CBSE NotesCBSE Notes Class 6 ScienceNCERT Solutions Science
CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets Pdf free download is part of Class 6 Science Notes for Quick Revision. Here we have given NCERT Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets.
CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
Natural Magnet: Magnetite is called natural magnet.
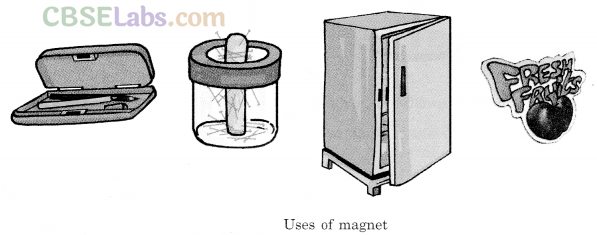
Uses of a Magnet: A magnet finds its use at a number of places. For example, refrigerator’s door, some pencil boxes, many toys, magnetic stickers, soap stand, pin stand, all make use of a magnet for their functioning.
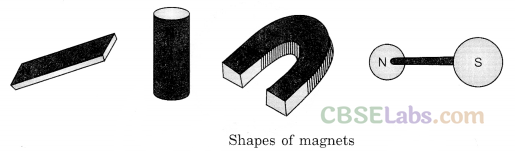
Shapes of Magnets: Magnets are made of different materials and in different shapes.
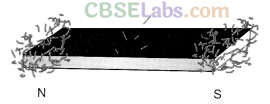
Effect of a magnet on materials: A magnet attracts certain materials, whereas some do not get attracted towards magnet.
Magnetic materials: The materials which get attracted towards the magnet are known as magnetic materials, e.g., iron, nickel, cobalt.
Non-magnetic materials: The materials which are not attracted towards the magnet are known as non-magnetic materials, e.g., leather, plastic, cloth, paper. Magnetic poles: Magnetic attraction is maximum near the ends of the magnet. These ends are called magnetic poles.
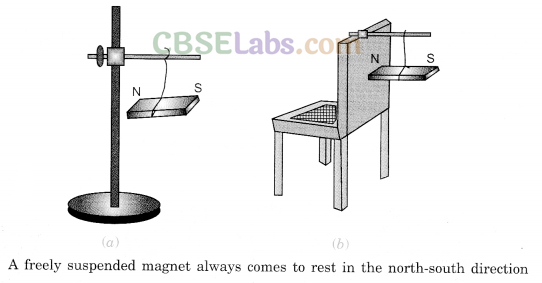
When suspended freely, magnet always aligns in north-south (N-S) direction.
Lode stone: It was a stone used by sailors in olden days to identify directions when they were in sea.
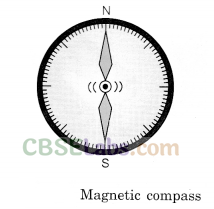
Compass: This is a small glass case containing a magnetised needle pivoted on a nail. The needle can rotate freely. Wherever it is kept, its needle always rests in north-south direction. Normally the north-pole of the needle is painted red or some other indication is given to identify north and south-poles. So using this needle, north and south can be identified.
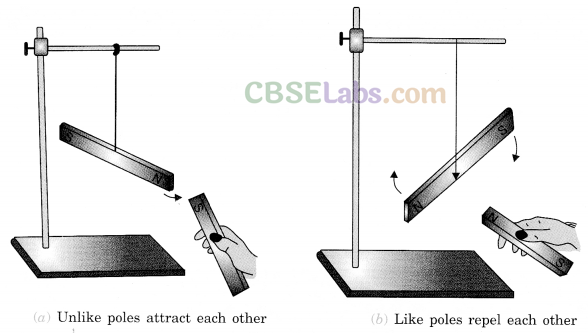
Attraction between two poles: Opposite poles of two magnets attract each other. It is called attraction.
Repulsion between two poles: Similar poles of two magnets repel each other. It is called repulsion.
Magnetic effect can pass through screen: Magnetic influence can pass through screens of some substances like cloth, plastic, paper, glass, etc.
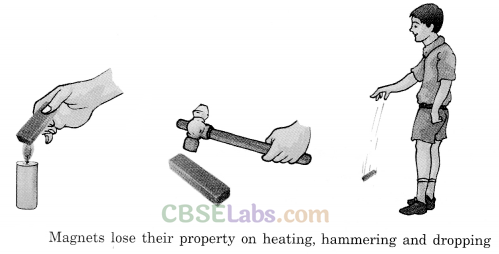
Magnets lose their properties if they are heated, hammered or dropped strongly and hardly.
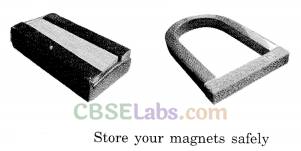
To keep them safe, bar magnets should be kept in pairs with their unlike poles on the same side. They must be separated by a piece of wood while two pieces of soft iron should be placed across their ends. For horse-shoe magnet, orfe should keep a piece of iron across the poles.
Compass: This is a small glass case containing a magnetised needle pivoted on a nail. The needle can rotate freely and always rests in north-south direction.
Magnet: A magnet is a metallic object which attracts iron or magnetic things. Magnetite: It is an ore of iron which has magnetic properties.
North pole: When suspended freely, one pole of the magnet always points towards north. This is known as north-pole.
South pole: When suspended freely, the end of a magnet points towards south. This is known as south-pole.
Look at the pictures shown below. Put a V’ mark against the object that you think would stick to a magnet and ‘x’ against the objects that would not stick to a magnet.
Let us now learn more about magnets. Answers : 1. False, 2. True, 3.True, 4.False, 5.False, 6.True.
Discovery Of Magnets
According to a legend, the first magnet was discovered by a Greek shepherd named Magnes. It is said that the nails in his shoes and the iron tip of his staff got stuck to a large black rock on which he was standing. Greeks named this strange type of rock ‘magnetite’. The Chinese also knew about magnets. Ancient Chinese sailors used magnets for navigation.
Magnets
Magnets are made of materials that attract objects made of certain substances like iron, cobalt, and nickel.
Magnets come in various shapes and sizes (Fig. 12.1). They can be found as horseshoe, ring, cylindrical, or bar shape.
Not all objects are attracted to magnets. Objects that are attracted by a magnet are said to be magnetic, e.g., iron and nickel. Objects that are not attracted by a magnet, are said to be non-magnetic, e.g., wood and plastic.

Poles Of a Magnet
When magnetic materials (like iron filings) are brought close to a magnet, they do not stick evenly to all parts of the magnet. They stick more on certain parts of the magnet. These are called the poles of the magnet. Magnetic forces are the strongest at the poles. For example, the two ends of a bar magnet are its poles.
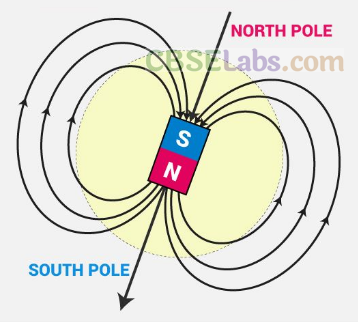
There are two types of poles in every magnet, irrespective of its shape. These are, by convention, called the North Pole (N) and the South Pole (S) (Fig. 12.2). The two poles cannot exist independently. That is, they always come in pairs.
If we break a bar magnet in the middle, we would get two pieces, each having a North Pole and a South Pole. We could go on breaking the magnet into smaller pieces, and everytime we would get both the poles in each piece.
Using a Magnet To Find Directions
Today, we use magnets for various purposes. In ancient times, the primary use of a magnet was to find directions.
If a magnet is allowed to move freely, it comes to rest in a direction very close to the Earth’s North-South direction. This property of a magnet was used to find directions on the surface of the Earth by travellers. An instrument with a magnet that is used to find directions is called magnetic compass.
It has a small magnetic needle at its centre. This needle can rotate freely and always points in the Earth’s North-South direction. Different directions (north, south, east, and west) are marked on the compass. Figure 12.3 shows how one can find directions using a magnetic compass.

Do you know why a freely suspended magnet always points in the Earth’s north-south direction? It behaves like it is under the influence of another magnet. But where is this other magnet? It is the Earth itself. This alignment happens because of the influence of the Earth, which itself acts like a giant bar magnet (Fig. 12.4). It influences all the magnets (within its region of influence) to align themselves along its North-South direction.
Attraction And Repulsion
When two magnets are brought close to each other, they are either pulled towards each other, or pushed away from each other. When the magnets are pulled towards each other, they are said to attract each other. When they are pushed away from each other, they are said to repel each other. Whether the magnets attract or repel depends on which poles of the magnets are facing each other.

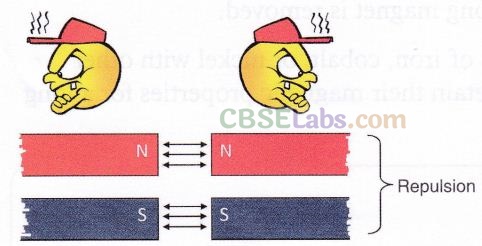
When like poles of the magnets (N-N or S-S) are brought close to each other, they repel. This is called repulsion.
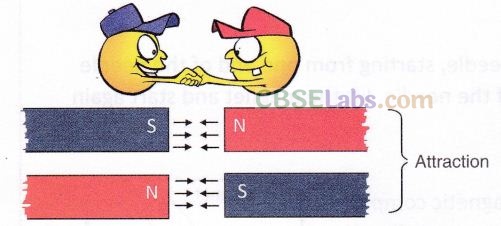
When unlike poles of the magnets (N-S or S-N) are brought close to each other, they attract. This is called attraction.
Types Of Magnets
There are two types of magnets: temporary and permanent. Magnets that retain their magnetic properties only for a short period of time are called temporary magnets. Magnets that retain their magnetic properties for a long period of time are called permanent magnets.
Temporary magnets are usually made of iron, cobalt, or nickel. These materials behave like magnets only when they are near a strong magnet. They quickly lose their magnetic property if the influence of the strong magnet is removed.
Permanent magnets are made from mixtures of iron, cobalt, or nickel with other materials. These make strong magnets and retain their magnetic properties for a long time.
Care Of Magnets
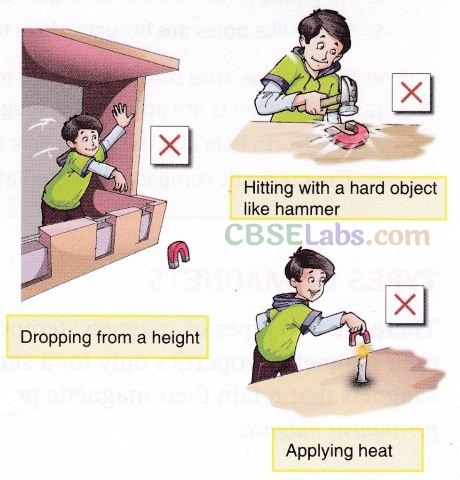
A magnet can lose its properties due to the following activities.
- Dropping from a height
- Hitting with a hammer
- Applying heat
- Improper storage can also cause loss of magnetic properties.
Bar magnets should be stored in pairs, with Dropping from a height unlike poles alongside each other. A horseshoe magnet should be stored with a piece of soft iron kept across its poles.
Uses Of Magnets
Magnets have several uses:
- Credit cards, ATM cards, and identity cards have a strip of magnetic material that stores information.
- Television and computer monitors use magnets.
- Computer hard discs and audio and video cassettes have magnetic material that store information.
- Magnets are used in picking up substances made of iron from scrapyard.

Magnet: An object that attracts substances like iron, cobalt, and nickel is called magnet.
Magnetic compass An instrument with a magnet that is used to find directions is called magnetic compass.
Temporary magnets: Magnets that retain their magnetic properties only for a short period of time are called temporary magnets.
Permanent magnets: Magnets that retain their magnetic properties for a long period of time are called permanent magnets.
Only magnetic materials are attracted by magnets.
Every magnet has two poles: the North Pole and the South Pole.
Magnetic forces are the strongest at the poles of the magnet.
A freely suspended magnet will come to rest in the Earth’s North-South direction.
Like poles of two magnets repel each other.
Unlike poles of two magnets attract each other.
Magnets can lose their properties if they are dropped from a height, hit with a hammer, heated, or stored in an improper manner.
We hope the given CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets Pdf free download will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.