NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Civics Social Science Chapter 8 Markets Around Us
1. In what ways is a hawker different from a shop owner?
Answer: A hawker provides door to door service. He sells his goods by calling out the names of his items. He generally owns a the which we may call a movable shop and keeps in it different items of our everyday use. He sells his goods at a minimum profit.
A shop owner runs his shop at one fixed place. Whenever we need anything we go there and purchase it. Here, we get things at a somewhat costlier rate.
2. Compare and contrast a weekly market and a shopping complex on the following:
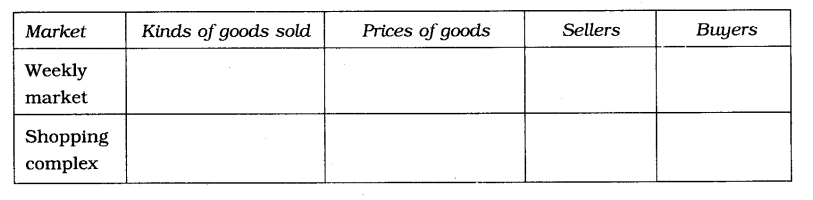
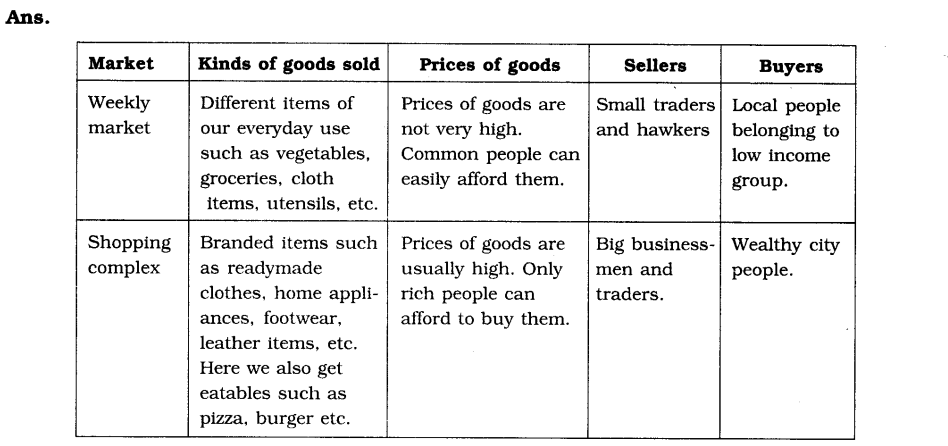
3. Explain how a chain of markets is formed. What purpose does it serve?
Answer: Goods are produced in factories, Goods are also produced in farms and in homes. But we are not required to go to factories or farms to buy goods of our need, because the producers are not interested in selling us small quantities. The wholesale traders do this job. They are the people who come in between the producer and the final consumer. They first buy goods in bulk. Then they sell these goods to the retailers, who finally sell this to the consumers.
From the above instance we come to the conclusion that from factories to final consumers a chain is formed, which we may call a chain of markets. We can better understand it through the flow chart given below:

It serves a great purpose. It maintains the flow of money. It makes easy availability of various items of our daily use. It also promotes coordination in society
4. ‘All persons have equal rights to visit any shop in a marketplace.’ Do you think this is true of shops with expensive products? Explain with examples.
Answer: It is true that all persons have equal rights to visit any shop in the marketplace. But this is not true of shops with expensive products. It is because of the following:
- People with high incomes can buy expensive products. Hence, these people go to the shops with expensive products and not the poor or people with low income.
- The low-income group people visit the shops or weekly markets to buy goods as these goods are available at cheaper rates.
Examples:
People with high income buy green vegetables from multiplexes or malls while poor people purchase green vegetables from small vegetable sellers or from hawkers.
5. ‘Buying and selling can take place without going to a marketplace’. Explain this statement with the help of examples.
Answer:
It is correct that buying and selling can take place without going to a market place. It is done in the following manner.
Examples:
- We can order goods that we need over the telephone and get their delivery.
- Over the internet, we can visit the concerned website and order the products.
- We can pay through internet banking or on the delivery of goods.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Why is a weekly market called so?
Answer: A weekly market is called so because it is held a specific day of the week.
2. Why is there a competition among the shops in the weekly market? [V. Imp.]
Answer: In the weekly market there are many shops that sell the same goods. This creates competition among them.
3. Who is Scunner? What does he do?
Answer: Sameer is a small trader in the weekly market. He buys clothes from a large trader and sells them in six different markets in a week.
4. Give some examples of roadside stalls.
Answer: Vegetable hawker, fruit vendor, mechanic.
5. How are shops in the neighbourhood useful?
Answer: These types of shops are close to our home and we can go there any time. As the buyer and seller know each other these shops also provide goods on credit.
6. Where are the goods produced?
Answer: Goods are produced in factories, on farms, and in homes.
7. Why do we not buy directly from the producer? [V. Imp.]
Answer: It is because the producer is not interested in selling goods in small quantities. 9*
8. Who is a retailer? [Imp.]
Answer: A retailer is a small trader who buys goods from the wholesale trader and sells this to the consumer.
9. Who is Aftab?
Answer: Aftab is a wholesaler in the city. He purchases vegetables in bulk and sells them to hawkers and shopkeepers.
10. How are buyers, different people?
Answer: There are many buyers who cannot afford even the cheapest of goods. While others frequently visit malls and buy different items.
11. What is done in the wholesale markets?
Ans. This is where goods first reach and are then supplied to other traders.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Write in brief about shopping complexes and malls.
Answer: Shopping complexes and malls are usually found in urban areas. These are large multi-storeyed air-conditioned buildings with shops on different floors. These shops sell both branded and non-branded goods. Fewer people visit malls because they sell costly items. Only well-to-do people can afford to buy these items.
2. What is the job of a wholesale trader? [V. Imp.]
Answer: A wholesale trader buys goods from the producer in large quantities. He then sells them to other traders, say small traders. These small traders sell different items to the final consumer. Thus, the wholesale trader establishes link between the producer and the consumer. It is through these links of traders that goods reach faraway places.
3. How are shop owners in a weekly market and those in a shopping complex very different people? [V. Imp.]
Answer: Both are undoubtedly different people.
(a) The shop owners in a weekly market are small traders who run their shop with little money. On the other hand, the shop owners of a shopping complex are big parties. They have a lot of money to spend on their shops.
(b) What these two types of shop owners earn is also not equal. The weekly market trader earns little compared to the profit of a regular shop owner in a shopping complex.
4. Write a brief note on ‘Aftab—the wholesaler in the city’.
Answer: Aftab is a wholesaler of vegetables. His work usually starts at around 2 o’clock in the early morning. This is the time when vegetables reach the market or mandi and with them start the activities. The vegetables come in trucks, matadors, etc. and soon the process of auctions begins. Aftab participates in this auction and decides what he will buy. He buys vegetables in bulk. After that, he sells them to hawkers and shopkeepers who usually come to him around six in the morning.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Do you see equality in the market? If not, why not? Explain with examples.[V. Imp.]
Or
Write in brief on ‘market and equality’.
Answer: We do not see equality in the market. Big and powerful business persons earn huge profits while small traders earn very little. For example, the shop owners in a weekly market and those in a shopping complex are two different people. One is a small trader who has little money to run the shop. Whereas the other has a lot of money to spend on the shop. The earning of these two people is also unequal. The weekly market trader earns little profit whereas the shopping complex owner gains huge income.
Not only the shop owners are different people, but also the buyers. In the market we see different types of buyers There are several buyers who Eire not able to afford even the cheapest of goods white others are busy shopping for different luxurious items in malls. Thus, we see no equality in the market place.
NCERT SolutionsMathsScienceSocialEnglishSanskritHindiRD Sharma