CBSE Class 12 Geography Notes Chapter 9 International Trade is part of Class 12 Geography Notes for Quick Revision. Here we have given NCERT Geography Class 12 Notes Chapter 9 International Trade.
Geography Class 12 Notes Chapter 9 International Trade
History of International Trade
- In ancient times, trade was restricted to local markets. Slowly long distance trade developed; of which Silk Route is an example. The route was 6000 km long connecting Rome to China and traders transported Chinese silk, Roman wool, metals, etc through this route. Later, sea and ocean routes were discovered and trade grew.
- The Slave Trade emerged in 15th century in which the Portuguese, Dutch, Spaniards and British captured African natives and sold to plantation owners in America. After Industrial Revolution, industrialised nations imported raw materials and exported finished products to non-industrial nations.
- International trade is the result of specialisation in production and division of labour. It is based on the principle of comparative advantage that is mutually beneficial to trading partners.
Basis of International Trade
The factors on which international trade depends are as follows:
- Difference in National Resources The resources are unevenly distributed in the world. These differences mainly refer to geology, mineral resources and climate.
- Geological Structure This means the relief features, type of land such as fertile, mountainous, lowlands, that support agriculture, tourism and other activities.
- Mineral Resources The regions rich in minerals will support industrial development that leads to trade.
- Climate It influences the type of flora and fauna that is found in a region, such as wool production in cold regions. Cocoa, rubber, Bananas can grow in tropical regions.
- Population Factors The size, distribution and diversity of population between countries affect the trade in respect of type and volume of goods. Large volume of internal trade than external trade takes place in densely populated areas due to consumption in local markets.
- Cultural Factors Distinctive forms of art and craft develop in certain cultures and give rise to trade e.g. porcelain and brocades of China, carpets of Iran, Batik cloth of Indonesia, etc.
- Stage of Economic Development
Industrialised nations export machinery, finished products and import foodgrains and raw materials. The situation is opposite in agriculturally important countries. - Extent of Foreign Investment Developing countries lack capital so foreign investment can boost trade in developing countries by developing plantation agriculture.
- Transport Lack of transport in older time restricted trade only to local areas. The expansion of rail, ocean and air transport, better means of refrigeration and preservation, trade has experienced spatial expansion:***’
Aspects of International Trade
There are three very important aspects of international trade:
- Volume of Trade It is measured simply as the total value of goods and services traded. However, actual tonnage of traded goods makes up the volume but services traded cannot be measured in tonnage.
- Composition of Trade Earlier primary’ goods were more in total traded goods, then there was dominance of manufactured goods and now there is dominance of service sector which includes transportation and other commercial services.
- Direction of Trade Earlier valuable goods and artefacts were exported to European countries by the developing countries. Later in the 19th century, manufactured goods from European countries were exchanged with foodstuffs and with raw materials from their colonies.
Types of International Trade
There are two types of international trade:
- Bilateral trade It is between two countries when they enter into an agreement to trade certain goods in which they are specialised.
- Multilateral trade It is conducted with many trading countries at the same time at goods which the countries are specialised in. The country may also grant the status of Most Favoured Nation (MNF) on some of trading partners.
Balance of Trade
- It refers to the volume of goods and services imported and exported by one country to other countries. Favourable balance of trade means the value of exports is more than its imports.
- Unfavourable balance of trade means that imports are more than exports. Balance of payments affects a country’s economy as negative balance means country’s expenses are more than its income.
Case for Free Trade
- Free trade or trade liberalisation is the act of opening up of economics so that more trade takes place. This is done by bringing down trade barriers like tarrifs. But trade liberalisation causes competition and can cause dumping.
- Dumping is the selling of a commodity in two countries at a price that differs for reasons not related to costs. Countries need to be cautious about dumped goods.
World Trade Organisation [WTO]
- General Agreement for Tariffs and Trade (GATT) was formed in 1948 to make the world free from tariffs as well as non-tariff barriers.
- On 1st January, 1995, the GATT was transformed into the World Trade Organisation to set-up an institution for the promotion of free and fair trade amongst different countries of the world.
- The WTO sets the rules for the global trading system. The headquarters of WTO is located in Geneva, Switzerland and 164 countries are its members.
- However, WTO has been criticised and opposed by those who are worried about the effects of free trade and economic globalisation. They argued that free trade is not beneficial to the ordinary people as it is widening the gap between rich and poor.
- They also argued that issues of health, workers’ rights, child labour and environment are ignored.
Regional Trade Blocs
These are developed as a response to the failure of global organisations. There are 120 regional trade blocs that generate 52% of the world’s trade.
Some of the trade blocs are as follows:
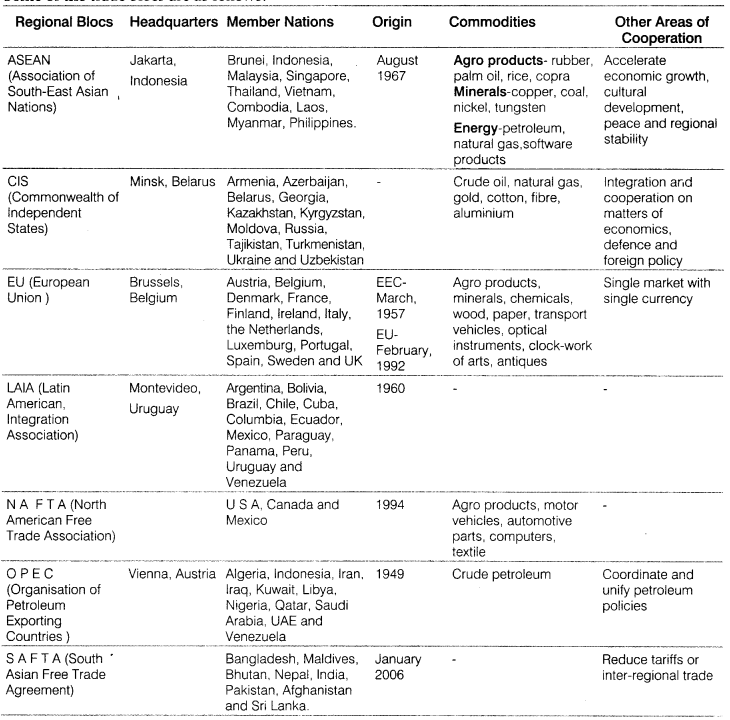
Concerns Related to International Trade
This can be summarised as merits and demerits of international trade.
- Merits of International Trade International trade is beneficial if it promotes regional specialisation, higher level of production, better standard of living, worldwide availability of goods and sendees, equalisation of price and wages and diffusion of knowledge and culture.
- Demerits of International Trade The demerits are, it leads to dependence on other countries, uneven levels of development, exploitation and commercial rivalry.
Gateways of International Trade
Harbours and ports are the chief gateways of international trade. These ports facilitate the passage of cargos and travellers as well as provide facilities of docking, loading, unloading and storage.
Types of Ports
Ports are generally, classified according to the types of traffic which handle. Types of ports on the basis of cargo handled are:
- Industrial Ports The ports that handle bulk cargo like grain, ores, oil, chemicals are called industrial ports.
- Commercial Ports Ports handling packaged products, manufactured goods, passengers are commercial ports.
- Comprehensive Ports Ports that handle bulk and general cargo in large volumes are called comprehensive ports. Most of the world’s great ports are classified as comprehensive ports.
Types of Ports on the basis of Location
- Inland Ports Ports located away from the sea coasts and linked to the sea through a river or a canal are inland ports, e.g. Mannheim on Rhine river.
- Out Ports Ports in deep waters built away from the actual ports and serving big ships are called out ports, e.g. Athens and its out port Piraeus in Greece.
Types of Ports on the basis of Specialised Functions
- Oil Ports Ports that deal in the processing and shipping of oil are known as oil ports. These are tanker ports like Tripoli in Lebanon and refinery’ ports like Abadon on the Gulf of Persia.
- Ports of Call Ports which originally developed as calling points on main sea routes where ships used to anchor for refuelling, watering and taking food items are called ports of call, e.g., Honolulu and Aden.
- Packet Station Also known as ferry ports, these are exclusively concerned with the transportation of passengers and mail across water bodies covering short distances, e.g., Dover in England and Calais in France.
- Entrepot Ports These are collection centres where the goods are brought from different countries for export, e.g., Singapore is an entrepot for Asia.
- Naval Ports These ports serve worships and have repair workshops for them, e.g., Kochi, Karwar in India.
We hope the given CBSE Class 12 Geography Notes Chapter 9 International Trade will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Geography Class 12 Notes Chapter 9 International Trade, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.