NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Micro Economics Chapter-4 Elasticity of Demand
NCERT TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS SOLVED
Question 1. Explain price elasticity of demand.
Answer: The degree of responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price of commodity is known as price elasticity of demand.
Question 2. Consider the demand for a good. At price Rs 4, the demand for the good is 25 units. Suppose price of the good increases to Rs 5, and as a result, the demand for the good falls to 20 units. Calculate the price elasticity? [3-4 Marks]
Answer:
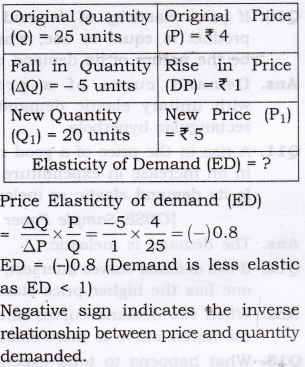
Question 3.

Answer:
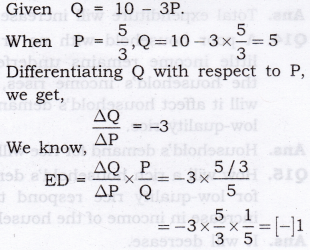
Negative Sign of ED indicates that inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
PED = 1 [Unitary elastic demand].
Question 4. Suppose the price elasticity of demand for a good is -0.2. If there is a 5% increase in the price of the good, by what percentage will the demand for the good go down?[3-4 Marks]
Answer:
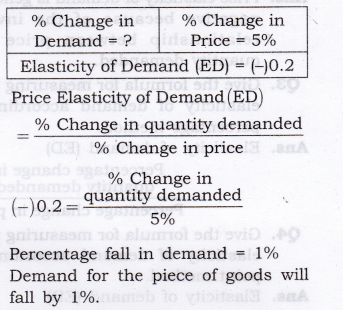
Question 5. Suppose the price elasticity of demand for a good is -0.2. How will the expenditure on the good be affected if there is a 10% increase in the price of the good? [1 Mark]
Answer: Total expenditure will rise if there is 10% rise in the price of the good since its demand is inelastic (Given ED = 0.2).
Question 6. Suppose, there was 4% decrease in the price of a good and as a result, the expenditure on the goods increased by 2%. What can you say about the elasticity of demand? [1 Mark]
Answer: As total expenditure has increased with a decrease in price, the demand is said to be highly elastic.
MORE QUESTIONS SOLVED
I. Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)
Question 1. Define price elasticity of demand.
Answer: The degree of responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price of the commodity is known as price elasticity of demand.
Question 2. Why is price elasticity of demand has negative sign always?
Answer: Price elasticity of demand is generally negative because of the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Question 3. Give the formula for measuring price elasticity of demand according to percentage method.
Answer: Elasticity of demand (ED)
Percentage change in quantity demanded Percentage change in price
Question 4. Give the formula for measuring price elasticity of demand according to point method.
Answer: Elasticity of demand (ED)
Lower Segment of demand curve (LS)
Upper Segment of demand curve (US)
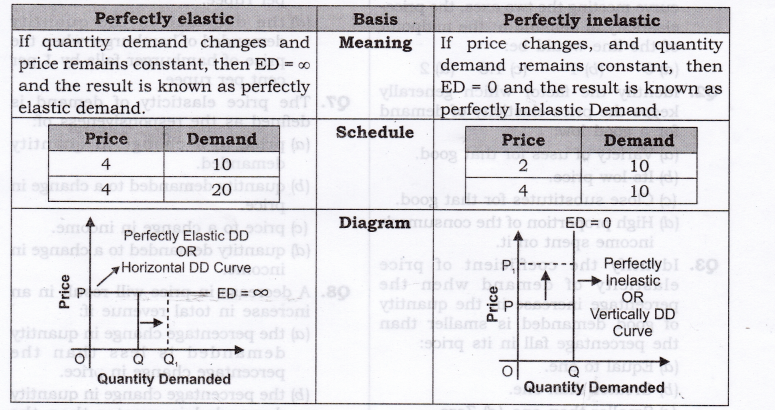
Question 5. Define perfectly inelastic demand.
Answer: If price changes, and quantity demand remains constant, ed = 0 and the result is known as perfectly inelastic demand.
Question 6. Define perfectly elastic demand.
Answer: If quantity demand changes and price remains constant, ed = o and the result is known as perfectly elastic demand.
Question 7. Demand for product X is perfectly ! elastic. What will be the change in price if demand rises from 50 per unit to 70 per unit?
Answer: There will be no change in price as demand is perfectly elastic.
Question 8. If ED < 1, in which portion the point would be located on a straight line demand curve?
Answer: In the lower half.
Question 9. When is the demand of a commodity said to be inelastic? [CBSE Sample Paper 2010]
Answer: When percentage change in the quantity demanded is less than percentage change in price, demand for such a commodity is said to be less elastic.
Question 10. If price elasticity of demand for a product is equal to one, what will be the nature of its demand curve?
Answer: Demand curve of a product with unitary elastic demand is a rectangular hyperbola.
Question 11. A rise in the price of a good results in an increase in expenditure on it. Is its demand elastic or inelastic? [CBSE Sample Paper 2008}
Answer: The demand is inelastic.
Question 12. If two demand curves intersect, which one has the higher price elasticity?
Answer: When two demand curves intersect, the flatter curve is more elastic.
Question 13. What happens to total expenditure on a commodity when its price falls and its demand is price elastic? [CBSE Sample Paper 2010}
Answer: Total expenditure will increase.
Question 14. A poor household with no or very little income remains underfed. If the household’s income rises, how will it affect household’s demand for low-quality rice.
Answer: Household’s demand for rice will rise.
Question 15. How will a rich household’s demand for low-quality rice respond to an increase in income of the household?
Answer: It will decrease.
II. Multiple Choice Questions (1 Mark)
Question 1. In case of a straight-line demand curve meeting the two axes, the price- elasticity of demand at the midpoint of the line would be:
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 1.5 (d) 2
Answer: (b)
Question 2. Identify the factor which generally keeps the price elasticity of demand for a good low:
(a) Variety of uses for that good.
(b) Its low price.
(c) Close substitutes for that good.
(d) High proportion of the consumer’s income spent on it.
Answer: (b)
Question 3. Identify the coefficient of price elasticity of demand when the percentage increase in the quantity of good demanded is smaller than the percentage fall in its price:
(a) Equal to one.
(b) Greater than one.
(c) Smaller than one. (d) Zero.
Answer: (c)
Question 4. If the demand for a good is inelastic, an increase in its price will cause the total expenditure of the consumers of the good to:
(a) remain the same, (b) increase.
(c) decrease. (d) Any of these.
Answer: (b)
Question 5. Which one of the following four possibilities, results in an increase in total consumer expenditure?
(a) Demand is unitary elastic and price falls.
(b) Demand is elastic and price rises.
(c) Demand is inelastic and price falls.
(d) Demand is inelastic and price rises.
Answer: (d)
Question 6. The price elasticity of demand for hamburger is:
(a) the change in the quantity demanded of hamburger when the hamburger increases by 30 paise per rupee.
(b) the percentage increase in the quantity demanded of hamburger when the price of hamburger falls by 1 per cent per rupee.
(c) the increase in the demand for hamburger when the price of hamburger falls by 10 per cent per rupee.
(d) the decrease in the quantity demanded of hamburger when the price of hamburger falls by 1 per cent per rupee.
Answer: (b)
Question 7. The price elasticity of demand is defined as the responsiveness of:
(a) price to a change in quantity demanded.
(b) quantity demanded to a change in price.
(c) price to a change in income.
(d) quantity demanded to a change in income.
Answer: (b)
Question 8. A decrease in price will result in an increase in total revenue if:
(a) the percentage change in quantity demanded is less than the percentage change in price.
(b) the percentage change in quantity demanded is greater than the percentage change in price.
(c) demand is inelastic.
(d) the consumer is operating along a linear demand curve at a point at which the price is very low and the quantity demanded is very high.
Answer: (b)
Question 9. An increase in price will result in an increase in total revenue if:
(a) The percentage change in quantity demanded is less than the percentage change in price.
(b) The percentage change in quantity demanded is greater than the percentage change in price.
(c) Demand is elastic.
(d) The consumer is operating along a linear demand curve at a point at which the price is very high and the quantity demanded is very low.
Answer: (a)
III. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Differentiate between perfectly elastic and perfectly inelastic demand. [3-4 Marks]
Answer:
Numerical Problems on Price Elasticity of Demand to Calculate PED
Question 2. When price is Rs. 20 per unit, demand for a commodity is 500 units. As the price falls to Rs. 15 per unit, demand expands to 800 units. Calculate elasticity of demand.
Answer:
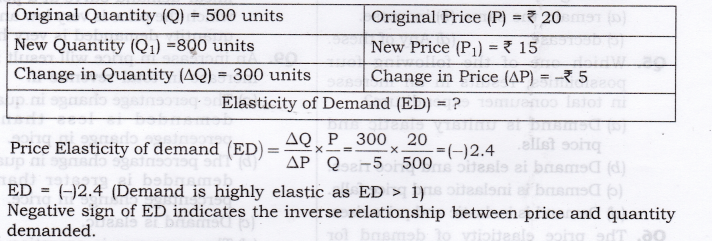
Question 3. The demand for a goods falls to 500 units in response to rise in price by Rs. 10. If the original demand was 600 units at the price of Rs. 30, calculate price elasticity of demand.
Answer:
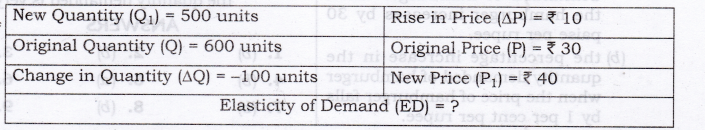

Question 4. A consumer spends Rs. 80 on a commodity when price is Rs. 1 per unit. If the price increases by Rs. 1, his expenditure becomes Rs. 96. Comment on PED.
Answer:
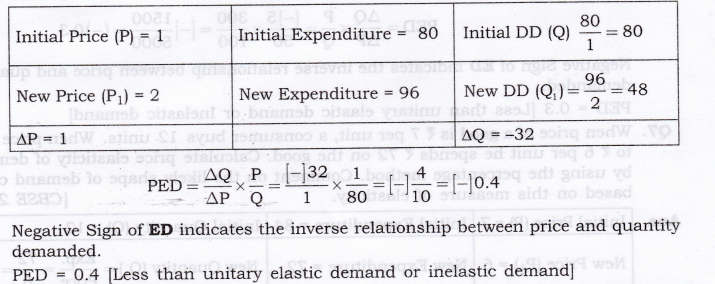
Question 5. A decline in the price of good X by Rs. 5 causes an increase in its demand by 20 units to 50 units. The new price is X 15. Calculate elasticity of demand.
Answer:

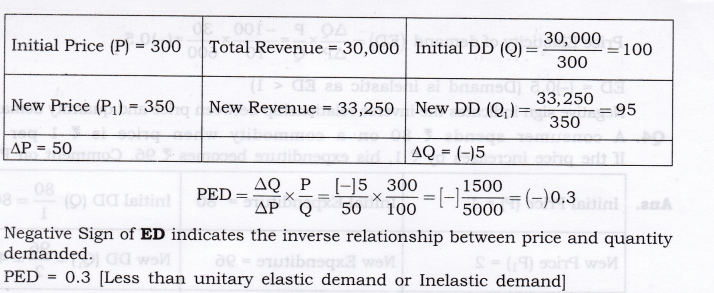
Question 6. A dentist was charging Rs. 300 for a standard cleaning job, and per month it used to generate total revenue equal to Rs. 30,000. She has increased the price of dental cleaning to Rs. 350 since last month. As the result of, few customers are now coming for dental clearing, but the total revenue is now Rs. 33,250. From this, what can we conclude about the elasticity of demand for such a dental service. Calculate PED by proportionate method.
Answer:
Question 7. Negative Sign of ED indicates the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. PED = 0.3 [Less than unitary elastic demand or Inelastic demand]
When price of a good is Rs. 7 per unit, a consumer buys 12 units. When price falls to Rs. 6 per unit he spends Rs. 72 on the good. Calculate price elasticity of demand by using the percentage method. Comment on the likely shape of demand curve based on this measure of elasticity. [CBSE 2012]
Answer:

ED is perfectly inelastic as quantity demanded does not change at all in response to change in price. Thus, its demand curve will be vertical/parallel to y-axis.
Question 8. A consumer buys 20 units of a good at a price of Rs. 5 per unit. He incurs an expenditure of Rs. 120 when he buys 24 units. Calculate price elasticity of demand using the percentage method. Comment upon the likely shape of demand curve based on this information. [CBSE 2012]
Answer:
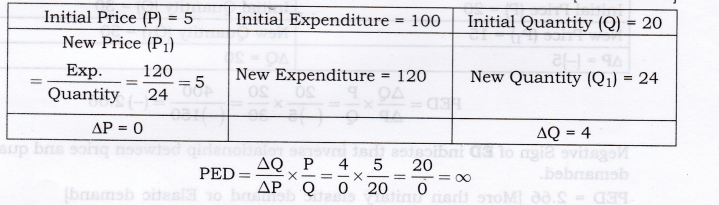
ED is perfectly elastic as price does not change at all in response to change in quantity demanded. Thus, its demand curve will be horizontal/parallel to x-axis.
Question 9. A consumer buys 10 units of a commodity at a price of Rs. 10 per unit. He incurs an expenditure of Rs. 200 on buying 20 units. Calculate price elasticity of demand by the percentage method. Comment upon the shape of demand curve based on this information. [AI 2012]
Answer:
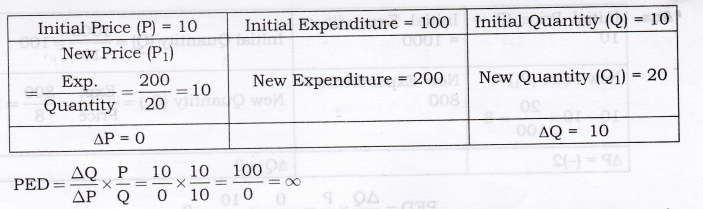
Question 10. ED is perfectly inelastic as quantity demanded does not change at all in response to change in price. Thus, its demand curve will be vertical/parallel to y-axis. A consumer spends Rs.1000 on a good priced at Rs.10 per unit. When its price falls by 20 per cent, the consumer spends Rs.800 on the good. Calculate the price elasticity of demand by the Percentage method. [AI 2015]
Answer:
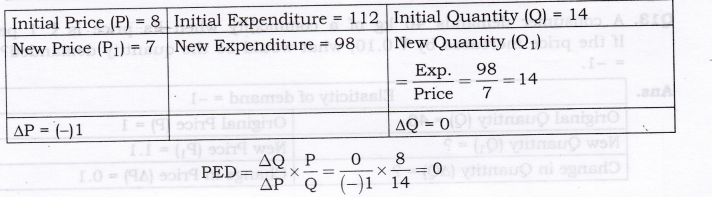
ED is perfectly inelastic as quantity demanded does not change at all in response to change in price. Thus, its demand curve will be vertical/parallel to y-axis.
Numerical Problems to Calculate Price or Quantity (When Price Elasticity of Demand is given)
Question 11. A consumer demands 40 kg of a commodity when its price is Rs. 1 per kg. If the price increases by Rs. 0.10, what would be the quantity demanded? PED = -1.
Answer:
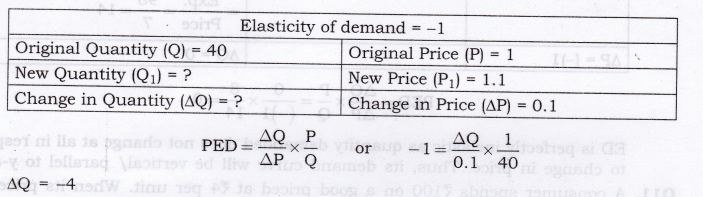
As, price is increasing, then quantity demanded must decrease by 4.
So, New Quantity = Initial quantity + AQ = 40 + (-4) = 36
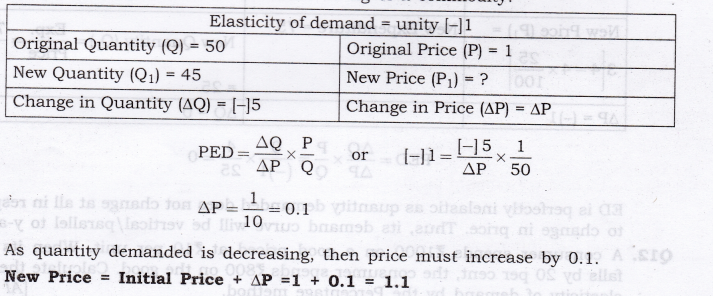
Question 12. PED = [-] 1. A consumer demands 50 units of a commodity when price is Rs 1 per unit. At what price will he demands 45 kg of a commodity?
Answer:
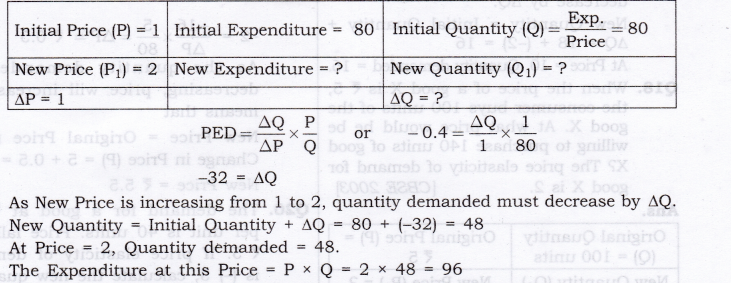
Question 13. A consumer spends Rs. 80 on a commodity when price is Rs 1 per unit. If the price increases by ?1, what would be his expenditure. PED = -0.4?
Answer:
Question 14. The market demand for a good at Rs. 5 per unit is 50 units. Due to increase in price, the market demand falls to 30 units. Find out the new price if the price elasticity of demand is (-)2.
Answer:
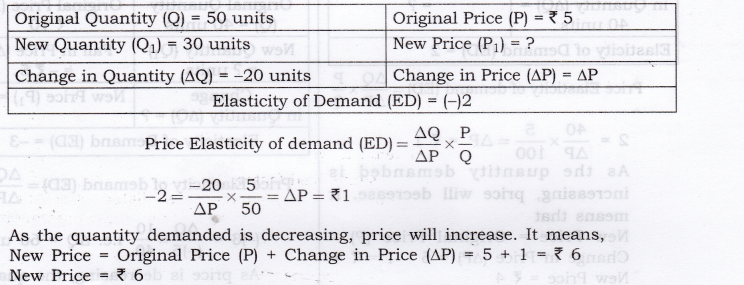
As the quantity demanded is decreasing, price will increase. It means,
New Price = Original Price (P) + Change in Price (AP) = 5 + 1 = Rs. 6 New Price = Rs. 6 v
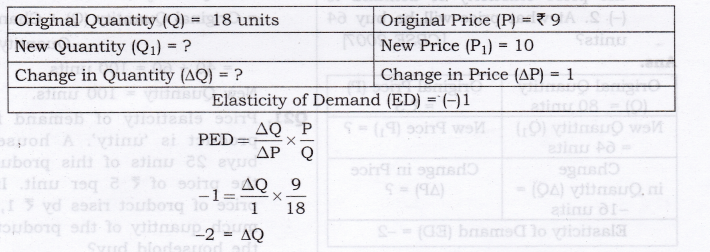
Question 15. A consumer buys 18 units of a good at a price of Rs 9 per unit. The price elasticity of demand for the good is (-)l. How many units the consumer will buy at a price of Rs 10 per unit? Calculate. [CBSE 2014]
Answer:
NCERT SolutionsAccountancyBusiness StudiesMicro EconomicsCommerce