Light, Shadows and Reflection Class 6 Notes
Source of light: An object which emits light, is called a source of light. For example, sun, torch, etc.
Non-luminous objects: These are the objects which do not emit light of their own. Such a body becomes visible when light falls on it. For example, the moon, the planets, etc.
Ray of light: A straight thin beam of light from a source to an object is called a ray of light.
Obstacle: An object which comes to the path of the light is called an obstacle.
Formation of a shadow
- All the opaque objects seem to form a dark shadow of their own.
- We need a source of light, an opaque object in the way, and a screen to see a shadow.
- Screen: This is a surface on which the shadow is formed. It may be a butter paper or simply ground.
- Shadows give us some information about shapes of objects.
- The colour of the opaque object does not affect the colour of the shadow.
- All the space behind the opaque object, up to some distance behind it seems to be filled with the shadow.
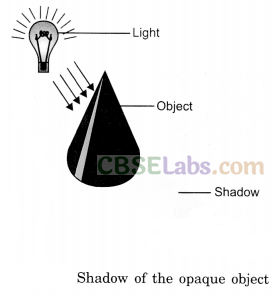
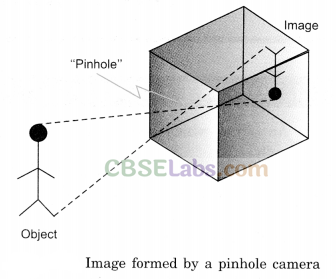
Image formed by a pinhole camera
Images formed by a pinhole camera are upside down. Here is a picture showing the path of rays of light coming from an object far away to a pinhole and then to screen.
When sunlight passes through the leaves of a tree, the gaps between the leaves act as the pinholes. These natural pinholes cast nice round images of the sun.
Rectilinear propagation: Light travels in a straight line. It is called rectilinear propagation of light.
Image formation by a plane mirror: We are able to see images through a mirror. Image formed by a mirror (flat) has following features:
- Reflected image retains the colour of the object.
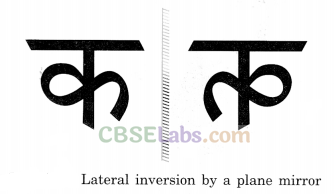
- Image is erect but laterally inverted.
Lateral inversion: Right side of the object appears as left side in the image formed by a plane mirror. For example, if we show our right hand, image in the mirror will show as left hand.
In a mirror, if you see another person, surely the other person can also see you in that mirror.
Luminous: Objects that give out or emit light of their own are called luminous objects.
Mirror: A smooth shining surface, which rebounds the light back in same or in different directions is called a mirror.
Opaque objects: If an object completely stops the passage of all the light falling on it, it is an opaque object.
Pinhole camera: It is a device which forms a photograph-like image of a bright object on a screen.
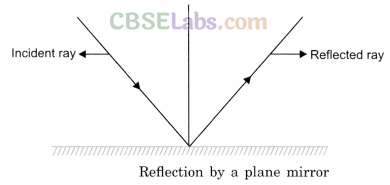
Reflection of light: When a ray of light falls on a smooth and polished surface, light returns back in the same medium. It is called reflection.
Shadow: Opaque objects do not allow light to pass through them and cast dark patches behind them. These dark patches are called shadows.
Translucent objects: Some objects allow only a part of light falling on them to pass through, such objects are called translucent objects. For example, a single thin sheet of paper.
Transparent objects: Those objects which allow all the light to pass through them are called transparent objects.
Sources Of Light
Any object that gives out light is called a source of light. Luminous objects are also called sources of light. Sources of light can be natural or artificial (man-made) (Fig. 13.1).

Examples of natural sources of light are ‘he sun and other stairs and insects like the firefly. Some artificial sources of light are candle, electric bulb, and laser.
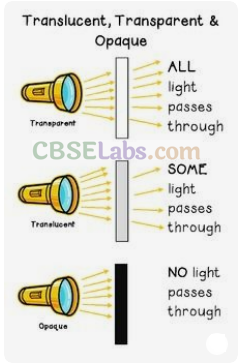
Transparent, Translucent, And Opaque Materials :
Different types of materials transmit light differently. Based on the way they transmit light, materials can be divided into transparent, translucent, and opaque materials.
Materials that allow light to pass through significant scattering or absorption [Fig. 13.2(a)] are called transparent materials. We will be able to see through these materials very clearly. Examples of transparent materials are clear air, clear glass, clean water, some kinds of plastic, and cellophane paper.
Materials that allow light to pass through them, but scatter or diffuse the light as it passes through, i.e., a parallel beam of light comes through in all directions are called translucent materials [Fig. 13.2(b)], That is why an object cannot be seen clearly through a translucent material. Examples of translucent materials are butter paper, a frosted glass, paper smeared with oil, and smoked glass.
Materials that completely block light are called opaque materials [Fig. 13.2(c)]. We will not be able to see through these materials at all. Examples of an opaque materials are metal, mud, cement, coal, and wood. A mirror is a very good example of opaque material. An ideal mirror does not let any light pass through it.
Propagation Of Light
Usually light travels in a straight line. When we want to represent the propagation of light with a diagram, we represent it with the help of rays and beams.
Ray A ray is a line with an arrow that shows the direction of propagation of light, and such a diagram is called a ray diagram.
Beam A group of light rays moving in an organized manner is called a beam of light.

The property of light to travel in straight lines explains many interesting phenomena related to light, like formation of shadows by opaque objects and formation of images in a pin-hole camera.
Shadows
An opaque object blocks the light falling on it. This creates an area of darkness on the side of the object away from the source of light. A translucent object also creates a faint area of darkness. An area of darkness formed by an opaque object obstructing light is called a shadow. The following three things are required for a shadow to form (Fig. 13.4):
- a source of light
- an opaque object
- a screen or irface behind the object.

A shadow will not form if any of these is absent. This explains why we cannot see a shadow in the dark. It is only when light rays are obstructed by an opaque object that we get a shadow of the object.
Let us perform an activity to learn about the characteristics of a shadow.
Characteristics of a Shadow:
A shadow has the following three characteristics:
- It is always black, regardless of the colour of the object used to make the shadow
- It only shows the shape or outline of the object and not the details.
- The size of a shadow varies depending on the distance between the object and the source of light, and the distance between the object and the screen.
Reflection Surfaces
We say light is reflected when it bounces off a surface. Reflection of light helps us to see most of the things around us.
Reflection of light by a surface depends on the nature of the surface. A rough and bumpy surface (also called an irregular surface) reflects a parallel beam of light incident upon it in different directions (Fig. 13.5). A good example of a rough surface is bark of a tree and blanket. This kind of reflection is called diffused reflection.
A smooth surface (a highly polished surface) reflects a parallel beam of light incident upon it in one direction. (Fig. 13.6). A good example of a smooth surface is a mirror. When you stand in front of a mirror, you can see yourself in the mirror. This is called your image.

A very interesting phenomenon occurs when an object forms an image by reflection. This is something all of us must have noticed while seeing ourselves in the mirror. When we lift our right hand, the image in the mirror appears to lift its left hand. This seeming left-right reversal is called lateral inversion.
An image is different from a shadow. Some of the differences between an image and a shadow are given in Table 13.1.

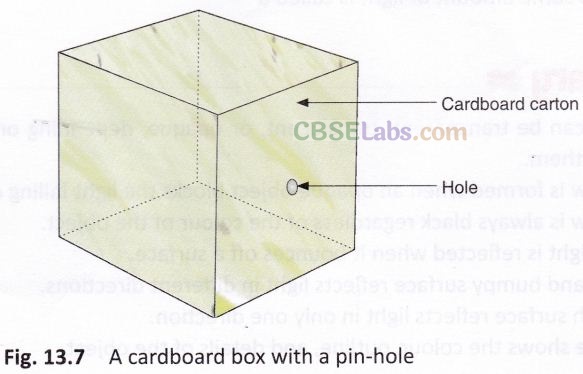
A Pin-hole Camera :
A pin-hole camera is just a box (Fig. 13.7) with a very tiny hole on one of its sides. Light falls on the hole, and an inverted image is formed on the side opposite to the hole. The human eye acts very much like a pin-hole camera.
Source of light: An object that gives out light (luminous object) is called a source of light.
Transparent material: A material that transmits all the light is called a transparent material.
Translucent material: A material that transmits some amount of light is called a translucent material.
Opaque material: A material that completely blocks the light is called an opaque material.
Shadow: An area of darkness formed by an opaque object obstructing light is called a shadow.
Objects can be transparent, translucent, or opaque, depending on how much light can pass through them.
A shadow is formed when an opaque object blocks the light falling on it.
A shadow is always black regardless of the colour of the object.
We say light is reflected when it bounces off a surface.
A rough and bumpy surface reflects light in different directions.
A smooth surface reflects light in only one direction.
An image shows the colour, outline, and details of the object.
We hope the given CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 11 Light, Shadows and Reflection Pdf free download will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 11 Light, Shadows and Reflection, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.