Hydrogen Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 9
• Electronic Configuration of Hydrogen 1s1
Position of hydrogen in the periodic table: Position of hydrogen in periodic table is not justified because it resembles both alkali metals as well as halogens.
• Resemblance of Hydrogen with Alkali Metals
(i) Electronic Configuration: Hydrogen has one electron in its valence shell like alkali metals.
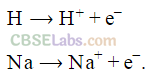
(ii) Both hydrogen and alkali metals form unipositive ions.
For example,
Na ———–> Na+ + e–
H ———-> H+ + e–
(iii) Hydrogen and alkali metals both shows +1 oxidation state.
(iv) Hydrogen as well as other alkali metals acts as reducing agents.
(v) Both have affinity for electronegative element For example, Na2O, NaCl, H20, HCl.
• Resemblance with Hologens
(i) Electronic configuration: Hydrogen and halogen family both require one electron to fulfil the inert gas configuration
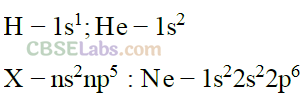
(ii) Ionisation energy of hydrogen is almost similar to halogens.
(iii) Hydrogen as well as halogens are Diatomic in nature.
(iv) Many compounds of hydrogen as well as of halogens are of covalent nature.
For example, CH4, SiH4CCl4, SiCl4
• Occurrence of Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. It is present in combined state as water, coal, animal and vegetable matter. All organic compounds contain hydrogen as an essential constituent.
• Isotopes of Hydrogen
Hydrogen has three isotopes.
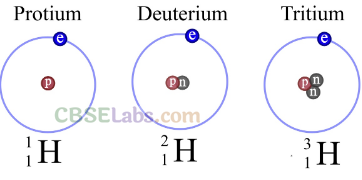
• Preparation of Dihydrogen, H2
Laboratory Preparation of Dihydrogen
(i) It is prepared by the reaction of granulated zinc with dil HCl.
Zn + 2HCl ——–> ZnCl2 + H2
(ii) It is prepared by the action of zinc with aqueous alkali.
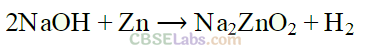
• Properties of Dihydrogen
Physical properties
(i) Dihydrogen is a colourless, odourless and tasteless gas.
(ii) It is a combustible gas.
(iii) It is insoluble in water.
(iv) It is lighter than air.
Chemical properties
Reaction with halogens: It reacts with halogens, X2 to give hydrogen halides. HX.
![]()
• Hydrides
The hydrides are classified into three types:
(i) Ionic or saline or salt like hydrides
(ii) Covalent or molecular hydrides (iii) Metallic or non-stoichiometric hydrides.
• Ionic or Saline Hydrides
Hydrides formed between hydrogen and electropositive element of group I and II belonging to s-block. These are known as stoichiometric compounds.
Properties of saline or ionic hydrides:
(i) The hydrides of lighter elements like Li, Be, Mg etc. have significant covalent character.
(ii) Ionic hydrides are crystalline, non-volatile and non-conducting in solid state.
(iii) They conduct electricity in molten state and liberate hydrogen at anode.
• Covalent or Molecular Hydrides
These are binary compounds of hydrogen with non-metals belonging to p-block.
For example, NH3, CH4, H20, HF They are mostly volatile compounds with low boiling points. They are classified as:
(i) Electron-Deficient Molecular Hydride: Molecular hydrides in which central atom does not have octet are called electron deficient hydrides e.g., BH3, MgH2, BeH2.
(ii) Electron precise hydrides: Those hydrides in which the central atom has its octet complete e.g., group 14 hydrides. They are tetrahedral in geometry.
(iii) Electron rich hydrides: Those metal hydrides which contain lone pair of electrons are called electron rich hydrides, e.g., NH3, PH3, H20 and H2S.
NH3 and PH3 has 1 lone pair and H20 and H2S have 2 lone pairs of electrons.
• Metallic or Non-Stoichiometric Hydrides
These hydrides are also known as interstitial hydrides. Transition metals group 3, 4 and 5 form metallic hydrides. In group 6, chromium alone has a tendency to form CrH. Metals of 7, 8 and 9 do not form hydrides. This is called as hydride gap.
Latest study shows that only Ni, Pd, Ce and Ac are interstitial in nature, that means they can occupy hydrogen atom in the interstitial sides. The hydrides are generally non-stoichiometric and their composition varies with temperature and pressure, for example, Ti H1.73, CeH2.7′ , LaH2.8 etc.
These hydrides have metallic lock and their properties are closely related to those of the parent metal. They are strong reducing agents in most of the cases due to the presence of free hydrogen atom in the metal lattice.
• Water
Human body has about 65% and some plants have nearly 95% water.
Physical properties of water:
(i) Freezing point of water is 273.15 K and boiling point 373.15 K.
(ii) Maximum density of water at 4°C is 1 gm cm-3
(iii) It is a colourless and tasteless liquid.
(iv) Due to hydrogen bonding with polar molecules, even covalent compounds like alcohol and carbohydrates dissolve in water.
Structure of Water:
In gas phase, it is a bent molecule with HOH bond angle 104.5° and O—H bond length of 95.7 pm. It is highly polar in nature. Its orbital overlap picture is also shown below.
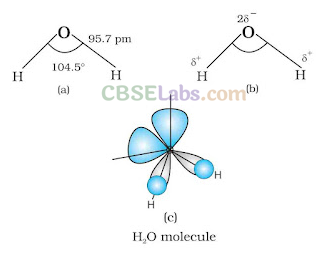
Water in Crystalline Form:
Ice is the crystalline form of water. At atmospheric pressure ice crystallise in the hexagonal form. At low temperature it condenses to cubic form. Density of ice is less than that of water. Therefore, ice cubes can float on water.
Structure of ice:
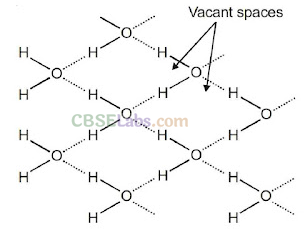
Chemical Properties of Water:
(i) Amphoteric nature: It behaves like an amphoteric substance because it can act as an acid as well as base.
![]()
Autoprotolysis of water also accounts for its amphoteric nature according to Bronsted-Lowry concept.
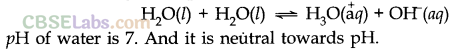
(ii) Oxidising and Reducing Nature: Water can act as an oxidising as well as reducing agent.
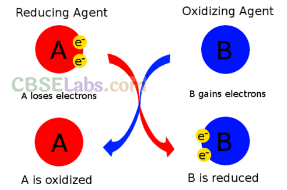
(iii) Hydrolysis Reaction: It has a very strong hydrating tendency. It can hydrolyse a large number of compounds such as oxides, halides, carbides etc.

• Hydrates Formation
From aqueous solutions many salts can be crystallised as hydrated salts. Hydrates are of three types:
(i) Coordinated water
For example: [Ni(H20)6]2+ (N03–)2 and [Cr(H20)6]3+ 3CP
(ii) Interstitial water
For example: BaCl2. 2H20
(iii) Hydrogen bonded water
For example: [Cu(H20)4]2+ S042- H20 in CuS04.5H20
• Hard and Soft Water
Hard water: Water which does not produce lather with soap easily is called hard water. Presence of calcium and magnesium salts in the form of hydrogen carbonate, chloride and sulphate in water makes the water hard.
Types of Hardness of Water:
(i) Temporary hardness: It is due to the presence of bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium in water. It is known as temporary because it can be easily removed by simple boiling of hard water.
(ii) Permanent hardness: It is due to the presence of chlorides and sulphates of calcium and magnesium. It cannot be removed on boiling water. Permanent hardness of water can be removed by chemical methods.
Soft water: Water which readily forms lather with soap is called soft water.
For example: rain water, distilled water.
• Hydrogen Peroxide (H202)
Preparation:
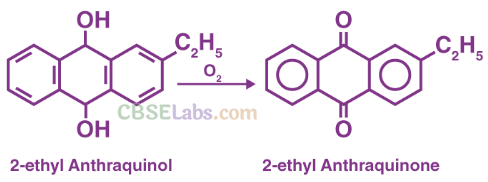
Uses of H202:
(i) It is used as a mild disinfectant. It is marketed as perhydrol (an Antiseptic).
(ii) It is used in the manufacture of high quality detergents.
(iii) It is used in the synthesis of hydroquinone tartaric acid and certain food products and pharmaceuticals.
(iv) It is used as bleaching agent for textilies, paper pulp etc.
(v) It is used for pollution control treatment of domestic and industrial effluents.
(vi) 93% H202 is used as an oxidant for rocket fuel.
• Heavy Water (D20)
It is used in the preparation of other deuterium compounds.
![]()
Uses of D2O:
(i) It is used as moderator in nuclear reactors.
(ii) It is used in the exchange reaction study of reaction mechanisms.
• Hydrogen as a Fuel
Hydrogen Economy: The basic principle of hydrogen economy is the transportation and storage of energy in the form of liquid or gaseous dihydrogen. Advantage is that energy is transmitted in the form of dihydrogen and not as electric power.
Advantage as a fuel:
– It is used as fuel cells for the generation of electric power.
– One major advantage of combustion of hydrogen is that it produces very little pollution and there is not any emission of unbumt carbon particles in the form of smoke.
– It is evident from the study that dihydrogen in the gaseous state as well as in liquefied form releases more energy on combustion as compared to the other fuel commonly used.
– 5% of dihydrogen is mixed in CNG for use in four wheeler vehicles.