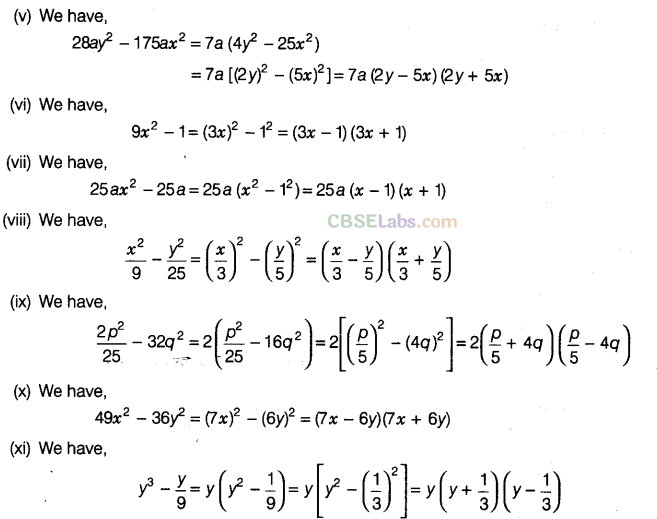
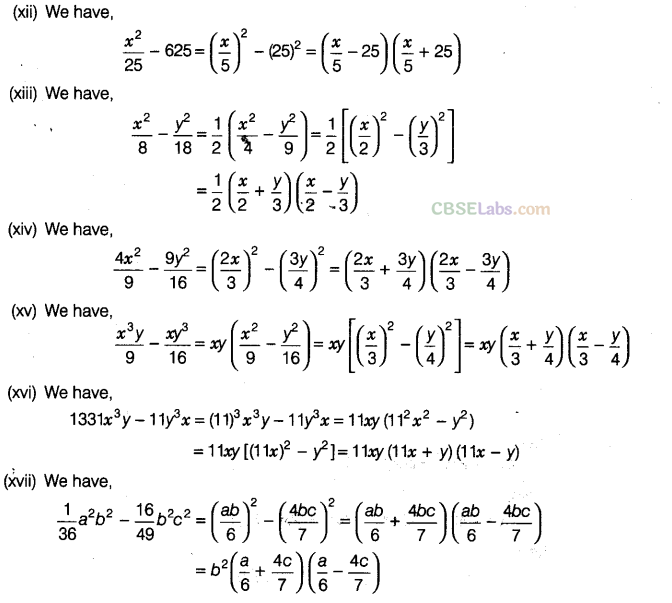


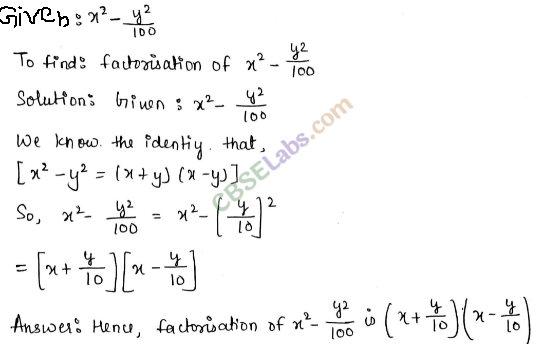
Question. 93 The following expressions are the areas of rectangles. Find the possible lengths and breadths of these rectangles.

Solution.

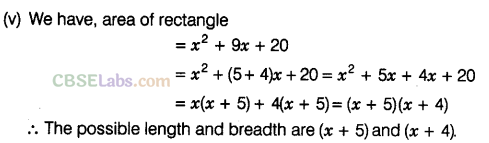
Question. 94 Carry out the following divisions:

Solution.
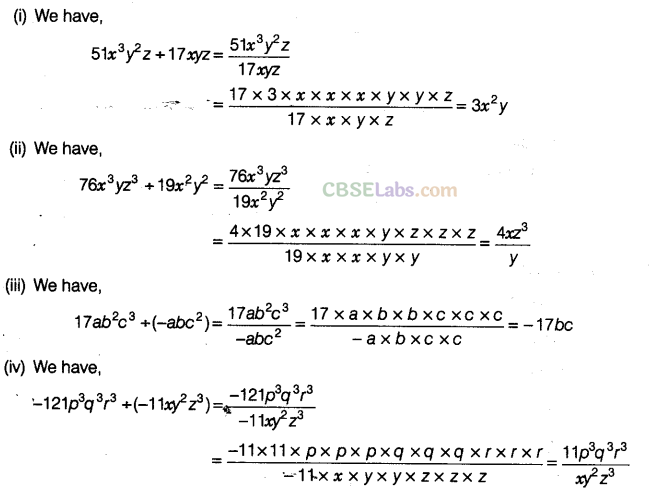
Question. 95 Perform the following divisions:
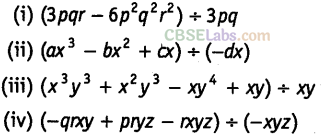
Solution.
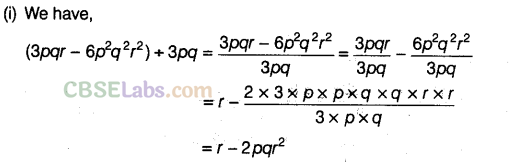
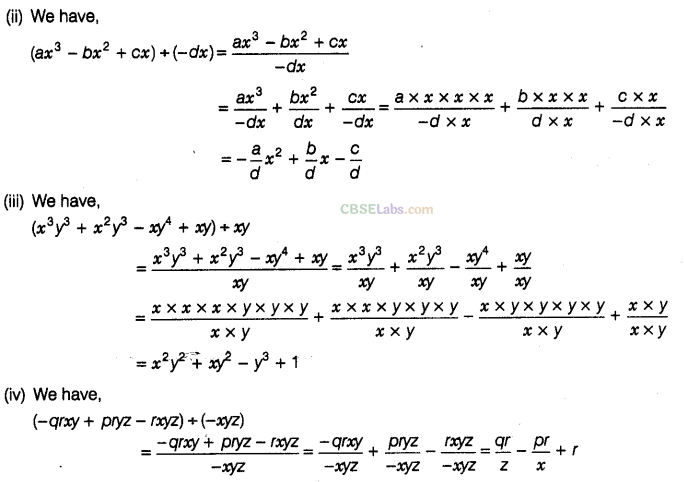
Question. 96 Factorise the expressions and divide them as directed.
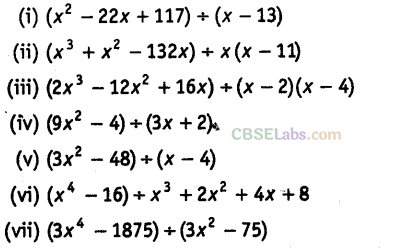
Solution.
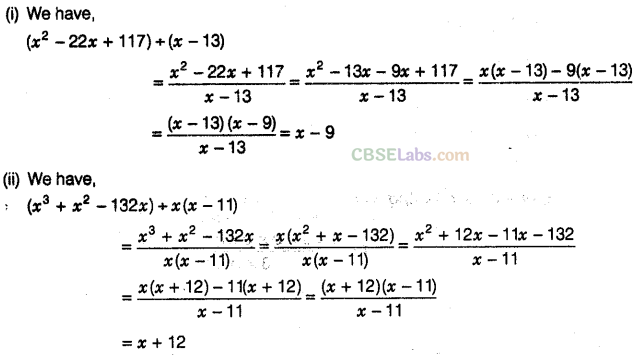
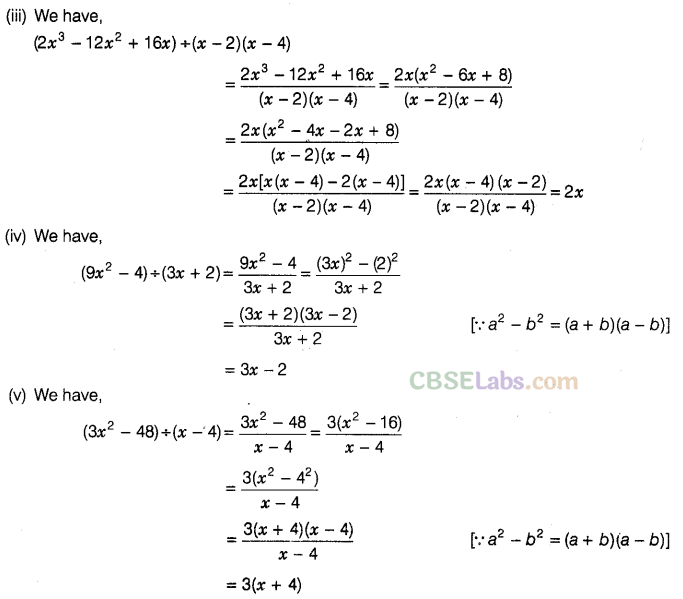
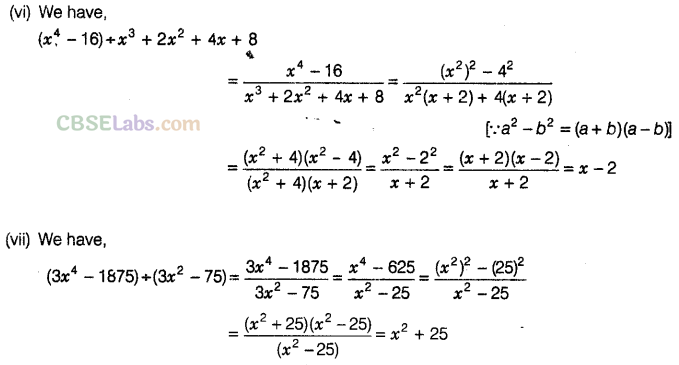
Question. 97 The area of a square is given by 4\({{x}^{2}}\)+ 12xy + 9\({{y}^{2}}\). Find the side of the square.
Solution.
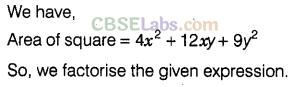
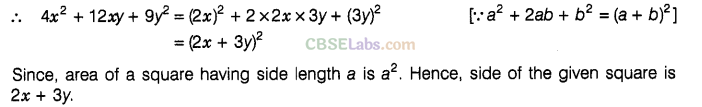
Question. 98 The area of a square is 9\({{x}^{2}}\) + 24xy + 16\({{y}^{2}}\). Find the side of the square.
Solution.

Question. 99 The area of a rectangle is \({{x}^{2}}\) + 7x + 12. If its breadth is (x + 3), then find its length.
Solution.
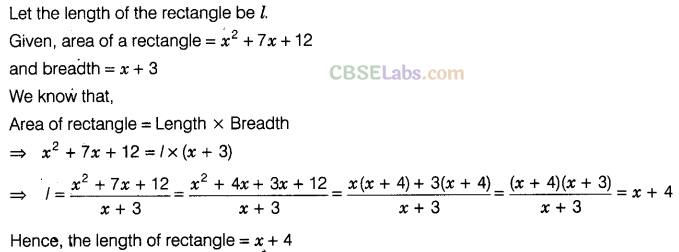
Question. 100 The curved surface area of a cylinder is \(2\pi ({ y }^{ 2 }-7y+12)\) and its radius is (y – 3). Find the height of the cylinder (CSA of cylinder = \(2\pirh\))
Solution.

Question. 101 The area of a circle is given by the expression \( \pi { x }^{ 2 }+6\pi x+9\pi \). Find the radius of the circle.
Solution.
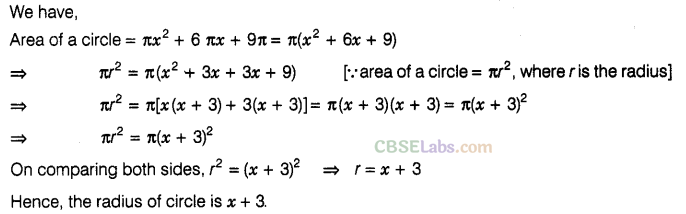
Question.102 The sum of first n natural numbers is given by the expression \(\frac { { n }^{ 2 } }{ 2 } +\frac { n }{ 2 }\) Factorise this expression.
Solution.
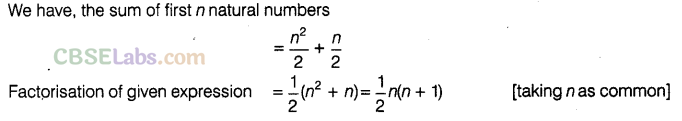
Question.103 The sum of (x + 5) observations is \({ x }^{ 4 }\) – 625. Find the mean of the observations.
Solution.

Question.104 The height of a triangle is \({ x }^{ 4 }\) + \({ y }^{ 4 }\) and its base is 14xy. Find the area of the triangle.
Solution.
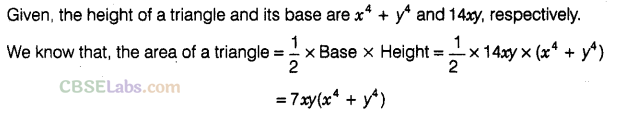
Question.105 The cost of a chocolate is Rs (x + 4) and Rohit bought (x + 4) chocolates. Find the total amount paid by him in terms of x. If x = 10, find the amount paid by him.
Solution.
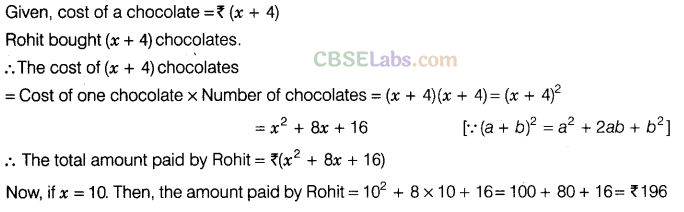
Question.106 The base of a parallelogram is (2x + 3) units and the corresponding height is (2x – 3) units. Find the area of the parallelogram in terms of x. What will be the area of a parallelogram of x = 30 units?
Solution.

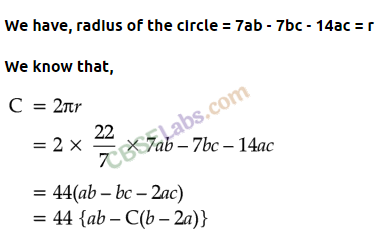
Question.107 The radius of a circle is 7ab – 7be – 14ac . Find the circumference of the circle,\( (\pi =\frac { 22 }{ 7 } )\)
Solution.
Question.108 If p + q = 12 and pq = 22, then find \({ p }^{ 2 }\) + \({ q }^{ 2 }\) .
Solution.
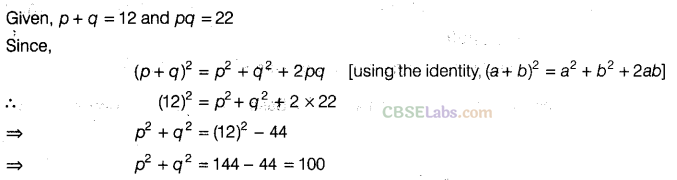
Question.109 If a + b = 25 and \({ a }^{ 2 }\) + \({ b }^{ 2 }\) then find ab.
Solution.
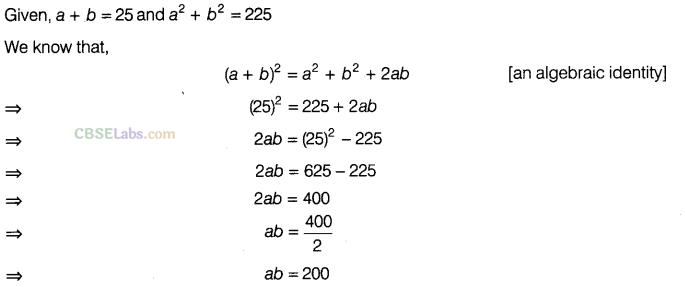
Question.110 If x – y = 13 and xy = 28, then find \({ x }^{ 2 }\) + \({ y }^{ 2 }\).
Solution.
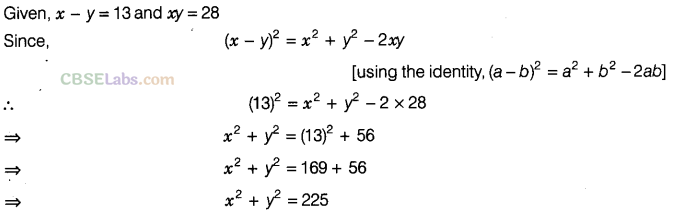
Question.111 If m – n = 16 and \({ m }^{ 2 }\) + \({ n }^{ 2 }\) = 400, then find mn.
Solution.

Question.112 If \({ a }^{ 2 }\) + \({ b }^{ 2 }\) = 74 and ab = 35, then find a + b ?
Solution.
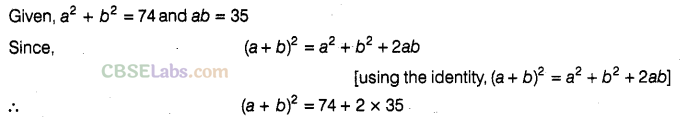
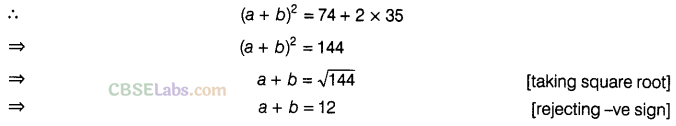
Question.113 Verify the following:
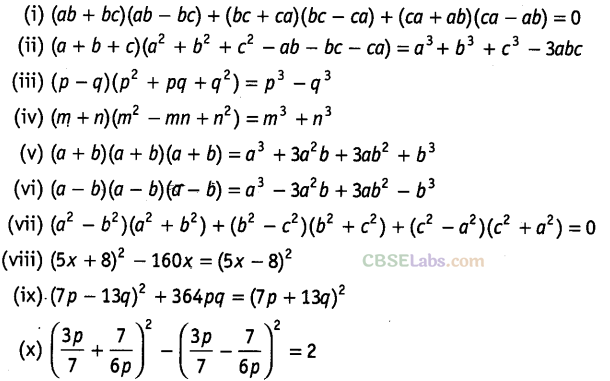
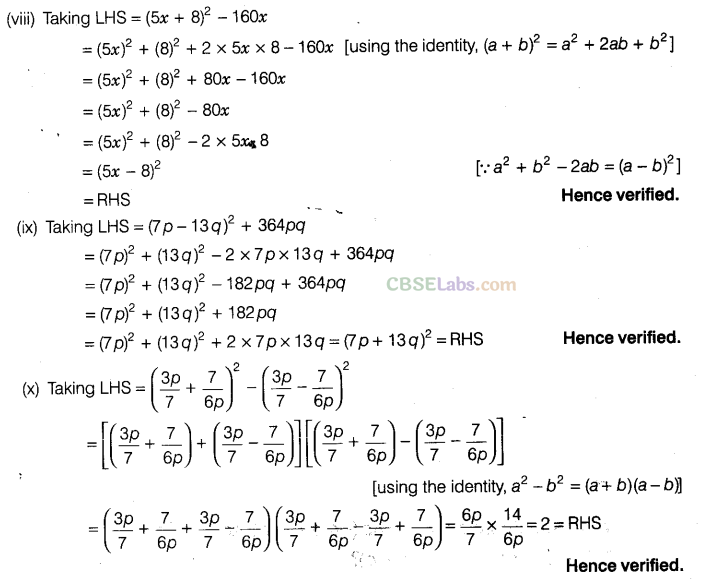
Solution.


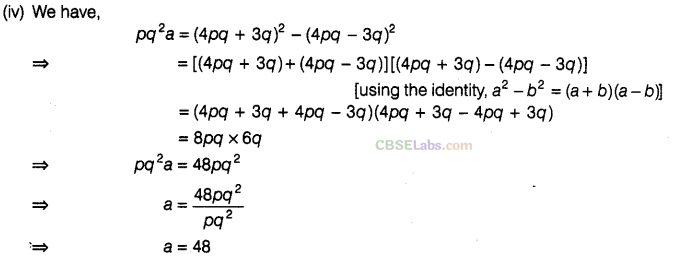
Question.114 Find the value of a, if
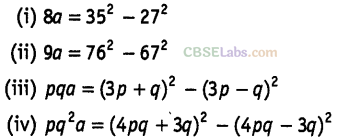
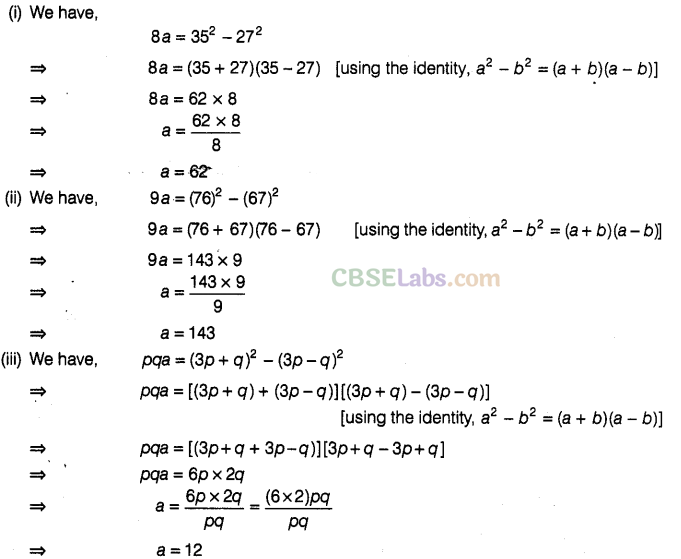
Solution.
Question.115 What should be added to 4c (-a + b + c) to obtain 3a(a + b + c) – 2b (a – b + c)?
Solution.
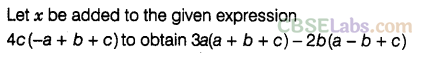
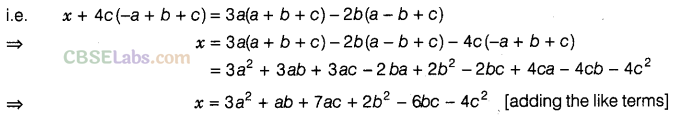
Question.116 Subtract b(\({ b }^{ 2 }\) + b – 7) + 5 from 3\({ b }^{ 2 }\) – 8 and find the value of expression obtained for b = – 3.
Solution.
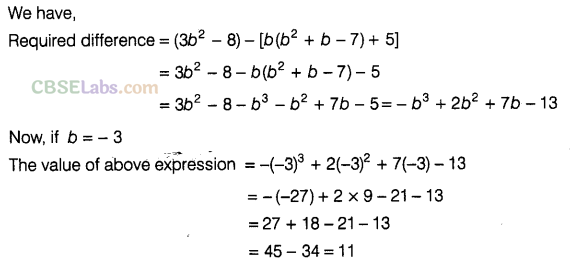
Question.117 If x – \(\frac { 1 }{ x }\) = 1, then find the value of \({ x }^{ 2 }+\frac { 1 }{ { x }^{ 2 } }\) .
Solution.
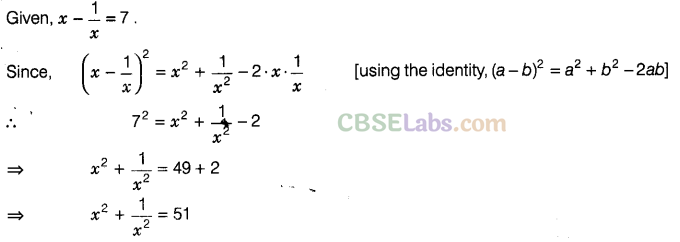
Question.118 Factorise \({ x }^{ 2 }+\frac { 1 }{ { x }^{ 2 } } +2-3x-\frac { 3 }{ x }\).
Solution.

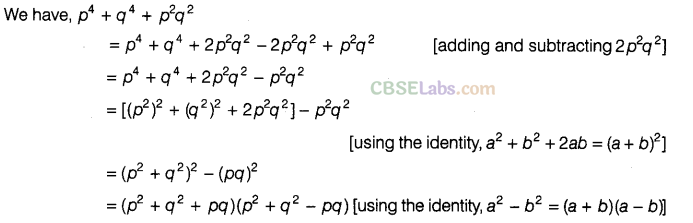
Question.119 Factorise \({ p }^{ 4 }+{ q }^{ 4 }+{ p }^{ 2 }{ q }^{ 2 }\).
Solution.
Question.120 Find the value of
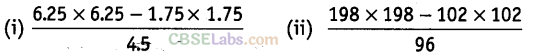
Solution.
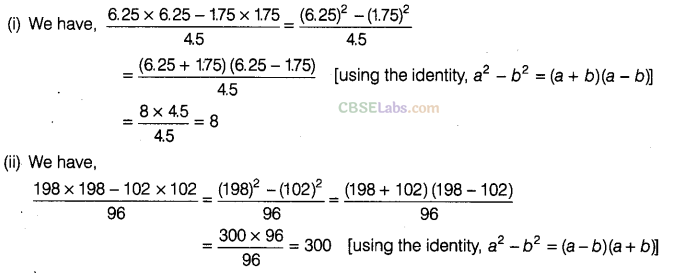
Question.121 The product of two expressions is \({ x }^{ 5 }\) + \({ x }^{ 3 }\)+ x . If one of them is \({ x }^{ 2 }\) + x + 1, find the other.
Solution.
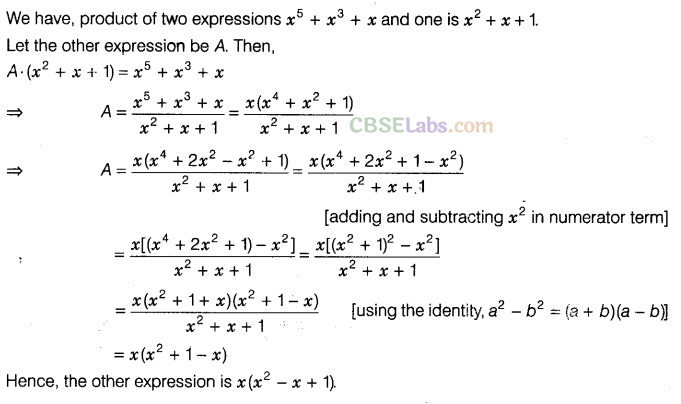
Question.122 Find the length of the side of the given square, if area of the square is 625sq units and then find the value of x.
Solution.

Question.123 Take suitable number of cards given in the adjoining diagram [G(x x x) representing \({ x }^{ 2 }\), R (x x 1) representing x and Y (1 x 1) representing 1] to factorise the following expressions, by arranging to cards in the form of rectangles: (i) 2\({ x }^{ 2 }\) + 6x + 4 (ii) \({ x }^{ 2 }\) + 4x + 4. Factorise 2\({ x }^{ 2 }\) + 6x + 4 by using the figure.
Calculate the area of figure.
Solution. The given information is incomplete for solution of this question.
Question.124 The figure shows the dimensions of a wall having a window and a door of a room. Write an algebraic expression for the area of the wall to be painted.
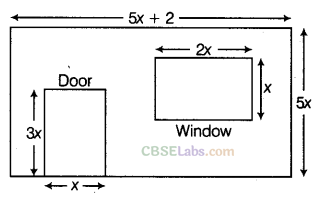
Solution.

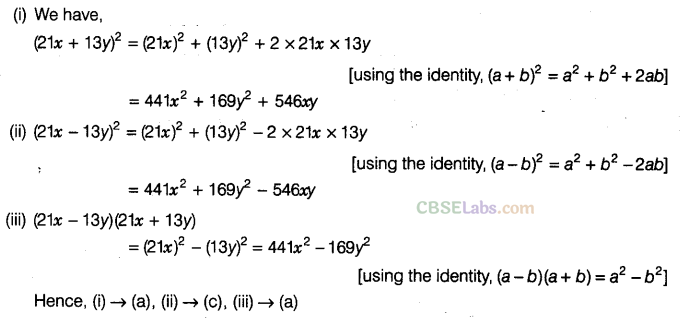
Question.125 Match the expressions of column I with that of column II

Solution.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 8 Maths
- Chapter 1 Rational Numbers
- Chapter 2 Data Handling
- Chapter 3 Square-Square Root and Cube-Cube Root
- Chapter 4 Linear Equations in One Variable
- Chapter 5 Understanding Quadrilaterals and Practical Geometry
- Chapter 6 Visualising Solid Shapes
- Chapter 7 Algebraic Expressions, Identities and Factorisation
- Chapter 8 Exponents and Powers
- Chapter 9 Comparing Quantities
- Chapter 10 Direct and Inverse Proportion
- Chapter 11 Mensuration
- Chapter 12 Introduction to Graphs
- Chapter 13 Playing with Numbers
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 7 Algebraic Expressions, Identities and Factorisation help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Chapter 7 Algebraic Expressions, Identities and Factorisation, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.