Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants – CBSE Notes for Class 12 Biology
NCERT SolutionsMathsPhysicsChemistryBiologyScience
Sexual reproduction is the process of fusion of haploid gametes, resulting in the production of a diploid zygote, which ultimately develops into a new organism. All flowering plants show sexual reproduction.
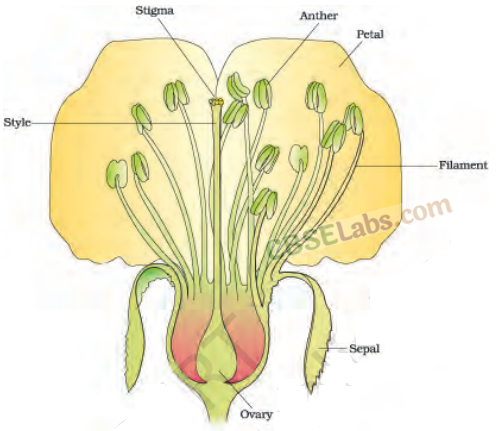
1. Flowers are the site of sexual reproduction in flowering plants.
(i) A flower has following parts arranged in four whorls, i.e. calyx (sepals), corolla (petals), androecium and gynoecium. These are attached to central axis called thalamus.
(iii) Flowers may contain both male (stamens) and female (carpels or pistils) reproductive parts or organs in it and is called bisexual.
(iii) In unisexual flowers, only either of the reproductive parts are present, e.g. corn, the tassels represent the male flowers (stamens) and the ears or silk represent the female flower (styles and stigma).
2. Stamen is the male reproductive unit of angiosperm.
It consists of the following two parts:
(i) The long and slender stalk called the filament.
(ii) The terminal generally bilobed structure called the anther.
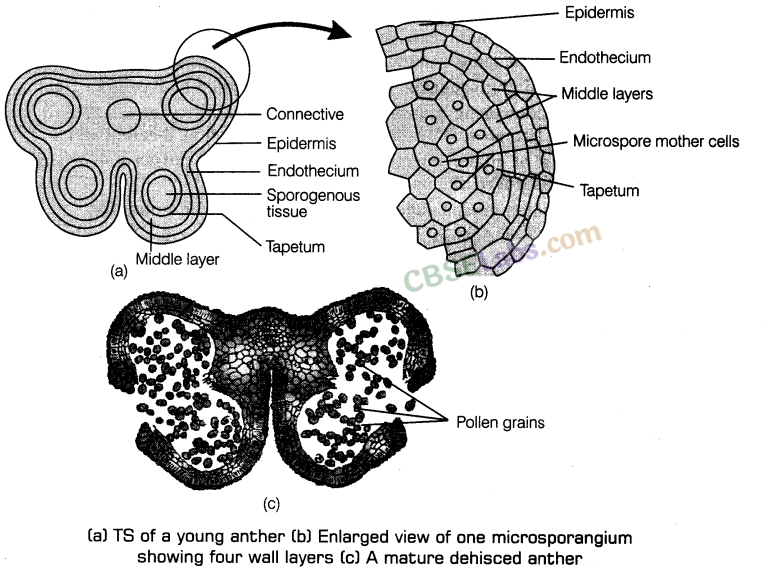
3. Anther is a bilobed structure with each lobe having two theca, therefore called dithecous. In a cross section, it is a four sided (tetragonal) structure consisting of four microsporangia, located at the corners, two in each lobe. Microsporangia develop and becomes pollen sacs. Pollen sacs contain pollen grains.
Structure of microsporangium contains following features in a transverse section:
(i) Appears nearly circular in outline.
(ii) It is surrounded by four wall layers. The outer three layers are epidermis, endothecium and middle layers. Outer three wall layers are protective in function and help in dehiscence of anther to release the pollen. The fourth and innermost layer called the tapetum nourishes developing pollen grains. It contains cells with dense cytoplasm and more than one nuclei.
(iii) A sporogenous tissue occupies the centre of each microsporangium in a young anther.
(iv) Each cell of sporogenous tissue undergo meiosis to form microspore tetrads. Each cell of the tetrad is known as microspore mother cell.
4. Microsporogenesis The formation of microspores from a pollen mother cell (each cell of sporogenous tissue) through meiosis is called microsporogenesis.
(i) Microspores are arranged as tetrad. As the anther mature and dehydrates they dissociate from each other and develop into pollen grains. Pollen grains or the male gametophytes are released by dehiscence of anther.
(ii) Pollen grains have the following characteristic features:
• Generally spherical, about 25-50 micrometers in diameter.
• Mature pollen grain comprises of two layers.
(a) Outer hard layer Exine made up of one of the most resistant organic material sporopollenin, that enables them to resist high temperatures and action of strong acids and alkali. Further no enzyme is yet known to degrade sporopollenin, because of which they are well preserved as fossils.
The region on exine where sporopollenin is absent are called germ pores. It helps in the formation of pollen tube, while the pollen grain germinates on stigma.
(b) Inner thin, continuous layer Intine made up of cellulose and pectin.
• A mature pollen grain contains two cells.
(a) Vegetative cell or tube cell It is larger as compared to other cell and possess vacuolated cytoplasm which is rich in reserve food, i.e. starch, protein, fat and cell organelles. The nucleus is large and irregular.
(b) Generative cell It is smaller cell usually spindle-shaped or spherical with thin dense cytoplasm and prominent nuclei. It divides mitotically to form two non-motile male gametes, prior to release of pollen grain.
(iii) In about 60% of angiosperms, pollen grains are shed at 2-celled stage.
(iv) In about 40% flowering plants, the generative cell divides mitotically to give rise to the two male gametes before pollen grains are shed at 3-celled stage.
(v) Pollen grains of many species (e.g. Parthenium) causes severe allergic, chronic respiratory disorders like asthma, bronchitis, etc.
(vi) Viability of pollen grains depends on temperature and humidity.
(vii) Pollen grains are richer in nutrients and are used as food supplements in form of pollen tablets and syrups. Its consumption has been claimed to increase the performance of athletes and race horses.
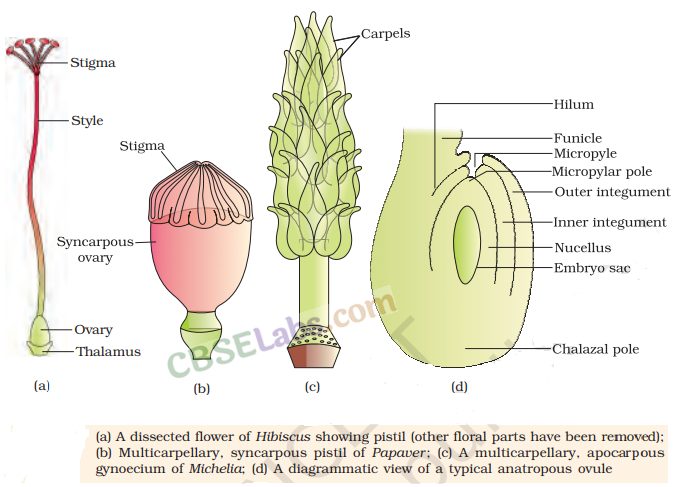
4. Pistil/Gynoecium It is the female unit of flower. A flower may be monocarpellary (having one pistil) or multicarpellary (having more than one pistils). Pistils may be syncarpous (fused together) or apocarpous (free).
The main parts of pistils are:
(i) Stigma receives pollen grains.
(ii) Style is the elongated slender part beneath the stigma.
(iii) Ovary the bulged part at the base of style.
Placenta is located inside the ovarian cavity or locule. Megasporangia, commonly called ovules arise from the placenta. Ovule is attached to the placenta by a stalk called funicle. The number of ovules in an ovary may be one (wheat, paddy and mango) to many (papaya, water melon and orchids).
The main parts of megasporangium (ovule) are:
(i) Hilum is a junction between ovule and funicle.
(ii) Each ovule has one or two protective envelopes called integuments.
(iii) Micropyle is an opening present at the tip where integument is absent.
(iv) Chalaza is opposite to the micropylar end representing the basal part of the ovule.
(v) The integuments encloses a mass of cells called the nucellus which have food reserves.
(vi) Embryo sac or female gametophyte is located in the nucellus (generally one formed from megaspores througth reductional division)
5. Megasporogenesis is the process of formation of megaspores from the Megaspore Mother Cell (MMC). The MMC is a large cell with dense cytoplasm and prominent nucleus. It undergoes meiosis resulting in the production of four megaspores.
6. Development of Female Gametophyte Different stages of development of female gametophyte are given below:
(i) One of the megaspores is functional, while the other three degenerate in majority of angiosperms.
(ii) Only the functional megaspore develops into the female gametophyte or embryo sac.
This is called monosporic development.
(iii) Nucleus of the functional megaspore divides mitotically to form two nuclei, which move to the opposite poles forming the 2-nucleate embryo sac.
(iv) Nuclear divisions result into the formation of 4-nucleate and later 8-nucleate stages
of the embryo sac.
(v) Six of the eight nuclei are surrounded by cell walls and organised into cells.
The remaining two nuclei called polar nuclei, are situated below the egg apparatus in the large central cell.
(vi) Three cells group together at the micropylar end and constitute the egg apparatus.
(vii) The egg apparatus consists of two synergids and one egg cell.
(viii) A filiform apparatus made of cellular thickenings of synergids at the micropylar end,
plays an important role in guiding the pollen tubes into the synergid.
(ix) At the chalazal end, three cells are present called antipodals.
(x) Thus, a typical angiosperm embryo sac, at maturity is 8-nucleate and 7-celled.
CBSE NotesCBSE Notes BiologyNCERT Solutions Biology