NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
Multiple Choice Questions
Single Correct Answer Type
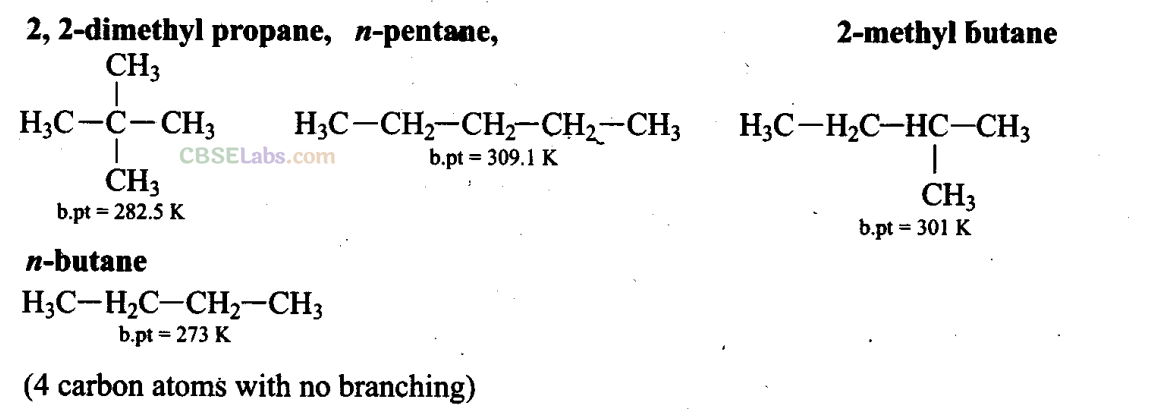
Q1. Arrange the following ia decreasing order of their boiling points.
(A) n-Butane
(B) 2-Methylbutane
(C) n-Pentane
(D) 2,2-Dimethylpropane
(a) A > B > C > D
(b) B > C > D > A
(c) D>C>B>A
(d) C >B>D > A
Sol: (d) As the number of carbon atom increases, boiling point increases. Boiling point decreases with branching.
Q2. Arrange the halogens F2, Cl2, Br2 and I2 in order of their increasing reactivity with alkanes.
(a) I2 < Br2 < Cl2 < F2
(b) Br2 < Cl2 < F2 < I2
(c) F2 < Cl2 < Br2 < I2
(d) Br2 < I2 < Cl2 < F2
Sol:(a) The reactivity order of halogens with alkanes is I2 < Br2 < Cl2 < F2
Q3. The increasing order of reduction of alkyl halides with zinc and dilute HCl is
(a) R-C1<R-I<R-Br
(b) R-Cl<R-Br<R-I
(c) R -1 < R – Br < R – Cl
(d) R-Br<R-I<R-Cl
Sol:(b) The reactivity of reduction bf alkyl halides with Zn/HCl increases as the strength of the C – X bond decreases, i.e., R – Cl < R – Bf < R -I.
Q4. The correct IUPAC name of the following alkane is
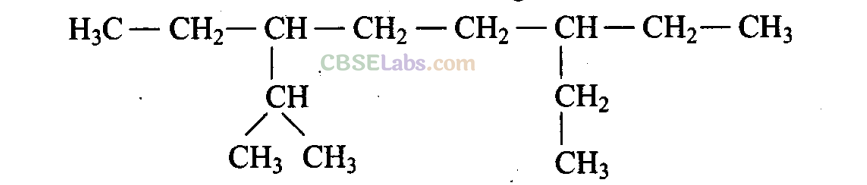
(a) 3,6-Diethyl-2-methyloctane
(b) 5-Isopropyl-3-ethyloctane
(c) 3-Ethyl-5-isopropyloctane
(d) 3-Isopropyl-6-ethyloctane
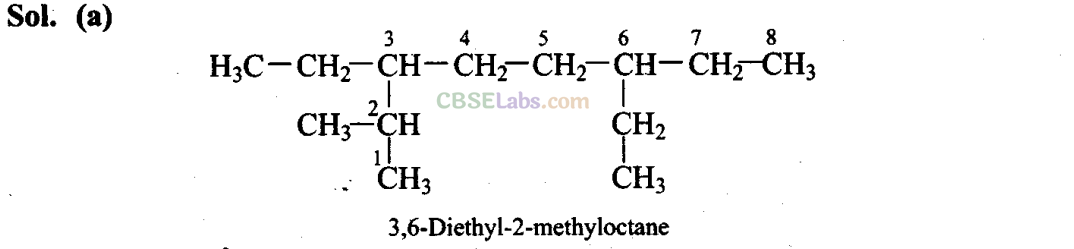
Q5. The addition of HBr to 1 -butene gives a mixture of products (A), (B) and (C).
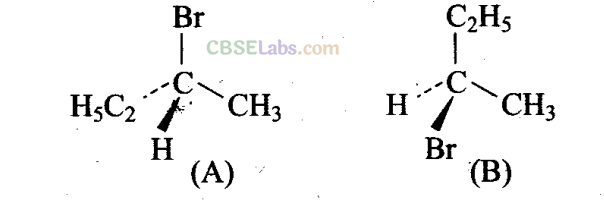
(C) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – Br
The mixture consists of
(a) (A) and (B) as major and (C) as minor products
(b) (B) as major, (A) and (C) as minor products
(c) (B) as minor, (A) andj(C) as major products
(d) (A) and (B) as minor and (C) as major products.
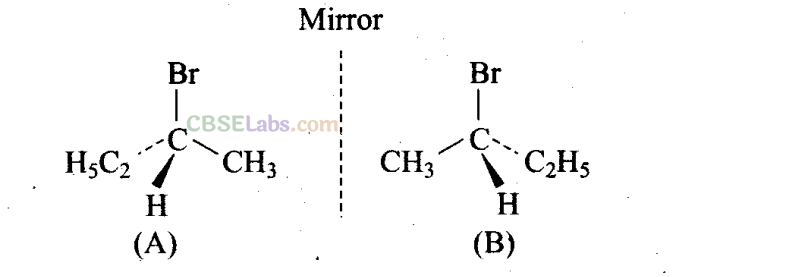
Sol: (a) The alkene is unsymmetrical, hence will follow Markovnikov rule to give major product.
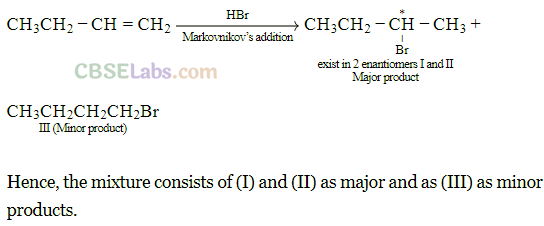
Since I contains a chiral carbon, it exists in two enantiomers (A and B) which are mirror image of each other.
Q6. Which of the following will nofshow geometrical isomerism?
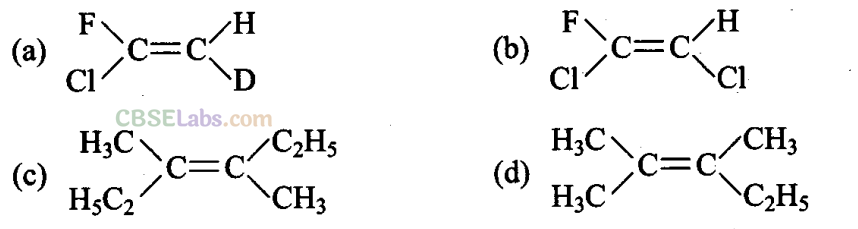

Q7. Arrange the following hydrogen halides in order of their decreasing reactivity with propene.
(a) HC1 > HBr > HI
(b) HBr>HI>HCl
(c) HI > HBr > HCl
(d) HCl>HI>HBr
Sol: (c) The decreasing order of reactivity of hydrogen halides with propene is HI > HBr > HC1. As the size of halogen increases, the strength of H – X bond decreases and hence, reactivity increases.
Q8. Arrange the following carbanions in order of their decreasing stability.
(A) H3C-C ≡ C–
(B) H-C ≡ C–
(C) H3C – CH–2
(a) A>B>C
(b) B>A>C
(c) C>B>A
(d) C>A>B
Sol: (b) The order of decreasing stability of carbanions is:
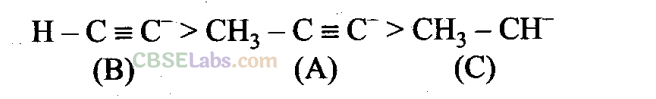
sp-hybridised carbon atom is more electronegative than sp3-hybridised carbon atom and hence, can accommodate the negative charge more effectively. – CH3 group has +1 effect, therefore, it intensifies the negative charge and, hence, destabilises the carbanion CH3 →C = C–.
Q9. Arrange the following alkyl halides in decreasing order of the rate of β -elimination reaction with alcoholic KOH.
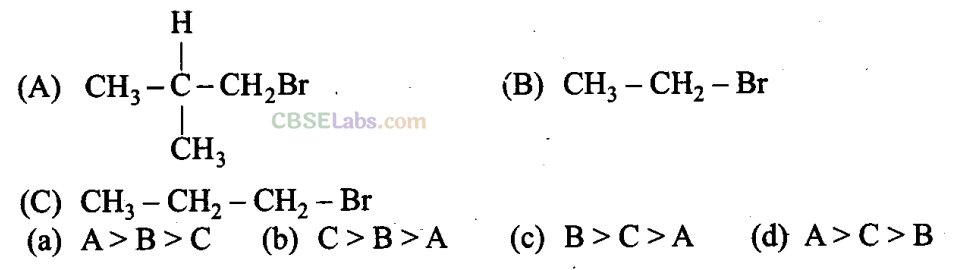
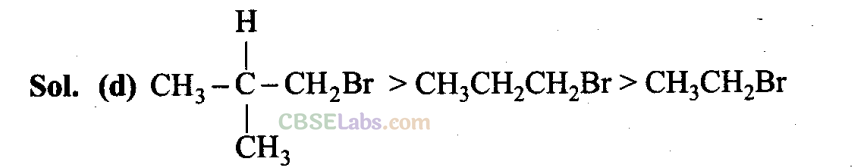
is the order of rate of β -elimination with alcoholic KOH.
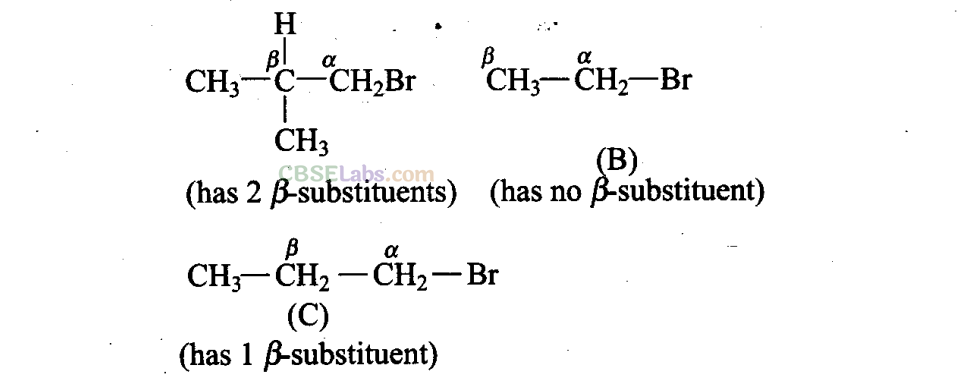
More the number of β-substituents (alkyl groups), more stable alkene will be formed on β -elimination and more will be the reactivity. Thus, the decreasing order of the rate of β -elimination reaction with alcoholic KOH is: A > C > B.
Q10. Which of the following reactions of methane is incomplete combustion?
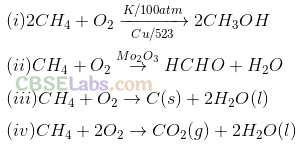
Sol: (c) Dining incomplete combustion of alkanes with insufficient amount of air or dioxygen, carbon black is formed which is used in the manufacture of ink, printer ink, black pigments and as filters. Thus,

More than One Correct Answef Type
Q11. Some oxidation reactions of methane are given below. Which of them is/are controlled oxidation reactions?
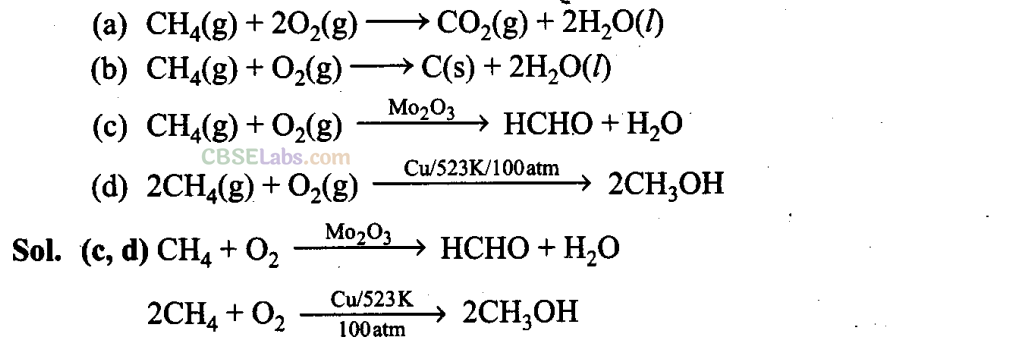
Reactions in which methane does not undergo complete combustion to give carbon dioxide and water or incomplete combustion to give carbon and water are controlled oxidation reactions.
Q12. Which of the following alkenes on ozonolysis gives a mixture of ketones only?
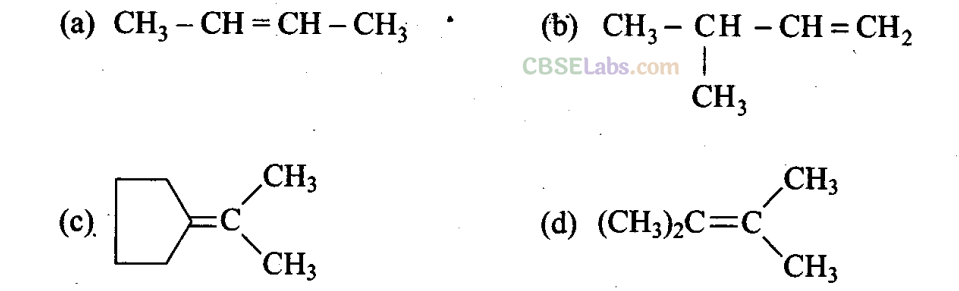
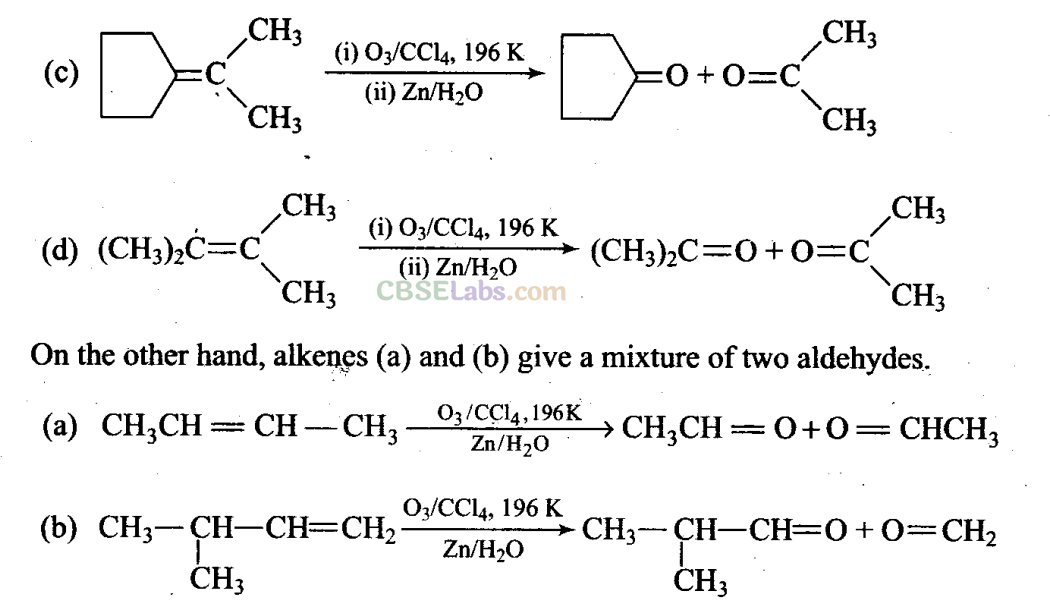
Sol: (c, d) Alkenes which have two substituents on each carbon atom of the double bond give a mixture of ketones on ozonolysis. Thus, options (c) and (d) give mixture of ketones.
Q13. Which are the correct IUPAC names of the following compound?
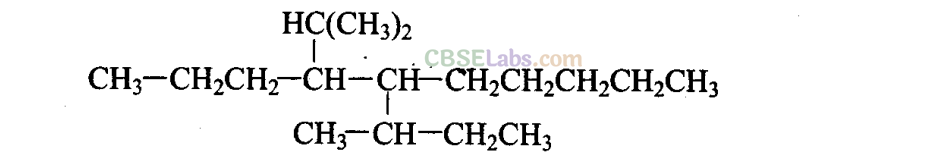
(a) 5-Buty 1-4-i sopropyldecane
(b) 5-Ethyl-4-propyldecane
(c) 5-sec-Butyl-4-iso-propyldecane
(d) 4-( 1 -Methylethyl)-5-( 1 -methylpropyl)decane
Sol: (c,d)
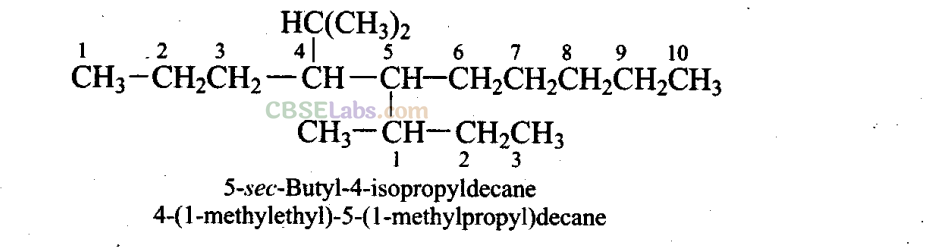
Q14. Which are the correct IUPAC names of the following compound
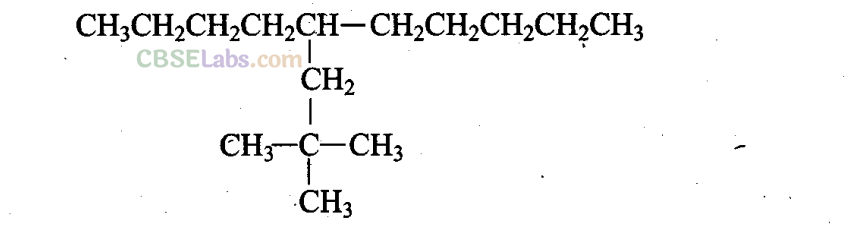
(a) 5-(2′,2′-Dimethylpropyl)decane
(b) 4-Butyl-2,2-dimethylnonane
(c) 2,2-Dimethyl-4-pentyloctane
(d) 5-neo-Pentyldecane

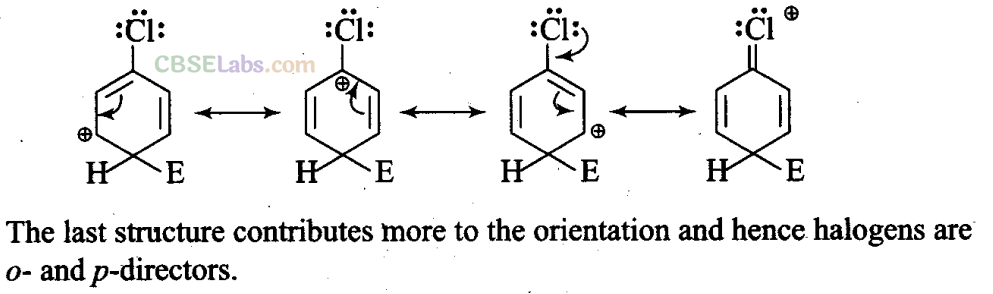
Q15. For an electrophilic substitution reaction, the presence of a halogen atom in the benzene ring ;
(a) deactivates the ring by inductive effect
(b) deactivates the ring by resonance
(c) increases the charge density at ortho and para-positions relative to meta-position by resonance
(d) directs the incoming electrophile to meta-position by increasing the
charge density relative to ortho and para-positions. ‘
Sol: (a, c) For an electrophilic substitution reaction, the presence of halogen atom in the benzene ring deactivates the ring by inductive effect and increases the charge density at ortho- and para-position relative to meta-position by resonance. –
When chlorine is attached to benzene ring, chlorine being more electronegative pulls the electrons because of its -1-effect. The electron cloud of benzene becomes less dense. Thus, chlorine makes the benzene ring in aryl halide somewhat deactivated. But due to resonance, the electron density on ortho- and para-positions is greater than on meta-position.
Q16. In an electrophilic substitution reaction of nitrobenzene, the presence of nitro group ________ ‘
(a) deactivates the ring by inductive effect
(b) activates the ring by inductive effect
(c) decreases the charge density at ortho- and para-positions of the ring relative to meta-position by resonance
(d) increases the charge density at meta-position relative to the ortho and para-positions of the ring by resonance
Sol: (a, c) Nitro group by virtue of-I-effect withdraws electrons from the ring and increases the charge and destabilizes carbocation.
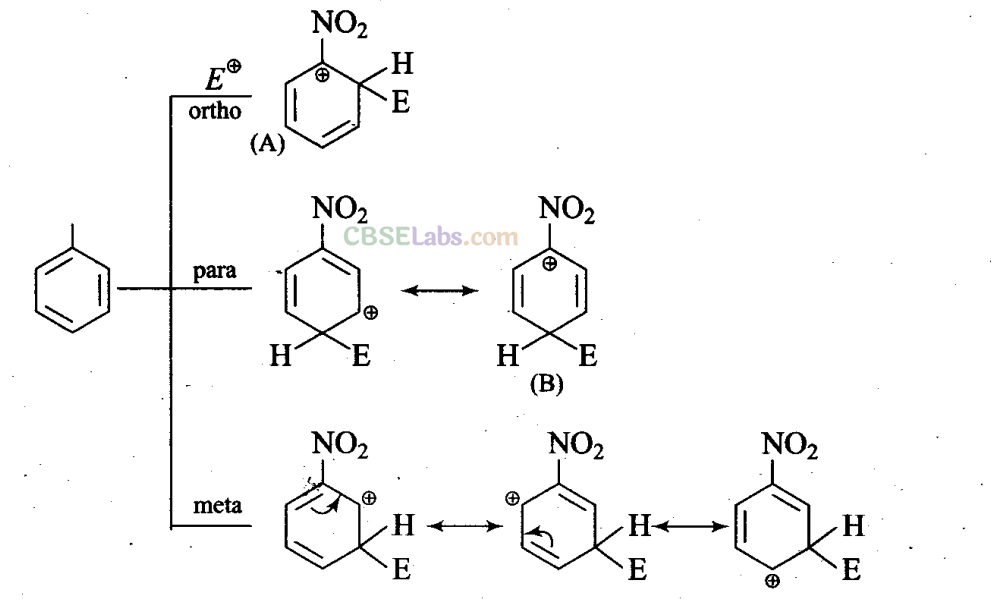
In ortho, para-attack of electrophile on nitrobenzene, we are getting two structures (A) and (B) in which positive charge is appearing on the carbon atom directly attached to the nitro group.
As nitro group is electron withdrawing by nature, it decreases the stability of such product and hence meta attack is more feasible when electron withdrawing substituents are attached.
Q17. Which of the following are correct?
(a) CH3 – O – CH+2 is more stable than CH3 – CH+2
(b) (CH3)2CH+ is less stable than CH3 – CH2 – CH+2
(c) CH2 = CH – CH+2 is more stable than CH3 – CH2 – CH+2
(d) CH2 = CH+ is more stable than CH3 – CH+2

Q18. Four structures are given in options (a) to (d). Examine them and select the aromatic structures.


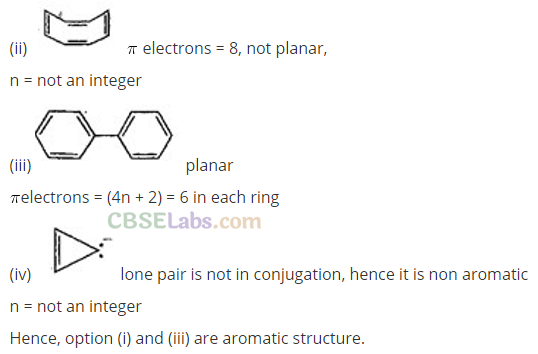
Cyclooctatetraene is non-planar and has 8π-electrons. It is not aromatic. Cyclopropenyl anion is planar but has 4 π -electrons. It is not aromatic.
Q19. The molecules having dipole moment are________ .
(a) 2,2-Dimethylpropane
(b) trans-Pent-2-ene
(c) cw-Hex-3-ene
(d) 2,2,3,3-Tetramethylbutane
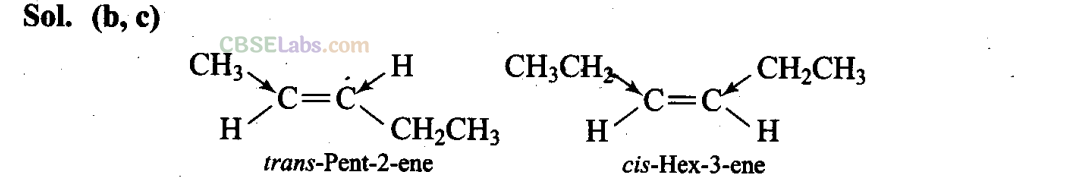
Since, the +1 effect of CH2CH3 group is higher than that of CH3 group, therefore, the dipole moments of C-CH3 and C-CH2CH3 bonds are unequal. Although these two dipoles oppose each other, yet they do not exactly cancel out each other and hence trans-2-pentene has small but finite dipole moment.
In cis-hex-3-ene, although the dipole moments of the two C – CH2CH3 bond are equal, but they are inclined to each other at an angle of 60° and hence have a finite dipole moment.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q20. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reaction? Explain.
Sol: Due to the presence of a π -electron cloud above and below the plane of alkenes and arenes, these are electron rich molecules and, therefore, provide sites for the attack of electrophiles. Hence, they undergo electrophilic reactions. Alkenes undergo electrophilic addition reactions because they are unsaturated molecules. For example,
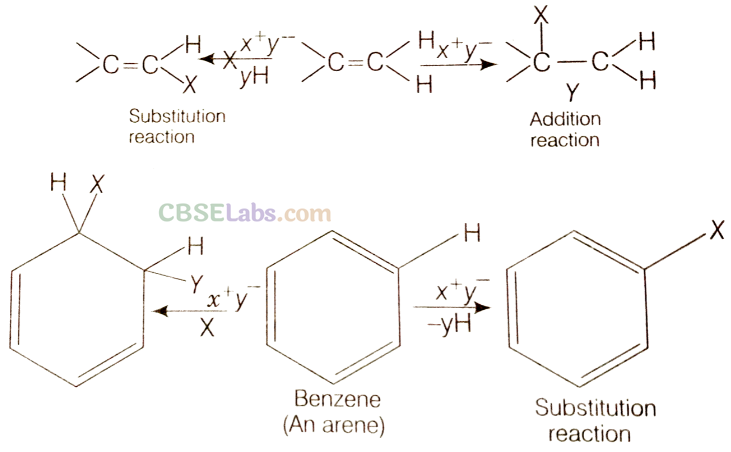
Arenes, on the other hand, cannot undergo electrophilic addition reactions. This is because benzene has a large resonance energy of 150.4 kJ mol-1. During electrophilic addition reactions, two new σ-bonds are formed but the aromatic character of benzene gets destroyed and, therefore, resonance energy of benzene ring is lost. Hence, electrophilic addition reactions of arenes are not energetically favourable. Arenes, in contrast, undergo electrophilic substitution reactions in which σ C – H bond is broken and new σ C – X bond is formed: The aromatic character of benzene ring is not destroyed and benzene retains its resonance energy. Hence, arenes undergo electrophilic substitution reactions.
Q21. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia form trans alkenes. Will butene formed on the reduction of but-2-yne show geometrical isomerism?
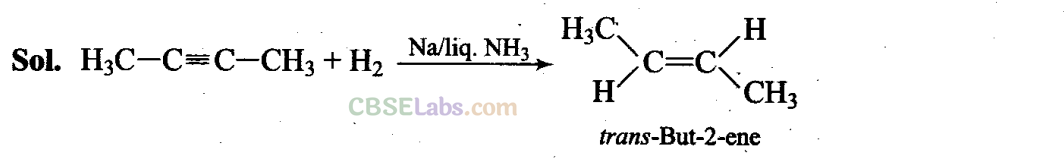
Thus, but-2-ene is capable of showing geometrical isomerism.
Q22. Rotation around carbon-carbon single bond of ethane is not completely free. Justify the statement.
Sol: Ethane contains carbon-carbon sigma (σ) bond. Electron distribution of the sigma molecular orbital is symmetrical around the intemuclear axis of the C – C bond which is not disturbed due to rotation about its axis. This permits free rotation around aC-C single bond. However, rotation around a C – C single bond is not completely free. It is hindered by a small energy barrier due to weak repulsive interaction between the adjacent bonds. Such a type of repulsive interaction is called torsional strain. Of all the conformations of ethane, the staggered form has the least torsional strain and the eclipsed form has the maximum torsional strain. The energy difference between the two extreme forms is of the order of 12.5 kJ mol-1, which is very small. It has not been possible to separate and isolate different conformational isomers of ethane.
Q23. Draw Newman and Sawhorse projections for the eclipsed and staggered conformations of ethane. Which of these conformations is more stable and why? .
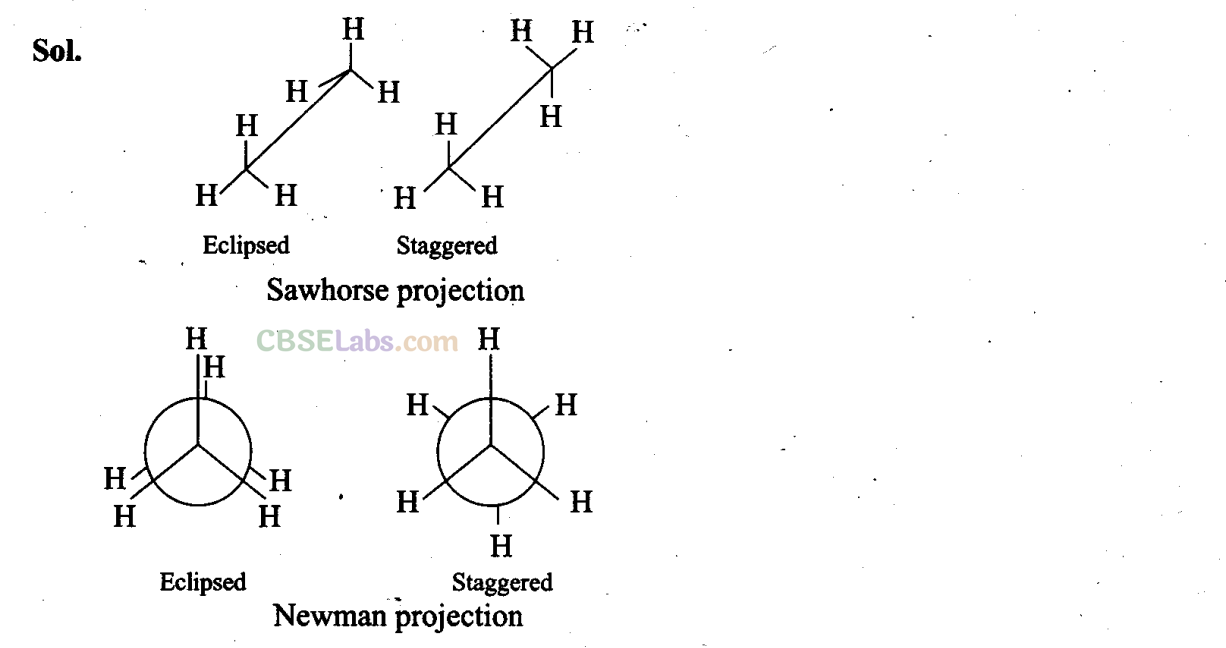
In staggered form of ethane, the electron clouds of carbon-hydrogen bonds are as far apart as possible. Thus, there are minimum repulsive forces, minimum energy and maximum stability of the molecule. On the other hand, when the staggered form changes into the eclipsed form, the electron clouds of the carbon-hydrogen bonds come closer to each other resulting in increase in electron cloud repulsions. To check the increased repulsive forces, molecule will have to possess more energy and thus has lesser stability.
Q24. The intermediate carbocation formed in the reactions of HI, HBr and HC1 with propene is the same and the bond energy of HCl, HBr and HI is 430.5 kJ mol-1,363.7 kJ mol–1 and 296.8 kJ mol-1 What will be the other of reactivity of these halogen acids?
Sol: The bond dissociation enthalpy decreases in the order HC1 > HBr > HI, therefore, the order of reactivity is in the reverse order i.e., HI > HBr > HCl.
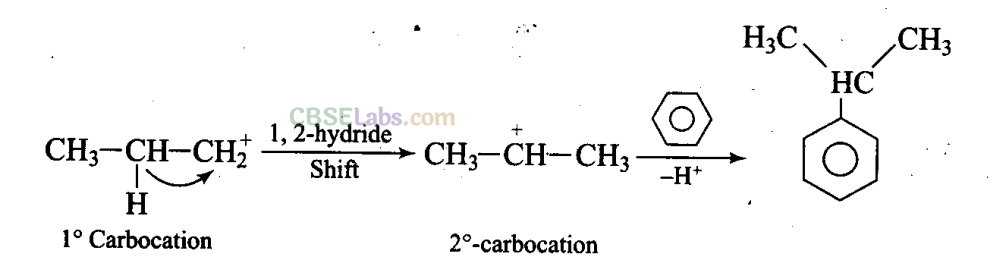
Q25. What will be the product obtained as a result of the following reaction and why?
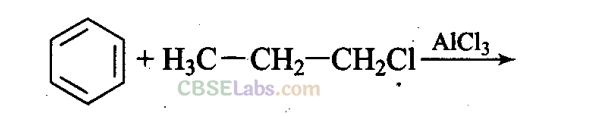
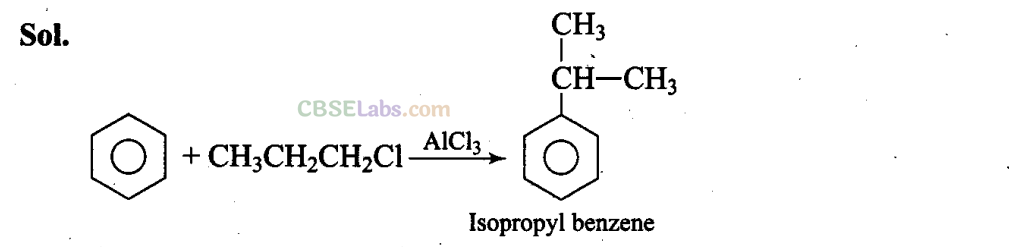
Propyl chloride forms CH3 – CH2 – CH+2 with anhydrous A1C13 which is less stable. This rearranges to a more stable carbocation as:
Q26. How will you convert benzene into
(i) p-nitrobromobenzene (ii) m-nitrobromobenzene
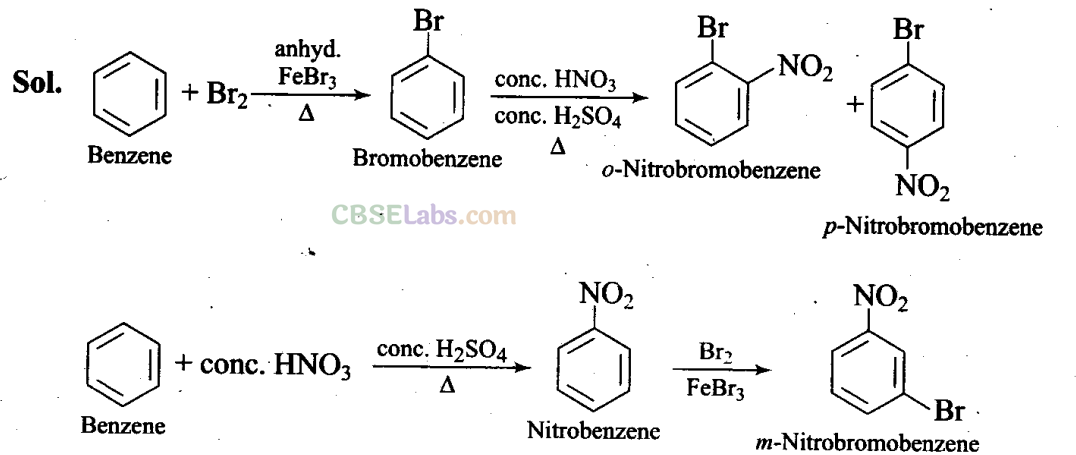
Q27. Arrange the following set of compounds in the order of their decreasing . relative reactivity with an electrophile. Give reason.
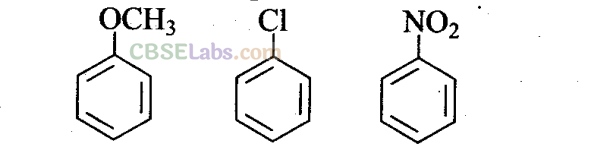
Sol: The methoxy group (-OCH3) is electron releasing group. It increases the electron density in beniene nucleus due to
resonance effect (+R-effect). Hence, it makes anisole more reactive than benzene towards the electrophile.
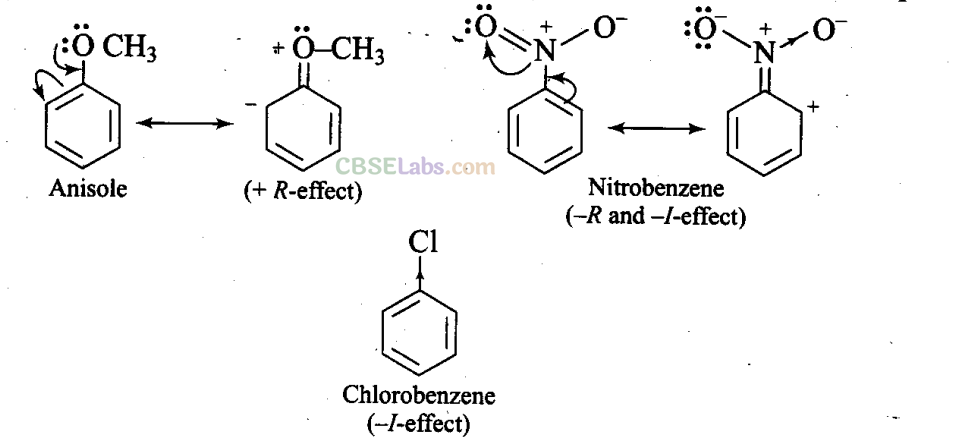
In case of alkyl halides, the electron density increases at ortho and para positions due to +R effect. However, the halogen atom also withdraws electrons from the ring because of its -I effect. Since the -I effect is stronger than the +R effect, the halogens are moderately deactivating. Thus, overall electron density on benzene ring decreases, which makes further substitution difficult.
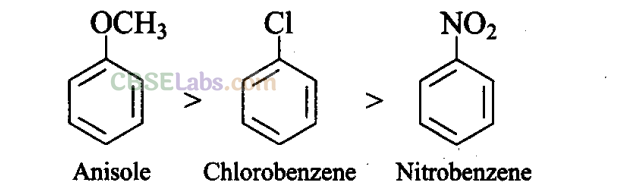
-N02 group is electron withdrawing group. It decreases the electron density in benzene nucleus due to its strong -R-effect and strong -I-effect. Hence, it makes nitrobenzene less reactive. Therefore, overall reactivity of these three compounds towards electrophiles decreases in the following order:
Q28. Despite their -I effect, halogens are o- andp-direction in haloarenes. Explain.
Sol: In case of aryl halides, halogens are little deactivating because of their strong -I effect. Therefore, overall electron density on the benzene ring decreases. In other words, halogens are deactivating due to -I effect. However, because of the +R-effect, i.e., participation of lone pairs of electrons on the halogen atom with the π-electrons of the benzene ring, the electron density increases more at o- and p-positions than at m-positions.
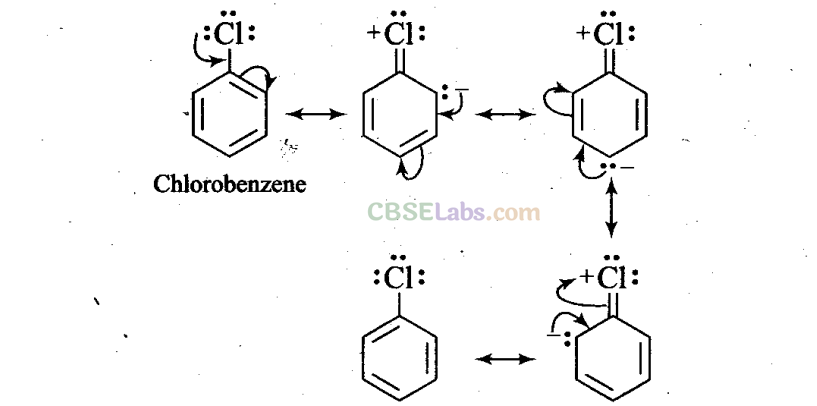
As a result, halogens are o-, p-directing. The combined result of +R-effect and -I-effect of halogens is that halogens are deactivating but o, p-directing.
Q29. Why does the presence of a nitro group-make the benzene ring less reactive in comparison to the unsubstituted benzene ring? Explain.
Sol: Nitro group is an electron withdrawing group (-R and -I effects). It deactivates the ring by decreasing nucleophilicity for further substitution.
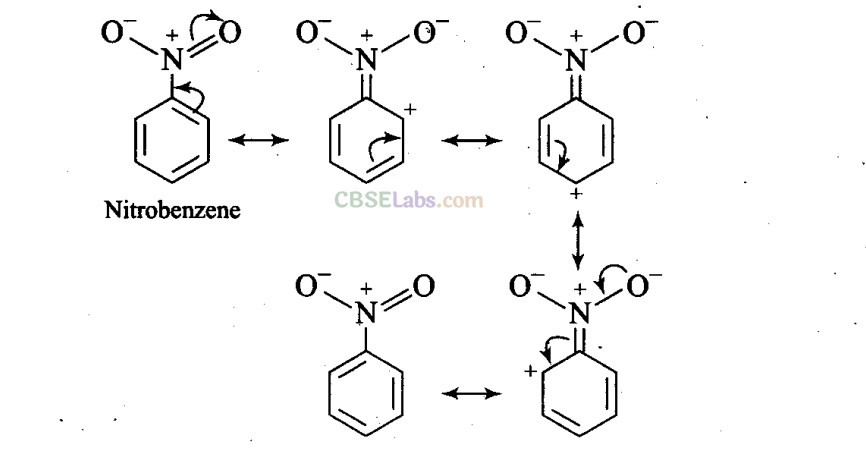
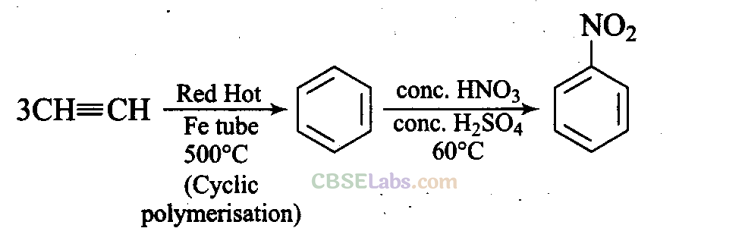
Q30. Suggest a route for the preparation of nitrobenzene starting from acetylene.
Sol: Acetylene when passed through red hot iron tube at 500°C undergoes cyclic polymerisation to give benzene which upon nitration gives nitrobenzene.
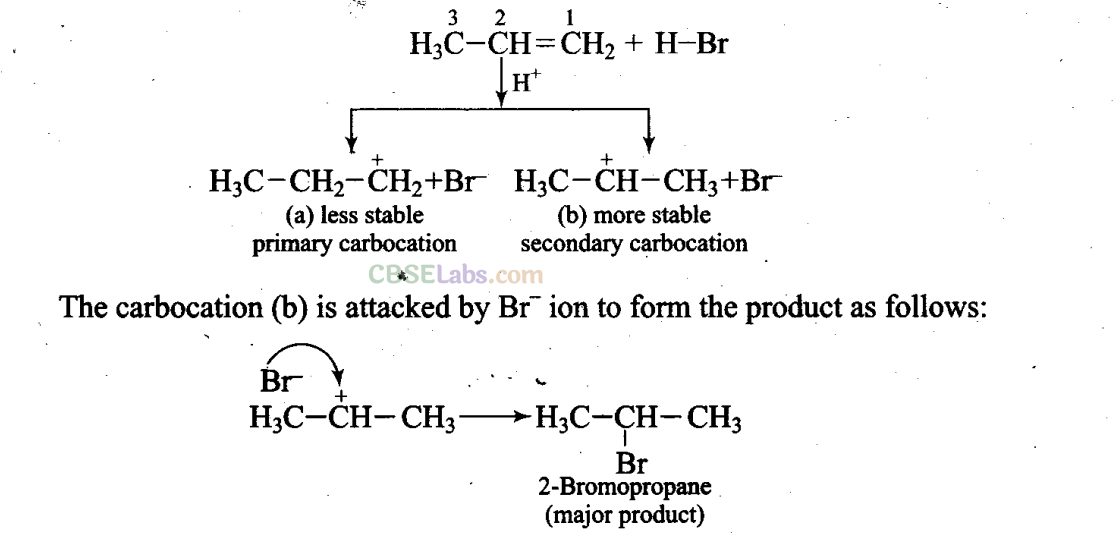
Q31. Predict the major product(s) of the following reactions and explain their formation.
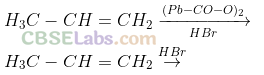
Sol: Addition of HBr to unsymmetrical alkenes follows Markonikov rule. It states that negative part of the addendum (adding molecule) gets attached to that carbon atom which possesses lesser number of hydrogen atoms.
Mechanism: Hydrogen bromide provides an electrophile, H+, which attacks the double bond to form carbocation as shown below:
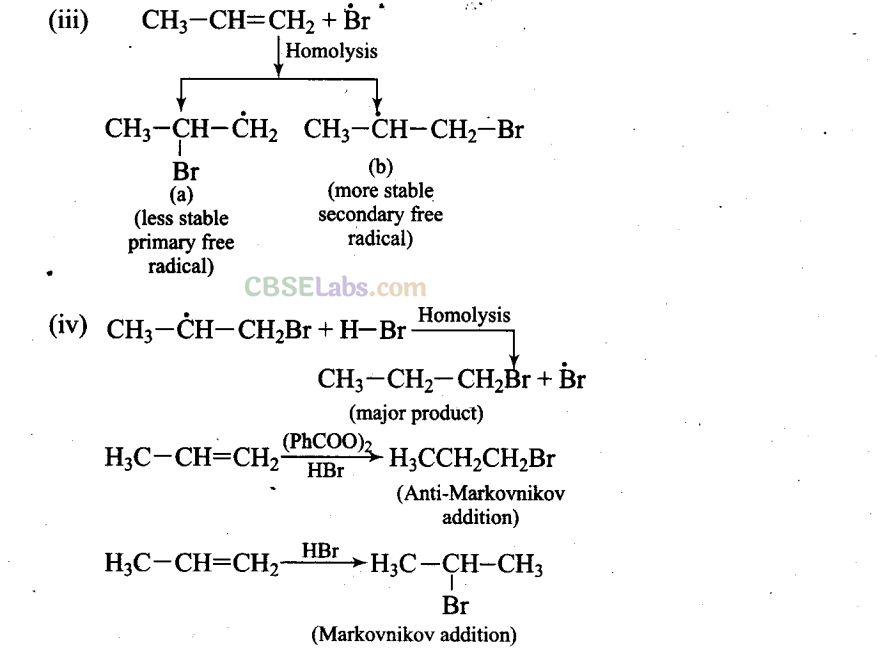
Addition reaction of HBr to unsymmetrical alkenes in the presence of peroxide follows anti-Markovnikov rule.
Mechanism: Peroxide effect proceeds via free radical chain mechanism as given below:
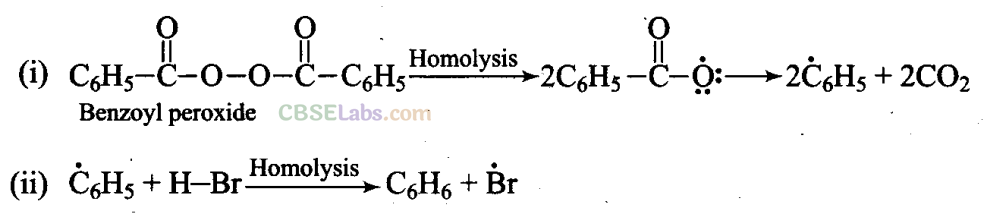
Q32. Nucleophiles and electrophiles are reaction intermediates having electron rich and electron deficient centres respectively. Hence, they tend to attack electron deficient and electron rich centres respectively. Classify the following species as electrophiles and nucleophiles.

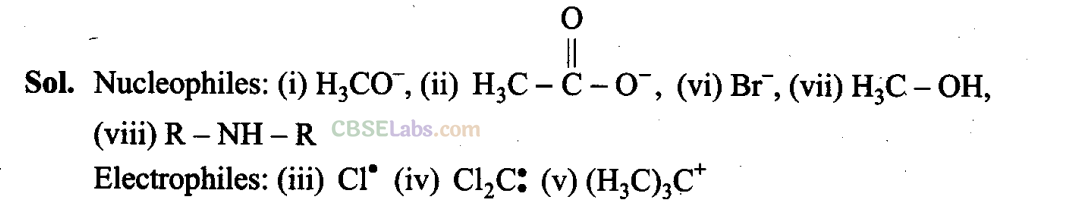
Q33. The relative reactivity of 1°, 2° and 3° hydrogens towards chlorination is 1: 3.8 : 5. Calculate the percentages of all monochlorinated products obtained from 2-methylbutane.
Sol:
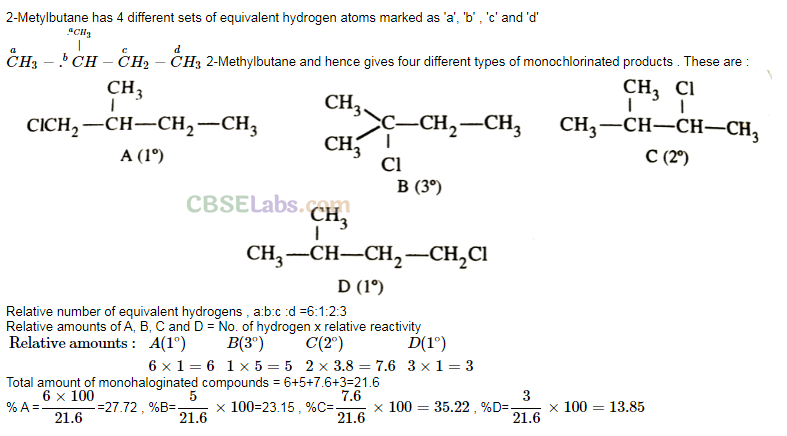
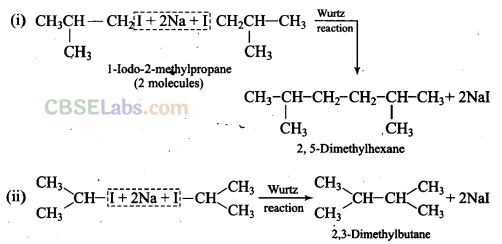
Q34. Write the structures and names of products obtained in the reactions of sodium with a mixture of l-iodo-2-methylpropane and 2-iodopropane.

NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Chapter 2 Structure of Atom
- Chapter 3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chapter 5 States of Matter
- Chapter 6 Thermodynamics
- Chapter 7 Equilibrium
- Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
- Chapter 9 Hydrogen
- Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements
- Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
- Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
- Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
NCERT Exemplar ProblemsMathsPhysicsChemistryBiology
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.