Class 11 History Notes Chapter 1 From the Beginning of Time
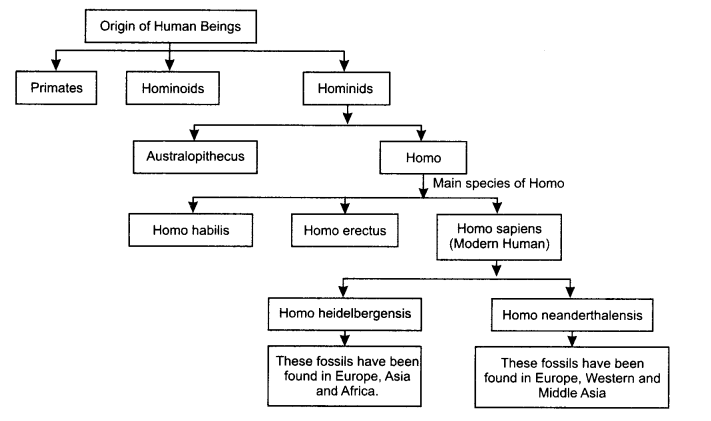
- The origin of human beings can be divided into many stages.
- Subgroup of a larger group of mammals is known as Primates.
- About 36-24 mya, Primates existed in Asia and Africa.
- The existence of Hominoids can be traced by about 24 mya.
- Apes came under Hominoids and had comparatively smaller brain.
- Hominoids had four legs. Although they moved on their four paws but were unable to walk erect. Hominids which
- evolved from Hominoids originated in Africa in 5.6 mya.
- The Hominids belonged to Hominidae family.
- Hominids are further subdivided into branches known as genus.
- Homo is originally a Latin word which means ‘man’. Homo came into existence approximately in 2.5 mya. Their fossils
- date back to 2.2 mya to 1.8 mya.
- Homo habilis were more intelligent in comparison to Australopithecus.
- Homo erectus were familiar with the art of walking.
- In many parts of Asia and Africa, fossils of Homo erectus have been found.
- Homo sapiens were the modern men. They were intelligent and wise.
- Homo sapiens came into existence between 0.19 to 0.16 mya.
- Fossils of Homo habilis have been found at Omo in Ethiopia and at Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania. The fossils of Homo
- erectus have been found in Africa and Asia.
- Homo sapiens were quite intelligent. They used sophisticated tools and languages.
- Homo neanderthalensis were also called Neanderthal men. Because their fossils have been found in Neander valley in Germany.
- Terra Amata in Southern France gives the most important evidence. The hut was made of thatch.
- The life of early men underwent a sea change due to the discovery of fire.
- Chesowanja in Kenya and Swartkrans in South Africa are the places where the traces of the use of fire have been found.
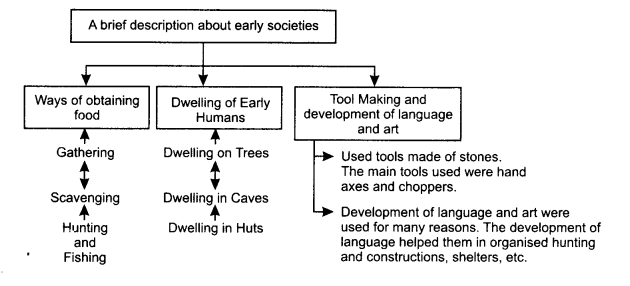
- The tools of early men were made of stones. The tools constituted hand axes, choppers and flake tools.
- The earliest evidence of stone tools were found in Ethiopia and Kenya.
- About 21,000 years ago, sewing needle was invented.
- The art of speech helped the man to develop culturally.
- The early human beings painted the pictures of flora and fauna, sun, moon, rivers and their daily activities.
- Paintings were done on the walls and roofs of the caves. Altamira, Lascaux and Chauvet are considered to be the earliest famous cave paintings.
- The early humans also made small sized sculptures.
- The Hadza were also fond of hunting and lived around the salty lake, Lake Eyasi.
- Altamira is a cave site in Spain.
- Marcelino Sanz deSautula and his daughter Maria brought into notice the cave paintings.
- Mary and Louis Leakey identified Otduvai.
- Some historians think that ethnographic data cannot be used without understanding of the past society.
- Ethnography stands for the analytical study of contemporary ethnic society.
- The early humans were completely dependent on nature.
- They gathered food by fishing and hunting.
- Hooks and harpoons were used to gather small and large fishes.
- Early men lived on trees, in caves and later on in huts.
- Early men began to live in caves around 400,000 years ago.
- Cave Lazaret is the earliest example of cave dwelling. It is in Southern France.
Important terms:
- Fossils: The remains of ancient plants, animals and humans which have become hard and turned into rock.
- Species: A group of organisms that can be bred to produce healthy and fertile offspring which are divided smaller than Genus.
- Primates: They are subgroup of a larger group of mammals, and have a long gestation period followed by birth, mammary glands, different types of teeth, and ability to maintain a constant body temperature.
- Artefacts: Objects made by human beings such as tools, painting, sculpture, engravings, etc.
- Anthropology: A branch of science which deals with human culture and evolutionary aspects of human biology.
- Ethnography: The study of contemporary ethnic group. It studies the modes of livelihood, gender, political institutions, social customs, etc.
- Australopithecus: Southern apes.
- Homo: A Latin word which means man.
- Homo erectus: Human who could walk erect on their legs.
- Homo sapiens: Wiseman, also known as modern humans.
| Timeline 1 (mya) | |
| 36-24 mya | Primates; Monkeys in Asia and Africa |
| 24 mya | (Superfamily) Hominoids; Gibbons, Asian orang-utan and African apes (gorilla, chimpanzee and bonobo or ‘pygmy’ chimpanzee) |
| 6.4 mya | Branching out of hominoids and hominids |
| 5.6 mya | Australopithecus |
| 2.6-2.5 | Earliest stone tools |
| 2.5-2.0 | Cooling and drying of Africa, resulting in decrease in woodlands and increase in grasslands |
| 2.5-2.0 mya | Homo |
| 2.2 mya | Homo habilis |
| 1.8 mya | Homo erectus |
| 1.3 mya | Extinction of Australopithecus |
| 0.8 mya | ‘Archaic’ sapiens, Homo heidelbergensis |
| 0.19-0.16 mya | Homo sapiens (modern humans) |
| Timeline 2 (years ago) | |
| Earliest evidence of burials | 300,000 |
| Extinction of Homo erectus | 200,000 |
| Development of voice box | 200,000 |
| Archaic Homo sapiens skull in the Narmada valley, India | 200,000-130,000 |
| Emergence of modern humans | 195,000-160,000 |
| Emergence of Neanderthals | 130,000 |
| Earliest evidence of hearths | 125,000 |
| Extinction of Neanderthals | 35,000 |
| Earliest evidence of figurines made of fired clay | 27,000 |
| Invention of sewing needles | 21,000 |
Flow-Learning: