NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Maths Playing With Numbers Exercise 3.3
- Playing with Numbers Class 6 Ex 3.1
- Playing with Numbers Class 6 Ex 3.2
- Playing with Numbers Class 6 Ex 3.3
- Playing with Numbers Class 6 Ex 3.4
- Playing with Numbers Class 6 Ex 3.5
- Playing with Numbers Class 6 Ex 3.6
- Playing with Numbers Class 6 Ex 3.7
- Playing with Numbers Class 6 Extra Questions
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 3 Playing With Numbers Ex 3.3
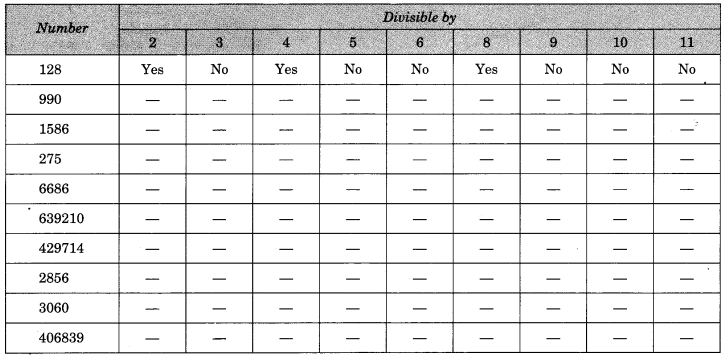
Question 1.
Using divisibility tests, determine which of the following numbers are divisible by 2, by 3, by 4, by 5, by 6, by 8, by 9, by 10, by 11 (Say, Yes or No)
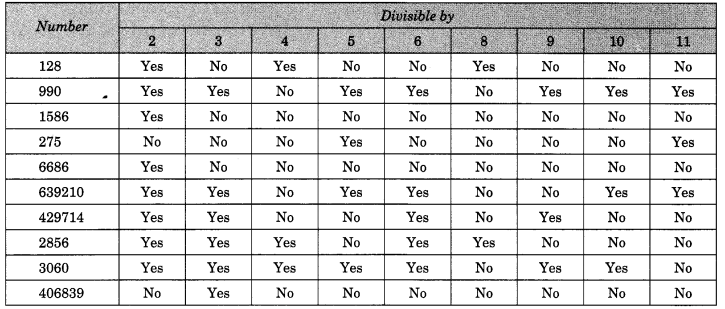
Solution:
Question 2.
Using divisibility tests, determine which of following numbers are divisible by 4; by 8.
(a) 572
(b) 726352
(c) 5500
(d) 6000
(e) 12159
(f) 14560
(g) 21084
(j) 2150
(h) 31795072
(i) 1700
Solution:
(a) Given number = 572
(i) Divisibility by 4
Here, the number formed by the last two digits of the given number is 72.
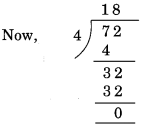
Remainder 0. Hence, 572 is divisible by 4.
(ii) Divisibility by 8
Here, the number formed by the last three digits of the given number is 572.
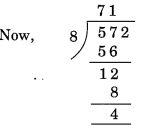
Remainder 4. Hence, 572 is not divisible by 8.
(b) Given number = 726352
(i) Divisibility by 4
Here, the number formed by the last two digits of the given number = 52.
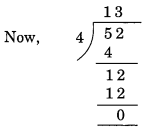
Remainder = 0.
Hence, 726352 is divisible by 4.
(ii) Divisibility by 8
Here, the number formed by the last three digits of the given number = 352
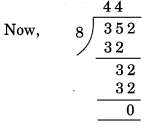
Remainder = 0.
Hence, 726352 is divisible by .
(c) Given number = 5500
(i) Divisibility by 4
Here the last two digits of the given number are 0. Hence, 5500 is divisible by 4.
(ii) Divisibility by 8
Here, the number formed by the last three digits of the given number = 500
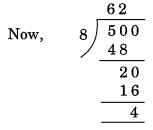
Remainder = 4. Hence, 5500 is not divisible by 8.
(d) Given number = 6000
(i) Divisibility by 4
Here, the last two digits of the given number are 0.
Hence, 6000 is divisible by 4.
(ii) Divisibility by 8
Here, the last three digits of the given number are 0.
Hence, 6000 is divisible by 8.
(e) Given number = 12159
(i) Divisibility by 4
Here, the number formed by last two digits of the given number = 59
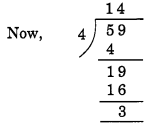
Remainder = 3.
Hence, 12159 is divisible by 4.
(ii) Divisibility by 8
Here, the number formed by the last three digits of the given number = 159
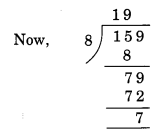
Remainder = 7.
Hence, 12159 is not divisible by 8.
(f) Given number = 14560
(i) Divisibility by 4
Here, the number formed by the last two digits of the given number = 60.
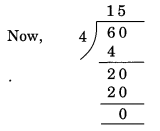
Remainder = 0.
Hence, 14560 is divisible by 8.
(g) Given number = 21084
(i) Divisibility by 4
Here, the number formed by the last two digits of the given number = 84.
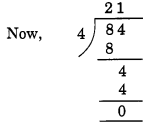
Remainder = 0. Hence, 21084 is divisible by 4.
(ii) Divisibility by 8
Here, the number formed by the last three digits of the given number = 084.
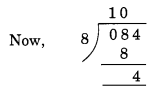
Remainder = 4.
Hence, 21084 is not divisible by 8.
(h) Given number = 31795072
(i) Divisibility by 4
Here, the number formed by the last two digits of the given number = 72.
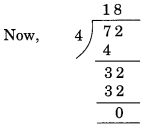
Remainder = 0. Hence, 31795072 is divisible by 4.
(ii) Divisibility by 8
Here, the number formed by the last three digits of the given number = 072.
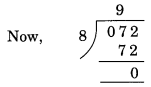
Remainder = 0. Hence, 31795072 is divisible by 8.
(i) Given number = 1700
(i) Divisibility by 4
Here, the last two digits of the given number is 0. Hence, 1700 is divisible by 4.
(ii) Divisibility by 8
Here, the number formed by the last three digits of the given number = 700
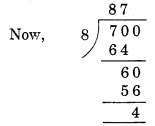
Remainder = 4. Hence, 1700 is not divisible by 8.
(j) Given number = 2150
(i) Divisibility by 4
Here, the number formed by the last two digits of the given number = 50.
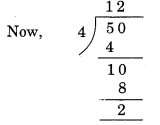
Remainder = 2. Hence, 2150 is not divisible by 4.
(ii) Divisibility by 8
Here, the number formed by the last three digits of the given number = 150
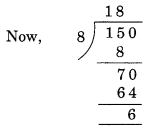
Remainder = 6. Hence, 2150 is not divisible by 8.
Question 3.
Using divisibility tests, determine which of the following numbers are divisible by 6:
(a) 297144
(b) 1258
(c) 4335
(d) 61233
(e) 901352
(f) 438750
(g) 1790184
(h) 12583
(i) 639210
(j) 17852
Solution:
We know that a number is divisible by 6 if it is also divisible by both 2 and 3.
(a) Given number = 297144
The given number 297144 has even digit at its ones place.
So, it is divisible by 2.
The sum of all the digits of 297144 = 2 + 9 + 7 + 1 + 4 + 4 = 27
which is divisible by 3.
Hence, the given number 297144 is divisible by 6.
(b) Given number = 1258
The given number 1258 has even digit i.e., 8 at its ones place.
So, it is divisible by 2.
The sum of all digits of 1258 = l + 2 + 5 + 8 = 16 which is not divisible by 3.
Hence, the given number 1258 is not divisible by 6.
(c) Given number = 4335
The digit at ones place of the given number is not even.
So, it is not divisible by 2.
The sum of all the digits of 4335 = 4 + 3 + 3 + 5 = 15 which is divisible by 3.
Since the given number 4335 is not divisible by both 2 and 3 therefore, it is not divisible by 6.
(d) Given number = 61233
The digit at ones place of the given number is not even.
So, it is not divisible by 2.
The sum of the digits of the given number 61233 = 6 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 3 = 15 which is divisible by 3.
Since, the given number is not divisible by both 2 and 3, it is not divisible by 6.
(e) Given number = 901352
The digit at ones place of the given number is even.
So, it is divisible by 2.
The sum of all the digits of the given number 901352 = 9 + 0 + 1 + 3 + 5 + 2 = 20 which is not divisible by 3.
Since, the given number is not divisible by both 2 and 3 hence, it is not divisible by 6.
(f) Given number = 438750
The digit at ones place of the given number is 0. So, it is divisible by 2.
The sum of all the digits of the given number 438750
=4 + 3 + 8 + 7 + 5 + 0 = 27 which is divisible by 3.
Hence, the given number is divisible by 6.
(g) Given number = 1790184
The digit at ones place of the given number is even.
So, it is divisible by 2.
The sum of all the digits of the given number 1790184
= 1 + 7 + 9 + 0 + 1 + 8 + 4 = 30 which is divisible by 3.
Hence, the given number is divisible by 6.
(h) Given number = 12583
The digit to ones place of the given number is odd.
So, it is not divisible by 2.
Sum of all the digits of the given number 12583
= 1 + 2 + 5 + 8 + 3 = 19
which is not divisible by 3.
Hence, the given number is not divisible by 6.
(i) Given number = 639210
The digit at ones place of the given number is 0.
So, it is divisible by 2.
The sum of all the digits of the given number 639210
= 6 + 3 + 9 + 2 + 1 + 0 = 21 which is divisible by 3.
Hence, the given number is divisible by 6.
(j) Given number = 17852
The digit at ones place of the given number is even.
So, it is divisible by 2.
The sum of all the digits of the given number 17852
= 1 + 7 + 8 + 5 + 2 = 23 which is not divisible by 3.
Hence, the given number is not divisible by 6.
Question 4.
Using divisibility tests, determine which of the following numbers are divisible by 11:
(a) 5445
(b) 10824
(c) 7138965
(d) 70169308
(e) 10000001.
Sol. We know that a number is divisible by 11 if the difference between the sum of the digits at odd places (from the right) and the sum of the digits at even places (from the right) of the number is either 0 or divisible by 11.
(a) Given number = 5445
Sum of the digits at odd places = 5 + 4 = 9
Sum of the digits at even places = 4 + 5 = 9
Difference = 9 – 9 = 0
Hence, the given number is divisible by 11.
(b) Given number = 10824
Sum of the digits at odd places = 4 + 8 + 1 = 13
Sum of the digits at even places = 2 + 0 = 2
Difference = 13 – 2 = 11
which is divisible by 11.
Hence, the given number is divisible by 11.
(c) Given number = 7138965
Sum of the digits at odd places = 5 + 9 + 3 + 7 = 24
Sum of the digits at even places = 6 + 8 + 1 = 15
Difference = 24 – 15 = 9
which is not divisible by 11.
Hence, the given number is not divisible by 11.
(d) Given number = 70169308
Sum of all the digits at odd places = 8 + 3 + 6 + 0 = 17
Sum of all the digits at even places = 0 + 9 + 1 + 7 = 17
Difference = 17-17 = 0
Hence, the given number is divisible by 11.
(e) Given number = 10000001
Sum of all the digits at odd places = 1 + 0 + 0 + 0 = 1
Sum of all the digits at even places = 0 + 0 + 0 + 1 = 1
Difference = 1 – 1 = 0
Hence, the given number is divisible by 11.
Question 5.
Write the smallest digit and the greatest digit in the blank space of each of the following numbers so that the number formed is divisible by 3.
(a) ____ 6724
(b) 4765 ____ 2
Solution:
We know that number is divisible by 3 if the sum of all the digits of the number is also divisible by 3.
(a) ___ 6724
Sum of the digits = 4 + 2 + 7 + 6 = 19
The smallest digit to be placed is blank space = 2
Then the sum = 19 + 2 = 21 which is divisible by 3.
The greatest digit to be placed in blank space = 8
Then, the sum = 19 + 8 = 27 which is divisible by 3
Hence, the required digits are 2 and 8.
(b) 4765 ____ 2.
Sum of digits = 2 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 4 = 24
The smallest digits to be place in blank space = 0
Then, sum = 24 + 0 = 24
which is divisible by 3.
The greatest digit to be placed in blank space = 9.
Then, the sum = 24 + 9 = 33 which is divisible by 3.
Hence, the required digits are 0 and 9.
Question 6.
Write a digit in the blank space of each of the following numbers so that the numbers formed is divisible by 11.
(a) 92 ___ 389
(b) 8 ___ 9484
Solution:
(a) 92 ___ 389
Sum of the digits at odd places = 9 + 3 + 2 = 14
Sum of the digits at even places = 8 + ( ) + 9 = 17
Difference = 17 + ( ) – 14 = () + 3
For the given number to be divisible by 11
( ) + 3 = 11
∴ ( ) = 11 – 3 = 8
So, the missing digit = 8
Hence, the required number is 928389.
(b) 8 ___ 9484
Sum of the digits at odd places = 4 + 4 + ( ) = 8 + ( )
Sum of the digits at even places = 8 + 9 + 8 = 25
∴ Difference = 25 – [8 + ( )]
= 25 – 8 – ( ) = 17 – ( )
For the given number to be divisible by 11
17 – 0 = 11
∴ 17 – 11 = 6
So, the missing digit = 6
Hence, the required number = 869484.
NCERT SolutionsMathsScienceSocialEnglishHindiSanskritRD Sharma