Relations and Mapping are important topics in Algebra. Relations & Mapping are two different words and have different meanings mathematically. Let’s get deep into the article to know all about the Relations, Mapping, or Functions like Definitions, Types of Relations, Solved Examples, etc.
- Ordered Pair
- Cartesian Product of Two Sets
- Relation in Math
- Domain and Range of a Relation
- Practice Test on Math Relation
- Functions or Mapping
- Domain Co-domain and Range of Function
- Math Practice Test on Functions
- Relation and Mapping Worksheets
What is a Relation?
A relation is a collection of ordered pairs. Relation in general defines the relationship between two different sets of information. An ordered pair is a point that has both x and y coordinates. Let us consider two sets x and y and set x has a relation with y. The values of set x are called Domain and the values of set y are called Range.
Relations can be represented using three different notations i.e. in the form of a table, graph, mapping diagram.
Example: (2, -5) is an ordered pair.
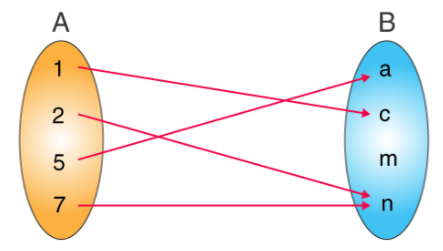
What is Mapping?
Mapping denotes the relation from Set A to Set B. Relation from A to B is the Subset of AxB. Mapping the oval on the left-hand side denotes the values of Domain and the oval on the right-hand side denotes the values of Range.
From the above diagram, we can say the ordered pairs are (1,c) (2, n) (5, a) (7, n).
Set{ 1, 2, 5, 7} represents the domain.
{a, c, n} is the range.
A function is a relation that derives the output for a given input.
Remember that all functions are relations but not all relations are functions.
Types of Relations
There are 8 different types of Relations and we have mentioned each of them in the following modules along with Examples.
- Empty Relation
- Universal Relation
- Identity Relation
- Inverse Relation
- Reflexive Relation
- Symmetric Relation
- Transitive Relation
- Equivalence Relation
Empty Relation:
Empty Relation is the one in which there will be no relation between elements of a set. It is also called a Void Relation. For instance, Set A = {3, 4, 5} then void relation can be R = {x, y} where | x- y| = 7.
For an Empty Relation R = φ ⊂ A × A
Universal Relation:
In Universal Relation every element of a set is related to each other. Consider a set A = {a, b, c}. Universal Relations will be R = {x, y} where, |x – y| ≥ 0.
For Universal Relation R = A × A
Identity Relation:
Every element of a set is related to itself in an Identity Relation. Consider a Set A = {a, b, c} then Identity Relation is given by I = { a,a}, {b,b}, {c, c}
I = {(a, a), a ∈ A}
Inverse Relation:
In Inverse Relation when a set has elements that are inverse pairs of another set. If Set A = {(a,b), (c,d)} then inverse relation will be R-1 = {(b, a), (d, c)}
R-1 = {(b, a): (a, b) ∈ R}
Reflexive Relation:
Every element maps to itself in Reflexive Relation. Consider Set A = { 3, 4} then Reflexive Relation R = {(3, 3), (4, 4), (3, 4), (4, 3)}. Reflexive Relation is given by (a, a) ∈ R
Symmetric Relation:
In the case of Symmetric Relation if a = b, then b = a is also true. Relation R is symmetric only if (b, a) ∈ R is true when (a,b) ∈ R.
aRb ⇒ bRa, ∀ a, b ∈ A
Transitive Relation:
In case of a transitive relation if (x, y) ∈ R, (y, z) ∈ R then (x, z) ∈ R
aRb and bRc ⇒ aRc ∀ a, b, c ∈ A
Equivalence Relation:
A Relation symmetric, reflexive, transitive at the same time is called an Equivalence Relation.
How to Convert a Relation to Function?
A relation that follows the rule that every X- Value associated with only one Y-Value is called a Function.
Example
Is A = {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, -8)}?
Solution:
Since the set has no duplicates or repetitions in the X- Value, the relation is a function.
Mapping Diagrams
Mapping Diagram consists of two columns in which one denotes the domain of a function f whereas the other column denotes the Range. Usually, Arrows or Lines are drawn between domain and range to denote the relation between two elements.
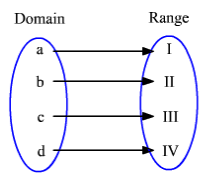
One-to-One Mapping
Each element of the range is paired with exactly one element of the domain. The function represented below denotes the One-to-One Mapping.
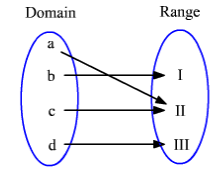
Many to One Mapping
If one element in the range is associated with more than one element in the domain is called many to one mapping. In the below diagram you can see the second number II is associated with more than one element in the domain.
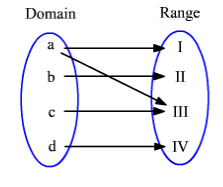
One to Many Mapping
If one element in the domain is mapped with more than elements in the range then it is called One to Many Mapping. In the below diagram the first element in the domain is mapped to many elements in the range therefore it is called One to Many Mapping.
Hope you got a complete idea on Relations and Mapping Concept. If you need any other help you can ask us through the comment section and we will get back to you at the earliest possibility.