Statistics for Economics Class 11 Notes Chapter 8 Index Numbers
Index Number
An index number is a statistical device for measuring changes in the magnitude of a group of related variables. It represents the general trend of diverging ratios from which it is calculated.
According to Croxton and Cowden, “Index numbers are devices for measuring difference in the magnitude of a group of related variables.”
Methods of Constructing Index Numbers
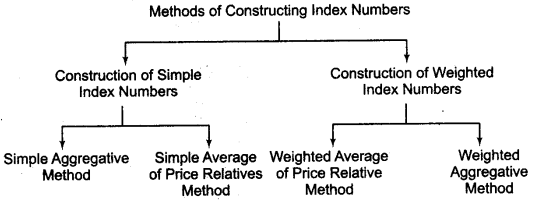
Construction of Simple Index Numbers
There are two methods of constructing simple index numbers.
(i) Simple Aggregative Method In this method, we use the following formula
\(P_{01}=\frac{\Sigma P_{1}}{\Sigma P_{0}} \times 100\)
Here, P01 = Price index of current year
ΣP1 = Sum of prices of the commodities in the current year
ΣP0 = Sum of prices of the commodities in the base year
(ii) Simple Average of Price Relatives Method
According to this method, we first find out price relatives from each commodity and then take simple average of all the prices relatives.
Price relatives, P01 = \(\frac{\text { Current year price }\left(P_{1}\right)}{\text { Base year price }\left(P_{0}\right)} \times 100\)
We can find out price index number of the current year by using the following formula
\(P_{01}=\frac{\sum\left[\frac{P_{1}}{P_{0}} \times 100\right]}{N}\)
Construction of Weighted Index Numbers
(i) Weighted Average of Price Relative Method
According to this method, weighted sum of the price relatives is divided by the sum total of the weight. In this method, goods are given weight according to their quantity, thus
\(P_{01}=\frac{\Sigma R W}{\Sigma W}\)
Here, P01 = Index number for the current year in relation to the base year
W = weight
R = price relative
(ii) Weighted Aggregative Method Under this method, different goods are accorded weight according to the quantity bought therefore, suggested different techniques of weighting some of well known methods are as under
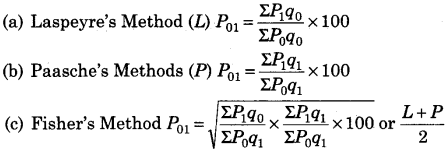
Fisher’s Method is considered as ‘Ideal’ because
- It is based on variable weights.
- It takes into consideration the price and quantities of both the base year and current year.
- It is based on Geometric Mean (GM) which is regarded as the best mean for calculating index number.
- Fisher’s index number satisfies both the Time Reversal Test and Factor Reversal Test.
Consumer Price Index or Cost of Living Index Number
The consumer price index is the index number which measures the averages change in prices paid by the specific class of consumers for goods and services consumed by them in the current year in comparison with base year.
Construction of Consumer Price Index
- Selection of the consumer class
- Information about the family budget
- Choice of base year
- Information about prices
- Weightage – There are two ways of according weights
- Quantity weight
- Expenditure weight
The following formula is used to find consumer’s price index
Consumer Price Index (CPI) = \(\frac{\Sigma W R}{\Sigma W}\)
Wholesale Price Index (WPI)
The Wholesale Price Index (WPI) measures the relative changes in the prices of commodities traded in the wholesale markets. In India, the wholesale price index numbers are constructed on weekly basis.
Industrial Production Index
The index number of industrial production measures changes in the level of industrial production comprising many industries. It includes the production of the public and the private sector. It is a weighted average of quantity relatives. The formula for the index is
\(P_{01}=\frac{\Sigma q_{1} \times W}{\Sigma W} \times 100\)
Construction of Index Number of Industrial Production
- Classification of industries
- Statistics or data related to industrial production
- Weightage
Agricultural Production Index
Index number of agricultural production is weighted average of quantity relatives.
Sensex
Sensex is the index showing changes in the Indian stock market. It is a short form of a Bombay Stock Exchange sensitive index. It is constructed with 1978-79 as the reference year or the base year. It consists of 30 stocks of leading companies in the country.
Purpose of Constructing Index Number
- Purpose of constructing index number of prices is to know the relative change or percentage in the price level over time. A rising general price level over time is a pointer towards inflation, while a falling general price level over time is a pointer towards deflation.
- Purpose of constructing index number of quantity is to know relative change or percentage change in the quantum or volume of output of different goods and services. A rising index of quantity suggests a rising level of economic activity and vice-versa.