Financial Management – CBSE Notes for Class 12 Business Studies
CBSE NotesCBSE Notes Business StudiesNCERT Solutions Business Studies
1. Business Finance Money required for carrying out business activities is called Business Finance.
2. Financial Management It refers to efficient acquisition of finance, efficient utilisation of finance and efficient distributing and disposal of surplus for smooth working of company.
According to Howard and Upton, “Financial management involves the application of general management principles to a particular financial operation.
3. Role of Financial Management
(i) Size and composition of fixed assets
(ii) Amount and composition of current assets
(iii) The amount of long term and short financing
(iv) Fixing debt equity ratio in capital
(v) All items in Profit and Loss account
4. Objectives of Financial Management
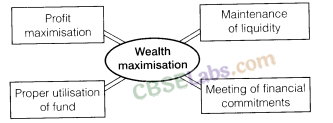
5. Financial Decisions
The financial functions relate to three major decisions which every finance manager has to take
(i) Investment decision
(ii) Financing decision
(iii) Dividend decision
6. Investment Decision (Capital Budgeting Decision)
This decision relates to careful selection of assets in which funds will be invested by the firms.
Factors affecting investment/capital budgeting decisions are
(i) Cash flow of the project (ii) Return on investment
(iii) Risk involved (iv) Investment criteria
7. Financing Decision This relates to composition of various securities in the capital structure of the company. Mainly sources of finance can be divided into two categories
(i) Owners fund
(ii) Borrowed fund
Factors affecting financing decisions are
(i) Cost (ii) Risk
(iii) Cash flow position (iv) Control consideration
(v) Floatation cost (vi) Fixed operating cost
(vii) State of capital market
8. Dividend Decision This relates to distribution of profit earned. The major alternatives are to retain the earnings or to distribute to the shareholders.
Factors affecting dividend decisions are
(i) Earning
(ii) Stability of earning
(iii) Cash flow position
(iv) Growth opportunities
(v) Stability of dividend
(vi) Preference of shareholders
(vii) Taxation policy
(viii) Access to capital market consideration
(ix) Legal restrictions
(x) Contractual constraints
(xi) Stock market reaction
9. Financial Planning It means deciding in advance how much to spend, on what to spend according to the funds at your disposal.
10. Objectives of Financial Planning
(i) To ensure availability of funds whenever these are required,
(ii) To see that firm does not raise resources unnecessarily.
11. Importance of Financial Planning
(i) It facilitates collection of optimum funds.
(ii) It helps in fixing the most appropriate capital structure.
(iii) Helps in investing finance in right projects.
(iv) Helps in operational activities.
(v) Base for financial control.
(vi) Helps in proper utilisation of finance.
(vii) Helps in avoiding business shocks and surprises.
(viii) Link between investment and financing decisions.
(ix) Helps in co-ordination.
(x) It links present with future.
12. Capital Structure Capital structure means the proportion of dept and equity used for financing the operations of business.
Capital Structure =Debt/Equity
13. Financial Leverage It refers to overall capital
Financial Leverage = E/D
Where, D = Debt, E = Equity
14. Factors Determining the Capital
(i) Cash flow position
(ii) Interest Coverage Ratio (ICR) = EBIT/Interest
(iii) Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR)
(iv) Return on investment
(v) Cost of debt
(vi) Tax rate
(vii) Cost of equity
(viii) Floatation cost
(ix) Risk consideration
(x) Flexibility
(xi) Control
(xii) Regulatory framework
(xiii) Stock market condition
(xiv) Capital structure of other companies
15. Fixed Capital Fixed Capital involves allocation of firm’s capital to long-term assets or projects.
16. Importance or Scope of Capital Budgeting Decision
(i) Long term growth (ii) Large amount of funds involved
(iii) Risk involved (iv) Irreversible decision
17. Factors Affecting Requirement of Fixed Capital
(i) Nature of business (ii) Scale of operation
(iii) Technique of production (iv) Technology up gradation (v) Growth prospects (vi) Diversification
(vii) Availability of finance and leasing facility (viii) Level of collaboration/joint ventures
18. Working Capital
Working Capital refers to excess of Current assets over Current liabilities.
There are two types of working capital
(i) Gross working capital (ii) Net working capital
19. Operating Cycle
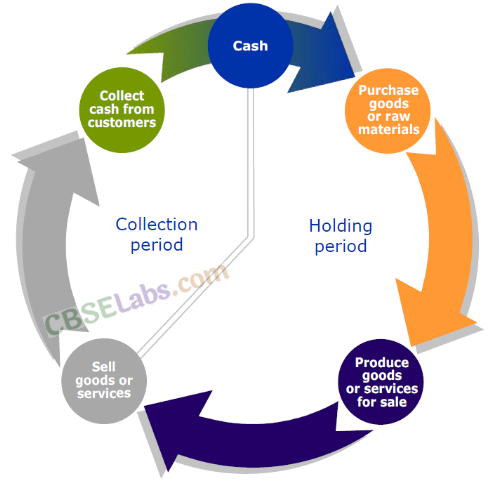
20. Factors Affecting the Working Capital
(i) Length of operating cycle
(ii) Nature of business
(iii) Scale of operation
(iv) Business cycle fluctuation
(v) Seasonal factors
(vi) Technology and production cycle
(vii) Credit allowed
(viii) Credit avail
(ix) Operating efficiency
(x) Availability of raw materials
(xi) Level of competition
(xii) Inflation
(xiii) Growth prospects