Changes Around Us Class 6 Notes
We can bring about a change in a substance by doing one or more of the following processes:
- Heating.
- Applying force.
- Mixing it with something else.
Changes caused by heating: When an object is heated, it gets affected in one or many possible ways.
- Some objects get hot but do not change in any other way.
- Some objects get hot and also expand in size.
- Some objects get hot and begin to bum.
- Some objects get hot and change their state.
Changes by applying pressure: When we apply force to an object,
- We can change its shape and size.
- Air can be compressed.
- Metals can be hammered into thin sheets.
- Elastic can be stretched.
- Cotton can be spun into thin threads.
Changes by mixing a substance with other: We can bring about a change in a substance by mixing it with another. For example, making solution by mixing water soluble substances in water.
Metals expand on heating and contract on cooling.
Chemical changes: These are the changes in which chemical properties of a substance change, and a new substance is formed. For example, cooking of food.
Physical changes: These are the changes in which only physical property of a substance changes and no new substance is formed.
Characteristics of physical changes:
- No new substances are formed.
- Products are identical to the reactants.
- These changes are reversible.
Characteristics of chemical changes:
- Properties of products are different from the properties of reactants.
- Most of the chemical changes are irreversible.
- These changes always result in energy changes.
Reversible changes: These are the changes that can be reversed. For example, stretching of rubber.
Irreversible changes: These are the changes which cannot be brought back to its original state. For example, burning of paper.
Melting point: A constant temperature at which a solid starts melting. This temperature is called the melting point of that solid.
Freezing: A process in which liquid changes into solid form is called freezing.
Force: A push or a pull acting on a body which tends to change its state of rest or motion is called a force.
Natural changes: The changes which occur in nature on their own are called natural changes. For example, change of day and night, change of season.
Slow changes: The changes which take longer time to occur are called slow changes. For example, rusting of iron, tooth decay.
Changes: Many changes are taken place around us on their own, e.g., flowers bloom and then wither away. We can also bring a change, e.g., change in the size of a balloon by blowing air in it.
Contraction: A process in which an object becomes smaller or shrinks is called contraction.
Evaporation: A process in which liquid changes into vapour is called evaporation.
Expansion: A process in which an object becomes bigger in size, e.g., metals expand on heating.
Melting: A process in which a solid melts to become a liquid on heating is called melting.
Reversible And Irreversible Changes:
Changes that occur around us can be broadly categorized as reversible or irreversible depending on whether or not they can be reversed.
Reversible Changes:
Changes that can he reversed are called reversible changes.
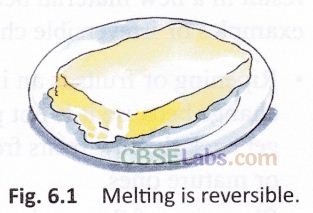
What happens to an ice cream if you do not finish it quickly? It melts. Can you change the molten ice cream back into a solid? Yes! Just keep it in the freezer. Molten ice cream can be changed back to its solid form. Thus, melting is a reversible change. Melting of butter and chocolate are also reversible changes (Fig. 6.1).
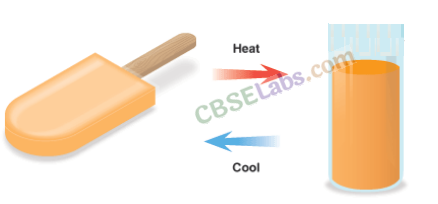
What about changes like condensation, freezing, and evaporation of materials? If you take out some ice cubes from the freezer and keep them outside, the ice cubes will absorb heat from the surrounding and melt. When this water (molten ice) is heated for some time, it starts boiling (liquid starts to evaporate) and steam escapes from the container [Fig. 6.2(a)]. Now, if you hold a lid over the container, the steam will again liquify or condense into small droplets of water on coming in contact with the cold lid [Fig. 6.2(b)]. This water can be cooled down further and then kept in the freezer to form ice again [Fig. 6.2(c)]. Thus, the three physical states of water are reversible and can be changed from one state to another by heating or cooling.
Irreversible Changes:
Changes that cannot be reversed are called irreversible changes.
There are a large number of irreversible changes that take place around us. These result in a new material being produced, which may or may not be useful. Some examples of irreversible changes are given below.
- Ripening of fruits is an irreversible change because it is not possible to get back the raw fruits from ripened or mature ones.
- Blooming of flowers is an irreversible change because flowers cannot change back into buds.
- Milk gets spoiled when not refrigerated, particularly in summer. This is called curdling or souring of milk, which is an irreversible change. Curdling of milk is also done by adding lemon juice to milk for making cottage cheese or paneer.

Burning of paper is an irreversible change. A new substance called ash is left or formed after a paper has been burnt. This new substance differs from the paper in its appearance and properties.

Cooking of food is an irreversible change because we cannot get back the ingredients in their original form after cooking them. For example, after a cake is baked using flour, egg, milk, chocolate, etc., we cannot get back the ingredients (Fig. 6.3).

Burning of a candle is often cited as an example of physical change because what we see immediately is melting of wax that solidifies on cooling. However, when a candle burns, the wax is undergoing two changes at the same time: first it melts, and then it burns. What burns is actually melted wax. The melted wax burns on the wick – the wick itself isn’t burning, it is just the wax on it.
Physical And Chemical Changes:
Changes in which no new substances are formed are called physical changes. For example, breaking of a glass (Fig. 6.4), freezing of water, tearing of paper, etc.
Changes in which new substances with different properties are formed are called chemical changes. Cooking of food, burning of substances are chemical changes as entirely new substances are formed. Burning of a candle wax releases carbon dioxide and water vapour (new substances).

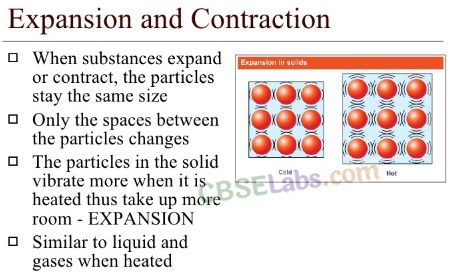
Expansion And Contraction Of Materials:
Some materials expand on heating and some contract on cooling. Heating makes the particles (that form the material) expand or become loose. Cooling makes the particles (that form the material) contract or become tight.
The amount of expansion differs in solids, liquids, Fig- 6-4 Physical change
and gases. Gases expand the most while solids expand the least.
Table 6.1 shows some examples of expansion.

Cooling does the opposite of heating. Cooling causes a material to contract. Solids contract the least while gases contract the most. Table 6.2 lists some examples of contraction.
Applications of Expansion and Contraction:
Expansion by heating can be used in several everyday activities.
The jammed metal lid of a jam jar can be opened by heating. The jar is inverted and just the lid is dipped in hot water. After some time, the lid can be opened easily as the lid gets slightly expanded.
The fact that materials expand on heating is used in thermometers. In many thermometers, mercury is used. When the bulb of the thermometer comes in contact with a hot object, the mercury expands and its level rises in the glass tube, indicating the temperature.
Why the electric lines are never hung tautly between the poles? Wires in the outside
environment are subjected to extreme weather conditions ranging from acute hot to cold temperatures. A taut wire on contraction in winters can snap.
Reversible change: A change that can be reversed is called a reversible change.
Irreversible change: A change that cannot be reversed is called an irreversible change.
Physical change: A change where no new substances are formed is called a physical change.
Chemical change: A change where new substances with different properties are formed is called a chemical change.
Changes happen around us and also within us.
Some changes are reversible, while some others are irreversible.
Some changes are physical changes; some are chemical changes.
Heating causes expansion in a material.
Cooling causes contraction in a material.
Gases expand the most and solids expand the least.
Gases contract the most and solids contract the least.
We hope the given CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 6 Changes Around Us Pdf free download will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 6 Changes Around Us, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.