NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 Transport in Plants are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Biology. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 Transport in Plants.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 Transport in Plants
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1. Which of the following statements does not apply to reverse osmosis?
(a) It is used for water purification.
(b) In this technique, pressure greater than osmotic pressure is applied to the system.
(c) It is a passive process.
(d) It is an active process.
Ans: (c) If pressure greater than the osmotic pressure is applied to the higher concentration, the direction of water flow through the membrane can be reverse. This is called reverse osmosis. Reverse osmosis occurs when water is moved across the membrane against the concentration gradient, from lower concentration to higher concentration. Reverse osmosis is an active process.
Q2. Which one of the following will not directly affect transpiration?
(a) Temperature
(b) Light
(c) Wind speed
(d) Chlorophyll content of leaves
Ans: (d) The chlorophyll content of leaves will not directly affect transpiration, while temperature, light and wind speed directly affect the transpiration.
Q3. The lower surface of leaf will have more number of stomata in a
(a) Dorsiventral leaf
(b) Isobilateral leaf
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Ans: (a) Usually, the lower surface of a dorsiventral (dicotyledonous) leaf has a greater number of stomata. On the upper surface, stomata may be even absent sometimes.
Q4. The form of sugar transported through phloem is
(a) Glucose (b) Fructose (c) Sucrose (d) Ribose
Ans: (c) Food, primarily sucrose, is transported by the vascular tissue phloem from a source to a sink.
Q5. The process of guttation takes place
(a) when the root pressure is high and the rate of transpiration is low
(b) when the root pressure is low and the rate of transpiration is high
(c) when the root pressure equals the rate of transpiration
(d) when the root pressure as well as rate of transpiration are high.
Ans: (a) The effect of root pressure is observable at night as well as early morning when evaporation is low. Excess water gets collected in the form of droplets around special openings of veins near the tip of grass blades and leaves of many herbaceous parts of plants such as Tropaeolum, Balsam and grasses. Such water loss in its liquid phase is known as guttation.
Q6. Which of the following is an example of imbibition?
(a) Uptake of water by root hair (b) Exchange of gases in stomata (c) Swelling of seed when put in soil (d) Opening of stomata
Ans: (c) Imbibition is a special type of diffusion. A classic example of imbibition is absorption of water by seeds and dry wood.
Q7. When a plant undergoes senescence, the nutrients may be
(a) accumulated
(b) bound to cell wall
(c) translocated
(d) None of the above
Ans: (c) Mineral ions are frequently remobilized (translocation), particularly from older senescing parts. Before the leaf fall in deciduous plants, minerals are translocated to other parts.
Q8. Water potential of pure water at standard temperature is equal to
(a) 10
(b) 20
(c) Zero
(d) None of these
Ans: (c) The water potential of pure water at standard temperature is equal to zero.
Q9. Choose the correct option. Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association of fungus with root system which helps in A. Absorption of water B. Mineral nutrition
C. Translocation D. Gaseous exchange
(a) Only A
(b) Only B –
(c) Both A and B
(d) Both B and C
Ans: (c) Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association of fungus with root system which helps in absorption of water and mineral nutrition.
Q10. Based on the figure given below, which of the following statements is not correct?
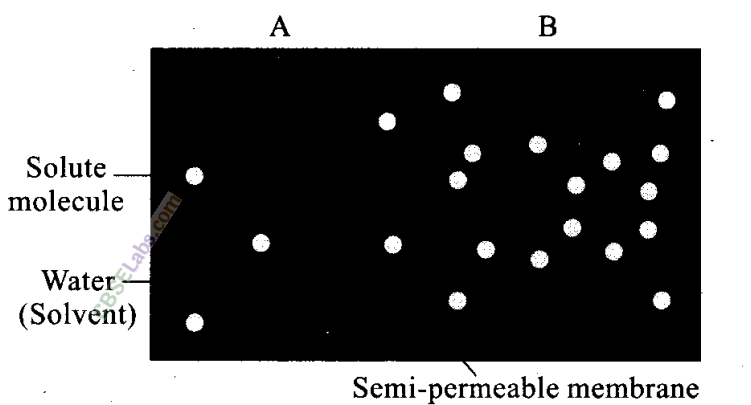
(a) Movement of solvent molecules will take place from chamber AtoB
(b) Movement of solute will take place from A to B
(c) Presence of a semipermeable is a prerequisite for this process to occur
(d) The direction and rate of osmosis depends on both the pressure gradient and concentration gradient.
Ans: (b) The movement of solute will take place from B to A
Q11. Match the following and choose the correct option.
| A. | Leaves | (i) | Anti-transpirant |
| B. | Seed | (ii) | Transpiration |
| C. | Roots | (iii) | Negative osmotic potential |
| D. | Aspirin | (iv) | Imbibition ‘ |
| E. | Plasmolyzed cell | (v) | Absorption |
Options:
(a) A—(ii), B—(iv), C—(v), D—(i), E—(iii)
(b) A—(iii), B—(ii), C—(iv), D—(i), E—(v)
(c) A—(i), B—(ii), C—(iii), D—(iv), E—(v)
(d) A—(v), B—(iv), C—(iii), D—(ii), E—(i)
Ans: (a)
| A. | Leaves | (ii) | Transpiration |
| B. | Seed | (iv) | Imbibition |
| e. | Roots | (v) | Absorption |
| D. | Aspirin | (i) | Anti-transpirant |
| E. | Plasmolyzed cell | (ii) | Negative osmotic potential |
Q12. Mark the mismatched pair.
(a) Amyloplast—Store protein granule
(b) Elaioplast—Store oils or fats
(c) Chloroplasts—Contain chlorophyll pigments
(d) Chromoplasts—Contain coloured pigments other than chlorophyll
Ans: (a) Aleuroplasts—Store proteins
Amyloplast—Store carbohydrate (starch)
Very Short Answer Type Questions .
Q1. Smaller, lipid soluble molecules diffuse faster through cell membrane, but the movement of hydrophilic substances are facilitated by certain transporters which are chemically ________.
Ans: Protein
Q2. In a passive transport across a membrane, when two protein molecules move in opposite direction and independent of each other, it is called as ________
Ans: Antiport
Q3. Osmosis is a special kind of’diffusion, in which water diffuses across the cell membrane. The rate and direction of osmosis depends upon both ________
Ans: Pressure and concentration gradient
Q4. A flowering plant is planted in an earthen pot and irrigated. Urea is added to make the plant grow faster, but after some time the plant dies. This may be due to ________.
Ans: Exosmosis
Q5. Absorption of water from soil by dry seeds increases the ________ thus helping seedlings to come out of soil.
Ans: Pressure
Q6. Water moves up against gravity and even for a tree of 20 m height, the tip receives water within two hours. The most important physiological phenomenon which is responsible for the upward movement of water is _________
Ans: Transpiration pull
Q7. The plant cell cytoplasm is surrounded by both cell wall and cell membrane. The specificity of transport of substances are mostly across the cell membrane, because _________ .
Ans: The cell wall is freely permeable to water and substances in solutions but membrane is selectively permeable.
Q8. The C4 plants are twice as efficient as C3 plants in terms of fixing C02 but lose only _________ as much water as C3 plants for the same amount of C02 fixed.
Ans: Half
Q9. Movement of substances in xylem is unidirectional while in phloem it is bidirectional. Explain.
Ans: The direction of movement in the phloem can be upwards or downwards, i.e. bi-directional. This contrasts with that of the xylem where the movement is always unidirectional, i.e. upwards. Hence, unlike one-way flow of water in transpiration, food in phloem sap can be transported in any required direction, as it is a source of sugar and works as a sink to use, store or remove the sugar
Q10. Identify the process occurring in I, II and III.
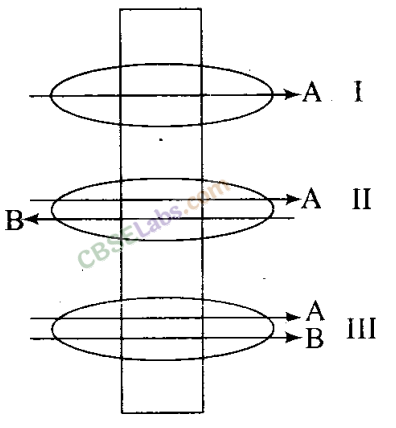
Ans: I—Uniport facilitated diffusion
II— Antiport facilitated diffusion
III— Symport facilitated diffusion
Q11. Given below is a table. Fill in the gaps.
| Property | Simple
diffusion |
Facilitated
transport |
Active
transport |
|
| i. | Highly selective | Yes | ||
| ii. | Uphill transport | Yes | ||
| iii. | Requires ATP | |||
Ans:
| Property | Simple
diffusion |
Facilitated
transport |
Active
transport |
|
| i. | Highly selective | No | Yes | Yes |
| ii. | Uphill transport | No | No , | Yes |
| iii. | Requires ATP | No | No | Yes |
Q12. Define water potential and solute potential.
Ans: Water potential is considered as the potential energy of water. It is also taken as a measure of the difference between the potential energy in a given sample of wafer and pure water.
If a solute is dissolved in pure water, the solution is considered having fewer free water and hence the concentration of water decreases. Thus, all solutions have lower water potential than pure water. The magnitude of lowering in water potential due to dissolution of solute is called solute potential.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Biology Solutions
- Chapter 1 The Living World
- Chapter 2 Biological Classification
- Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom
- Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
- Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell: The Unit of Life
- Chapter 9 Biomolecules
- Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Chapter 11 Transport in Plants
- Chapter 12 Mineral Nutrition
- Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants
- Chapter 15 Plant Growth and Development
- Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption
- Chapter 17 Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation
- Chapter 19 Excretory Products and Their Elimination
- Chapter 20 Locomotion and Movement
- Chapter 21 Neural Control and Coordination
- Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and Integration
NCERT Exemplar ProblemsMathsPhysicsChemistryBiology
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 Transport in Plants help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 Transport in Plants, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.