Frank ICSE Class 10 Physics Solutions Heat
Formulae Handbook For ICSE Class 9 and 10Educational Loans in India
Frank ICSE Class 10 Physics Solutions Heat
Solution 1
PAGE NO-259:
(a)J/kg oC(b)2000 / (4 x 3) J/kg oC(c)AB and CD(d)Latent heat is emitted(e)The first time when temperature is constant represents change of state from solid to liquid and the second time temperature is constant represents change of state from liquid to vapour.
PAGE NO-260:
Solution 2
(a)Heat capacity of a body is the quantity of heat required to raise its temperature by 1oC. It depends upon the mass and the nature of the body.Units: J/oC or calorie/oC(b)Change in temperature = (50-30) = 20oC Amount of heat required, Q = m x C x ?T = 0.5 x 4200 x 20 = 42000 J
Solution 3
(a)This means that 390 J of heat is required to raise the temperature of 1kg of copper by 1oC.(b)Change in temperature = (100-30) = 70oC = 70 KAmount of heat given out, Q = m x C x T = 0.6 x 900 x 70 = 37800 J
Solution 4

Solution 5
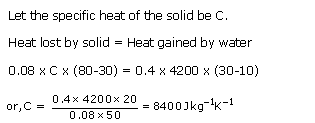
Solution 6
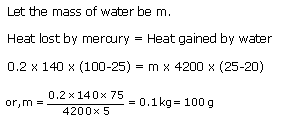
Solution 7

Solution 8
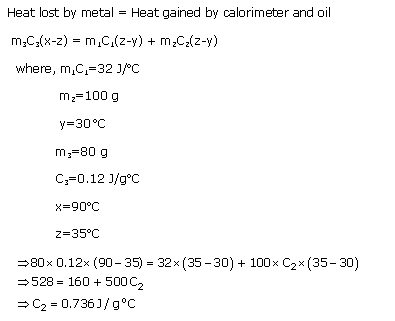
Solution 9
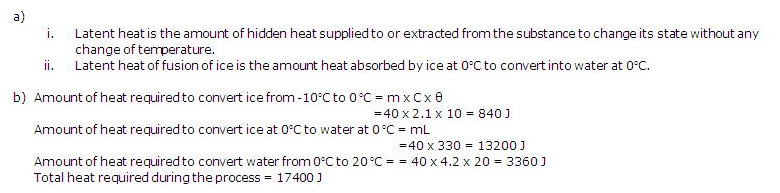
Solution 10

Solution 11
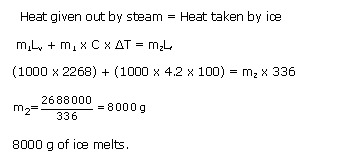
Solution 12
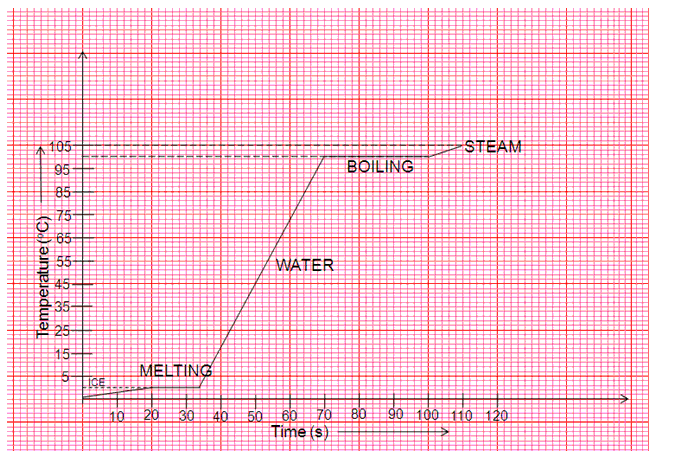
Solution 13
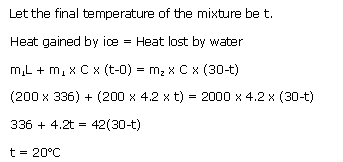
Solution 14

PAGE NO-261:
Solution 15

Solution 16
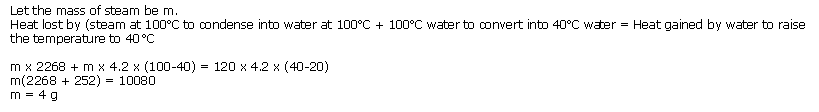
Solution 17
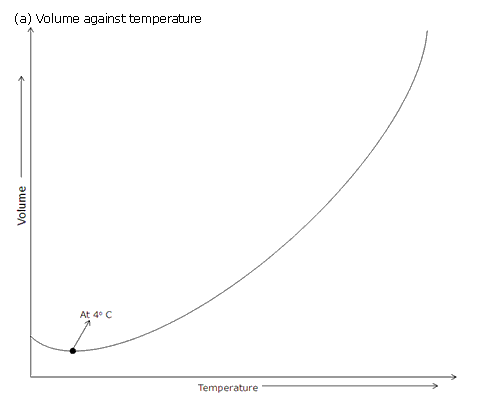
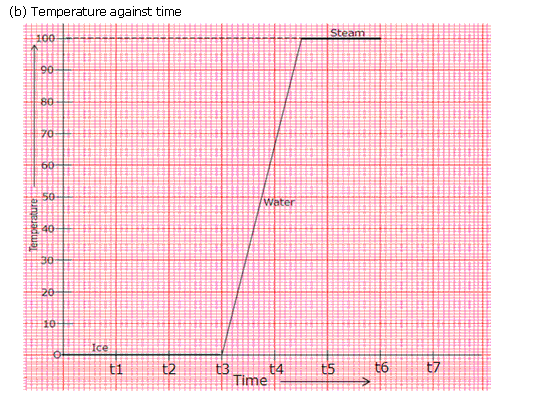
Solution 18
(a) Ice melts under pressure. So, when the steel blades of the skates pressed on the ice, the ice melts. The water formed makes the skates slide easily over the ice, reducing friction. So, when we are skating on ice, we are skating on a thin film of water, which acts like lubricating oil. Nothing such happens in case of glass.
(b) Sand improves the friction between car tyres and the road, so cars don’t skid on icy surfaces. Salt is spread so as to decrease the melting point of ice. Ice on the roads melt, making the roads less slippery.
(c) Steam burn is worse than a hot water burn because 1 g of steam gives out 540 calories of additional heat.
(d) Lumps of ice cool better than cold water because each gram of ice requires additional 80 calories of heat to get converted into water. Hence, cooling capacity of lumps of ice is more than cold water.
Solution 19

Solution 20
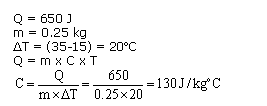
Solution 21

Solution 22
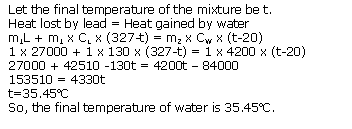
Solution 23

Solution 24

Solution 25
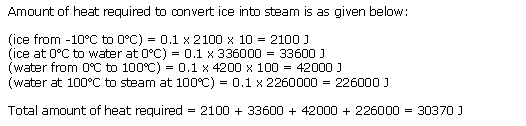
Solution 26
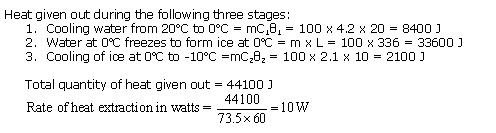
Solution 27
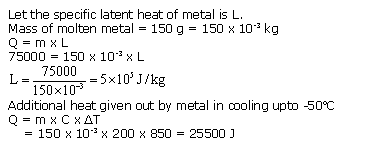
Solution 28
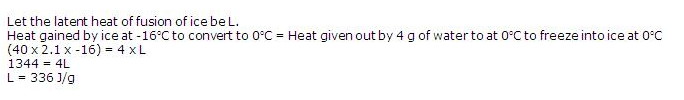
Solution 29
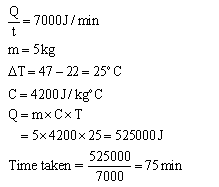
Solution 30
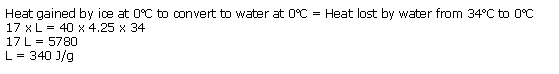
Solution 31
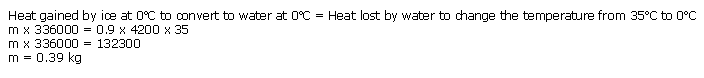
PAGE NO-262:
Solution 32
Steam at 100oC will produce more severe burns because every gram of steam gives out 2260 J of heat energy while condensing. This much amount of heat is additional to the heat contained in one gram of boiling water.
Solution 33
Ice cream appears colder to mouth than water at 00C because it can extract approximately 80 cal/g (latent heat of fusion of ice)more heat from as compared to water at 0 0C.
Solution 34
Although both ice cubes and iced water are at 0oC but ice cubes cool more quickly because each gram of ice requires additional 80 calories of heat to get converted into water at the same temperature, i.e., at 0oC. Hence, the cooling capacity of ice cubes is more than that of iced water.
Solution 35

Solution 36

Solution 37
1 gram of ice at 0oC requires 80 calories of heat to get converted into 1 gram of water at 0oC. So, water has more heat.
Solution 38
1 gram of water at 100oC requires 540 calories of heat to get converted into 1 gram of steam at 100oC. So, steam has more heat.
Solution 39
1 gram of ice at 0oC requires additional 80 calories of heat to get converted into water at 0oC. Then, heat is provided to raise the temperature to 10oC. Therefore, ice requires more heat than water and the additional heat is known as ‘Latent heat of fusion of ice’.
Solution 40
Pressure cooker increases the pressure and hence the boiling point increases. So, the boiling point becomes greater than 373kelvin
RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions
Video Solutions