NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Ecosystem
Topics and Subtopics in NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 Ecosystem:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 14 | Ecosystem |
| 14.1 | Ecosystem–Structure and Function |
| 14.2 | Productivity |
| 14.3 | Decomposition |
| 14.4 | Energy Flow |
| 14.5 | Ecological Pyramids |
| 14.6 | Ecological Succession |
| 14.7 | Nutrient Cycling |
| 14.8 | Ecosystem Services |
| 14.9 | Summary |
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK SOLVED
1. Fill in the blanks.
(a) Plants are called as————- because they fix carbon dioxide.
(b) In an ecosystem dominated by trees, the pyramid (of numbers) is————- type.
(c) In aquatic ecosystems, the limiting factor for the productivity is————- .
(d) Common detritivores in our ecosystem are————- .
(e) The major reservoir of carbon on earth is————- .
Ans: (a) Autotrophs
(b) Spindle
(c) Sunlight
(d) Earthworm, bacteria & fungi of decay and vulture
(e) Oceans
2. Which one of the following has the largest population in a food chain?
(a) Producers
(b) Primary consumers
(c) Secondary consumers.
(d) Decomposers
Ans: (d)
3. The second trophic level in a lake is-
(a) Phytoplankton
(b) Zooplankton
(c) Benthos
(d) Fishes
Ans: (b)
4. Secondary producers are
(a) Herbivores
(b) Producers
(c) Carnivores
(d) None of the above
Ans: (d)
5. What is the percentage of photo synthetically act., radiation (PAR), in the incident solar radiation?
(a) 100%
(b) 50 %
(c) 1-5%
(d) 2-10%
Ans: (b)
6. Distinguish between
(a) Grazing food chain and detritus food chain
(b) Production and decomposition
(c) ‘Upright and inverted pyramid
(d) Food chain and food web
(e) Litter and detritus
(f) Primary and secondary productivity
Ans: (a) Grazing Food Chain (GFC) begins with primary producers or plants and ends in carnivores (tertiary or top carnivores) whereas Detritus Food Chain (DFC) begins with detritus or dead organic matter and it ends in carnivores. In GFC, energy for the food chain comes from sun whereas in DFC, energy for the food chain comes from organic remains or detritus.
(b) Production is the phenomenon in which the energy is produced by the process of synthesis of organic compound from inorganic substances (such as CO2, H2O & minerals) utilizing generally the sunlight. It traps energy.
Decomposition refers to the breakdown of complex organic matter into simpler ones. It releases energy.
(c) In upright pyramid (e.g., grassland & cropland ecosystem), biomass or number of organisms or amount of energy decreases
on moving to upper trophic levels while in an inverted pyramid (eg. tree ecosystem) these quantities tend to increase on going to successive trophic levels.
(d) A food chain is a sequence of different types of organisms by which the flow of energy occurs from one trophic level to another whereas food web is the network of various food chains inter-connected to each other. Food webs increase adaptability and competitiveness of the organisms.
(e) Litter is the dead organic material fallen on the surface of the soil like leaves, remains of animals and excreta. Detritus is the dead organic matter found below the soil surface which is eaten up by the detritivores or broken down by decomposers.
(f) Primary productivity is the rate of synthesis of biomass or energy fixation by the plants. It is comparatively quite high.
Secondary productivity is the rate of synthesis of biomass by consumers (herbivores and carnivores). It is small and decreases with rise of trophic level.
7. Describe the components of an ecosystem.
Ans: The components of an ecosystem are as follows :
- Abiotic components or non living components : These include inorganic substances or minerals (standing state or standing quality), organic substances and different climatic conditions like temperature, pH, light, etc.
- Biotic components or living components :
(a) Autotrophs or producers which have capacity to manufacture their own food or which can fix radiant energy of sun into chemical energy, e.g., green plants and photosynthetic bacteria.
(b) Heterotrophs or consumers which are unable to manufacture their own food and depend upon other organisms for their food. These are of following types:
- Primary consumers or herbivores which depend upon producers or green plants for their food.
- Secondary consumers or carnivores which live upon herbivores.
- Top consumers or top carnivores which live upon secondary consumers.
(c) Decomposers or microconsumers decompose dead organic substances of producers and consumers into simple substances and thus continue mineral cycles, e.g., bacteria, fungi, actinomycetes etc.
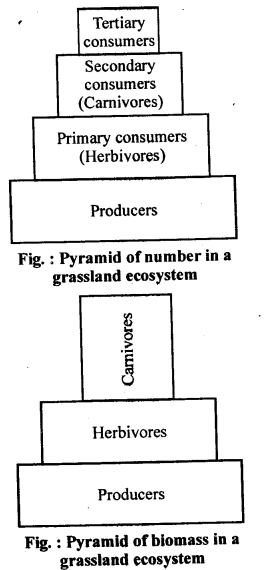
8. Define’ecological pyramids and describe with examples, pyramids of number and biomass.
Ans: Ecological pyramid is a graphical method to show the number of organisms or biomass or amount of energy present at different trophic levels. Pyramid of number: Number of individuals at each trophic level is shown in pyramid. The pyramid of number (for example of a grassland) is upright. In this there is a decrease in the number of organisms starting from primary producers (plants) to top consumers (carnivores). Pyramid of biomass : Pyramid of biomass is graphic representation of amount of biomass per unit area sequence wise in rising trophic levels with producers at the base and top carnivores at the apex. Pyramids of biomass of a tree or . grassland ecosystem are upright and the pyramid of a pond ecosystem is inverted.
9. What is primary productivity? Give brief description of factors that affect primary productivity.
Ans: Primary productivity of an ecosystem is the amount of energy fixed or biomass synthesized by primary producers or green plants per unit area per unit time during photosynthesis. Factors affecting primary productivity are –
-Plant species inhabiting a particular area
-Sunlight
-Temperature
-Soil water
-Nutrients
lit deserts, sunlight is abundant but water is scarce or nutrients are lacking. Therefore, in such areas, water & nutrients supply become the limiting factors.
10. Define decomposition and describe the processes and products of decomposition.
Ans: The process by which decomposers break down complex organic remains (dead plants, animal remains and excretions) into inorganic substances like carbon dioxide, water and nutrients is called decomposition. The important steps in the process of decomposition are fragmentation, leaching, catabolism, humification and mineralisation. Detritivores (e.g., earthworm) break down detritus into smaller particles. This process is called fragmentation.
By the process of leaching, water-soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts.
Bacterial and fungal enzymes degrade detritus into simpler inorganic substances. The process is called as catabolism.
All the above steps in decomposition operate simultaneously on the detritus. Humification and mineralisation occur during decomposition in the soil.
Humification leads to accumulation of a dark coloured amorphous substance called humus that is highly resistant to microbial action and undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate. Being colloidal in nature it serves as a reservoir of nutrients.
The humus is further degraded by some microbes and release of inorganic nutrients occur by the process known as mineralisation.
11. Give an account of energy flow in an ecosystem.
Ans: Flow of energy in an ecosystem is unidirectional. The ultimate source of energy is sun. The solar energy is captured by the green plants which utilize it in synthesizing their own food. The energy fixed by the green plants is transferred to herbivores which feed on them. The energy is then transferred to higher trophic levels (carnivores). At every step, considerable amount of energy is lost. According to 10% law, only 10% of total energy stored in a trophic level is transferred to the next trophic level of a food chain.
12. Write important features of a sedimentary cycle in an ecosystem.
Ans: The movement of nutrient elements through various components of an ecosystem takes place by a biogeochemical cycle. It is of 2 types – gaseous and sedimentary. A nutrient that does not enter the atmosphere easily is said to have a sedimentary cycle. Sedimentary cycle involve cycling of sulphur, phosphorus etc. which are located in earth’s crust.
Phosphorus is a very important element as it is present in various substances found in living beings. The cycling of phosphorus in an ecosystem occurs in such a way that plants obtain it from soil or rocks. The animals or primary consumers obtain it from plants. Secondary consumers or carnivores take it from herbivores while omnivores (like man) receive it both from plants and animals. Phosphorus present in organisms is also released during decomposition.
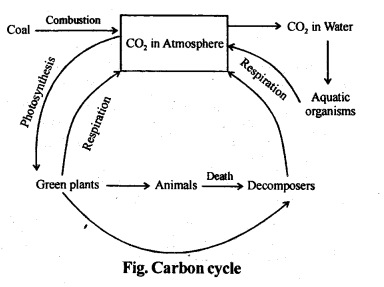
13. Outline salient features of carbon cycling in an ecosystem.
Ans: Carbon is an important constituent of living matter. Green plants take it in the form of C02 from atmosphere and fix it as carbohydrates. Carbon which is also present in proteins, fats etc. is transferred to the organisms of other trophic levels. Apart from being released in atmosphere as C02 during respiration, carbon is also released in atmosphere through burning of wood, fossil fuel and decomposition of organic matter by microbes.
More Resources for CBSE Class 12:
NCERT SolutionsMathsPhysicsChemistryBiologyScience