CBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 15 Light Pdf free download is part of Class 7 Science Notes for Quick Revision. Here we have given NCERT Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 15 Light.
CBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 15 Light
In this world, we usually see a variety of objects. Sometimes, we are unable to see anything in a dark room but on lighting up the room, we are able to see the things in the room. Since, it is an obvious question arising that what makes thing visible.
So, its answer is light. Light is a form of energy which enables us to see objects from where it comes or reflected. We can detect light with our eyes.
Light Travelling along a Straight Line
By seeing the phenomena around us like a beam of sunlight enters a room through a narrow opening or a hole and beams of light coming out from the headlamps of cars, scooters, engines, torch, etc.
From the above examples, we can conclude that light travels along a straight line.
Reflection of Light
There are some certain situations in which a mirror or shiny surfaces like stainless steel plate, shining steel spoon act as a mirror, can change the direction of light that falls on it. So, this process of change in direction of light by a mirror is called a reflection of light. The surface of the water can also act as a mirror and can also change the path of light and that is why we see the reflection of trees or buildings in the water.
Image of An Object
Generally, when we look into a mirror, then we see our face. Actually, what we see in the mirror it is exactly a reflection of our face, hence it is known as an image of our face. In this case, our face is the object and what we see in the mirror is its image. The image of our face seen in the mirror is formed where light rays, after reflection from the mirror, seems to originate from. The image of our face appears to be situated behind the mirror.
There are two types of images:
Real image: It is an image which can be obtained on a screen, e.g. the image formed on a cinema screen. When the light rays coming from an object actually meet at a point after reflection from the mirror, then it results in the formation of a real image.
Virtual image: It is an image which cannot be obtained on a screen, e.g. image formed by a plane mirror. When the light rays coming from an object appear to meet after reflection from the mirror, then it results in the formation of virtual image. It is not possible to form a virtual image on the screen because light rays actually do not pass the screen or cannot be received on a screen.
Characteristics of the Images Formed by a Plane Mirror
Now, we will describe the various characteristics of the images formed in a plane mirror by taking the example of the image of the candle.
(i) When we see the mirror, the image of candle appears to be formed behind the mirror.
(ii) Now, put a vertical screen behind the plane mirror (where the image of candle appears to be situated), then we will notice that the image of candle cannot be formed on the screen. Even if the screen is placed in front of the plane mirror, then the image of candle cannot be formed on the screen. Since, the image of candle formed in the plane mirror cannot be formed on a screen, which means that the image of candle in the plane mirror is a virtual image.
(iii) If we see the figure, then we will find that the length and breadth of the image of the candle and its flame to be the same as that of the original candle and its flame. The image of candle in the plane mirror is of the same size as the original candle.
(iv) Also if we see the figure, then we will find that the candle has a flame at the top and the image of candle also has a flame at the top. So, the top of the candle remains at the top in the image. In the same way, the bottom of candle remains at the bottom in an image. Such an image is called an erect image (or upright image). Therefore, the image formed by a plane mirror is erect.
Side Inversion (Right ⇔ Left)
When we see our image in a plane mirror, is it exactly like us? There is an interesting difference between us and our image. Let us find out this difference with the help of an example.
If we stand in front of a plane mirror and lift our right hand, then we see our image lift its left hand. And if we lift our left hand, then the image appears to lift its right hand.
This means that the right side of our body becomes the left side in the image while the left side of our body becomes the right side of the image. It appears as if our image has been ‘reversed side ways’ with respect to your body. The effect of reversing the sides of an object and its image is called lateral inversion.
So, we say that image formed in a plane mirror is laterally inverted.
So, we can understand why the word AMBULANCE is written as 3DMAJU9MA. When a driver of a vehicle ahead of an ambulance look in his/her rear view mirror, then he/she can read AMBULANCE written on it and give way to it. So, it is the duty of everyone of us to allow an ambulance to pass without blocking its way.
Spherical Mirrors
All the mirrors are not straight like plane mirror as some of the mirrors are curved mirror. There is a common example of a curved mirror, i.e. spherical mirror. A mirror whose reflecting surface is the part of a hollow sphere of glass is known as a spherical mirror.
Image Formed by Spherical Mirror
It is a fact that spherical mirrors form images of the objects placed in front of them. So, these images are formed, when light rays coming from the object fall on the mirror, get reflected and converge or diverge. We can use a spoon in order to understand the image formation by a spherical mirror.
The inside surface of a hollow sphere of glass is bent in or concave but the outside surface is bulging out or convex. So, the spherical mirrors are of two types:
- Concave mirror
- Convex mirror
e.g. A shining steel spoon represents both a convex mirror as well as a concave mirror. As the front side (or inner side) of a spoon is bent inward, so the front side of a shining spoon represents a concave mirror while the back side (or outer side) of a spoon is bulging outward, so the back side of a shining spoon represents a convex mirror as shown in figure.
Concave Mirror (Converging Mirror)
The mirror whose reflecting surface is concave (and polished surface is convex) is called a concave mirror.
The concave mirror reflects the parallel rays of light in such a way that after reflection, all the rays converge (or meet) at one point called focus in front of the mirror. Since a concave mirror converges a beam of parallel light rays. Therefore, a concave mirror is also known as a converging mirror.
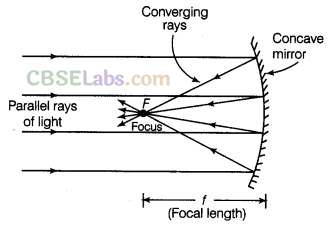
Image Formed by a Concave Mirror When the Object is Far Off
A concave mirror forms a real image of the sun. We can understand the formation of the image by a concave mirror when the object is far off by an activity.
Therefore, we can conclude that the image formed by a concave mirror is much smaller than the object (highly diminished) and real because it can be obtained on a sheet of paper (which is a kind of screen).
So, when an object is placed at a far off distance front a concave mirror, then image formed by a concave mirror is
- real
- inverted
- much smaller than the object.
Image Formed by a Concave Mirror When the Object is Placed Close to Concave Mirror
Let us perform an activity to understand the formation of image by a concave mirror when the object is placed close to the concave mirror.
Since the image can be observed only by looking into the concave mirror and cannot be formed on the screen, therefore, the image is virtual. If we look at the image in the concave mirror, we find it to be the same side up as the candle, so the image is erect. And if we compare the size of the candle and its image, then we will find that the image is larger than the candle. Therefore, the image is larger than the object (enlarged or magnified).
Hence, we can conclude that when an object is placed close to a concave mirror, the image formed by the concave mirror is
- virtual
- erect
- larger than the object (enlarged or magnified).
Uses of Concave Mirrors
- To see the large image of teeth of a patient, concave mirrors are used by the dentist.
- In torches, headlights of vehicles and searchlights to get a strong, straight beam of light, etc., concave mirrors are used as reflectors.
- To see a large image of the face, then concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors.
Convex Mirror (Diverging Mirror)
The mirror whose reflecting surface is bulging or convex (polished surface is concave) is called the convex mirror. After reflection from the convex mirror, the parallel rays of light are spreading out. When the parallel rays of light spread out, we can say that the rays of light are diverging.
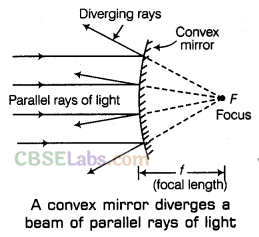
Now, we can say that a beam of parallel light rays diverges (spreads out) after reflection from a convex mirror.
Since a convex mirror diverges a beam of parallel light rays, therefore, it is also known as a diverging mirror.
Image Formed By a Convex Mirror
Let us perform an activity to understand the formation of an image by a convex mirror.
The image of the candle can be seen only by looking into the convex mirror and cannot be formed on a screen. It is a virtual image. If we look at the image in the convex mirror, we will find that it is the same side up as the candle. So, the image is erect. And if we compare the size of the candle and its image, the image appears to be smaller. Therefore, the image is smaller in size than the object (or diminished). Even if we change the distance of candle (object) from the convex mirror, we will notice that in every case, the image of the candle formed by the convex mirror remains virtual, erect and smaller in size than the candle.
So, we can conclude that whatever be the distance of the object from a convex mirror, the image formed by a convex mirror is always
- virtual
- erect and
- smaller than the object (or diminished).
Uses of Convex Mirrors
- To see the traffic at the rear side or backside on the road, convex mirrors are used as rear view mirrors or side view mirrors in vehicles such as cars, scooters, buses, etc.
- Big convex mirrors are used as shop security mirrors. By installing a convex mirror in the shop, the shop owner can keep an eye on the customers.
Image Formed by Lenses
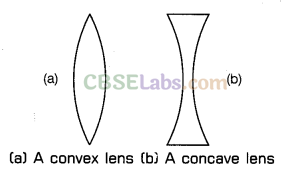
Since a lens is a piece of transparent glass bound by the two spherical surfaces. Lenses are transparent so that light can pass through lenses. Lenses are of two types:
- Convex lens
- Concave lens
Get some lens and try to touch them, we will find that some are thicker in the middle than at the edges and some are thinner in the middle than at the edge.
Convex Lens (Converging Lens)
The convex lens is the lens which is thicker in the middle than at the edges. A beam of parallel rays of light falls on a convex lens from the left side. After passing through the convex lens, the beam of parallel rays of light converges at a point as shown in the figure given below. Hence, a convex lens is a converging lens.
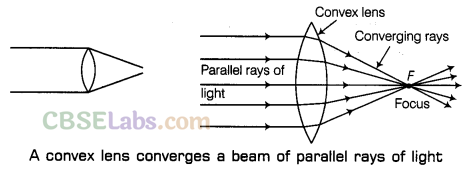
Image Formed by a Convex Lens
The nature and size of the image formed by a convex lens depend on the distance of the object from the convex lens.
Thus, we can conclude that when an object is placed at a far off distance from a convex lens, then the image formed by the convex lens is real, inverted and much smaller than the object (or highly diminished).
Now, change the distance of the candle from the lens and try to obtain the image of the candle flame every time on the screen by moving it. So, is it possible to get in any position of the object for which image was erect and, magnified? Yes, it is possible when the candle is placed very close to the convex lens.
Uses of Convex Lenses
- Convex lenses are used as a magnifying glass.
- In the manufacturing of spectacles, camera, microscope, telescope and binoculars, convex lenses are used.
Concave Lens (Diverging Lens)
A concave lens is a lens which is thinner in the middle than at the edge. A parallel beam of light falls on a concave lens as shown in the figure. After passing through the concave lens, the rays of light are diverging (or spreading out).
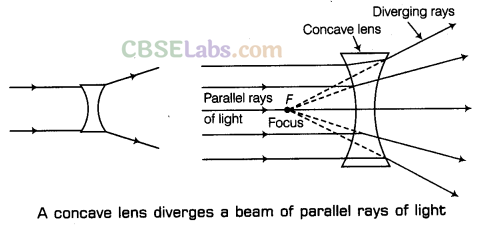
Since a concave lens diverges light rays falling on it, therefore, it is also called a diverging lens.
Image Formed by a Concave Lens
In the case of a convex lens, we have studied that the nature of image formed depends on the distance of the object from the convex lens. But, this is not followed in the case of a concave lens.
Let us perform an activity to understand the formation of an image by a concave lens.
Uses of Concave Lenses
- In order to see the image of the person standing outside, concave lenses are used in the peepholes in the door of hotel rooms.
- Concave lenses are used in making spectacles.
Sunlight: White or Coloured
We might have noticed a rainbow which usually appears after the rain when the sun is low in the sky. An arc of seven colours seen in the sky is known as the rainbow. The seven colours of a rainbow are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. We might also have seen that when we blow soap bubbles, they appear colourful. Similarly, when light is reflecting from the surface of a Compact Disc (CD), we can see many colours. The rainbow is produced by the dispersion of sunlight by tiny raindrops suspended in the atmosphere.
Dispersion of Light
In the year 1665, Newton discovered by his experiments with glass prisms that white light (like sunlight) consists of a mixture of lights of seven colours. Newton found that if a beam of white light is passed through a glass prism, then the white light splits to form a band of seven colours on a white screen. The band of seven colours formed on a white screen, when a beam of white light is passed through a glass prism, is known as a spectrum of white light. The seven colours of the spectrum are Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo and Violet.
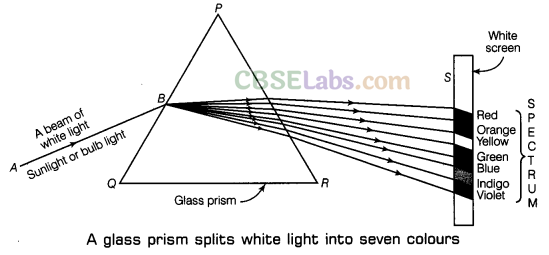
So, dispersion of light is the phenomenon of splitting up of white light into seven colours on passing through a transparent medium like a glass prism. The formation of a spectrum of seven colours indicates that white light is a mixture of seven colours. White light can be sunlight. So, now we can say that sunlight consists of seven colours.
We can mix these colours to get white light. This can be done by using Newton’s disc, let us try this.
We hope the given CBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 15 Light Pdf free download will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 15 Light, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.