Practical Work in Geography Class 11 Solutions Chapter 3 Latitude, Longitude and Time
Class 11 Practical Work in Geography Chapter 3 NCERT Textbook Questions Solved
1. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
Question 1(i).
Which are the two natural points of references on the earth?
Answer:
North Pole and South Pole are the two natural points of references on the earth.
Question 1(ii).
What is a great circle?
Answer:
Equator is also called a great circle. The line drawn midway between the North Pole and the South Pole is called the equator. It is the largest circle and divides the globe into two equal halves.
Question 1(iii).
What are coordinates?
Answer:
The latitudes and longitudes are commonly referred to as geographical coordinates as they provide systematic network of lines upon which the position of various surface features of the earth, can be represented.
Question 1(iv).
Why does the sun appear to be moving from east to west?
Answer:
The earth rotates from west to east and therefore, the sun appears to be moving from west to east.
Question 1(v).
What is meant by local time?
Answer:
The rate of the time at which the sun traverses over certain degrees of longitudes is used to determine the local time of an area with respect to the time at the Prime Meridian (0°Longitude).
2. Distinguish between latitudes and longitudes:
Answer:
The difference between latitudes and longitudes is as follows:
| Basis | Longitude | Latitude |
| Meaning | The meridians of longitude refer to the angular distance, in degrees, minutes, and seconds, of a point east or west of the Prime (Greenwich) Meridian. | The parallels of latitude refer to the angular distance, in degrees, minutes and seconds of a point north or south of the Equator. |
| Name | Lines of longitude are often referred to as meridians. | Lines of latitude are often referred to as parallels. |
| Reference point | 0° longitude is called prime meridian. | 0° latitude is called equator. |
| Division | It divides the earth into eastern hemisphere and western hemisphere. | It divides the earth into northern hemisphere and southern hemisphere. |
| Number | These are 360 in number: 180 in the eastern hemisphere and 180 in the western hemisphere. | These are 180 in number: 90 in southern hemisphere and 90 in northern hemisphere. |
| Importance | It helps to determine time of a place. | It helps to determine temperature of a place. |
| Equality | These are not equal. | These are equal. |
ACTIVITY
1. Find out the locations of the following places with the help of your atlas and write their latitudes and longitudes.
Answer:
| Place | Latitude | Longitude |
| Mumbai | 19° Northern Latitude | 73° Eastern Longitude |
| Vladivostok | 43° Northern Latitude | 132° Eastern Longitude |
| Cairo | 30° Northern Latitude | 30° Eastern Longitude |
| New York | 41° Northern Latitude | 74° Western Latitude |
| Ottawa | 45° Northern Latitude | 76° Western Latitude |
| Geneva | 47° Northern Latitude | 7° Western Latitude |
| Johannesburg | 27° Southern Latitude | 27° Western Latitude |
| Sydney | 34° Southern Latitude | 152° Eastern Latitude |
2. What would be the time of the following cities if the time at Prime Meridian is 10 a.m.? Tokyo 7:18 p.m.
Paris 10:8 a.m.
Answer:
Delhi 3 p.m.
London 10 a.m.
Tokyo 7:18 p.m.
Paris 10:8 a.m.
Cairo 12 noon
Moscow 12: 32 p.m.
Class 11 Practical Work in Geography Chapter 3 NCERT Extra Questions
Class 11 Practical Work in Geography Chapter 3 Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Where is equator located?
(a) 0° latitude
(b) 23 V2 0 latitude
(c) 66 ¥2 ° latitude
(d) 90° latitude.
Answer:
(a) 0° latitude
Question 2.
On which longitude is International Date Line fixed?
(a) 180° longitude
(b) 0° longitude
(c) 150° longitude
(d) 90° longitude.
Answer:
(a) 180° longitude
Question 3.
Where is Greenwich located?
(a) 180° longitude
(b) 0° longitude
(c) 150° longitude
(d) 90° longitude.
Answer:
(b) 0° longitude
Question 4.
On which latitude has Indian Standard Time been determined?
(а) 23° western longitude
(b) 23 1/2° eastern longitude
(c) 82 1/2° western longitude
(d) 82 1/2° eastern longitude.
Answer:
(d) 82 1/2°eastern longitude
Question 5.
In how many time zones is the world divided?
(a) 10
(b) 12
(c) 20
(d) 24.
Answer:
(d) 24.
Class 11 Practical Work in Geography Chapter 3 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is a latitude?
Answer:
The parallels of latitude refer to the angular distance, in degrees, minutes and seconds of a point north or south of the Equator. Lines of latitude are often referred to as parallels.
Question 2.
What is a longitude?
Answer:
The meridians of longitude refer to the angular distance, in degrees, minutes, and seconds, of a point east or west of the Prime (Greenwich) Meridian. Lines of longitude are often referred to as meridians.
Question 3.
What is the relationship between longitude and time?
Answer:
When we move from west to east longitude, 4 minutes get added on and when we move from west to east, 4 minutes get subtracted.
Question 4.
What is the longitudnal extent of the earth?
Answer:
There are 180 eastern longitudes and 180 western longitudes. The longitudes vary from 0° to 180° eastward and westward of the Prime Meridian. The part of the earth east of the Prime Meridian is called the eastern hemisphere and in its west referred to as the western hemisphere.
Question 5.
What is the latitudinal extent of the earth?
Answer:
There are 90 southern latitudes and 90 northern latitudes. 0° latitude is called equator, latitude to the south of equator make up southern hemisphere and latitudes to the north of equator make up northern hemisphere.
Question 6.
How can you say that the earth is not a circle but sphere?
Answer:
The earth is nearly a sphere. It is because of the fact that the equatorial radius and the polar radius of the earth is not the same.
Question 7.
Why are latitudes and longitudes measured in degrees?
Answer:
Latitudes and longitudes are measured in degrees (°) because they represent angular distances.
Question 8.
How can we determine latitude of a place?
Answer:
Latitude of a place may be determined with the help of the altitude of the sun or the Pole Star.
Question 9.
What is 1ST?
Answer:
The Indian Standard Time is calculated from 82°30’E meridian passing through Mirzapur. 1ST is plus 5.30 hours from the GMT ((82°30’ x 4) (330 minutes = 5 hours 30 minutes).
Question 10.
Which countries have more than one time zone?
Answer:
The countries with large east-west span may choose more than one standard meridian to get more than one time zone such as Russia, Canada and the United States of America.
Class 11 Practical Work in Geography Chapter 3 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
When it is 12:00 noon in Greenwich then what will be the time at Thimbu, capital of Bhutan which is located at 90° east?
Answer: At one degree time changes by 4 minutes Difference between Greenwich and Thimbu is equal to 90°
Therefore time difference = 90 x 4
= 360 minutes = 6 hours (360/60)
Question 2.
When it is 12:00 noon in Greenwich then what will be the time at New Orleans which is located at 90° west?
Answer:
At one degree time changes by 4 minutes Difference between Greenwich and New Orleans is equal to 90°
Therefore time difference = 90 x 4
= 360 minutes = 6 hours (360/60)
Since it is towards, west, time will decrease by 4 minutes on each longitude. Therefore, it will be 6 am in the morning.
Question 3.
When it is 12:00 noon in Greenwich then what will be the time at New York which is located at 74° west?
Answer:
At one degree time changes by 4 minutes Difference between Greenwich and New York is equal to 74°
Therefore time difference
= 74 x 4
= 296 minutes
= 4 hours 56 minutes (296/60)
Since it is towards, west, time will decrease by 4 minutes on each longitude.
Therefore, it will be 7:04 am in the morning.
Question 4.
What is International Date Line? What
is its importance?
Answer:
The world is divided into 24 time zones, there has to be a place where there is a difference in days, somewhere the day truly “starts” on the planet. The 180° line of longitude is approximately where the International Date Line passes. The time at this longitude is exactly 12 hours from the 0° longitude, irrespective of one travels westward or eastward from the Prime Meridian. Time decreases east of the Prime Meridian and increases to its west. Hence, for a person moving east of the Prime Meridian, the time would be 12 hours less than the time at 0° longitude. For another person moving westward, the time would be 12 hours more than the Prime Meridian. For example, a person moving eastward on Tuesday will count the day as Wednesday once [ the International Date Line is crossed.
Similarly, another person starting his journey on the same day, but moving westward will count the day as Monday after crossing the line.
Class 11 Practical Work in Geography Chapter 3 Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the relationship between r longitude and time,
Answer:
The earth rotates from west to east over its axis. It makes the sun rise in the east and set in the west. The rotation of
the earth over its axis takes 24 hours to complete one circle or 360° of longitudes. As 180° of longitudes fall both east and west of the Prime Meridian, the sun, thus takes 12 hours’ time to traverse the eastern and western hemispheres. In other words, the sun traverses 15° of longitudes per hour or one degree of longitude in every four minutes of time. The time decreases when we move from west to east and increases with our westward movement. The rate of the time at which the sun traverses over certain degrees of longitudes is used to determine the local time of an area with respect to the time at the Prime Meridian (0°Longitude). For example when it is 2 pm in Greenwich, it will be 3 pm in 15° east. (15×4 = 60 minutes = 1 hour).
Question 2.
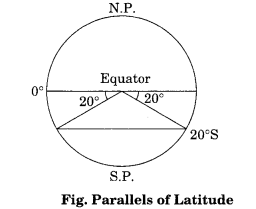
Explain the process or drawing latitudes.
Answer:
Process of drawing latitudes:
- Draw a circle.
- Divide it into two equal halves by drawing a horizontal line in the centre. This represents the equator.
- Place a protractor on this circle in a way that 0° and 180° line on the protractor coincide with the equator on the paper.
- Now to draw 20°S, mark two points at an angle of 20° from the equator, east and west in the lower half of the circle.
- The arms of the angle cut the circle at two points. Join these two points by a line parallel to the equator. It will be 20°S.
Question 3.
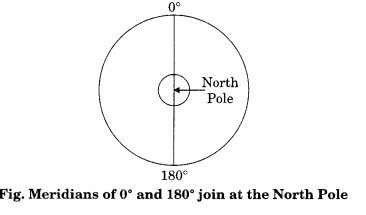
Explain the process of drawing longitudes Ans. Process of drawing longitudes:
Answer:
- Draw a circle whose centre represents the North Pole. The circumference will represent the equator.
- Draw a vertical line through the centre of the circle, i.e. crossing the North Pole. This represents the 0° and 180° meridians, which meet at the North Pole as shown in figure given below:
- To draw a longitude, imagine that you are on the North Pole, i.e. at the centre of the circle as shown in Figure given above.
- Observe now that the relative directions of east and west would reverse in this case and east would be towards your left while west would be towards your right.
- Now, draw 45° E and W as shown in Figure given below:
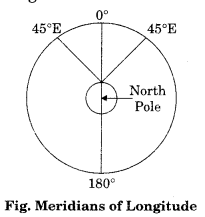
- For this, place your protractor along the vertical line, coinciding with the 0° and 180° meridians and then measure 45° on both the sides, which will denote 45° . E meridian and 45° W meridian on your left and right, respectively.
- The diagram will represent the appearance of the earth if we look at it from directly above the North Pole.
Class 11 Practical Work in Geography Chapter 3 Viva Questions
Question 1.
How many longitudes are there?
Answer:
There are 360° of longitude, 180° each in the east and west of the Prime Meridian. The latitudes are used to determine the local time.
Question 2.
How many latitudes are there?
Answer:
There are 180 latitudes, 90 in the south and 90 in the north.
Question 3.
What happens to time when we move from west to east and increases with our westward movement?
Answer:
The time decreases when we move from west to east and increases with our westward movement.
Question 4.
Name some countries having more than one standard time.
Answer:
Russia, Canada and the United States of America.
Question 5.
Give other name for great circle.
Answer:
Equator.
Question 6.
In how many time zones is the world divided?
Answer:
24
Question 7.
What is 1ST?
Answer:
The Indian Standard Time is calculated from 82°30’E meridian passing through Mirzapur. 1ST is plus 5.30 hours from the GMT ((82°30’ x 4) (330 minutes = 5 hours 30 minutes).
Question 8.
Why there is a time gap of 4 minutes in one degree of longitude?
Answer:
The sun traverses 15° of longitudes per hour or one degree of longitude in every four minutes of time.\
Latitude, Longitude and Time Notes
- The value of equator is 0° and the latitude of the poles are 90°N and 90°S. If the earth were a perfect sphere, the length of 1° of latitude (a one degree arc of a meridian) would be a constant value, i.e. Ill km everywhere on the earth. But on equator this distance is 110.61cm and on poles, it is 111.7 km.
- There are 90 southern latitudes and 90 northern latitudes and 180 eastern longitudes and 180 western longitudes.
- For convenience of numbering, the meridian of longitude passing through the Greenwich observatory (near London) has been adopted as the Prime Meridian by an international agreement and has been given the value of 0°.
- The longitudes vary from 0° to 180° eastward and westward of the Prime Meridian. The part of the earth east of the Prime Meridian is called the eastern hemisphere and in its west referred to as the western hemisphere.
- The distance between latitudes is approximately two longitudes is 111 km maximum at the equator (111.3 km) and minimum at the poles (0 km). Midway, at 45° of latitude, it is 79 km.
- There are 360° of longitude, 180° each in the east and west of the Prime Meridian. The latitudes are used to determine the local time.
- The rotation of the earth over its axis takes 24 hours to complete one circle or 360° of longitudes. As 180° of longitudes fall both east and west of the Prime Meridian, the sun, thus takes 12 hours’ time to traverse the eastern and western hemispheres. In other words, the sun traverses 15° of longitudes per hour or one degree of longitude in every four minutes of time.
- The time decreases when we move from west to east and increases with our westward movement. The rate of the time at which the sun traverses over certain degrees of longitudes is used to determine the local time of an area with respect to the time at the Prime Meridian (0° Longitude).
- The Indian Standard Time is calculated from 82°30’E meridian passing through Mirzapur. Therefore, 1ST is plus 5.30 hours from the GMT ((82°30’ x 4) (60 minutes = 5 hours 30 minutes).
- All countries of the world choose the standard meridian within their territory to determine the time within their administrative boundaries. The countries with large east-west span may choose more than one standard meridian to get more than one time zone such as Russia, Canada and the United States of America.
- While the world is divided into 24 time zones, there has to be a place where there is a difference in days, somewhere the day truly “starts” on the planet. The 180° line of longitude is approximately where the International Date Line passes.
- The time at this longitude is exactly 12 hours from the 0° longitude, irrespective of one travels westward or eastward from the Prime Meridian. Time decreases east of the Prime Meridian and increases to its west. Hence, for a person moving east of the Prime Meridian, the time would be 12 hours less than the time at 0° longitude. For another person moving westward, the time would be 12 hours more than the Prime Meridian. For example, a person moving eastward on Tuesday will count the day as Wednesday once the International Date Line is crossed. Similarly, another person starting his journey on the same day, but moving westward will count the day as Monday after crossing the line.
Latitude, Longitude and Time Important Terms
- Parallels of Latitude: The parallels of latitude refer to the angular distance, in degrees, minutes and seconds of a point north or south of the Equator. Lines of latitude are often referred to as parallels.
- Meridians of Longitude: The meridians of longitude refer to the angular distance, in degrees, minutes, and seconds, of a point east or west of the Prime (Greenwich) Meridian. Lines of longitude are often referred to as meridians.
- Geographical Coordinates: The latitudes and longitudes are commonly referred to as geographical coordinates as they provide systematic network of lin es upon which the position of various surface features of the earth, can be represented.
- Equator: The line drawn midway between the North Pole and the South Pole is called the equator. It is the largest circle and divides the globe into two equal halves. It is also called a great circle.
- International Date Line: The 180° line of longitude is approximately where the International Date Line passes. The time at this longitude is exactly 12 hours from the 00 longitude, irrespective of one travels westward or eastward from the Prime Meridian.
- Prime Meridian: For convenience of numbering, the meridian of longit ude passing through the Greenwich observatory (near London) has been adopted as the Prime Meridian by an international agreement and has been given the value of 0°.
- Small Circles: All the other parallels except equator get smaller in size, in proportion to their distance from the equator towards the poles and divide the earth into two unequal halves, also referred to as the small circles.
- Eastern Hemisphere: The part of the earth east of the Prime Meridian is called the eastern hemisphere.
- Western Hemisphere: The part of the earth west of the Prime Meridian is called the western hemisphere.
- Parallel: Lines joining places with the same latitudes are called parallels.
- Grid: The grid consists of two sets of horizontal and vertical lines, which are called parallels of latitudes and the meridians of longitudes.