NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable Ex 2.6
- Class 8 Maths Linear Equations in One Variable Exercise 2.1
- Class 8 Maths Linear Equations in One Variable Exercise 2.2
- Class 8 Maths Linear Equations in One Variable Exercise 2.3
- Class 8 Maths Linear Equations in One Variable Exercise 2.4
- Class 8 Maths Linear Equations in One Variable Exercise 2.5
- Class 8 Maths Linear Equations in One Variable Exercise 2.6
- Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable Exercise 2.6
Solve the following equations.
Ex 2.6 Class 8 Maths Question 1.
\(\frac { 8x-3 }{ 3x } =2\)
Solution:
We have \(\frac { 8x-3 }{ 3x } =2\)
⇒ \(\frac { 8x-3 }{ 3x }\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 1 }\)
⇒ 8x – 3 = 2 × 3x (Cross-multiplication)
⇒ 8x – 3 = 6x
⇒ 8x – 6x = 3 (Transposing 6x to LHS and 3 to RHS)
⇒ 2x = 3
⇒ x = \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)
Ex 2.6 Class 8 Maths Question 2.
\(\frac { 9x }{ 7-6x }\) = 15
Solution:
we have \(\frac { 9x }{ 7-6x }\) = 15
⇒ \(\frac { 9x }{ 7-6x }\) = \(\frac { 15 }{ 1 }\)
⇒ 9x = 15(7 – 6x) (Cross-multiplication)
⇒ 9x = 105 – 90x (Solving the bracket)
⇒ 9x + 90x = 105 (Transposing 90x to LHS)
⇒ 99x = 105
⇒ x = \(\frac { 105 }{ 99 }\)
⇒ x = \(\frac { 35 }{ 33 }\)
Ex 2.6 Class 8 Maths Question 3.
\(\frac { z }{ z+15 } =\frac { 4 }{ 9 }\)
Solution:
We have \(\frac { z }{ z+15 } =\frac { 4 }{ 9 }\)
⇒ 9z = 4 (z + 15) (Cross-multiplication)
⇒ 9z = 4z + 60 (Solving the bracket)
⇒ 9z – 42 = 60
⇒ 5z = 60
⇒ z = 12
Ex 2.6 Class 8 Maths Question 4.
\(\frac { 3y+4 }{ 2-6y } =\frac { -2 }{ 5 }\)
Solution:
we have \(\frac { 3y+4 }{ 2-6y } =\frac { -2 }{ 5 }\)
⇒ 5(3y + 4) = -2(2 – 6y) (Cross-multiplication)
⇒ 15y + 20 = -4 + 12y (Solving the bracket)
⇒ 15y – 12y = -4 – 20 (Transposing 12y to LHS and 20 to RHS)
⇒ 3y = -24 (Transposing 3 to RHS) -24
⇒ y = -8
Ex 2.6 Class 8 Maths Question 5.
\(\frac { 7y+4 }{ y+2 } =\frac { -4 }{ 3 }\)
Solution:
we have \(\frac { 7y+4 }{ y+2 } =\frac { -4 }{ 3 }\)
⇒ 3(7y + 4) = -4 (y + 2) (Corss-multiplication)
⇒ 21y + 12 = -4y – 8 [Solving the bracket]
⇒ 21y + 4y = -12 – 8 [Transposing 4y to LHS and 12 to RHS]
⇒ 25y = -20 [Transposing 25 to RHS]
⇒ y = \(\frac { -4 }{ 5 }\)
Ex 2.6 Class 8 Maths Question 6.
The ages of Hari and Harry are in the ratio 5 : 7. Four years from now the ratio of their ages will be 3 : 4. Find their present ages.
Solution:
Let the present ages of Hari and Harry be 5x years and 7x years respectively.
After 4 years Hari’s age will be (5x + 4) years and Harry’s age will be (7x + 4) years.
As per the conditions, we have
\(\frac { 5x+4 }{ 7x+4 } =\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\)
⇒ 4(5x + 4) = 3(7x + 4) (Cross-multiplication)
⇒ 20x + 16 = 21x + 12 (Solving the bracket)
⇒ 20x – 21x = 12 – 16 (Transposing 21x to LHS and 16 to RHS)
⇒ -x = -4
⇒ x = 4
Hence the present ages of Hari and Harry are 5 × 4 = 20years and 7 × 4 = 28years respectively.
Ex 2.6 Class 8 Maths Question 7.
The denominator of a rational number is greater than its numerator by 8. If the numerator is increased by 17 and the denominator is decreased by 1, the number obtained is \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\). Find the rational number.
Solution:
Let the numerator of the rational number be x.
Denominator = (x + 8)
As per the conditions, we have
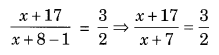
⇒ 2(x + 17) = 3(x + 7) (Cross-multiplication)
⇒ 2x + 34 = 3x + 21 (Solving the bracket)
⇒ 2x – 3x = 21 – 34 (Transposing 3x to LHS and 34 to RHS)
⇒ -x = -13
⇒ x = 13
Thus, numerator = 13
and denominator = 13 + 8 = 21
Hence the rational number is \(\frac { 13 }{ 21 }\).
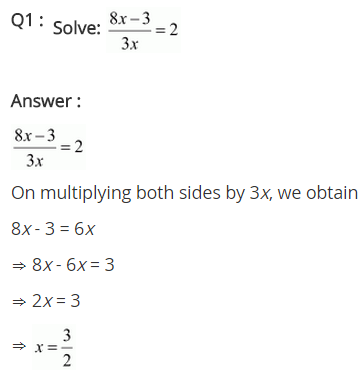



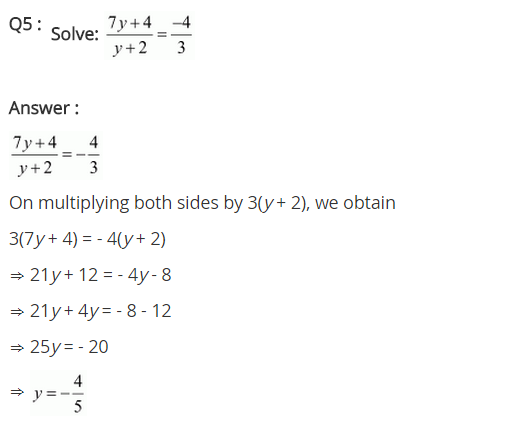


More CBSE Class 8 Study Material
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 English Honeydew
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 English It So Happened
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Sanskrit
- NCERT Solutions