NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Motions of the Earth
Question 1.
Answer the following questions briefly.
(a) What is the angle of inclination of the earth’s axis with its orbital plane?
(b) Define rotation and revolution.
(c) What is a leap year?
(d) Differentiate between the Summer and Winter Solstice.
(e) What is an equinox?
(f) Why does the Southern Hemisphere experience Winter and Summer Solstice in different times than that of the Northern Hemisphere?
(g) Why do the poles experience about six months day and six months night?
Answer:
(a) The earth remains tilted to one side while it revolves around the earth at an angle of 66.
(b) (1) Rotation. The movement/motion of the earth on its axis in 24 hours is defined as rotation.
(2) Revolution. The movement/motion of the Earth around the Sun in its orbit in 365\(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) days is called revolution.
(c) It is a year when the month of February has 29 days instead of 28 days. Every fourth year is a leap year.
(d) Difference between Summer and Winter Solstice
| Summer Solstice | Winter Solstice |
| 1. Summer solstice occurs on 22nd June in 1 Northern hemisphere. | 1. Winter solstice occurs on 22nd December in Northern hemisphere. |
| 2. The whole Northern hemisphere experiences more heat and light. | 2. Northern hemisphere experiences less heat and light. |
| 3. It is summer in the Northern hemisphere. | 3. It is winter in the Northern hemisphere. |
| 4. Days are longer, nights are shorter. | 4. Days are shorter, nights are longer. |
| 5. Reverse conditions prevail in the Southern hemisphere. | 5. Reverse conditions prevail in the Southern hemisphere. |
(e) On 21st March and September 23rd, direct rays of the sun fall on the equator. At this position, neither of the poles is tilted towards the sun. Therefore, the entire earth experiences equal days and equal nights. This phenomenon is called an equinox.
(f) The seasons in Southern Hemisphere and Northern Hemisphere are exactly the opposite.
(g) When the rays of the sun fall directly on the Tropic of Cancer (21st June), the areas near the South Pole receive less heat. The North Pole is inclined towards the sun and places beyond the Arctic circle experience continuous daylight. At this time, the Southern Hemisphere has the opposite season. The nights are long and areas beyond the Antarctic circle get continuous nights. The reverse will happen on 22nd December.
2. Tick the correct answer.
(a) The movement of the earth around the sun is known as
(i) Rotation (ii) Revolution (iii) Inclination.
(b) Direct rays of the sun fall on the equator on
(i) 21 March (ii) 21 June (iii) 22 December.
(c) Christmas is celebrated in summer in
(i) Japan (ii)India (iii)Australia
(d) The cycle of the seasons is caused due to
(i) Rotation (ii)Revolution (iii)Gravitation
Answers: (a)—(ii), (b)—(i), (c)—(iii), (d)—(ii).
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks.
(а) A leap year has ________ number of days.
(b) The daily motion of the Earth is ___________ .
(c) The Earth travels around the Sun in __________ orbit.
(d) The Sun’s rays fall vertically on the Tropic of _________________ on 21st June.
(e) Days are shorter during _________________ season.
Answer:
(a) 366
(b) rotatio
(c) fixed
(d) Capricorn
(e) winter
Hope the data shared above regarding the NCERT Class 6 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Motions of the Earth PDF has aided in your exam preparation. If you ever need any assistance you can always reach us and our team will guide you at the soonest possibility.
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct option to complete the sentences given below:
(i) The axis of the earth is a/an……………..
(a) imaginary line (b) straight line
(c) curved line (d) real line.
(ii) The earth receives light from the ……………
(a) Moon (b) Stars
(c) Meteors (d) Sun.
(iii) The time taken by the earth to complete one rotation around its axis is…………………
(a) 24 hours (b) 12 hours
(c) 36 hours (d) 18 hours.
(iv) The earth completes one revolution in ……………
(a) 366 days (b) 370 days
(c) 365 1/4 days (d) 366 1/4 days.
(v) It is spring in the Northern Hemisphere and autumn in the Southern Hemisphere on ………………………….
(a) 23rd September (b) 21st March
(c) 22nd December (d) 21st June.
Answer: (i)—(a), (ii)—(d), (iii)—(a), (iv)—(c), (v)—(b).
II. Fill in the Blanks
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words to complete each sentence:
- Days and nights occur due to …………… of the earth.
- Only half of the earth gets light from the sun at a time due to its……………. shape.
- The period of rotation is known as the ……………..
- The sun’s rays fall vertically at the Tropic of…………….. on 22nd December.
- On ………… it is autumn season in the Northern Hemisphere and spring in the Southern Hemisphere.
Answer:
- rotation
- spherical
- earth day
- Capricorn
- 23rd September.
III. True/False
Stale whether these sentences are true (T) or false (F).
- The axis of the earth makes an angle of 23V& with its orbital plane.
- Every five years, February is of 29 days instead of 28 days.
- Season changes due to the change in the position of the earth around the sun.
- When there is summer in the Northern Hemisphere, it is spring in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Life is not possible in extreme conditions.
Answer:
- False
- False
- True
- False
- True.
IV. Matching Skill
Match the items in column A correctly with those given in column B.
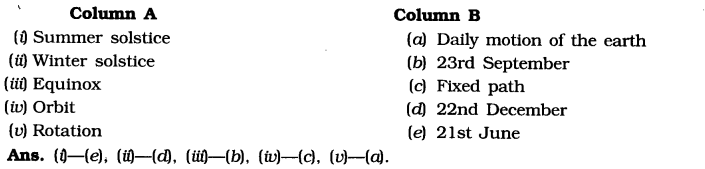
Motions of the Earth Class 6 Geography Chapter 3 Very Short Answer Type Questions
1. Define the circle of illumination.
Answer: The circle that divides the day from night on the globe is known as the circle of illumination.
2. Which motion of the earth is associated with the changes in season?
Answer: Revolution.
3. Why do seasons change? [V. Imp.]
Answer: Seasons change due to the change in the position of the earth around the sun.
4. Why do the areas near the poles receive less heat?
Answer: It is because the rays of the sun are slanting on the poles.
5. When do the longest day and the shortest night occur in the Northern Hemisphere?
Answer: On 21st June.
6. In which Hemisphere does Australia lie?
Answer: Australia lies in the Southern Hemisphere.
Class 6 Geography Chapter 3 NCERT Solutions Short Answer Type Questions
1. What would happen if the earth did not rotate? Imp.]
Answer: In such a condition the portion of the earth facing the sun would always experience day, and thus there would be continuous warmth in the region. At the same time, the other half would always remain dark and be freezing cold all the time. These are extreme conditions which are not suitable for life. Thus, we can say that if the earth did not rotate life would not have been possible.
2. How does leap year occur? [V. Imp.]
Answer: The earth takes 36514 days Le. one year to complete one revolution around the sun. We consider a year as consisting of 365 days only and ignore six hours for our convenience. Six hours saved every year are added to make one day Le. 24 hours over a span of four years. This surplus day is added to the month of February. Thus every fourth year, February of 29 days instead of 28 days. Such a year with 366 days is called a leap year.
3. Explain the following with a diagram:
(a) Summer solstice (b) Winter solstice (c) Equinox.
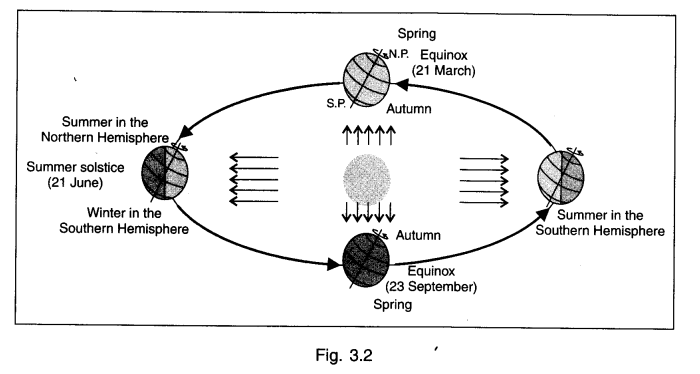
Answer: (a) Summer solstice. The Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the sun on 21st June. As the rays of the sun fall directly on the Tropic of Cancer, these areas receive more heat. But the size of the area to the poles receives less heat due to the slanting rays of the sun. The North Pole is inclined towards the sun the places beyond the Arctic Circle experience continuous daylight for about six months.
Since a large area of the Northern Hemisphere is getting light from the sun, it is summer in the regions north of the equator. The longest day and the shortest night at these places occur on 21st June. These conditions are reversed in the Southern Hemisphere at this time. It is winter season there having longer nights and shorter days. This position of the earth is known as the summer solstice.
(b) Winter solstice. On 22nd December, the Tropic of Capricorn receives direct rays of the sun as the South Pole tilts towards it. As the sun’s rays fall vertically at the Tropic of Capricorn, a larger portion of the Southern Hemisphere gets light. Hence, the Southern Hemisphere enjoys summer having longer days and shorter nights. This position of the earth is called the winter solstice.
(c) On 21st March and 23rd September direct rays of the sun fall on the equator. At this position, neither of the poles is tilted towards the sun. As a result, the entire earth experiences equal days and equal nights. This phenomenon is known as an equinox.