Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography with Solutions Set 9 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Set 9 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
General Instructions
This question paper contains 30 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper is divided into five sections – Sections A, B, C, D, and E.
- Section A – Questions no. 1 to 17 are Multiple Choice (MCQ) Type Questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B – Questions no. 18 and 19 are Source Based Questions carrying 3 marks each.
- Section C – Questions no. 20 to 23 are Short Answer (SA) Type Questions carrying 3 marks each. Answer to these questions shall be written in 80 to 1oo words.
- Section D – Questions no. 24 to 28 are Long Answer (LA) Type Questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to these questions shall be written in 120 to 150 words.
- Section E – Questions no. 29 and 30 are Map-Based Questions.
Section A
Section A consists of 17 questions of 1 mark each
Question 1.
Out of the total population in India, what is the percentage of population lives in urban areas (2011)? (1)
(a) 38%
(b) 10.8%
(c) 31%
(d) 31.5%
Answer:
(c) 31%
Question 2.
Match the following. (1)
| List I (Type) | List II (Town) |
| A. Industrial town | 1. Pachmarhi |
| B. Satellite town | 2. Hugli |
| C. Tourist town | 3. Ujjain |
| D. Cultural town | 4. Ghaziabad |

Answer:
(d) 2 4 1 3
Question 3.
‘Landing’ is the name of which of the following agricultural systems? (1)
(a) Plantation agriculture
(b) Primitive subsistence agriculture
(c) Mixed farming
(d) Dairy farming
Answer:
(b) Primitive subsistence agriculture
![]()
Question 4.
National Waterway 1 (NW1) stretches from (1)
(a) Sadiya-Dhubri
(b) Allahabad-Haldia
(c) Kottapuram-Kollam
(d) Kollam-Dhubri
Answer:
(b) Allahabad-Haldia
Question 5.
Which of the following can be a consequence of very high population growth? (1)
(a) Depletion of resources
(b) Rise in epidemics
(c) Shortage of food supply
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 6.
In which among the following Five Year Plans, the Hill Area Development Programme was started? (1)
(a) Fifth Five-Year Plan
(b) Seventh Five-Year Plan
(c) Third Five-Year Plan
(d) Sixth Five-Year Plan
Answer:
(a) Fifth Five-Year Plan
Question 7.
Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched? (1)
Activity Regions
(a) Hunting – Cold region
(b) Gathering – High Iatitude zones
(c) Nomadic herding Magnolia
(d) Transhumance – Delhi
Answer:
(d) Transhumance – Delhi
Question 8.
Which of the following is not a pillar of human development? (1)
(a) Equity
(b) Equality
(c) Sustainability
(d) Empowerment
Answer:
(b) Equality
Question 9.
Which of these countries is in the first stage of Demographic transition? (1)
(a) Bangladesh
(b) India
(c) Bhutan
(d) Canada
Answer:
(a) Bangladesh
![]()
Question 10.
Low latitude zone includes which of the following areas where gathering is still practiced? (1)
(a) Amazon Basin
(b) Tropical Africa
(c) Northern Fringe of Australia
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 11.
Which of these have the heighest percentage of rural population? (1)
(a) Himachal Pradesh
(b) Uttarakhand
(c) Bihar
(d) Arunachal Pradesh
Answer:
(c) Bihar
Question 12.
Which of the states operates the Konkan Railway? (1)
(a) Maharashtra
(b) Goa
(c) Karnataka
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 13.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes given below. (1)
Assertion (A) Negative balance of trade occurs when the value of imports is more than the value of exports.
Reason (R) A country’s economy is largely affected by balance of payment.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is false, but R is true
(d) A is true, but R is false
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
Question 14.
Consider the following statements. (1)
I. North Atlantic sea route is busiest sea route in the world.
II. North Atlantic sea route connects USA with Europe.
Codes
(a) Only statement I is correct
(b) Only statement II is correct
(c) Both the statement are correct, and statement II correctly explain statement I
(d) Both the statement are true, but not related with each other
Answer:
(c) Both the statement are correct, and statement II correctly explain statement I
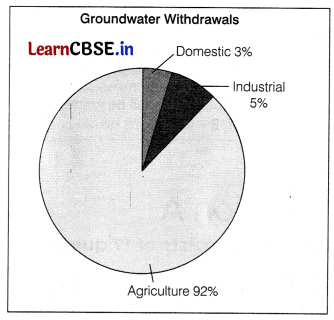
Directions Read the following graph and answer the question no. 15 to 17.
Question 15.
What is the combined percentage of groundwater withdrawals by the industrial and domestic sectors? (1)
(a) 3.6%
(b) 5%
(c) 8%
(d) 92%
Answer:
(c) 8%
Question 16.
What sector has the lowest contribution to groundwater withdrawals?
(a) Agriculture
(b) Industrial
(c) Domestic
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Domestic
![]()
Question 17.
Which sector has the highest contribution to groundwater withdrawals?
(a) Agriculture
(b) Domestic
(c) Industrial
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Agriculture
Section B
Section B consists of 2 Source based questions of 3 marks each
Question 18.
Read the given passage carefully and answer the questions that follow. Nuclear energy has emerged as a viable source in recent times. Important minerals used for the generation of nuclear energy are uranium and thorium. Uranium deposits occur in the Dharwar rocks. Geographically, uranium ores are known to occur in several locations along the Singbhum Copper belt. It is also found in Udaipur, Aiwar and Jhunjhunu districts of Rajasthan, Durg district of Chhattisgarh, Bhandara district of Maharashtra and Kullu district of Himachal Pradesh. Thorium is mainly obtained from monazitc and ilmenite in the beach sands along the coast of Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
World’s richest monazite deposits occur in Palakkad and Kollam districts of Kerala, near Vishakhapatnam in Andhra Pradesh and Mahanadi river delta in Odisha. Atomic Energy Commission was established in 1948, progress could be made only after the establishment of the Atomic Energy Institute at Trombay in 1954 which was renamed as the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre in 1967.
The important nuclear power projects are Tarapur (Maharashtra), Rawatbhata near Kota (Rajasthan), Kalpakkam (Tamil Nadu), Narora (Uttar Pradesh), Kaiga (Karnataka) and Kakrapar (Gujarat). When the magma from the interior of Earth, comes out on the surface, tremendous heat is released. This heat energy can successfully be tapped and converted to electrical energy. Apart from this, the hot water that gushes out through the geyser wells is also used in the generation of thermal energy. It is popularly known as geothermal energy. This energy is now considered to be one of the key energy sources which can be developed as an alternate source. The hot springs and geysers are being used since Medieval period. In India, a geothermal energy plant has been commissioned at Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh.
(i) Thorium is obtained from which mineral? (1)
(ii) Which source of energy is renewable in nature? (1)
(iii) In which region, the deposits of copper were found? (1)
Answer:
(i) Thonum is obtained from Monazite.
(ii) Geothermal energy is a form of renewable source of energy.
(iii) The deposits of copper found in the region of Singhbhum.
Question 19.
Study the given map and answer the following questions.
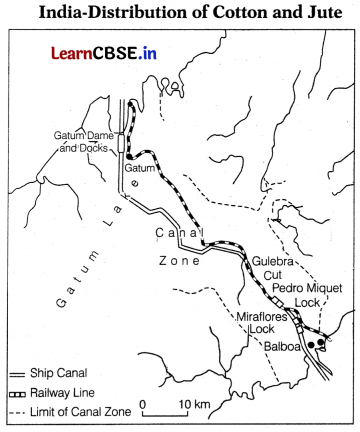
(i) Identify and name the canal shown in the map. (1)
(ii) Mention any one characteristic of this canal. (1)
(iii) Which oceans are connected through this canal? (1)
Answer:
(i) This map shows Panama canal.
(ii) It is 72 km long and involves a very deep cutting for a length of 12 km.
(iii) It connects the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean.
Section C
Section C consists of 4 questions of 3 marks each
Question 20.
Highlight the importance of medical tourism in India. (3)
Or
“Outsourcing has resulted in opening up a large number of job opportunities in several countries”. Analyse the statement with three suitable examples. (3)
Answer:
India has emerged as the leading country for medical tourism in the world. World-class hospitals located in metropolitan cities cater to patients all over the world. Medical tourism brings abundant benefits to developing country like India. These benefits are
Medical tourism creates employment opportunities in India.
- It contributes to the GDP of the country by generating income.
- It helps in increasing the foreign exchange reserves by increasing foreign exchange earnings.
- It helps in developing medical infrastructure in the country.
- It leads to innovation in healthcare services.
- It also raises India’s image as a global leader in healthcare industry.
- India has nearly 18% of global medical tourism market in the world.
or
Outsourcing has resulted in the opening up of a large number of call centres in India, China, Eastern Europe, Israel. Philippines and Costa Rica. It has created new jobs in these countries. Outsourcing is coming to those countries where cheap and skilled workers are available. These are also out-migrating countries.
This can be explained through these examples
- The Knowledge Processing Outsourcing (KPO) industry involves highly skilled workers that are available in the developing countries at lower wages.
- In developing counties, skilled IT staff is available with good communication skills at lower wages as compared to developed countries.
- Data processing is another IT-related service that employs large number of people in Asian countries.
![]()
Question 21.
What is possibilism? Describe with examples. (3)
Answer:
The concept of possibilism states that there are no necessities, but possibilities everywhere and man is referred to as a master of these possibilities. He/she is not influenced by the constraints imposed by natural environment. Man can adopt. adjust and modify the forces of his physical environment with his strength and innovation. His imprints could be seen everywhere. For instance
- Health resorts on highlands
- Huge urban sprawls
- Agricultural fields
- Orchards and pastures in plains and rolling hills
- Ports on the coasts
- Oceanic routes on the oceanic surface
- Satellites in the space
Question 22.
Explain distance as most important factor in determing the location of industries. (3)
Or
What are the basis on which industries are classified? (3)
Answer:
Distance is the most important factor in determining the location of industries because:
- Access to market for the products of industry depends upon the distance between the location of industry and the nearby market,
- Distance between the site of raw material and industry influences the location of industry.
- Heavy industries depend upon power sources. Hence, they are located close to the sources of power.
- Efficient transportation system, which can travel large distances in short time s essential for the development of industries.
Or
Industries are classified on various basis. These are:
- On the Basis of Size On the basis of size, Industries are classified as cottage or household industries, small scale industries and large scale industries. The size is determined by capital, number of workers and volume of production.
- On the Basis of Inputs/Raw Materials On this basis, industñes are agro based industries, chemicals based industries, mineral based industries, etc. The nature of input determines their operations.
- Industries Based on Output/Product On this basis, industries are classified as basic industries and consumer goods/non basic industries.
- On the Basis of Ownership On this basis, industries are classified into public sector, private sector and joint sector industries.
Question 23.
What are the major problems associated with road transport in the world? (3)
Answer:
Road trnsportation ¡s considered most efficient and cost effective way of transportation for short distance. Although it is gaining prominence in recent days, there are certain problems associated with it as well.
These problems are as follows
- During rainy days, the roads which are unmetalled are damaged seriou&y. Even unmetalled roads are washed away by floods, which results in breaking up the road network.
- The road transport system records heavy traffic. When roads cannot cope up with the demands of traffic on the road, they are heavily congested.
- Huge amounts of money is required for construction and maintenance of roads which affects the quality of roads, mainly in developing countries.
Section D
Section D consists of 5 questions of 5 marks each
Question 24.
Discuss the religious composition in population of India which shows the secular fabric of Indian society. (5)
Or
The decadal and annual growth rates of population in India are both very high and steadily increasing over time. “Substantiate
the statement. (5)
Answer:
The spatial distribution of religious communities in the country shows that there are certain states and districts having large numerical strength of one religion. India is the land of multiple religions. It is a place of origin of various religions like Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism but there are large numbers of Christians, Muslims and Zoroastrians.
The distribution of religious communities shows the statistical facts which proves the above argument:
- Hindus They range from 70-90 per cent and are found in majority in various states except Jammu and Kashmir and in some North-East states.
- Muslims They are the largest minority religious groups and covers 14.23% of total population. They are concentrated in Jammu and Kashmir, West Bengal.
- Kerala, Uttar Pradesh, Delhi and Lakshadweep and are in majority in Jarnmu and Kashmir and Lakshadweep.
Christians They are 2.30% of total population and are concentrated along the Western coast of Goa. - Kerala, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Chota Nagpur plateau and hills of Manipur.
- Sikhs Population of Sikh community is 1.72% but they are the most prosperous religious community, They are concentrated in small area of country particularly in Punjab, Haryana and Delhi.
Jains and Buddhists They are the smallest religious groups. Jams are concentrated in Western part of India in the states of Rajasthan, Gujarat and Maharashtra, Buddhists are concentrated in Maharashtra, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh and Ladakh.
Zoroastrians These are the natives of Iran and are concentrated in Mumbai, Goa and Gujarat. This community is very progressive in business and trade.
Or
Growth of population is the change in the number of people living in a particular area between two points of time. The decadal and annual growth of population in India are very high and steadily increasing over time. In India, the annual and decadal growth rate of population is more than the other developed countries.
In the decades of 1951-81, mortality rate declined rapidly but the fertility and rate of population was high in the country. This resulted in high decadal and annual growth rate. The developmental activities and improvement in socio-economic condition further increased growth rate. But after the year 1981 the decadal and annual growth rate started declining. At present the annual growth of India’s population is 1.64% (2011). Still, the growth rate of population in India is high as compared to the developed countries.
![]()
Question 25.
What are the major characteristics of subsistence agriculture? (5)
Answer:
Subsistence agriculture refers to the type of agriculture where nearly all of the production is consumed by the producers or the local people themselves. In this type of agriculture, the producers themselves becomes consumers. The subsistence agriculture is divided into primitive subsistence agriculture and intensive subsistence agriculture.
Characteristics of primitive subsistence agriculture are
- Here, the vegetation is usually cleared by fire and the ashes produced improves the fertility of the soil.
- The cultivated land is very small in area and it is cultivated by primitive tools like stick and hoes.
- The land is cultivated for 3 to 5 years after which the soil loses its fertility. The farmer shifts to another patch of land and clears it for cultivation.
- Farmers return to the earlier patch of land, when that land regains its fertility.
- It is practiced in tropical regions such as Africa. South and Central America and South East Asia.
- Intensive subsistence agriculture ¡s divided into two categories. One is subsistence agriculture dominated by paddy and another which is dominated by crops other than paddy.
Question 26.
What are the characteristics of road transport in India? (5)
Or
Which apex body develops the Border roads? Explain its importance. (1+4)
Answer:
Characteristics of road transport in India are as follows:
- With a total length of 54.8 lakh km of roads, India has placed itself among the countries which have a large road network.
- Road transport carries about 85% of passenger and 70% of freight traffic every year. it is preferred for short-distance travel as it provides door-to-door service.
- Roads are mainly concentrated and around urban areas, rural and remote areas are least connected by the roads.
- Distribution of roads is not even throughout the country. Road density is highest in Kerala and lowest in Jammu and Kashmir. Most of the Northern and Southern states have highly dense network of roads as compared to North-East and Himalayan region.
- In India, roads are classified on the basis of purpose of construction and maintenance in National Highways (NH), State Highways (SH), major district roads and rural roads.
- A part from above roads, there are border roads which are constructed for defence purpose and international roads which are constructed to link and connect with neighbouring countries. They are also used for strategic purposes.
Or
The apex organization for developing border roads in India the Border Road Oganisation (BRO). The organisation was established in May 1960 for accelerating economic development and strengthening defence preparedness through rapid and coordinated improvement of strategic roads aiong the Northern and North-Eastern borders. The importance of border roads for India is:
- These are meant to promote harmonious relationship with the neighbouring countries of India by providing
effective links and routes. - These roads are suitable for carrying out international trade with the bordering countries of India which leads to economic development.
- They are most suitable during foreign attacks as troops and defence materials can be easily transported to border posts with the use of these roads.
- These roads are used to provide essential items to the unaccessible areas such as mountain regions in states of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Arunachal Pradesh etc.
- These roads integrate the far off areas of India with the Indian mainland that helps in National integration and unity.
![]()
Question 27.
Noise pollution has become hazardous in big cities of India. Explain. (5)
Answer:
Noise pollution has become hazardous in many big cities of India such as Delhi and Mumbai due to the following factors
- With the increase in population, the volume of traffic and passengers has increased, This has led to more noise pollution due to vehicular noise.
- More people have become prosperous in the cities. As a result of this, the number of private vehicles such as cars have increased significantly. This has led to traffic jams during peak hours i.e. in the morning and in the evening when people go to and come from their work places. This has increased noise pollution on the roads.
- Rapid industrialisation in and around the residential colonies has also increased noise pollution due to operation of machinery. Small and cottage industries are operate in the areas near the markets.
- Construction activities have increased to accommodate the ever increasing population in the big cities. These activities generate too much noise.
- Religious activities, social functions, rallies, etc. create noise pollution particularly in the late hours of the day.
Question 28.
Why does 90% of world population lives in about 10% of its total area, whereas 10% population reside in 90% of land area? (5)
Or
Briefly explain trends in population growth of the world with special reference to the help of science and technology. (5)
Answer:
The population around the world is unevenly distributed. About 90% lived in 10% of total area and 10% resides in 90% of area. Almost 60% of world population lives in 10 countries, There are many factors that influence this form of uneven distribution of
population. But, most important amongs them are Cultural Factors Traditions and culture of a place influence the distribution of population. People like to migrate in areas where common tradition and culture are found.
Physical Factors Relief, climate, soil, and mineral are the physical factors which determine the population of any place. Tibet is the region of very less population, whereas Indo-Gangetic Plain is overpopulated.
Means of Transport Regions with better facilities of means of transport lead to better economic condition. This leads to high density of population. Mumbai-Pune industrial region is the best example.
Economic Condition
Industrial and agricultural regions of the world are thickly populated due to presence of huge employment opportunities and
favourable living conditions. For example, industrial regions of India, USA, Japan and UK.
Or
During the last few hundred years population has increased at an alarming rate. Technological advancement has helped in the reduction of death rate and provided a stage for accelerated population growth.
After the evolution and introduction of agriculture about 12,000 to 8,000 years ago, the size of population was small – roughly 8 million.
- In the first century A.D. it was below 300 million. The expanding world trade during the sixteenth and seventeenth century, set the stage for rapid population growth.
- Around 1750, with the beginning of Industrial Revolution, the world population was 550 million. In, 2020 world population has reached 7.8 billion.
- Science and technology also help in population growth in following ways
- World population exploded in the eighteenth century after the technological revolution in form of Industrial Revolution,
advancement in means of transportation and improvement in agricultural techniques.
Section E
Section E consists of 2 Map based questions of 5 marks each
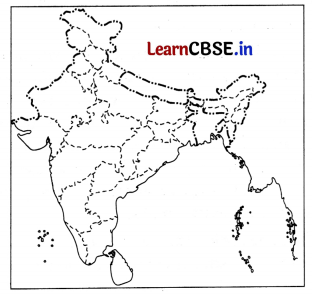
Question 29.
On the political map of India, locate and label any five of the following with appropriate symbols. (5)
(i) A bauxite mine in Madhya Pradesh
(ii) A International Airport
(iii) A leading producer of jute
(iv) An oil refinery
(v) An iron-ore mine in Chhattisgarh
(vi) A coal mine in Tamil Nadu
(vii) State with highest population density
Answer:
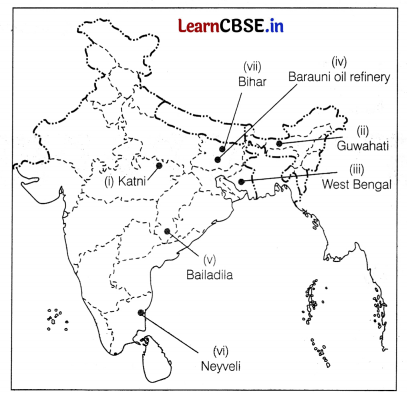
![]()
Question 30.
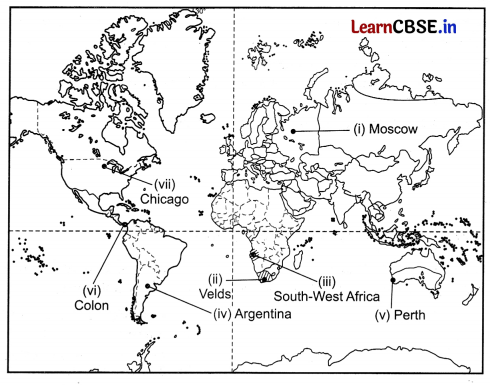
On the given political map of the world, the following seven features are shown. Identify any five of these features and write their correct names on the lines marked near each feature. (5)
(i) A major Airport in Europe
(ii) An area of extensive commercial grain farming
(iii) An area under nomadic herding
(iv) An area of mixed farming
(v) West Terminal Station of Trans-Australian Railway
(vi) A major seaport
(vii) A major seaport in South America
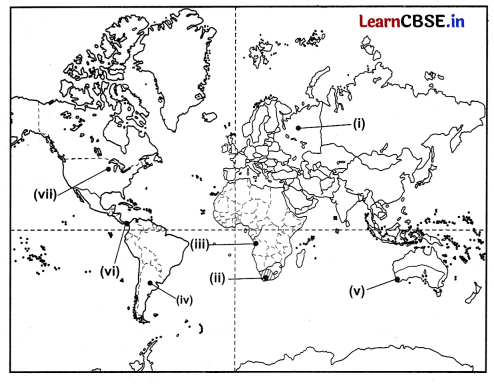
Answer: