Ecosystem – CBSE Notes for Class 12 Biology
NCERT SolutionsMathsPhysicsChemistryBiologyScience
Ecosystem—Structure and Function,- Productivity and Decomposition:
1. An ecosystem is a functional unit of nature, where living organisms interact among themselves and also with the surrounding physical environment. The word ‘Ecosystem’ was coined by Sir AG Tansley (1935).
2. The size of an ecosystem varies greatly from a small pond to a large forest or a sea.
3. Ecosystem can be grouped into two main categories:
(i) Terrestrial ecosystem Forest, grassland, desert, etc.
(ii) Aquatic ecosystem Pond, lake, river, wetland, estuary, etc.
4. Crop fields and an aquarium are considered as man-made ecosystems.
5. Structure and Function of Ecosystem
(i) Each ecosystem consists of biotic (autotrophs, herbivores and carnivores) and abiotic components and their interactions with each other results in a physical structure, that is characteristic for each type of ecosystem.
(ii) Identification and enumeration of plant and animal species of an ecosystem gives its specific composition.
(iiii) Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels is called stratification. For example, trees occupy top vertical strata or layer of a forest, shrubs the second and herbs and grasses occupy the bottom layers.
(iv) Major functional components of an ecosystem are:
(a) Productivity (b) Decomposition
(c) Energy flow (d) Nutrient cycling
(v) Let us understand these components in a pond ecosystem:
(a) A pond is a shallow water body in which all the above mentioned basic structural and functional components are present.
(b) Abiotic components are water with all the dissolved inorganic and organic materials and soil deposited at the bottom.
(c) Autotrophic components are phytoplanktons, some algae and the floating, submerged and marginal plants found at the edges.
(d) Consumers are zooplanktons, which are free swimming and bottom dwellers.
(e) Decomposers are the fungi, bacteria and flagellates found abundantly in the bottom.
(f) Functioning of pond ecosystem occurs in following steps:
* Autotrophs convert inorganic material into organic material with the help of solar energy.
* Heterotrophs consume autotrophs.
* Decomposers decompose dead organic materials and mineralise it to release them back for reuse by the autotrophs.
* The above events are repeated again and again.
Unidirectional movement of energy occur towards the higher trophic levels and lost in the form of heat to the environment.
6. Productivity is the rate of biomass production. It is expressed in g-2 yr-1 or (kcal m-2) yr-1.
(i) The amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by plants during photosynthesis is called primary production.
(ii) The primary productivity can be divided into:
(a) Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) of an ecosystem is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis. A considerable amount of GPP is utilised by plants in respiration.
(b) Net Primary Productivity (NPP) is gross primary productivity minus respiratory losses (R).
NPP = GPP – R
NPP is the available biomass for the consumption to heterotrophs, i.e. herbivores and decomposers.
(iii) Secondary productivity is defined as the rate of formation of new organic matter by . consumers.
(iv) Primary productivity of an ecosystem depends on:
(a) Plant species inhabiting a particular area.
(b) Availability of nutrients.
(c) Photosynthetic capacity of plants.
(d) Variety of environmental factors.
(v) Annual net primary productivity of the whole biosphere is about 170 billion tons (dry weight) of organic matter. Of this, despite of occupying about 70% of the surface of earth, the productivity of the oceans are only 55 billion tons.
7. Decomposition is the process in which decomposers breakdown complex organic matter into inorganic substances like carbon dioxide, water and nutrients.
(i) The raw materials called detritus are dead plant remains such as leaves, barks, flowers and dead remains of animals, including faecal matter.
(ii) Process of decomposition occurs in the following steps:
(a) Fragmentation is the breakdown of detritus into smaller particles by detritivores, e.g. earthworm.
(b) Leaching is the process by which water soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts.
(c) Catabolism is the process of degradation of detritus into simple inorganic substances by bacterial and fungal enzymes.
(d) Humification is the process of accumulation of a dark coloured amorphous substance called humus. It is highly resistant to microbial action, undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate and serves as a reservoir of nutrients.
(e) Mineralisation is the process by which humus is further degraded by some microbes to release inorganic substances.
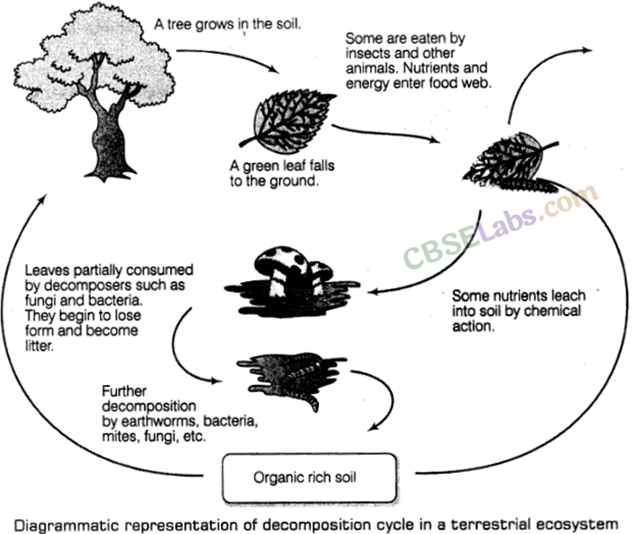
Leaves partially consumed by decomposers such as fungi and bacteria.
They begin to lose form and become litter.
Diagrammatic representation of decomposition cycle in a terrestrial ecosystem
(iii) Decomposition rate depends on
(a) Oxygen availability
(b) Chemical composition of detritus
(c) Climatic factors
(d) Temperature and soil moisture
(iv) Decomposition rate is slower, if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin. It is quicker, if detritus is rich in nitrogen and water soluble substances like sugars.
(v) Warm and moist environment speeds up decomposition, whereas low temperature and anaerobiosis inhibits decomposition and causes the formation of organic materials.
CBSE NotesCBSE Notes BiologyNCERT Solutions Biology