NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity.
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity
Shod Answer Type Questions
1.Three 2 Ω resistors, A, B and C are connected as shown in figure. Each of them dissipates energy and can withstand a maximum power of 18 W without melting. Find the maximum current that can flow through the three resistors.
Answer.
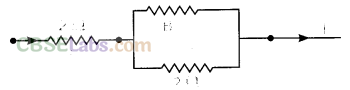
Here, P = 18 W
Since A is in series with the parallel combination of B and C. So, it carries maximum current.

Let IB and Ic be the current flowing through B and C respectively. As they are in parallel, potential difference across them will be same, so
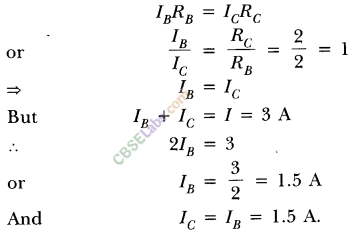
2.Should the resistance of an ammeter be low or high? Give reason.
Answer.The resistance of an ammeter should be low so that it will not disturb the magnitude of current flowing through the circuit when connected in series in a circuit.
3.How does use of a fuse wire protect electrical appliances?
Answer. The fuse wire is always connected in series with the live wire or electrical devices. If the flow of current exceeds the specified preset value due to some reason, the heat produced melts it and disconnects the circuit or the device from the mains. In this way, fuse wire protects the electrical appliances.
4.What is electrical resistivity? In a series electrical circuit comprising a resistor made up of a metallic wire, the ammeter reads 5 A. The reading of the ammeter decreases to half when the length of the wire is doubled. Why?
Answer. The resistance offered by a metallic wire of unit length and unit cross-sectional area is called electrical resistivity.
We know that
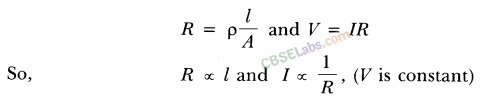
Hence, when the length of wire is doubled, the resistance becomes double and current decreases to half.
5.A current of 1 ampere flows in a series circuit containing an electric lamp and a conductor of 5 D when connected to a 10 V battery. Calculate the resistance of the electric lamp.
Now if a resistance of 10 Ω is connected in parallel with this series combination, what change (if any) in current flowing through 5 Ω conductor and potential difference across the lamp will take place? Give reason.
Answer. Given : In series circuit containing lamp and resistor,
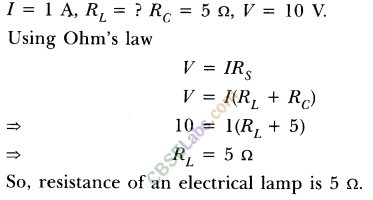
According to the given condition, circuit can be redrawn as shown.
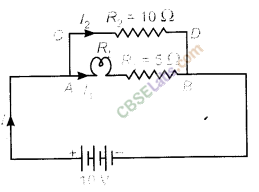
So, effective resistance of parallel combination.
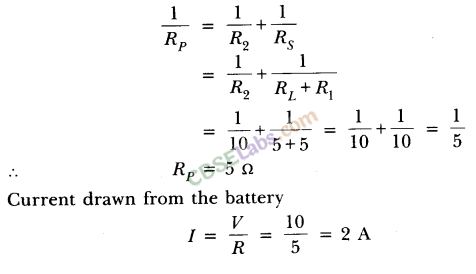
As in parallel combination, potential difference across them remains same. So
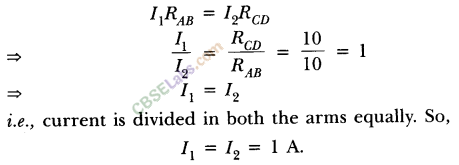
i.e., current is divided in both the arms equally. So,
l1 = l2 = lA.
Hence, there will be no change in the current through 5 n conductor.
Also there will be no change in the potential difference across the lamp as in both cases, current through the lamp remains same i.e. l A.
6.Why is parallel arrangement used in domestic wiring?
Answer.Parallel arrangement is used in domestic wiring because
- Each appliance gets the same voltage as that of the mains supply.
- If one component is switched off, others can work properly.
- Fault in any branch of the circuit can be easily identified.
7.B1 B2 and B3 are three identical bulbs connected as shown in figure. When all the three bulbs glow, a current of 3A is recorded by the ammeter A
Answer.
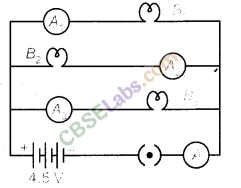
- What happens to the glow of the other two bulbs when the bulb B1 gets fused?
- What happens to the reading of A1, A2, A3 and A when the bulb gets fused?
- How much power is dissipated in the circuit when all the three bulbs glow together?
(i) Since B1 ,B2 and B3 are in parallel, the potential difference across each of them will remain same. So when the bulb Bx gets fused,B1 ,B2 and B3 have the same potential and continues with the same energy dissipated per second, i.e. they will glow continuously as they were glowing before.
(ii) Resistance of the parallel combination when all the three bulbs are glowing
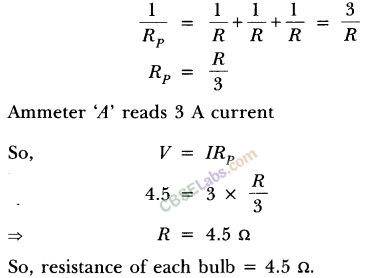
Now when bulb B2 gets fused, the equivalent resistance of parallel combination
of B1 and B3 is
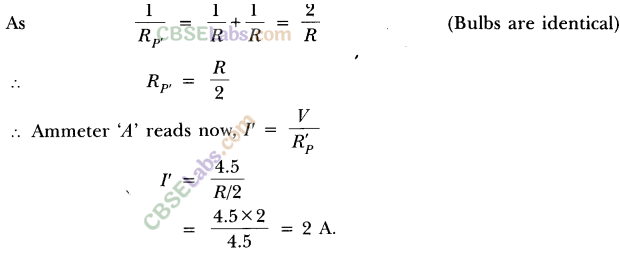
Since resistance of each arm is same and p.d. is also same, current divides them equally. So lA current will pass through each bulb Bl and By
Therefore, ammeter A1 and A3 reads l Acurrent while A2 will read zero and ammeter A read 2 A current.
(iii) In parallel, total power consumed
Peq =P1 + P2 + P3
So, when all the three bulbs glow together

Long Answer Type Questions
8. Three incandescent bulbs of 100 W each are connected in series in an electric circuit. In another circuit, another set of three bulbs of the same wattage are connected in parallel to the same source.
(а) Will the bulb in the two circuits glow with the same brightness? Justify your answer.
(b) Now let one bulb in both the circuits get fused. Will the rest of the bulbs continue to glow in each circuit? Give reason.
Answer. For three identical bulbs,
In series, Rs = 3R
In parallel, Rp = R/3
(a) The bulbs in the two circuits will not glow equally bright as the current through them is not the same.
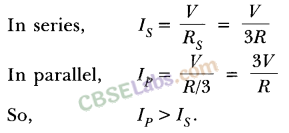
(b) As one bulb fuses, the other bulbs in the series circuit will not glow because the circuit becomes an open circuit. While the rest of bulbs in parallel circuit will continue to glow without getting disturbed because in parallel combination, current gets additional paths to flow.
9.Find out the following in the electric circuit given in figure:
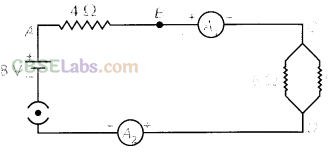
(a) Effective resistance of two 8 Ω resistors in the combination,
(b) Current flowing through 4 Ω resistor,
(c) Potential difference across 4 Ω resistance,
(d) Power dissipated in 4 Ω resistor, and
(e) Difference in ammeter readings, if any.
Answer.
(a) Effective resistance, the two 8 Ω resistors in parallel,

NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Solutions
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World
- Chapter 12 Electricity
- Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 15 Our Environment
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Electricity, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.