Communication Systems Class 12 Notes Chapter 15
Topic 1 Communication
1. Communication Communication is the act of transmission and reception of information.
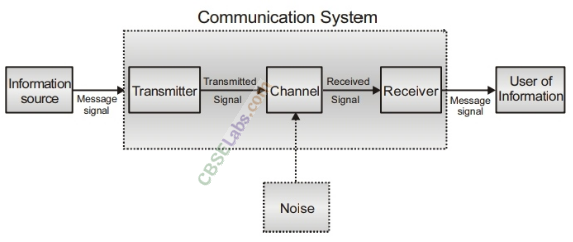
2. Communication System A system comprises of transmitter, communication channel and receiver.
A block diagram of a generalised communication system is shown as below:
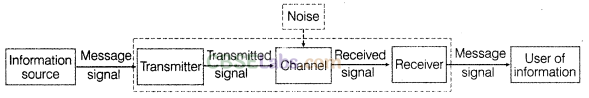
3. Transmitter It consists of transducer/signal generators, modulators and transmitting antenna.
4. Receiver Its main function is to decode the original signals. The main function involves picking up the signals, demodulating and displace the original message signal.
5. Communication Channel The physical path between the transmitter and receiver is known as communication channel. They are of two types namely
(i) Guided (point-to-point) (ii) Unguided
6. Bandwidth of Communication Channel The range of frequencies used to pass through channel is known as bandwidth.
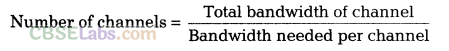
7. The following table shows the various things used in communication system.
8. There are two basic modes of communication given as below:
(i) Point-to-point In this type of communication mode, communication takes place over a link between a signal transmitter and a receiver, e.g. telephony.
(ii) Broadcast In the broadcast mode, there are a large number of receivers corresponding to a signal transmitter, e.g. radio and TV.
9. Basic Terminology used in Electronic Communication Systems
(i) Signal Information converted into electrical form and suitable for transmission is called a signal.
(ii) Transducer Any device/arrangement that converts one form of energy into another is called a transducer, e.g. microphone.
(iii) Noise It refers to the unwanted signals that tends to disturb the transmission and processing of message signals in communication system.
(iv) Attenuation It refers to the loss of strength of a signal during its propagation through the communication channel.
(v) Amplification It is the process by which amplitude of a signal is increased using an electronic circuit called the amplifier.
(vi) Range It is the largest distance between a source and a destination up to which the signal is received with sufficient strength.
(vii) Baseband Band of frequencies representing the original signal is called baseband.
(viii) Repeater Repeaters are erected at suitable distances between the transmitter and receiver. Repeaters are used to extend the range of a communication system.
10. Message Signals A time varying electrical signal generated by a transducer out of original signal is termed as message signal.
The electrical signals are of two types such as below:
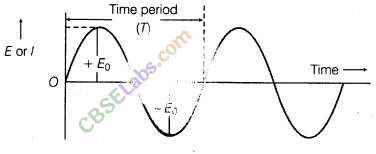
(i) Analog signal A continuous signal value which at any instant lies within the range of a maximum and a minimum value.
Graphical representation of analog signal can be represented as given below:
(ii) Digital Signal (Pulse Signal) Digital signals are those which can take only discrete stepwise values e.g. output of a computer, fax, etc.

11. Coding schemes used for digital communication are given as below:
(i) Binary Coded Decimal (BCD) In this, a digit is represented by two binary numbers 0 or 1.
(ii) American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) It is a universally popular digital code to represent numbers, letters and certain characters.
12. Bandwidth of Signals Bandwidth of signal is defined as the difference between the upper and lower frequencies of signal. In a communication system, the message signal can be voice, music, picture or computer data. This has been shown in the table given as below:
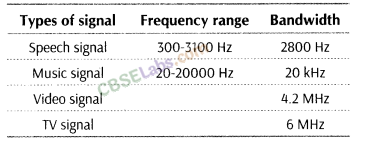
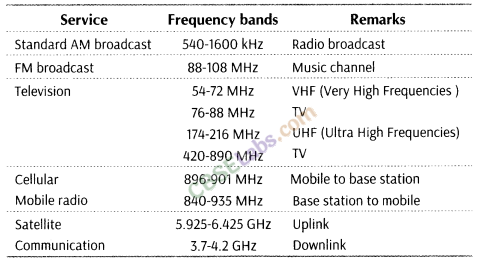
13. Bandwidth of Transmission Medium The commonly used transmission media are wire, free space, fibre optic cable (750 MHz ) and optical fibre (100 GHz.)
This range is sub-divided further and allocated for various services as indicated in the table given as below:
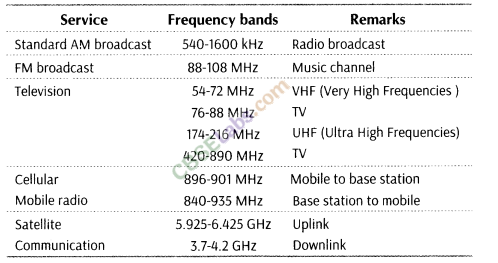
14. Antenna Antenna is a device which acts as an emitter of electromagnetic waves and it also acts as a first receiver of energy. It is generally a metallic object often a wire or collection of wires.
(i) Hertz Antenna It is a straight conductor of length equal to half the wavelength of radio signals to be transmitted or received.
i.e, l = λ/2
(ii) Marconi Antenna It is a straight conductor of length equal to a quarter of the wavelength of radio signals to be transmitted of received, i.e. l = λ/4
(iii) Dipole Antenna It is used in transmission of radio waves. It is omni directional.
(iv) Dish-Type Antenna It is a directional antenna. Such antenna has a parabolic reflector with an active element.
15. Propagation of Electromagnetic Waves In communication using radio waves, an antenna at the transmitter radiates the EM waves, which travel through the space and reach the receiver at the other end.
16. Depending upon frequency and ways of propagation, electromagnetic waves categorised as follows
(i) Ground Wave Propagation (f< 2MHz) In ground wave propagation, the radio waves (AM) travel along the surface of the earth. These waves are guided along the earth surface and they follow the curvature of the earth.
(ii) Sky Wave Propagation (2 MHz < f < 30 MHz) Long distance communication can be achieved by ionospheric reflection of radio waves back towards earth. This mode of propagation is called sky wave propagation and is used by short wave broadcast services. The ionosphere is so called because of the presence of a large number of ions. It extends from height of 65 km to about 400 km above the earth’s surface.
The details are in the table as below:
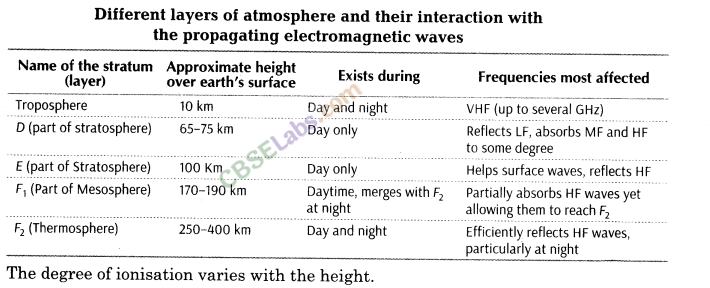
The density of atmosphere decreases with height.
The ionospheric layer acts as a reflector for a certain range of frequencies. These phenomena are shown as below:
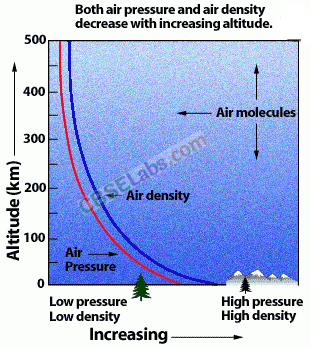
(a) Maximum Usable Frequency (MUF) It is a limiting frequency, but for some specific angle of incidence other than the normal and is given by
MUF = fc secθ
where, θ is the angle between normal and the direction of incidence of waves.
(b) Skip Distance It is the shortest distance from a transmitter measured along the surface of earth at which a sky wave of fixed frequency c more than fc will be returned to earth.
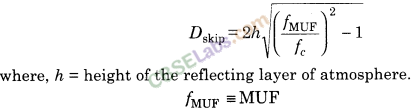
(c) Critical Frequency For a given layer, it is the highest frequency that will return down to earth by that layer.
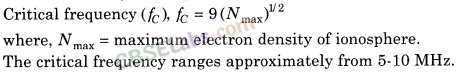
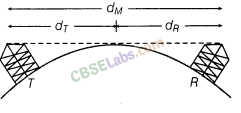
(iii) Space Wave Propagation (LoS) (f > 30 MHz) A space wave travels in a straight line from transmitting anteiina to the receiving antenna.
Space waves are used for Line-of-Sight (LoS) communication as well as satellite communication.
Because of LoS nature of propagation, these waves are get blocked at some point by curvature of earth as shown below:
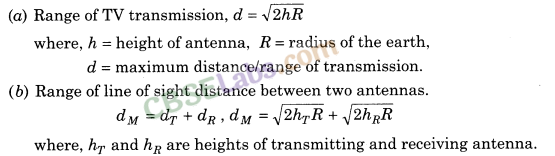
17. Satellite Communication In this communication, frequency band 5.9 GHz to 6.4 GHz is used for uplinking and 3.7 GHz to 2 GHz is used for down linking.
Topic 2 Modulation
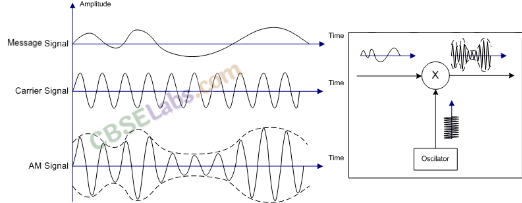
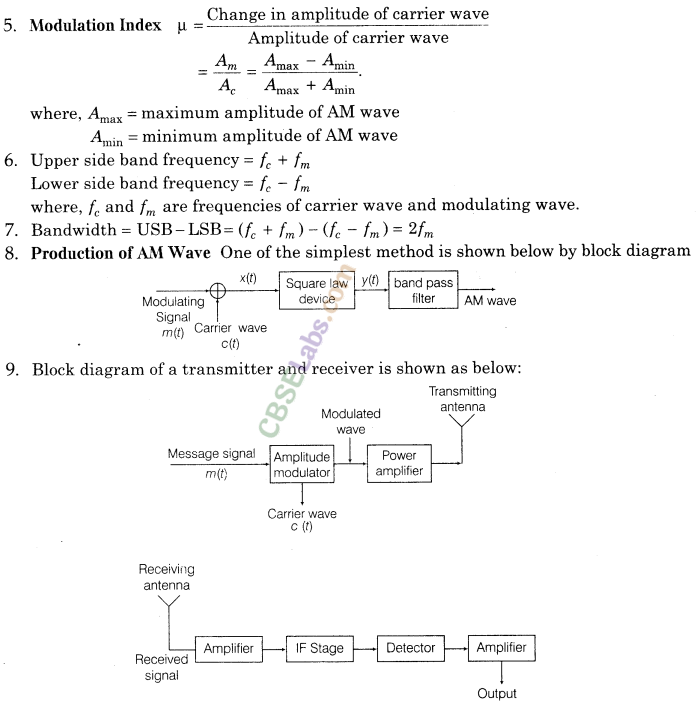
1. Modulation Modulation is the process of variation of some characteristics of a carrier wave in accordance with the instantaneous value of a modulating signal.
2. Need for Modulation It is due to the fact that low frequency signal

3. Types of modulations
(i) Amplitude modulation (ii) Frequency modulation
(iii) Phase modulation (iv) Pulse modulation
4. Amplitude Modulation In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the carrier is varied in accordance with the information signal.
11. Types of pulse modulation
(i) PAM (Pulse Amplitude Modulation) (ii) PDM (Pulse Duration Modulation)
(iii) PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) (iv) PCM (Pulse Code Modulation)
12. Internet It is a network of computers, printers disk drives or other devices, connected in a network topology that allows the device to communicate.
13. Local Area Network In is a group of computers and associated devices that share a common communication line or wireless link. Typically, connected device share the resources of a single processor or server within a small geographic area.
14. Wide Area Network A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a network that covers a broad area (i. e. any tele-communications network that links across metropolitan, regional, national or international boundaries) using leased telecommunication lines.
15. Client Computer Every computer that extracts information from a server is called a client computer.
16. Webpage A hypertext document connected to the world wide area is known as webpage. It may contain text, videos, etc.
17. Website A location connected to the internet that maintains one or more web pages.
18. Internet Service Providers An Internet Service Provider (ISP) is an organisation that provide services for accessing using or participating in the internet.
19. People use internet for many purposes like searching and viewing information on any topic of interest for sending electronic mails, for e-banking, e-shopping, e-booking, etc.
20. Electronic mail Electronic mail is the exchange of computer-stored messages by telecommunication.
21. Mobile telephony is the provision of telephone services to phones which may move around freely rather than stay fixed in one location. Mobile phones connect to a terrestrial cellular network of base stations, whereas satellite phones connect to orbiting satellites.
22. A cellular network or mobile network is a wireless network distributed over land areas called class, each served by at least one fixed location transceiver, known as a cell site or base station.
23. All network related works including handling of all the incoming and outgoing calls are managed by a central control room called Mobile. Telephone Switching Office (MTSO)
24. A telephone numbering plan is a type of numbering schemes used in telecommunication to assign telephone numbers to subscriber telephones or other telephony endpoints.
25. 1G is the first generation of mobile network which are based on analog radio signal.
2 G is based on narrow band digital signal. 3 G is the increased data transfer speed.
4 G is provide a high-speed internet facility.
26. Global positioning system is a space based satellite navigation system that provides location and time information in all weather conditions.
27. Twelve number of satellites is required for correct and accurate location indentification in the global positioning system.