Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Informatics Practices with Solutions Set 3 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Informatics Practices Set 3 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 70
General Instructions:
- This question paper contains five sections, Section A to E.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Section A has 18 questions carrying 01 mark each.
- Section B has 07 Very Short Answer type questions carrying 02 marks each.
- Section C has 05 Short Answer type questions carrying 03 marks each.
- Section D has 02 questions carrying 04 marks each.
- Section E has 03 questions carrying 05 marks each.
- All programming questions are to be answered using Python Language only.
Section – A
Question 1.
As soon we get any good news from any source in social media: [1]
(a) We should forward to many people so that they can be benefited.
(b) We should never forward to anyone.
(c) We should confirm the news from any reliable source before forwarding.
(d) We should forward to our family and friends only.
Answer:
(c) We should confirm the news from any reliable source before forwarding.
Question 2.
………. is a set of moral principles that governs the behaviour of a group or an individual and regulates the use of computers. [1]
(a) Copyright
(b) Computer ethics
(c) Property rights
(d) Privacy law
Answer:
(b) Computer ethics
Question 3.
series1 = pd.Series ({'India' : 'New Delhi', 'UK' : 'London', 'Japan' : 'Tokyo'})
print(series1)
Above code is an example of
(a) creating series from dictionary
(b) creating series from scalar values
(c) creating series from an array
(d) creating series from tuple
Answer:
(a) creating series from dictionary
![]()
Question 4.
Abhishek uses computer and mobile for his personal use. He uploaded one video on his youtube channel, where he used one background music downloaded from somewhere on Internet, he may be violating _____. [1]
(a) copyright
(b) intellectual property right
(c) plagiarism
(d) None of these
(a) copyright
Answer:
Question 5.
Identify single-row functions of MySQL amongst the following
(a) TRIM()
(b) MAX()
(c) ROUND()
(d) Both (a) and (c)
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer:
Question 6.
Which of the following function is used to create DataFrame?
(a) DataFrame()
(b) NewFrame()
(c) CreateDataFrame()
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) DataFrame()
Question 7.
In India, e-Waste management assumes greater significance because
(a) generation of own e-Waste
(b) dumping of e-Waste from developed countries
(c) lack of awareness
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 8.
Method or function to add a new row in a DataFrame is
(a) .loc()
(b) .iloc()
(c) join()
(d) add()
Answer:
(a) .loc()
Question 9.
_____ refers to a small, single site network.
(a) DSL
(b) RAM
(c) WAN
(d) PAN
Answer:
(d) PAN
Question 10.
Write the output of the following SQL command.
SELECT ROUND(47.89):
(a) 47.88
(b) 47.8
(c) 48.0
(d) 50
Answer:
(c) 48.0
Question 11.
_____ network topology in which there are bi-directional links between each possible node.
(a) Ring
(b) Mesh
(c) Tree
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Mesh
Question 12
Which function returns the length of the string in bytes?
(a) LENGTH ( )
(b) DATE ()
(c) TIME ()
(d) MATH ()
Answer:
(a) LENGTH ( )
Question 13.
A software which is available for free and the code is open for all, it is called as
(a) Proprietary software
(b) Free and open source software
(c) Free software
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Free and open source software
![]()
Question 14.
Consider a table DOCTOR(ID, DocName,Department, DOJ,Gender, Salary). Which of the following query will display the names and salaries of doctors in descending order of salaries. [1]
(a) SELECT DocName, Salary FROM DOCTOR ORDER BY Salary DESC;
(b) Salary FROM DOCTOR WHERE ORDER BY Salary ASC;
(c) Salary FROM DOCTOR ORDER BY Salary ASC;
(d) Salary FROM DOCTOR WHERE ORDER BY Salary DESC;
Answer:
(a) Salary FROM DOCTOR ORDER BY Salary DESC;
Question 15.
Which SQL clause is used to restrict the rows returned by a query? [1]
(a) SELECT
(b) ORDER BY
(c) WHERE
(d) GROUP BY
Answer:
(c) WHERE
Question 16.
Which of the following is not a Mathematical function? [1]
(a) LENGTH()
(b) POWER()
(c) MOD()
(d) ROUND()
Answer:
(a) LENGTH()
Directions (Q.Nos. 17-18) Assertion and Reason based Questions.
Question 17.
Assertion (A) A router is a network device that connects multiple networks together. [1]
Reason (R) Routers operate at the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model and can forward data packets based on their IP addresses.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 18.
Assertion (A) A Series is a one-dimensional array containing a sequence of values of any data type (int, float, list, string, etc). [1]
Reason (R) Pandas Series can be imagined as a column in a spreadsheet.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Section – B
Question 19.
Write down any two points of differences among LAN, MAN and WAN. [2]
Or
Define home page. Give two advantages of home page.
Answer:
Two major points of differences among LAN MAN and WAN are as follows
| Basics | LAN | MAN | WAN |
| Geographical Area | Generally within a building | Within a city | Across the continents |
| Distance | Upto 5 km | Upto 160 km | Unlimited |
Or
A home page is the first page of a website. Two advantages of home page are as follows
- It helps viewers to find out what they can find on that site.
- Publicity of an individual or a community.
Question 20.
Aditi is a travel agent, she has stored the data of all passengers in a table Travel(Pno, Pname,Tdate,Km, Coach). [2]
She has given the following command to count the number of passengers in each coach from Travel table.
SELECT PName, COUNT(Coach) FROM Travel ORDER BY Coach;
But she is not getting the desired result.
Help her for identifying the reason of the error and write the correct query by suggesting the possible correction(s).
Answer:
SELECT Coach, COUNT(Coach) FROM Travel GROUP BY Coach;
Question 21.
State differences between date functions NOW() and DAY() of MySQL. [2]
Answer:
| NOW() | DAY() |
| This function returns the current date and time in the format ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS’ or YYYYMMDDHHMMSS format. | This function returns the day of the month (from 1 to 31) from a date specified as an argument. |
| Syntax SELECT NOWO; | Syntax SELECT DAY(‘ 2021-09-31 ’); |
Question 22.
The Python code written below has syntactical errors. Rewrite the correct code and underline the corrections made. [2]
import Pandas as pd
data = {'A': 1, 'B'; 2. 'C': 3}
my_series = Pd.Series(data)
print(my_series)
Answer:
Correct code is:
import pandas as pd
data = {'A': 1, ’B’: 2, 'C': 3}
my_series = pd.Series(data)
print(my_series)
![]()
Question 23.
What is digital property rights? Write the names of some digital property rights. [2]
Answer:
Digital property includes data, internet accounts and other rights in the digital world, including contractual rights and intellectual property rights. Data are the files and information stored and used by computers. Digital property right dispute arise when some form of counterfeiting or piracy occurs between companies.
Question 24.
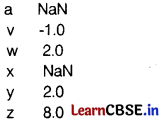
Write the output of the given code. [2]
import pandas as pd S1=pd.Senes([5, 6, 7, 8, 10], index=['V', 'W', ‘x’, ‘y', ‘z’]) l=[2, 6, 1, 4, 6] S2=pd.Series(l.index=['z', 'y', 'a', 'w', ‘v']) print(S1 - S2)
Answer:
Question 25.
Complete the given Python code to given two DataFrames ‘df1’ and ‘df2’, merge them on the ‘ID’ column to get a single DataFrame ‘merged_df’. [2]
import ____ as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'ID': [1, 2, 3], 'Name': ['Riya', 'Preeti', 'Neeta’]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'ID': [1, 2, 4], 'Age': [25, 30, 22]})
merged_df = pd.merge(dfl, df2, on=____)
print(merged_df)
Answer:
Correct code is:
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'ID': [1, 2, 3], 'Name': ['Riya', 'Preeti', 'Neeta']})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'ID': [1, 2, 4], 'Age': [25, 30, 22]})
merged_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='ID’)
print(merged_df)
Settion – C
Question 26.
Consider the table BOOK given below. [3]
Table: BOOK
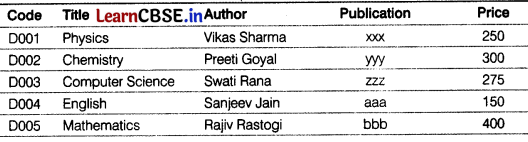
Give the output of the following SQL commands.
(i) SELECT SUBSTR(Title, 2, 3) FROM BOOK WHERE Code=’D002’;
(ii) SELECT CONCAT(Author, Publication) FROM BOOK WHERE Price=250;
(iii) SELECT MAX (Price) FROM BOOK;
Answer:

Question 27.
Mr. Ankit is working in an organisation as data analyst. He uses Python Pandas and Matplotlib for the same. He got a dataset of the passengers for the year 2010 to 2012 for January, March and December. [3]
| Year | Month | Passengers | |
| 0 | 2010 | Jan | 25 |
| 1 | 2010 | Mar | 50 |
| 2 | 2012 | Jan | 35 |
| 3 | 2010 | Dec | 55 |
| 4 | 2012 | Dec | 65 |
Help him to write the Python code to create the above DataFrame.
Answer:
import pandas as pd
data={“Year”:[2010,2010.2012,2010.2012],“Month”:["Jan”."Mar",“Jan”,“Dec”,"Dec”],
“Passengers”:[25,50,35,55,65]}
df=pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)
Question 28.
Sanyukta is the event incharge in a school. One of her students gave her a suggestion to use Python Pandas and Matplotlib for analysing and visualising the data, respectively. She has created a DataFrame “df ” to keep track of the number of First, Second and Third prizes won by different houses in various events. [3]
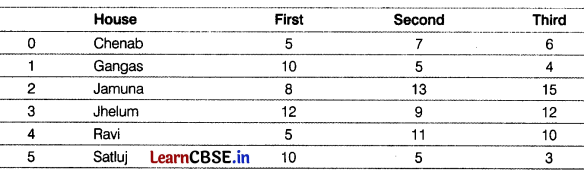
Help her to write Python commands to do the following questions:
(i) Display the House names where the number of Second prize are in the range of 12 to 20.
(ii) Display all the records in the reverse order.
(iii) Display the bottom 3 records.
Answer:
(i) df[‘House’][(df[‘Second’]>=12) and (df [‘Second’ ]<=20) ]
(ii) print(df.iloc[::-1])
(iii) df .tail (3)
Question 29.
The school offers Wi-Fi to the students of Class XII. For communication, the network security-staff of the school is having a registered URL “schoolwifi.edu”. On 17th September 2017, E-mails were received by all the students regarding expiry of their passwords. Instructions were also given renew their password within 24 hours by clicking on particular URL provided. On the bases of the above information, answer the questions: [3]
(i) Identify the name of cyber crime which is done by given information.
(ii) Ideally, what characters should be used in a password to make it strong?
(iii) What are unsolicited E-mails called as?
Or
Explain the features of IT Act 2000.
Answer:
(i) Phishing is the fraudulent act of getting the confidential information of people like bank account ids, email ids, etc., by looking to be authentic phone calls, messages, SMS, etc. The given situation is also a case of phishing that is trying to acquire personal information by prompting to click on a link.
(ii) A combination of all types of characters, letters in mixed case, numbers and special characters would make it difficult for unauthentic users to guess the password.
(iii) Spam
Or
Some features of IT Act 2000 are as follows
- It helps to promote E-commerce.
- It includes high penalty for cyber crime.
- It provides filing online forms.
- It enhances the corporate business.
Question 30.
Consider the following table Bookhouse. [3]
Table: Bookhouse
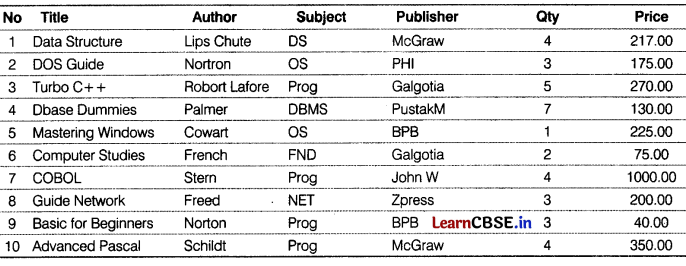
Write the SQL statements for the following
(i) Display number of books and average Price for each type of Publisher.
(ii) Display Title, Price in descending order of Price.
(iii) Display total number of books available in stock published by BPB.
Or
Differentiate between COUNT () and COUNT (DISTINCT) functions. Explain with the help of example.
Answer:
(i) SELECT COUNT (*), AVG (Pri ce), Publ i sher FROM Bookhouse GROUP BY Publisher;
(ii) SELECT Title, Price FROM Bookhouse ORDER BY Price DESC;
(iii) SELECT SUM(Qty) FROM Bookhouse WHERE Publ isher=’BPB’;
Or
| COUNT() function | COUNT (DISTINCT) function |
| This function returns the total number of records of a specified column. | This function returns the number of distinct rows in a specified table. |
| COUNT() will count the number of records. | COUNT (DISTINCT) will count the number of records where column name is not null. |
| e.g. To count the total number of employees from table PAYMENTS.
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM PAYMENTS; |
e.g. To count distinct values of column Department from PAYMENTS table.
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT department) FROM PAYMENTS; |
Section – D
Question 31.
Consider the table Sports given below. Write commands in SQL for the following: [4]
Table: Sports
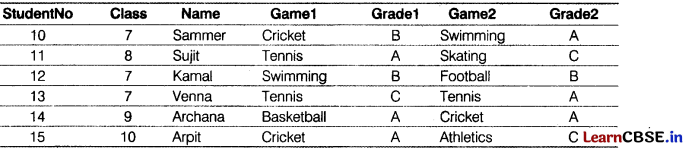
(i) Display the names of the students who have grade ‘A’ in either Gamel or Game2 or hot
(ii) Display the number of students having game ‘Cricket’.
(iii) Display the names of students who have same game for both Gamel and Game2.
(iv) Display the highest class of the students who has opted for swimming as Game 1 or Game2.
Answer:
(i) SELECT Name FROM Sports WHERE Gradel=‘A’ OR Grade2=‘A’;
(ii) SELECT C0UNT(*) FROM Sports WHERE Gamel=‘Cricket’ OR Game2=‘Cricket’;
(iii) SELECT Name FROM Sports WHERE Gamel=Game2;
(iv) SELECT MAX(CLASS) FROM Sports WHERE GAME1=“SWIMMING” OR GAME2=‘‘SWIMMING”;
![]()
Question 32.
Naman has created the following DataFrame “Climate” to record the data about climatic conditions of four years: [4]
| Year | MaxTemp | MinTemp | Rainfall |
| 2017 | 32 | 20 | 123 |
| 2018 | 33 | 22 | 140 |
| 2019 | 35 | 21 | 135 |
| 2020 | 34 | 23 | 160 |
(a) What will be the output of the following?
(i) Climate.iloc[1:3, 1:2]
(ii) printed(Cimate.head(2))
(b) Write the Python code to display the temperature difference between MaxTemp and MinTemp for all the rows in the DataFrame Climate.
(c) List 1st, 2nd and 3rd rows.
Or (Option for part (c) only)
The exact number of values in each column of the DataFrame?
Answer:
(a)
(i)
| MaxTemp | Rainfall |
| 33 | 140 |
| 35 | 135 |
(ii)
| Year | MaxTemp | MinTemp | Rainfall |
| 2017 | 32 | 20 | 123 |
| 2018 | 33 | 22 | 140 |
(b) print(Climate[“MaxTemp”]
(c) Climate.iloc [0 : 3, :]
Or
print(Climate.count( )) printed imate. count (0))
Section – E
Question 33.
Write the output of following queries. [5]
(i) SELECT ROWER(9, 3);
(ii) SELECT MID(‘SHUCHI GOYAL’, 8, 5):
(iii) SELECT RIGHT(‘ Dushyant ’, 5);
(iv) SELECT INSTR(‘SQL FUNCTIONS’, ‘C’);
(v) SELECT LEFT(‘Arihant’,2);
Or
Consider the following table CLUB.
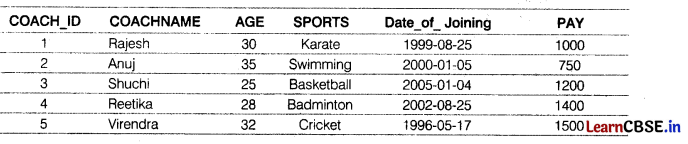
Give the answer of the following questions on the basis of the above table.
(i) Write a query to display the substring of 4 characters of the name of each coach, starting from second character, with their age.
(ii) What will be the output of the following query?
mysql>SELECT CONCAT (COACHNAME, AGE) FROM CLUB WHERE AGE> 30;
(iii) Write a query to display the day for the Date_of_Joining column.
(iv) What will be the ouput of the following query?
mysql>SELECT PAY *0.25 + 1000
FROM CLUB
WHERE COACHNAME LIKE * R%’;
(v) Write a query to display 3 characters from left of coach name.
Answer:
(i) 729
(ii) GOYAL
(iii) hyant
(iv) 8
(v) Ar
Or
(i) mysql >SELECT SUBSTR (COACHNAME, 2,4), AGE FROM CLUB;
(ii)

(iii) mysql >SELECT DAY (Date_of_Joi ni ng);
(iv)
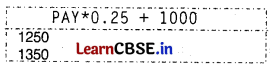
(v) mysql>SELECT LEFT (‘COACHNAME’, 3);
Question 34.
Eduminds University of India is starting its first campus in a small town Parampur of central India with its centre admission office in Delhi. The university has three major buildings comprising of Admin Building, Academic Building and Research Building in the 5 km area campus. As a network expert, you need to suggest the network plan as per (i) to (v) to the authorities keeping in mind the distances and other given parameters. [5]
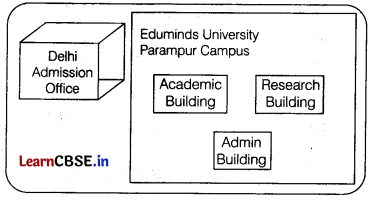
Expected wire distances between various locations:
| Research Building to Admin Building | 90 m |
| Research Building to Academic Building | 80 m |
| Academic Building to Admin Building | 15 m |
| Delhi Admission Office | 5 |
Expected number of computers to be installed at various locations in the university are as follows
| Research Building | 20 |
| Academic Building | 150 |
| Admin Building | 35 |
| Delhi Admission Office | 5 |
(i) Suggest the authorities, the cable layout amongst various buildings inside the university campus for connecting the building.
(ii) Suggest the most suitable place (i.e. building) to house the server of this organisation, with a suitable reason.
(iii) Suggest an efficient device to be installed in each of the buildings to connect all computers,
(iv) University is planning to provide online facility to students for clearing their doubts. Which of the following is the online textual or multimedia conversation will they use?
(a) VoIP
(b) Chatting
(c) HTML
(d) None of these
(v) Which software will students use to connect to Internet, create websites and view sites on web?
Answer:
(i) The suggested cable layout is as follows :
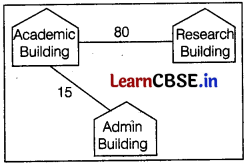
(ii) The most suitable place (i.e. building) to house the server of this university is Academic Building, because there are maximum number of computers and according to 80-20 rule 80% of traffic in a network should be local.
(iii) The efficient device to be installed in each of the Building to connect all the computers is Switch.
(iv) (b) Chatting, i.e. a virtual means of communication that involves the sending and receiving of messages, share audio and video between users located in any part of the world.
(v) Web Browsers
![]()
Question 35.
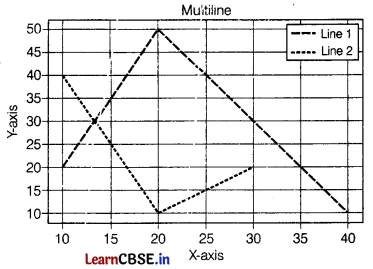
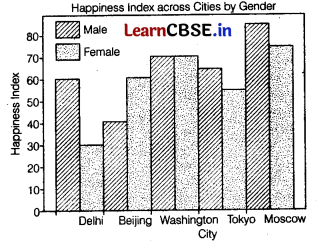
Write the Python code to create a plot as given below:
Or
Draw the approximate graph which display the multiline in same plot.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x1 = [10, 20, 40]
y1 = [20, 50, 10] ,
plt.plot(x1, y1, label = "line 1")
x2 = [10, 20, 30]
y2 = [40, 10, 20]
plt.plot(x2, y2, label = "line 2")
plt.xlabe1('X - axis')
plt.ylabe1(‘Y - axis')
plt.title('Multiline')
plt.legend( )
plt.show( )
Answer:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
City=['Delhi', 'Beijing', 'Washington', 'Tokyo', 'Moscow']
Gender=['Male', ‘Female’]
Happiness_Index_Male=[60, 40, 70, 65, 85]
Happiness_Index_Female=[30, 60, 70, 55, 75]
plt.bar([0.25, 1.25, 2.25, 3.25, 4.25],Happiness_Index_Male.color='blue', label=" Male”,width=.5)
pit.bar([.75, 1.75, 2.75, 3.75, 4.75], Happiness_Index_Female, color=‘Green', width=.5, label=“Female”) pos=range(len(City))
print(pos)
plt.xticks (pos.City, fontsize=10)
plt.xlabe1('City', fontsize=16)
plt.ylabe1('Happiness_Index', fontsize=16)
plt.title("Happiness Index across cities by gender",fontsize=18)
plt.legend( )
plt.show( )
Or