Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 Extra Questions Science Chapter 3
Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Name a natural fibre.
Answer:
Cotton
Question 2.
Name the basic component of animal fibres.
Answer:
Protein
Question 3.
Name some artificial fibres.
Answer:
Nylon, terylene, PET, acrylic, teflon, etc.
Question 4.
Which fibre is known as artificial silk?
Answer:
Rayon
Question 5.
In which country was rayon first time synthesised?
Answer:
England
Question 6.
Name the first fully synthetic fibre.
Answer:
Nylon
Question 7.
Name the largest producer unit of rayon in the world.
Answer:
Grasim India
Question 8.
Name a common variety of polyester.
Answer:
Terylene
Question 9.
What is ester?
Answer:
Ester is sweet-smelling compound.
Question 10.
Name some objects made of plastics.
Answer:
Containers, buckets, bottles, chairs, baskets, etc.
Question 11.
What is polythene?
Answer:
Polythene is a polymer of ethene.
Question 12.
Give some examples of thermoplastics.
Answer:
Polythene and polyvinyl chloride.
Question 13.
Give some examples of thermosetting plastics.
Answer:
Bakelite and melamine.
Question 14.
What is the full form of PVC?
Answer:
Polyvinyl Chloride
Question 15.
What is 4R’s?
Answer:
4R’s stands for Redue, Reuse, Recycle and Recover.
Question 16.
Whether cotton cloth a biodegradable or non-biodegradable?
Answer:
Biodegradable
Question 17.
Name the form of polyester which is replacing materials like glass and used for making bottles and jars.
Answer:
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
Question 18.
Which of two is thermosetting plastic—PVC or bakelite?
Answer:
Bakelite
Question 19.
Name a synthetic fibre which is polyamide.
Answer:
Nylon
Question 20.
Give the name of a plastic used for making fibres.
Answer:
Nylon
Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 Extra Questions Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are polymers?
Answer:
Polymers are compounds that are made up of same, small repeating units, joined together through bonds in a linear pattern.
Question 2.
What is cellulose?
Answer:
Cellulose is a polymer made up of large number of glucose units.
Question 3.
List the two ways in which synthetic fibres can be synthesised.
Answer:
Synthetic fibres may be synthesised by two ways:
- By regenerating them from natural fibres, like in rayon.
- By using entirely chemicals and chemical reactions, like in nylon.
Question 4.
What is rayon?
Answer:
Rayon is a man-made fibre which is produced by the chemical processing of wood pulp, i.e., a natural substance.
Question 5.
List two uses of rayon.
Answer:
The two uses of rayon are:
- It is used to make apparels like shirts, blouses, etc.
- It is used to make furnishings and upholstery.
Question 6.
List any two properties of rayon.
Answer:
The two properties of rayon are:
- Rayon is a versatile fibre.
- It can be dyed in different colours.
Question 7.
Draw a diagram to show the:
(a) linear arrangement of units in plastic.
(b) cross-linked arrangement of units in plastic.
Answer:
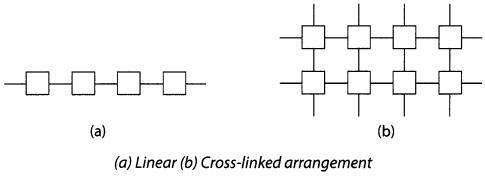
Question 8.
Write some advantages of synthetic fibres.
Answer:
Advantages of synthetic fibres are:
- Synthetic fibres are strong and durable.
- They do not shrink.
- They are moth and insect resistant.
Question 9.
What are plastics?
Answer:
Plastics are those substances which are mostly synthetic in nature, obtained mainly from petrochemi¬cal sources and can be moulded into different shapes.
Question 10.
What is plasticity?
Answer:
Plasticity is the property of materials by which they can be moulded into any shape.
Question 11.
What are thermosetting plastics?
Answer:
Thermosetting plastics are those which when moulded once, cannot be softened again and lose their plasticity.
Question 12.
List any three properties of plastics.
Answer:
The three properties of plastics are:
- They are non-corrosive in nature.
- They are light in weight and durable.
- They do not conduct heat.
Question 13.
What are the uses of polyester?
Answer:
The uses of polyester are:
- It is used in making home furnishings and apparels.
- Polyester is used for finishing on guitars and pianos.
Question 14.
Why is it advised not to wear synthetic clothes while working in a laboratory or working with fire in the kitchen?
Answer:
The synthetic fibres melt on heating. This is actually a disadvantage with synthetic fibres. If the cloth catches fire it can be very disastrous. The fabric melts and sticks to the body of the person wearing it. It is therefore advised not to wear synthetic clothes while working in a laboratory or working with fire in the kitchen.
Question 15.
Write some properties and uses of melamine.
Answer:
Melamine is a versatile material. It resists fire and can tolerate heat better than other plastics. It is used for making floor tiles, kitchenware and fabrics which resist fire.
Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 Extra Questions Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Describe about nylon. Write its uses and properties.
Answer:
Nylon is the strongest amongst all the synthetic fibres. It is fully synthetic polymer which is prepared from coal, water and air. It is a polymer of amides. It was made in 1931 for the first time. It was used as a supplement of silk when silk got deficient during World War II for many military applications. Uses of Nylon
- Nylon is used in toothbrushes, combs, etc.
- It is used to make parachutes, tents, ropes, etc.
- It is used to make socks and stockings as it is elastic.
- It is widely used for making clothes, carpets, etc.
Properties of Nylon
- It melts on heating.
- It absorbs less water.
- It is resistant to moths and fungi.
- It has high tensile strength.
- It is durable.
Question 2.
Write the advantages of synthetic fibres.
Answer:
Synthetic fibres has many advantages as compared to natural fibres. Some of them are as follows:
- They are very strong and durable.
- They are cheaper in cost as compared to natural fibres.
- They absorb less water and are quick to dry.
- They do not shrink.
- They are very useful for saving our trees and animals as they are made up of chemicals.
- They are moth and insect resistant.
Question 3.
List the common varieties of polyester. Also mention the natural fibres which are used for blending to enhance their properties.
Answer:
Polyester could be blended with natural fibres to enhance its properties. The common varieties of polyester are:
- PET (Polyethylene terephthalate)
- Terrycot: It is made by blending polyester and cotton.
- Terrysilk: It is made by blending polyester iaiid silk.
- Terrywool: It is made by blending polyester and wool.
Question 4.
Explain the properties of plastics.
Answer:
Plastics are those substances which are mostly synthetic in nature.
Following are the properties of plastics:
- Plastics are non-corrosive in nature, i.e., they do not react easily with air and water. They are unaffected by most of the chemicals in normal conditions.
- Plastics are the bad conductor of heat. They do not get heated up like metals.
- Plastics are non-biodegradable, i.e., they do not get decomposed by microorganisms.
- Plastics are very durable.
Question 5.
‘Plastics are hazard to environment’. Explain this statement.
Answer:
Yes, plastics are hazard to environment. They make versatile materials but are very dangerous to the environment. Plastics are non-biodegradable in nature. It takes more than 100 years to decompose. If use of plastics are not reduced, our earth would turn into a big garbage bin.
The major problems due to plastics are:
- If plastics are burnt, they evolve poisonous gases. These gases destroys the ozone layer of the earth and also pollute the environment.
- If the plastics are disposed in drains, they choke the drains causing waterlogging.
- If these plastics are swallowed by the innocent animals along with their food, they harm their di-gestive system which leads to their death.
- They are manufactured by the consumption of a large amount of petroleum.
Question 8.
List the strategies for plastic waste management.
Answer:
Some of the strategies for plastic waste management are:
- We should use paper bags and jute bags instead of using plastic bags.
- The government should ban the use of plastic bags.
- Plastics should be recycled to make other useful products which do not harm the environment.
- We should use a special garbage bins to dispose plastic wastes.
- We should not throw plastic wastes in water bodies.
- Practicing 4R’s principle, i.e., Reuse, Recycle, Reduce and Recover should be encouraged.
Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 Extra Questions Higher Order Thinking Skills
Question 1.
Cotton is a natural polymer. What is its chemical name?
Answer:
Cellulose.
Question 2.
Why plastic items are available in all possible shapes and sizes?
Answer:
Plastics can be moulded to any shape. So they are available in all possible shapes and sizes.
Question 3.
What nature of plastics makes them a good storage containers for most of the articles?
Answer:
Plastics are non-reactive.
Question 4.
A lady went to the market to buy a blanket. The shopkeeper showed her blankets made of acrylic fibres as well as made of wool. She preferred to buy an acrylic blanket. Can you guess why?
Answer:
Blanket made of acrylic is cheap, durable, light in weight, available in variety of colours and provide the same warmth as that of wool.
Question 5.
Is using plastics for storing food safe?
Answer:
Though storing and carrying food in plastic container is more efficient. But chemicals used for manu-facturing plastics leeches out into the food and contaminates it. Though it is in very small amount but continuous use of it is exposing our body to harmful and poisonous chemicals.
Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 Extra Questions Value-Based Question
Question 1.
Riya’s father got a transfer to another place. While sorting out the things Riya found many of her clothes of various fabrics were not fitting her or worn-out. She thought of burning them to get rid of them. But her friend Shweta suggested to donate it to some charity house so that it can be reused.
(a) What are the two main types of fibres?
(b) Which fabrics are known to be skin friendly? Why?
(c) Why we should not burn synthetic clothes?
(d) Why synthetic clothes are famous than natural fabrics?
(e) What values of Riya and Shweta are shown here?
Answer:
(a) Two main types of fibres are natural and man-made fibres.
(b) Natural fabrics are known to be skin friendly because they absorb moisture and do not contain chemicals as that of synthetic fibres which may cause skin irritation.
(c) Synthetic clothes emits poisonous gases on burning.
(d) Synthetic clothes are famous than natural clothes because they are light, durable, cheaper, easy to maintain, moth resistant and available in various colours.
(e) Riya is ignorant and non-ecofriendly whereas Shweta is insightful and eco-friendly.
Question 2.
Piku is very fond of art and craft. She decided to make some items like pen keeper, purses, toys, etc., using old fabrics and plastics. She donated these in a charity.
(a) Is it practical to say completely ‘NO’ to plastics?
(b) How can we reuse any plastic items?
(c) What value of Piku is shown here?
Answer:
(a) No, it is not at all practical to say completely ‘NO’ to plastics because nowadays plastics are insepa-rable part of our daily life.
(b) We can reuse plastic bags for storing dry things. We can reuse plastic bottles for storing dry food grains or a pen keeper, etc.
(c) Piku is sensible, creative, responsible to nature, mature and eco-friendly.
Activities and Projects
Question 1.
Have you heard of the campaign: “Say No To Plastics”. Coin a few more slogans of this kind. There are certain governmental and non-governmental organisations who educate the general public on how to make wise use of plastics and develop environment friendly habits. Find out organisations in your area which are carrying out awareness programmes. If there is none, form one.
Answer:
Slogans-
- ‘Stop using plastics, save earth.’
- ‘If you litter, future will be bitter.’
- ‘Go green, plastic is obscene.’
- ‘Reuse plastics.’
Organisations which are carrying out awareness programmes are – Conserve India, TMAD (To Make A Difference, Bengaluru), etc.
Question 2.
Organise a debate in the school. Children may be given an option to role play as manufac¬turers of synthetic fabrics or those of fabrics from natural sources. They can then debate on the topic ‘My Fabric is Superior’.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Question 3.
Visit five families in your neighbourhood and enquire about the kind of clothes they use, the reason for their choice and advantages of using them in terms of cost, durability and maintenance. Make a short report and submit it to your teacher.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Question 4.
Devise an activity to show that organic waste is biodegradable while plastic is not.
Answer:
Take some organic waste (like peels of fruits, vegetables) in a beaker and some plastic waste materials in other beaker. Mark them as A and B respectively. Cover the wastes in both the beakers with soil. Observe both the beakers after one or two months.
It is observed that organic waste has been disappeared in the soil while plastics are still in the beaker. This shows that organic waste are biodegradable whereas plastics are non-biodegradable.
Question 5.
If you wish to know more about fibres and plastics and the products made from them, you may explore the following website:
http:/ /www.pslc.ws/macrog/index.htm
Answer:
Do it yourself.
I. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Choose the correct option.
Question 1.
Which of the following is natural fibre?
(a) Rayon
(b) Nylon
(c) Polyester
(d) Cotton
Question 2.
Which of the following is synthetic fibre?
(a) Nylon
(b) Cotton
(c) Silk
(d) Wood
Question 3.
The basic component of plant fibres is
(a) protein
(b) cellulose
(c) starch
(d) none of these
Question 4.
Raw materials for preparation of synthetic fibres are
(a) coal
(b) petroleum
(c) natural gas
(d) all of these
Question 5.
Which of the following is known as artificial silk?
(a) Nylon
(b) Rayon
(c) Polyester
(d) Silk
Question 6.
In which year was nylon made?
(a) 1931
(b) 1964
(c) 1948
(d) 1950
Question 7.
Which fibre is used as artificial wool?
(a) Acrylic
(b) Rayon
(c) Nylon
(d) Cotton
Question 8.
Which of the following fibre has highest tensile stren
(a) Cotton
(b) Silk
(c) Rayon
(d) Nylon
Question 9.
Common variety of polyester is
(a) terylene
(b) polymer
(c) viscose
(d) spinneret
Question 10.
Polymers are made up of small units called
(a) layers
(b) molecules
(c) cells
(d) monomers
Question 11.
Which of the following polyester is made by blending polyester and cotton?
(a) Terrywool
(b) Terrycot
(c) Terrysilk
(d) PET
Question 12.
Wood pulp is used to make
(a) plastic
(b) wool
(c) jute
(d) rayon
Question 13.
The property of materials by which they can be moulded into any shape is called
(a) conductivity
(b) elasticity
(c) plasticity
(d) none of these
Question 14.
Which of the following is a thermoplastic?
(a) Bakelite
(b) Melamine
(c) PVC
(d) All of these
Question 15.
Which of the following are made from thermosetting plastic?
(a) Bottles
(b) Crockery
(c) Shoes
(d) Handbags
Question 16.
Polycarbonate is used to make
(a) compact discs
(b) straws
(c) bottles
(d) jars
Question 17.
Synthetic fibres are
(a) durable
(b) wrinkle free
(c) economical
(d) all of these
Question 18.
Plastics that retain their plasticity on repeated heating are called
(a) thermosetting plastics
(b) thermoplastics
(c) thermal plastics
(d) none of these
Question 19.
Which of the following is a characteristic of plastics?
(a) Electrical conductors
(b) Heat conductors
(c) Biodegradable
(d) Non-biodegradable
Question 20.
Plastic that can resist fire is
The property of materials by which they can be moulded into any shape is called
(a) bakelite
(b) melamine
(c) PVC
(d) duroplast
Answer:
1. (d)
2. (a)
3. (b)
4. (d)
5. (b)
6. (a)
7. (a)
8. (d)
9. (a)
10. (d)
11. (b)
12. (d)
13. (c)
14. (c)
15. (b)
16. (a)
17. (d)
18. (b)
19. (d)
20. (b)
II. Fill in the Blanks
Fill in the blanks with suitable word/s.
1. Clothes we wear are made up of thin strands called ____________.
2. Fibres may be natural or ____________.
3. Raw materials for preparation of synthetic fibres are obtained from substances like ____________, ____________ and ____________.
4. ____________ are made up of small repeating units, joined together through bonds in linear pattern.
5. Rayon synthesised for the first time in ____________.
6. Artificial silk is another name of ____________.
7. ____________ fibre is stronger than steel wire of same thickness.
8. ____________ is the property of materials by which they can be moulded into any shape.
9. ____________ is an example of thermosetting plastics.
10. Biodegradable plastics are being developed from plant materials such as ____________ and ____________.
11. Practicing 4R’s, i.e.,____________ ,____________, ____________ and ____________ should be encouraged.
12. A device with holes which is used to make fibres is called ____________.
13. Acrylic resembles ____________.
14. Synthetic fibres do not absorb much ____________.
15. Synthetic fibres ____________ on heating.
Answer:
1. fibres
2. man-made
3. coal, petroleum, natural gas
4. Polymers
5. England
6. rayon
7. Nylon
8. Plasticity
9. Crockery
10. cellulose, starch
11. Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Recover
12. spinneret
13. wool
14. water
15. melts
III. Match the following
Match the items given in column I suitably with those given in column II.
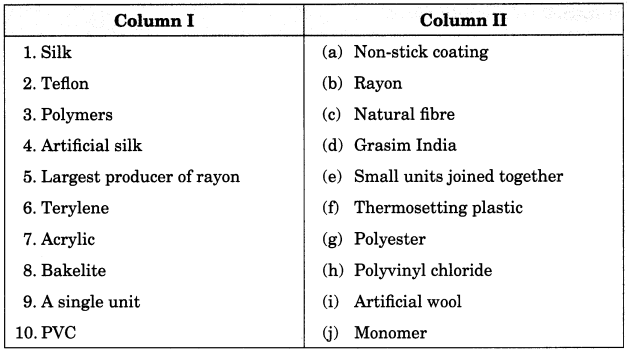
Answer:
1. (c)
2. (a)
3. (e)
4. (b)
5. (d)
6. (g)
7. (i)
8. (f)
9. (j)
10. (h)
IV. True or False
State whether the given statements are true or false.
1. Rayon is a natural fibre.
2. Artificial silk is another name for silk.
3. Rayon synthesised for the first time in England.
4. Nylon was made in 1931.
5. Polyester is the strongest synthetic fibre.
6. Rayon is the first man-made cellulose fibre.
7. Synthetic fibres shrink a lot when washed.
8. Terylene is a common variety of polyester.
9. Terrywool is made by blending polyester and silk.
10. Nylon is used in combs and toothbrushes.
11. Bakelite and melamine are thermoplastics.
12. Synthetic fibres are moth and insect resistant.
13. If plastics are burnt, they evolve oxygen gas.
14. Jammu & Kashmir has banned the use of plastic bags.
15. Plastics are corrosive in nature.
Answer:
1. False
2. False
3. True
4. True
5. False
6. True
7. False
8. True
9. False
10. True
11. False
12. True
13. False
14. True
15. False