Lakhmir Singh Biology Class 10 Solutions How do Organisms Reproduce
Lakhmir Singh Biology Class 10 Solutions Page No:141
Question 1:
Which life process ensures that a plant or animal species will not disappear from this earth ?
Solution :
Reproduction.
Question 2:
What is the name of the reproductive process :
(a) which involves two parents ?
(b) which involves only one parent ?
Solution :
(a) Sexual reproduction.
(b) Asexual reproduction.
Question 3:
State whether the following statement is true or false :
Spores produced by the bread mould plant are actually its seeds.
Solution :
False.
Question 4:
Most of the plants reproduce by sexual method. Name two plants which can reproduce asexually.
Solution :
Ferns and mosses.
Question 5:
Which type of reproduction :
(a) involves gametes ? .
(b) does not involve gametes ?
Solution :
(a) Sexual reproduction.
(b) Asexual reproduction.
Question 6:
State whether human beings reproduce by sexual method or asexual method.
Solution :
Sexual method.
Question 7:
(a) Name two animals which reproduce sexually.
(b) Name two animals which reproduce asexually.
Solution :
(a) Dogs and cows.
(b) Amoeba and Hydra.
Question 8:
Name one organism which reproduces by spore formation.’
Solution :
Bread mould (Rhizopus fungus).
Question 9:
Name the method by which Paramecium reproduces. Is this method sexual or asexual ?
Solution :
Binary fission; Asexual method.
Question 10:
Name two plants :
(a) which can be grown from their broken stems.
(b) which can be grown from their leaves.
Solution :
(a) Bryophyllum and money plant.
(b) Bryophyllum and Begonia
Question 11:
Name the asexual method of reproduction in yeast.
Solution :
Budding.
Question 12:
Name the asexual method of reproduction in
(a) Hydra, and
(b) Plasmodium.
Solution :
(a) Budding and regeneration.
(b) Multiple fission.
Question 13:
What is the name of asexual reproduction method in :
(i) Spirogyra, and
(ii) Leishmania ?
Solution :
(i) Fragmentation.
(ii) Binary fission.
Question 14:
Name the artificial propagation mehod used for the propagation of
(a) rose plants, and
(b) apple trees.
Solution :
(a) Cutting.
(b) Grafting.
Question 15:
Which artificial propagation method is used for the production of jasmine plants ?
Solution :
Layering.
Question 16:
Name the natural method by which strawberry plants are propagated.
Solution :
Layering.
Question 17:
Name two plants which are propagated by layering method.
Solution :
Hibiscus and Bougainvillea.
Question 18:
Name any two plants which are propagated by cuttings method.
Solution :
Rose and grapes.
Question 19:
Write down the different methods of asexual reproduction.
Solution :
The different methods of asexual reproduction are:
(i) Fission
(ii) Budding.
(iii) Spore formation.
(iv) Regeneration.
(v) Fragmentation.
(vi) Vegetative propagation.
Question 20:
Why are budding, fragmentation and regeneration, all considered to be asexual type of reproduction ?
Solution :
Because all these methods involves a single parent for the production of a new organism, without the involvement of gametes.
Question 21:
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words :
(a) The process of………ensures continuity of life on earth.
(b) Plasmodium reproduces by the process of……..fission whereas Paramecium reproduces by the process of……….fission.
(c) Rose plants and sugar cane crop are usually grown by the………..method.
(d) Vegetative reproduction of potato plants is done by using………..
(e) Strawberry plants are propagated by the natural………..method.
Solution :
(a) Reproduction.
(b) Multiple; Binary.
(c) Cutting.
(d) Tubers.
(e) Layering.
Question 22:
(a) What is the basic difference between asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction ?
(b) Which of the following organisms reproduce by sexual method and which by asexual method ?
Amoeba, Cats, Humans, Hydra, Birds
Solution :
(a)
Asexual Reproduction
(i) The offspring arises from a single parent.
(ii) The production of new organism does not involve gametes
Example:- Amoeba, Yeast.
Sexual Reproduction
(i) The offspring arises from two parents of different sexes.
(ii) The production of new organisms involves the use of gametes.
Example:- Fish, Frogs, etc.
(b)
(i) Sexual Method: Cats, Humans, birds.
(ii) Asexual method: Amoeba, Hydra.
Question 23:
(a) What is meant by regeneration ? Name two animals which can regenerate fully from their cut body
parts.
(b) Explain why, more complex multicellular organisms cannot give rise to new organisms through regeneration.
Solution :
(a) The process of getting back a full organism from its body parts is called regeneration. The two animals which can regenerate fully from the cut body parts are ? Planaria and Hydra.(b)In complex multicellular organisms, specialized cells makeup tissues; tissues makeup organs; organs makeup organs systems and finally organs systems makeup organisms. Since complex Multi cellular organisms have a high degree of organisation in their body, they cannot be reproduced from their cut body parts by the process of regeneration.
Question 24:
Explain vegetative propagation with the help of two examples. List two advantages of vegetative propagation.
Solution :
In vegetative propagation, new plants are obtained from the parts of old plants (stems, roots and leaves), without the help of reproductive organs. Example ? Bryophyllum plant reproduces from its leaves and money plant grows from its stem. Advantages of vegetative propagation:-
(i) Plants grow faster by the process of vegetative propagation.
(ii) They need less care.
Question 25:
(a) What is meant by the term ‘artificial propagation of plants’ ?
(b) Name three common methods which are used for the artificial propagation of plants.
(c) Name two plants which are usually propagated by artificial propagation methods. Name the method of artificial propagation used in each case.
Solution :
(a) The process of growing many plants from one plant by man-made methods is called artificial propagation of plants.
(b) The methods used for artificial propagation of plants are:
(i) Cutting
(ii) Layering and
(iii) Grafting
(c)
(i) Rose grows by means of cutting.
(ii) Jasmine grows by layering
Lakhmir Singh Biology Class 10 Solutions Page No:142
Question 26:
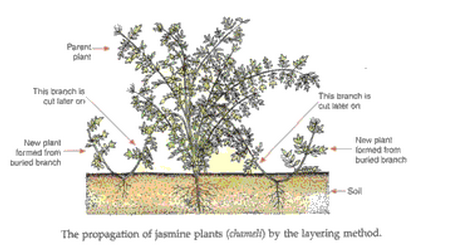
Describe the layering method for the artificial propagation of plants. Illustrate your answer with the help of a labelled diagram. Name any five plants which are propagated by the layering method.
Solution :
Layering – In this method, a branch of the plant is pulled towards the ground and the part of it is covered with moist soil leaving the tip of the branch exposed above the ground. After some time, new roots develop from the part of the branch buried in the soil. The branch is then cut off from the parent plant. The part of the plant which has developed roots grows to become a new plant. The layering method is used for the propagation of plants like Jasmine, Strawberry, Raspberry, Lemon and Guava.
Question 27:
(a) What is meant by the term ‘fission’ as used in biology ?
(b) How does binary fission differ from multiple fission ?
(c) Name one organism which reproduces by binary fission and another which reproduces by multiple fission.
(d) State whether the above named organisms are animals or plants.
Solution :
(a) Fission means the splitting of an organism into two new organisms.
(b) Binary Fission
(i) In binary fission, the parent organism splits to form two new organisms.
(ii) It occurs during normal conditions.
Multiple Fission
(i) In multiple fission, the parent organisms splits to form many new organisms.
(ii)It takes place during unfavourable conditions.
(c) Amoeba reproduces by binary fission and Plasmodium reproduces by multiple fission.
(d) Both the above mentioned organisms are animals.
Question 28:
(a) Can you consider cell division as a type of reproduction in unicellular organisms ? Give reason.
(b) What is a clone ? Why do offsprings formed by asexual reproduction exhibit remarkable similarity ?
Solution :
(a) Yes, because it leads to the formation two daughter cells.
(b) The new organisms produced by one parent through asexual reproduction (which are genetically identical to the parent) are called clones. The offspring’s formed by asexual reproduction exhibit remarkably similarity because the replication of DNA in the cells is done by certain biochemical reactions which synthesise more of genetic material. When the DNA already present in the nucleus of the parent cell is replicated by making more DNA at the time of asexual reproduction then slight variations come in the two copies formed. Due to this the two DNA molecules formed will be similar but not identical.
Question 29:
(a) The yeast cells fail to multiply in water but they multiply rapidly in sugar solution. Give one reason for
it.
(b) Why does bread mould grow profusely on a moist slice of bread but not on a dry slice of bread ?
Solution :
(a) Water does not provide any energy to the yeast cells. So, yeast cells fail to multiply in water due to inadequate energy in its cells. Sugar provides energy to them to carry out reproduction by multiplying rapidly.
(b) Moisture is necessary for the growth of bread mould. The moist slice of bread provides both moisture and nutrients due to which bread mould grows profusely. On the other hand, the dry slice of bread provides nutrients but no moisture. So, in the absence of moisture, bread mould does not grow on the dry slice of bread.
Question 30:
(a) What is a tuber ? Name one stem tuber and one root tuber.
(b) What is name of the organ of propagation present in a tuber ?
(c) Name one commonly used vegetable which is propagated by using tubers.
Solution :
(a) A tuber is the thickened, underground stem (or root) of a plant which is swollen with stored food. Stem tuber: Potato; Root tuber: Sweet potato.
(b) Buds.
(c) Potatoes.
Question 31:
(a) What is meant by vegetative propagation ?
(b) Vegetative propagation involves the growth and development of ‘something’ present in the old part of the plant to form a new plant. What is this ‘something’ ?
(c) Why do green grass plants spring up in dry fields on their own after the rains ?
Solution :
(a) Vegetative propagation is an asexual method of reproduction in which new plants are obtained from the parts of old plants (like stems, roots and leaves) without the help of any reproductive organs.
(b) Buds.
(c) The fields have dry stems of the old grass plants all over them. These dry stems have buds which are in the inactive state. By getting rainwater, the buds present on the dry grass stems get activated and grow to produce new grass plants.
Question 32:
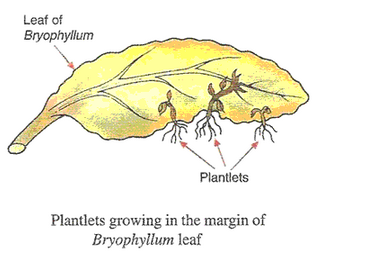
(a) Explain how, new Bryophyllum plants can be produced from the leaves of the old plant ? Illustrate your
answer with the help of a labelled diagram.
(b) How can you grow money plant bv vegetative propagation ?
Solution :
(a) Bryophyllum can be reproduced by vegetative propagation by using either a piece of its stem or leaves. The leaves of a Bryophyllum plant have special buds in their margins which may get detached from the leaves, fall to the ground and then grow to produce a new plant.
(b) Money plant can be grown by vegetative propagation by using a piece of its stem which has at least one leaf on it. One end of the stem is dipped in water and after a few days new roots appear at the point where the leaf was attached. This piece of stem grows gradually into a new money plant.
Question 33:
Match the organisms given in column I with the methods of reproduction/propagation given in column II:

Solution :
(i) – (j)
(ii) – (g)
(iii) – (f)
(iv) – (k)
(v) – (b)
(vi) – (h)
(vii) – (a)
(viii) – (d)
(ix) – (c)
(x) – (e)
(xi) – (i)
(xii) – (i)
Question 34:
(a) What is meant by reproduction ?
(b) What are the two general methods of reproduction in organisms ?
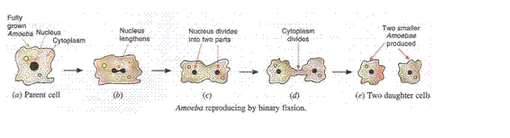
(c) How does an Amoeba reproduce ? Describe the process of reproduction in Amoeba with the help of labelled diagrams of different stages in its reproduction process.
(d) What is the name of the process by which Amoeba reproduces ?
(e) Name two organisms which reproduce by the same asexual process as that of Amoeba.
Solution :
(a) Theproduction of new organisms from the existing organisms of the same species is known as reproduction.
(b) The two methods of reproduction in living organisms are asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
(c) Amoeba reproduces by binary fission by dividing its body into two parts. When the amoeba cell reaches its maximum size, the nucleus of amoeba lengthens and divides into two parts. After that the cytoplasm of amoeba divides into two parts, one part around each nucleus. In this way one parent amoeba divides to form two smaller amoebae.
(d) Binary fission.
(e) Paramecium and Leishmania.
Question 35:
(a) What is the difference between the two asexual methods of reproduction : fission and fragmentation ?
(b) Name one organism which reproduces by fission and another which reproduces by fragmentation.
(c) What is meant by multiple fission ? Name one organism which reproduces by the process of multiple fission.
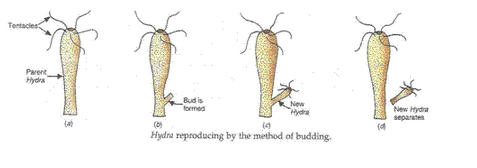
(d) Describe the process of reproduction in Hydra with the help of labelled diagrams. What is the name of this process of reproduction ?
(e) Name one unicellular organism which reproduces by the same asexual process as Hydra.
Solution :
(a)
Fission
(i) It is a process in which an organism splits to form two or more new organisms.
(ii) Fission occurs in unicellular organisms.
Example : Amoeba.
Fragmentation
(i) It is a process in which the body breaks up into two or more pieces on maturing, each of which subsequently grows to form a complete new organism.
(ii) It takes place in multicellular organisms.
Example : Spirogyra.
(b) Amoeba reproduces by fission and spirogyra reproduces by fragmentation.
(c) Multiple fission is a process in which a parent organism splits to form many new organisms at the same time. Plasmodium reproduces by multiple fission.
(d) Hydra reproduces by budding. In hydra, first a small outgrowth called bud is formed on the side of its body by repeated mitotic divisions of its cells. This bud then grows gradually to form a small hydra by developing a mouth and tentacles. The tiny new hydra detaches itself from the parent body and develops into a separate organism.
(e) Yeast.
Lakhmir Singh Biology Class 10 Solutions Page No:143
Question 36:
(a) Name the method by which bread mould (Rhizopus fungus) reproduces. Is this method sexual or asexual ?
(b) What is yeast ? Describe the process of reproduction in yeast with the help of labelled diagrams.
(c) Name a tiny fresh-water animal which reproduces by the same method as that of yeast ? What is this method known as ?
(d) Name two marine organisms which also reproduce by the same method as yeast but form colonies.
Solution :
(a) Spore formation; asexual reproduction.
(b) Yeast is tiny, unicellular non green plant which reproduces by budding. In yeast, first a bud appears on the outside of the cell wall. The nucleus of the parent yeast cell divides into two parts and one part of the nucleus moves into the bud. Ultimately, the bud separates off from the parent yeast cell and forms a new yeast cell.
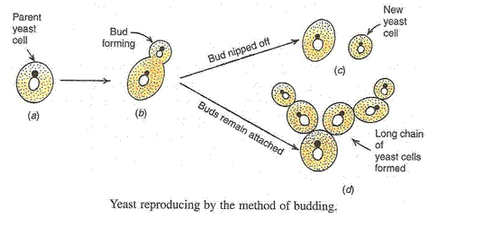
(c) Hydra; Budding.
(d) Sponge and corals.
Question 37:
(a) What is meant by ‘grafting’ as a means of propagation in plants ?
(b) Define ‘stock’ and ‘scion’.
(c) Describe the grafting method for the artificial propagation of plants with the help of labelled diagrams.
(d) Name two fruit trees which are usually propagated by grafting method.
(e) State two advantages of grafting method of artificial propagation of plants.
(f) What is the difference between the cuttings method and grafting method for the artificial propagation of plants ?
Solution :
(a) Grafting – It is a method in which the cut stems of two different plants (one with roots and other without roots) are joined together in such a way that the stems join and grow as a single plant.
(b) The cut stem of a plant having roots is called stock and the cut stem of the other plant without roots is called scion.
(c) In grafting, two plants are chosen which are used as scion and stock. First the stem is removed from the plant chosen to be made scion by giving a slanting cut. The scion is placed over the stock and is fitted together by binding tightly by a piece of cloth or plastic sheet. The cut soon heals and the stock and scion of two plants grow together to become one plant.
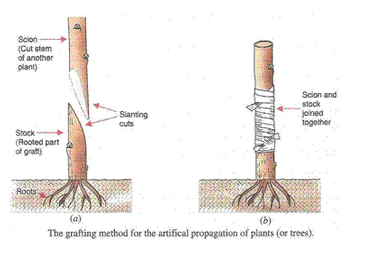
(d) Banana and pineapple.
(e) Advantages of grafting method:
(i) It enables us to combine the most desirable characteristics of the two plants in its flowers and fruits.
(ii) It can be used to produce varieties of seedless fruits.(f)
Cutting
Grafting
(i) A small part of the plant which is removed by making a cut with a sharp knife is called cutting.
(ii) The new plant formed is exactly similar to the parent plant.
(i) It is a method in which the cut stems of two different plants (one with roots and other without roots) are joined together in such a way that the stems join and grow as a single plant.
(ii) The new plant produced has the characteristics of both the parent plants.
Question 38:
(a) What is tissue culture ?
(b) Name any four types of ornamental plants which are being produced by tissue culture technique.
(c) What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction ? Explain with an example.
(d) How does reproduction help in providing stability to populations of species ?
(e) Why is variation during reproduction beneficial to the species but not necessarily for the individual ?
Solution :
(a) The production of new plants from a small piece of plant tissue (or cells) removed from the growing tips of a plant in a suitable growth medium is called tissue culture.
(b) Orchids, dahlia, carnation, chrysanthemum.
(c)
(i) The chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell contains information for the inheritance of features from the parents to the next generation in the form of DNA molecules so the characteristics of a parent organism are transmitted to their offsprings.
(ii) When the DNA already present in the nucleus of a parent cell is copied by making more of DNA by certain biochemical reactions, then slight variations come in the two copies formed. Thus, variations are produced in the offspring’s during reproduction which form the basis of evolution. Example: Offspring’s produced by asexual reproduction have slight variations from their parents.
(d) The process of reproduction introduces some variations in the individual organisms of a species which enables them to survive even in adverse environmental conditions such as excessive heat or cold, etc. In this way, the introduction of variations during reproduction provides stability to the populations of various species.
(e) Variation is useful for the survival of species even in adverse environmental conditions. This happens as follows: There may be some drastic changes like excessive heat or cold etc in the habitat of a species of organisms. If all the organisms of a population living in that habitat are exactly identical, then there is a danger that all of them may die and no one would survive under these conditions. This will eliminate the species from that habitat completely however, if some variations are present in some individual organisms to tolerate these drastic changes then there is a chance for them to survive and flourish even in adverse environment. Example: Certain bacteria living in temperate water – If the temperature of water increases too much due to global warming most of them will not be able to tolerate excessive heat and would die however, if there are bacteria with variation then there is a chance for them to survive.
Question 39:
(a) What is a ‘cutting’ in respect of plants for propagation purposes ?
(b) What care should be taken while making a cutting from a plant ?
(c) Describe the cuttings method for the artificial propagation of plants. Illustrate your answer with the help of labelled diagrams.
(d) Name any two plants which are usually propagated by the cuttings method.
Solution :
(a) A small part of the plant which is removed by making a cut with a sharp knife is called cutting.
(b) While making a cutting, care should be taken to see that there are some buds on it.
(c) In this method, a cutting of the parent plant having some buds on it is taken and its lower part is buried in the moist soil. After few days, the cutting develops roots and shoot, and grows into a new plant which is exactly similar to the parent plant.
(d) Rose and Bougainvillea.
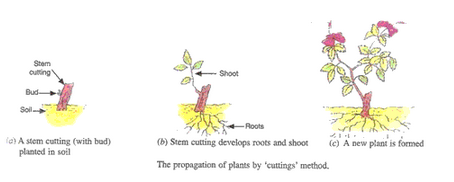
Lakhmir Singh Biology Class 10 Solutions Page No:168
Question 1:
Where are a plant’s sex organs located ?
Solution :
In flowers.
Question 2:
What is the function of a flower ?
Solution :
The function of a flower is to make male and female gametes and to ensure that fertilisation will take place to make new seeds for the reproduction of plant.
Question 3:
What are the reproductive organs in a flower ?
Solution :
Stamen and carpel.
Question 4:
What is the name of :
(a) male part of a flower ?
(b) female part of a flower ?
Solution :
(i) Stamen.
(ii) Carpel.
Question 5:
What is the name of female organ of a flower (other than carpel) ?
Solution :
Pistil.
Question 6:
What is the other name of sex cells ?
Solution :
Gametes.
Question 7:
What is the name of sex cells (other than gametes) ?
Solution :
Germ cells.
Question 8:
Name the male and female gametes in animals.
Solution :
The male gamete in animals is sperm and the female gamete is ovum (egg).
Question 9:
Where is the male gamete formed :
(i) in humans ?
(ii) in flowering plants ?
Solution :
(i) Testes.
(ii) Anther.
Question 10:
Where is the female gamete formed :
(i) in humans ?
(ii) in flowering plants ?
Solution :
(i) Ovary.
(ii) Ovary.
Question 11:
Name two animals which undergo external fertilisation and two animals which undergo internal fertilisation ?
Solution :
(i) External fertilisation: Frog and fish
(ii) Internal fertilisation: Dogs and cows.
Question 12:
Define sexual reproduction.
Solution :
The reproduction which takes place by the combination of special reproductive cells called ‘sex cells’ is called sexual reproduction.
Question 13:
Do all organisms give birth to individuals like humans ?
Solution :
No. All organisms do not give birth to individuals like humans.
Question 14:
Write the full forms of the following as they occur in biology :
(i) STD
(ii) AIDS
(iii) HIV
Solution :
(i) STD – Sexually Transmitted Diseases.
(ii) AIDS – Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
(iii) HIV – Human Immunodeficiency virus.
Question 15:
What is the causative organism for the following diseases ?
(i) Gonorrhoea
(ii) Syphilis
(iii) AIDS
Solution :
(i) Bacteria.
(ii) Bacteria.
(iii) Virus.
Question 16:
What are the organs in humans which produce the gametes ?
Solution :
Testes in males and ovaries in females.
Question 17:
(a) What are the male sex cells in humans called ?
(b) Name the organ which produces male sex cells.
Solution :
(a) Sperms.
(b) Testes.
Question 18:
(a) What are the female sex cells in humans called ?
(b) Name the organ which produces female sex cells.
Solution :
(a) Eggs.
(b) Ovaries.
Question 19:
Which part of the human body :
(a) produces sperms ?
(b) produces ova ?
(c) passes Sperms from a man to a woman ?
Solution :
(a) Testes.
(b) Ovaries.
(c) Penis.
Question 20:
(a) What do the testes in a man produce ?
(b) What do the ovaries in a woman produce ?
Solution :
(a) Sperms.
(b) Ova (eggs).
Question 21:
(a) Where in the human body does an ovum get fertilised ?
(b) Where does a fertilised ovum develop into a baby in the human body ?
Solution :
(a) Oviduct (fallopian tube).
(b) Uterus (womb).
Question 22:
Name the liquid that contains sperms
Solution :
Semen.
Question 23:
What is the name of the process in which thickened uterus lining alongwith blood vessels is removed from the body of a human female through vaginal bleeding
Solution :
Menstruation.
Question 24:
(a) For how much time does menstruation last in human females (or women) ?
(b) What is the frequency of menstrua] cycle in human females (or women) ?
Solution :
(a) 3 to 5 days.
(b) Once every 28 days.
Question 25:
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words :
(a) Pollen grains contain………… gametes of a plant.
(b) Ovules contain………… gametes of a plant.
(c) The ovary of a flower becomes………… after fertilisation.
(d) The ovule becomes a……. after fertilisation.
(e) Flowering plants reproduce by…………. method of reproduction.
(f) The female organ of reproduction in the flower is the………………
(g) The male organ of reproduction in the flower is the……………….
(h) The name of the structure in the flower in which the male gamete is formed is…………
(i) The………. at the base of the carpel contains egg cells.
(j) The term used to refer to the transfer of pollen from the stamen of one flower to the carpel of another
flower of the same species is………….
(k) The cells involved in sexual reproduction are called……………
(l) Fusion of gametes gives rise to a single cell called …………..
(m) The process of fusion of gametes is called…………
(n) A multicellular animal starts its life from a……….. through sexual reproduction.
(o) The union of a sperm nucleus with an egg nucleus is known as…………… and results in a……………. egg.
(p) The menstrual cycle is controlled by……………..
Solution :
(a) Male.
(b) Female.
(c) Fruit.
(d) Seed.
(e) Sexual.
(f) Carpel.
(g) Stamen.
(h) Anther.
(i) Ovary.
(j) Cross pollination.
(k) Gametes.
(l) Zygote.
(m) Fertilisation.
(n) Single cell (zygote).
(o) Fertilisation; fertilised.
(p) Hormones.
Lakhmir Singh Biology Class 10 Solutions Page No:169
Question 26:
(a) What are gametes ?
(b) In which sort of reproduction are gametes involved ?
(c) What is formed when two gametes fuse ?
(d) What is this act of fusion called ?
Solution :
(a) The cells involved in sexual reproduction are called gametes. (b) Sexual reproduction. (c) Zygote is formed when two gametes fuse. (d) Fertilisation.
Question 27:
(a) Write the names of (a) male sex hormone, and (b) female sex hormones.
(b) What name is given to the fusion of sperm and ovum ?
(c) Name the tissue through which the foetus gets all the requirements from the mother’s body.
Solution :
(a)
(i) Testosterone.
(ii) Oestrogen and Progesterone.
(b) Fertilisation.
(c) Placenta.
Question 28:
(a) Draw a neat sketch of the stamen of a flower. Mark in it filament and anther.
(b) Draw a neat sketch of the carpel of a flower. Mark in it stigma, style and ovary.
(c) What is made in (i) anther, and (ii) ovary, of a flower ?
Solution :
(a)
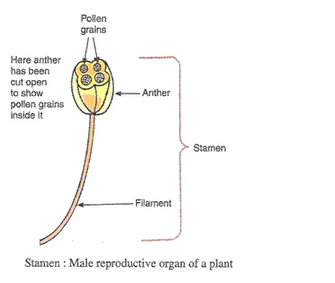
(b)
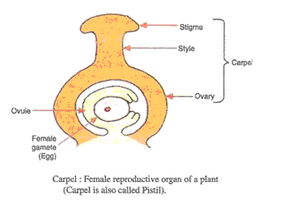
(c)
(i)Male gametes(insides pollen).
(ii) Female gametes (inside ovum).
Question 29:
(a) Explain the terms ‘self pollination’ and ‘cross-pollination’ ?
(b) How do the insects help in cross-pollination ?
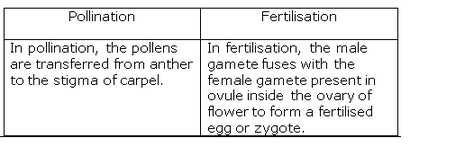
(c) How is the process of pollination different from fertilization ?
Solution :
(a)
(i) Self pollination ? When the pollen grains from the anther of a flower are transferred to the stigma of the same flower (or another flower on the same plant), it is called self pollination.
(ii) When the pollen grains from the anther of a flower on one plant are transferred to the stigma of a flower on another similar plant, it is called cross pollination.
(b) When an insect sits on the flower of a plant for sucking nectar, then the pollen grains from the anther of this flower sticks to its body. And when this insect sits on another flower of another similar plant, then the pollen grains sticking to its body are transferred to the stigma of this second flower. In this way, the insect transfers the pollen grains from the anther of flower in one plant to the stigma of flower in another plant and causes cross pollination.
(c)
Question 30:
(a) Explain the term ‘fertilisation’.
(b) Give some examples of different modes of fertilisation in nature ?
(c) What type of fertilisation takes place in
(i) fish, and
(ii) birds ?
Solution :
(a) The fusion of male and female gamete to form zygote during sexual reproduction is called fertilisation.
(b) Internal and external fertilisation.
(c)
(i) External fertilisation.
(ii) Internal fertilisation.
Question 31:
(a) What are the male and female gonads in human beings ? Mention their functions.
(b) State the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction.
Solution :
(a) In males, the gonads are testes. The function of testes is to make sex cells called sperms and to make sex hormone called testosterone. In females, the gonads are ovaries. The function of the ovaries is to make mature female sex cell called ova or egg and also to make female sex hormones called oestrogen and progesterone.
(b) Advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction:
(i) Sexual reproduction combines DNA from two individuals (male and female) due to which the offspring has lot of variations. On the other hand, in asexual reproduction, only the DNA of one individual is copied due to which the variations in the offspring are extremely small.
(ii)Due to lot of variations, sexual reproduction allows species to change to more advanced forms from one generation to the next and speed up evolution whereas asexual reproduction does not allow a species to change much from one generation to the next and hence, evolution becomes very slow.
Question 32:
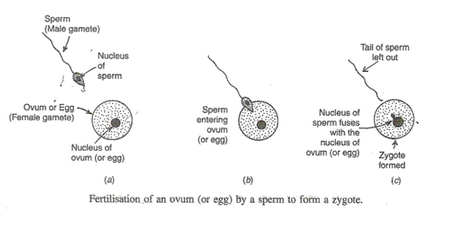
Describe the various steps involved in the sexual reproduction in animals. Draw labelled diagrams to show the fertilisation of an ovum (or egg) by a sperm to form a zygote.
Solution :
The sexual reproduction in animals takes place in the following steps:
(i) The male parent produces male gamete called sperms. The sperm is a small cell with a long tail (flagellum) for movement.
(ii) The female parent produces female gamete called ova which is much bigger cell than the sperm, having a lot of cytoplasm.
(iii) The sperm enters into the ovum and fuses with it to form a new cell called zygote and this process is called fertilisation.
(iv) The zygote then divides again and again to form a large number of cells and ultimately the zygote grows and develops to form a baby.
Question 33:
Why does menstruation occur ? Describe the menstrual cycle in human females (or women).
Solution :
(a) Since the ovary of female release one egg every month, therefore, the uterus also prepares every month to receive a fertilised egg. The inner lining of the uterus becomes soft and thick with lots of blood capillaries in it. This preparation is necessary as in case the egg is fertilised by the sperm, it helps to keep the egg and nourish it. If however, the egg is not fertilised, then the thick lining of the uterus is not required and the uterus lining breaks down and comes out through the vagina in the form of blood and mucous. This is called menstruation.
(b) Menstruation cycle in females:
(i) When a girl reaches puberty at the age of 10 ? 12 years, the sex hormones released it her blood cause some of the ova in the ovaries to become mature.
(ii) Usually one mature egg is released from the ovary into the oviduct once every 28 days. This is called ovulation.
(iii) Before ovulation, the inner lining of the uterus becomes thick and spongy, and full of blood capillaries, and prepares itself to receive the fertilised egg.
(iv) If the ovum does not get fertilised, then the thick and soft inner lining of the uterus is no longer needed and hence it breaks and the dead ovum comes out from vagina in the form of bleeding called menstruation.
(v) Menstruation usually occurs 14 days after ovulation and usually lasts for 3 to 5 days.
(vi) After menstruation is over, the inner lining of the uterus starts building up again so that it becomes ready to receive the next ovum in case it gets fertilised.
(vii) If the ovum does not get fertilised even now, then the menstruation takes place again and this cycle goes on repeating.
Question 34:
(a) Write the various steps involved in the sexual reproduction in plants.
(b) Name two plants which reproduce by sexual reproduction method and two plants which reproduce by asexual reproduction methods.
Solution :
(a) The sexual reproduction in plants takes place in the following steps:
(i) The male organ of flower called ‘stamen’ makes the male gametes of the flower. These male gametes are present in pollen grains.
(ii) The female organ of a flower called ‘carpel’ makes the female gametes present in the ovules and are called ova or egg.
(iii) The male gametes present in the pollen grains fertilises the female gametes or egg cells present in the ovules.
(iv) The fertilised egg cells grow within ovules and become seeds.
(v) The seeds produce new plants on germination.
(b) Sexual reproduction: Wheat plant and sunflower plant; Asexual reproduction: Ferns and mosses.
Question 35:
(a) What type of plants reproduce by sexual reproduction method ?
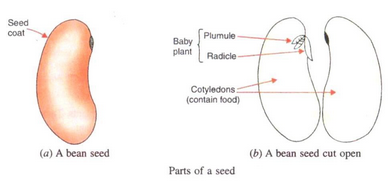
(b) What is a seed ? What are the parts of a seed ? Explain with the help of a labelled diagram.
Solution :
(a) Flowering plants.
(b) A seed is the reproductive unit of a plant (which can be used to grow a new plant). Plumule, radical and cotyledon are the parts of seed.
Question 36:
(a) What is puberty ? Who attains puberty at an earlier age in human beings : male or female (boy or girl) ?
(b) Mention two functions each of
(i) human testes, and
(ii) human ovaries.
Solution :
(a) The age at which the sex hormones begin to be produced and the boy and girl become sexually mature (able to reproduce) is called puberty. Females attain puberty at an age of 10-12 years.
(b)
(i) The function of testes is to make sex cells called sperms and to make sex hormone called testosterone.
(ii) The function of the ovaries is to make mature female sex cell called ova or egg and also to make female sex hormones called oestrogen and progesterone.
Question 37:
(a) What is gestation period ? How much is the gestation period in humans ?
(b) Name one method of contraception which also protects against sexually transmitted diseases.
(c) Name one sexually transmitted disease for which no definite cure has been found so far. What is the causative organism of this disease ?
Solution :
(a) The time period from the fertilisation up to the birth of a baby is called gestation. The average gestation period in humans is about 9 months (about 38 weeks).
(b) Condoms.
(c) AIDS has no cure. Its causative organism is HIV (human Immunodeficiency Virus).
Question 38:
What are the three types of methods used for birth control (or regulating child birth) ? Give one example of each type.
Solution :
(a) Barrier method – Condom.
(b) Chemical method – Oral pills.
(c) Surgical method – Vasectomy.
Question 39:
(a) What is the name of surgical method of birth control in human males in which the sperm ducts are cut and ligated (tied) at both ends ?
(b) What is the name of surgical method of birth control in human females in which the oviducts are cut and ligated (tied) at both ends ?
(c) Name the contraceptive device used by the human males which acts as a sheath over the male organ and traps the sperms in it.
(d) Name the contraceptive device used by human females which is put over the cervix.
Solution :
(a) Vasectomy.
(b) Tubectomy.
(c) Condom.
(d) Diaphragm.
Lakhmir Singh Biology Class 10 Solutions Page No:170
Question 40:
(a) Describe the surgical methods of birth control (i) for men, and (ii) for women.
(b) Name two devices used in the barrier method of birth control.
Solution :
(a)
(i) Vasectomy
(ii) Tubectomy.
(b)
(i) Condom
(ii) Diaphragm.
Question 41:
(a) What is meant by contraception ? What are the different methods of contraception ?
(b) What is done in the contraception method known as (i) vasectomy, and (ii) tubectomy ?
(c) If a woman is using copper-T for contraception, will it protect her from sexually transmitted diseases ?
Solution :
(a) The prevention of pregnancy in women (by preventing fertilisation) is called contraception. There are 3 methods of contraception:
(i) Barrier method
(ii) Chemical method
(iii) Surgical method.
(b)
(i) Vasectomy – In males, a small portion of the sperm duct (Vasdeferens) is removed by surgical operation and both the cut ends are ligated properly. This prevents the sperms from coming out.
(ii) Tubectomy – In females, a small portion of the oviducts is removed by surgical operation and the cut ends are ligated. This prevents the ovum from entering into the oviducts.
(c) No.
Question 42:
(a) What are sexually transmitted diseases ? Give two examples of sexually transmitted diseases.
(b) Which method of contraception prevents fertilised egg from being implanted in the uterus ?
Solution :
(a) The diseases which are spread by sexual contact with an infected person are called Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Example: Aids, Syphilis.
(b) IUCD (Copper – T).
Question 43:
(a) What substances are contained (i) in oral pills, and (ii) in vaginal pills, used as contraceptives ? How do
they work ?
(b) How does copper-T prevent pregnancy ?
(c) Name the disease caused by HIV.
Solution :
(a) (i) The oral pills contain hormones which stop the ovaries from releasing ovum into the oviduct. (ii) The vaginal pills contain the chemicals called spermicides which kill the sperm.
(b) Copper- T is effective in preventing pregnancy. It is placed inside the uterus and it prevents the flow of sperms in the uterus.
(c) AIDS.
Question 44:
(a) What is the name of surgical method of birth control (or preventing pregnancy) which is carried out (i) in
men, and (ii) in women ?
(b) Name the part of a seed which (i) contains stored food (ii) grows into root, and (iii) grows into shoot.
Solution :
(a)
(i) Vasectomy
(ii) Tubectomy.
(b)
(i) Cotyledons
(ii) Radicle
(iii) Plumule.
Question 45:
Explain how, offsprings and parents of organisms reproducing sexually have the same number of chromosomes.
Solution :
The offsprings and parents of organisms reproducing sexually have same number of chromosomes due to reduction division (meiosis) during gamete formation which reduces the number of chromosomes into half in both male and female gametes. During fertilisation when male and female gametes fuse the original numbers of chromosomes as in parents is restored in the offspring.
Question 46:
In tobacco plant, the male gametes have 24 chromosomes.
(i) What is the number of chromosomes in the female gamete ?
(ii) What is the number of chromosomes in the zygote ?
Solution :
(a) 24.
(b) 48.
Question 47:
(a) What would be the ratio of chromosome number between an egg and its zygote ?
(b) Distinguish between a gamete and a zygote.
Solution :
(a) 1:2.
(b)
Gamete
Gamete represents the sex cell or germ cell in sexual reproduction and it is of two types: Male gametes (Sperm) and Female gamete (Eee).
Zygote
It is the product of fertilization in which a male and a female gamete fuse with each other.
Question 48:
(a) Fertilisation in humans can occur only once in a month. Why ?
(b) What is the scientific name of
(i) womb, and (ii) birth canal ?
Solution :
(a) Fertilisation in humans can occur only once in a month because ovulation takes place once every month i.e. an egg is released once every month by ovary.
(b)
(i) Uterus.
(ii) Vagina.
Question 49:
The diagram shows female reproductive system. Name the parts labelled A to D.
(a) In which part do the sperms enter ?
(b) Which part releases the egg ?
(c) In which part does fertilisation take place ?
(d) In which part does the foetus develop ?
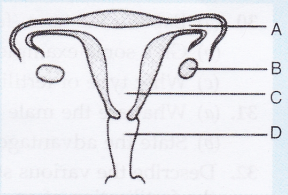
Solution :
A – Oviduct (Fallopian tube);
B – Ovary;
C – Uterus (Womb);
D – Vagina.
(a) Part D – (Vagina).
(b) Part B – (Ovary).
(c) Part A – Oviduct.
(d) Part C – Uterus.
Question 50:
Why is it an advantage for the testes to be situated in the scrotal sac outside the main body cavity ? Can you think of one disadvantage ?
Solution :
The testes are situated in the scrotal sac outside the main body cavity because the formation of sperms requires a lower temperature than the normal body temperature. Its disadvantage of being outside the main body cavity is that it is more prone to injury.
Question 51:
Which structures in human female are equivalent to the following structures in the male ?
(a) testes
(b) vas deferens
(c) penis
In each case say in what respect the structures are equivalent ?
Solution :
(a) Ovaries in female; Both make gametes.
(b) Oviducts in females; Both transport gametes.
(c) Vagina in female; Both are copulatory organs.
Question 52:
People who die from AIDS are not killed by the virus itself. Explain.
Solution :
AIDS damages the body’s immune system so that the body becomes weak and cannot protect itself against infection thus the virus does not kill the humans directly.
Question 53:
(a) What is the life support system of a fetus ?
(b) How long does a human baby take to develop before birth ?
(c) What is the name of the narrow opening between the uterus and the vagina.
Solution :
(a) Placenta.
(b) About 9 months.
(c) Cervix.
Question 54:
(a) What is meant by ‘unisexual flowers’ and ‘bisexual flowers’ ? Give two examples of each.
(b) What is pollination ? How does pollination occur ?
(c) Describe the process of fertilisation in a flower with the help of labelled diagrams.
(d) What changes take place in the flower after fertilisation which lead to the formation of seeds and fruit ?
Solution :
(a) The flowers which contain only one sex organ, either stamens or carpels are called unisexual flowers like Papaya and watermelon plants. The flowers which contain both the sex organs i.e. both the stamen and the carpel are called bisexual flowers like Hibiscus and Mustard plant.
(b) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a stamen to the stigma of a carpel is called pollination. It takes place when pollen grains are carried from the anther to the stigma of the flower.
(c) When a pollen grain falls on the stigma of the carpel, it bursts open and grows into a pollen tube downwards through the style towards the female gamete in the ovary. A male gamete moves down the pollen tube and enters the ovule in the ovary. The tip of the pollen tube bursts open and male gamete comes out of the pollen tube which combines with the nucleus of the female gamete present in the ovule to form a fertilised egg called zygote.
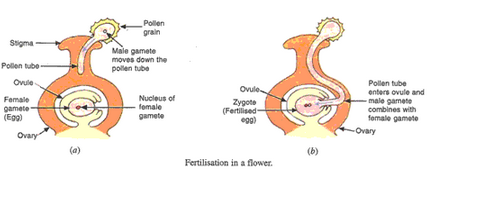
(d) The fertilised egg divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule which develops a tough coat around it and is gradually converted into a seed. The ovary of the flower develops and becomes a fruit with seeds inside it.
Question 55:
(a) Draw a neat diagram of a flower showing its various parts. In this diagram mark stem, receptacle, sepals,
petals, stamen and carpel.
(b) What name is given to
(i) all the petals of a flower, and
(ii) all the sepals of a flower ?
(c) What are
(i) stamen, and
(ii) carpel, in a flower?
(d) What is the other name of carpel of a flower ?
(e) What is the name of yellow powdery substance present in the anther of a flower ?
Solution :
(a)
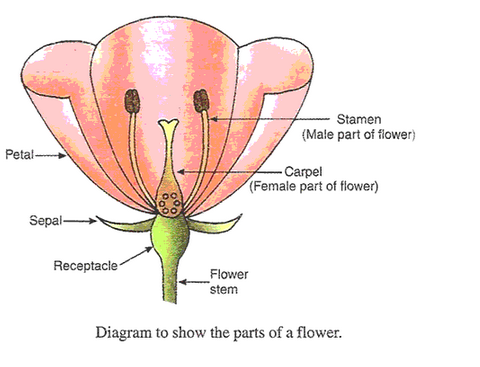
(b)
(i) Corolla
(ii) Calyx.
(c)
(i) Stamen is the male reproductive organ of the plant.
(ii) Carpel is the female reproductive organ of the plant.
(d) Pistil.
(e) Pollen grains.
Lakhmir Singh Biology Class 10 Solutions Page No:171
Question 56:
(a) What changes are seen in boys at the time of puberty ?
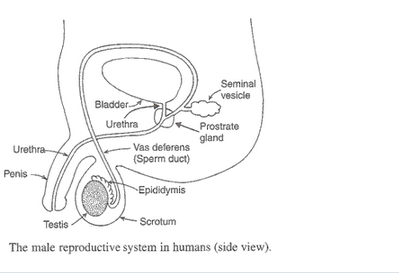
(b) Name the organs which produce sperms in human males.
(c) Draw a labelled diagram of the human male reproductive system. With the help of this diagram, describe the working of human male reproductive system ?
(d) What is the role of seminal vesicles and prostrate gland in human male reproductive system ?
Solution :
(a) The changes observed in boys during puberty are: Hair grows under armpits, pubic region between the thighs, chest and face. Body becomes more muscular due to the development of muscles. The voice deepens. Chest and shoulder broaden. The penis and testes become larger. Feelings and sexual drives associated with adulthood begin to develop.
(b) Testes.
(c) Working of human male reproductive system: The human male reproductive system consists of:
(i) Testes – Are the primary reproductive organs in males which are in pair. These are oval shaped organs which lie outside the abdominal cavity. It makes the male sex cells called sperms and produces male sex hormones called testosterone.
(ii) Scrotum – Is a muscular pouch which houses the testes. It is present outside the abdominal cavity and maintains a lower temperature than the normal body temperature.
(iii) Epididymis – The sperms formed in the testes goes into a coiled tube called epididymis which stores the sperms temporarily.
(iv) Vas Deferens (sperm duct) – It is a long tube which carries the sperms from epididymis to another tube called urethra.
(v) Seminal vesicles and prostrate gland – Both these glands are present along the path of vas deferens and add their secretions to sperms which allows them to transport easily.
(vi) Penis – It is an organ which pass?s the sperms from the man’s body into the vagina in the women’s body during mating.
(d) The secretions of seminal vesicles and prostrate gland provide nutrition to the sperms and also make their transportation easier by secreting a thick liquid.
Question 57:
(a) What changes are seen in girls at the time of puberty ?
(b) Name the organs which produce ova (or egg cells) in human females.
(c) Draw a labelled diagram of the human female reproductive system. With the help of this diagram, explain the working of human female reproductive system.
(d) Describe the process of fertilisation in humans and development of embryo briefly.
Solution :
(a) The changes observed in girls during puberty are: Hair grows under armpits and pubic region. Mammary glands develop and breasts become enlarged. The hips broaden and extra fat is deposited in various parts of the body like hips and thighs. Fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina enlarge. Ovaries start to release eggs and menstruation starts. Feelings and sexual drives associated with adulthood begin to develop.
(b) Ovaries.
(c) Working of human female reproductive system: The human female reproductive system consists of:
(i) Ovaries – These are the primary reproductive organs in women. They are oval shaped organs which are inside the abdominal cavity of a woman near the kidneys and produces mature female sex cells called ova or eggs. They also produce female sex hormones called Oestrogen and Progesterone. Each ovary is composed of several thousand follicles which mature to form ripe eggs at puberty.
(b) Oviduct – These are paired tubes which have funnel shaped openings that cover the ovaries. The ovum released by an ovary goes into the oviduct through its funnel shaped opening. The fertilisation of egg by a sperm takes place in it. It is also known as fallopian tube.
(c) Uterus – It is a bag like organ in which the fertilised egg develops into a baby. It is connected through a narrow opening called cervix to another tube called vagina. It is commonly called womb.
(d) Vagina – It is a tubular structure. It receives the penis for putting sperms into the women’s body. It is also called birth canal because it is the passage through which the baby is born.
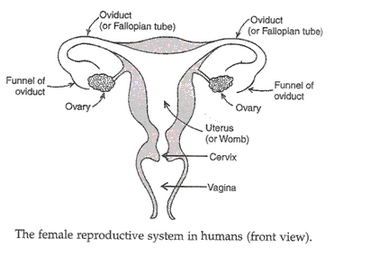
Question 58:
(a) What is ovulation ? How often does it happen in human females ?
(b) Where does fertilisation take place in human females ?
(c) Explain why, fertilisation is possible if mating takes place during the middle of menstrual cycle.
(d) What is meant by implantation ?
(e) What is placenta ? What is its function ?
(f) What joins embryo to placenta in mother’s body ?
Solution :
(a) The release of an ovum from an ovary is called ovulation. In human females, the ovaries start releasing ovum once every 28 days from the age of puberty.
(b) Oviducts.
(c) Fertilisation is possible if mating takes place during the middle of menstrual cycle because in a normal healthy girl the ovulation takes place on the 14th day of the beginning of menstrual cycle of 28 days.
(d) The embedding of embryo in the thick lining of the uterus is called implantation.
(e) Placenta – Placenta is a disc like special tissue which develops between the uterus wall and the embryo after implantation. Its function is the exchange of nutrients, oxygen and waste products between the embryo and the mother.
(f) Umbilical cord.