Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography with Solutions Set 7 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Set 7 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
General Instructions
This question paper contains 30 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper is divided into five sections – Sections A. B. C, ID arid E.
- Section A – Questions no. 1 to 17 are Multiple Choice (MCQ) Type Questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B – Questions no. 18 arid 19 are Source Based Questions carrying 3 marks each.
- Section C – Questions no. 20 to 23 are Short Answer (SA) Type Questions carrying 3 marks each. Answer to these questions shall be written in 80 to 100 words.
- Section D – Questions no. 24 to 28 are Long Answer (LA) Type Questions carrying S marks each. Answer to these questions shall be written in 120 to 150 words.
- Section E – Questions no. 29 and 30 are Map-Based Questions.
Section A
Section A consists of 17 questions of 1 mark each
Question 1.
The approach of spatial organization emerged in geography during which period? (1)
(a) Late 1960s to early 1970s
(b) Late 1950s to late 1960s
(c) 1970s
(d) 1990s
Answer:
(b) Late 1950s to late 1960s
Question 2.
Match the following. (1)
| List I (Pollution) | List II (Effects) |
| A. Water pollution | 1. Smog |
| B. Air pollution | 2. Alkalinity |
| C. Land pollution | 3. Diarrhea |

Answer:
(c) 2 3 1
Question 3.
The subject matter of cultural geography has been taken from (1)
(a) Demography
(b) Psephology
(c) Economics
(d) Anthropology
Answer:
(d) Anthropology
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following symbols is used in place of ‘isthmus’? (1)
(a) Neck
(b) Nose
(c) Mouth
(d) Stomach
Answer:
(a) Neck
Question 5.
Which of the following towns is not a religious or cultural town? (1)
(a) Haridwar
(b) Pushkar
(c) Shimla
(d) Ujjain
Answer:
(c) Shimla
Question 6.
Semi-clustered settlements are found in (1)
(a) Chhattisgarh plateau
(b) Gujarat plains
(c) BundeLkhand plateau
(d) Himalayas
Answer:
(b) Gujarat plains
Question 7.
Which among the following pair is incorrectly matched?
| List-I (Cities) | List – II (Basis of Development) |
| (a) Prayagraj (Allahabad) | On religious and cultural basis |
| (b) Lucknow | Based on remnants of ancient city |
| (c) Kolkata | Based on culture |
| (d) Mumbai | Commercial port. |
Answer:
(c) Kolkata – Based on culture
Question 8.
Arrange the following States/Ut’s in decreasing order of their percentage of urban population correctly. (1)
I. Assam
II. Delhi
III. Maharashtra
IV. Kerala
Codes
(a) I. II, III, IV
(b) I, IV, III, I
(c) III, II, I, IV
(d) IV, I, II, III
Answer:
(b) I, IV, III, I
Question 9.
‘The Radical School of Geography was influenced by which of the following? (1)
(a) Marxian Theory
(b) Kant’s Theory
(c) Gandhian Philosophy
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Marxian Theory
Question 10.
Which of the following States has the lowest population density? (1)
(a) Mizoram
(b) Nagaland
(c) Assam
(d) Himachal Pradesh
Answer:
(a) Mizoram
![]()
Question 11.
Which of the following areas/regions are characterised by very less density of population? (1)
(a) Asia
(b) Arabian Desert
(c) South-East Asia
(d) North-West Europe
Answer:
(b) Arabian Desert
Question 12.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct statement. (1)
I. Watershed Management is an effective way to prevent land degradation.
II. Watershed Management programmes acknowledge the linkages between land, water, and vegetation and improves the
livelihoods of people through natural resources, management, and community participation.
Codes
(a) Only statement I is correct
(b) Both statements are correct and statement II correctly explains statement I
(c) Only statement II is correct
(d) Both the statements are correct, but statement II does not explains statement I
Answer:
(b) Both statements are correct and statement II correctly explains statement I
Question 13.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct statement. (1)
I. Density of population is expressed as number of person per unit area.
II. It helps in getting a better understanding of the spatial distribution of population.
Codes
(a) Both the statements are true
(b) Only statement I is true
(c) Only statement ¡lis true
(d) Both the statements are false
Answer:
(a) Both the statements are tru
Question 14.
There are two statements marked as
Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes given below. (1)
Assertion (A) The period from 1901-1921 is referred to as period of stagnant or stationary phase of growth of population in India.
Reason (R) During this period, both the birth and death rates were high.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(c) Both A and R are false
(d) A is true, but R is false
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
Directions Study the following data and answer the question no. 15 to 17.
Direction of India import trade
| Region Imports | ||
| 2010-11 | 2016-17 | |
| Europe | 3323857 | 403972 |
| Africa | 118612 | 193327 |
| North America | 100602 | 195332 |
| Latin America | 64576 | 115762 |
| Asia and ASEAN | 1029881 | 1544520 |
Question 15.
Which region contributes to largest share in India’s imports? (1)
(a) Europe
(b) Africa
(c) Asia and ASEAN
(d) North America
Answer:
(c) Asia and ASEAN
Question 16.
The largest proportion of India’s exports and imports are carried out by (1)
(a) land routes
(b) sea routes
(c) air routes
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Question 17.
Which among the following measures can help in increasing India’s international trade? (1)
(a) Import liberalisation
(b) Licencing
(c) Increasing import duties
(d) Strict patent laws
Answer:
(a) Import liberalisation
![]()
Section B
Section B consists of 2 Source based questions of 3 marks each
Question 18.
Read the given passage carefully and Answer the questions that follow. Gathering and hunting are the oldest economic activity known. These are carries out at different levels with different orientations. Gathering is practiced in regions with harsh climatic conditions. It often involves primitive societies, who extract, both plants and animals to satisfy their needs for food, shelter and clothing.
This type of activity requires a small amount of capital investment and operates at very low level of technology. The yield per person is very low and little or no surplus is produced. Gathering is practiced in high latitude zones which include Northern Canada, Northern Eurasia, and Southern Chile; low latitude zones such as the Amazon Basin, tropical Africa, Northern fringe of Australia, and the interior parts of Southeast Asia. Gatherers collect valuable plants such as leaves, barks of trees and medicinal plants and after simple processing sell the products in the market.
Synthetic products often of better quality and at lower prices, have replaced many items supplied by the gatherers in tropical forests. It is led to a decrease in gathering activity.
(i) In which type of climatic region, gathering is practiced? (1)
(ii) What is the reason behind constant reduction in gathering activities? (1)
(iii) How do gatherers sustain their life? (1)
Answer:
(i) It is practiced in very harsh climatic regions where other forms of economic activities are not possible.
(ii) Gathering activities have reduced because other cost-effective synthetic products provided an alternative of that
(iii) Gatherers sustain their life by collecting valuable and medicinal plant leaves, banks, etc. They process them and sell it to the markets, to earn a livelihood.
Question 19.
Study the following table and answer the questions that follow:
World: Imports and Exports (in millions of U.S. $)
| Year | Exports Total Merchandise | Imports Total Merchandise |
| 1955 | 95,000 | 99,000 |
| 1965 | 1,90,000 | 1,99,000 |
| 1975 | 8,77,000 | 9,12,000 |
| 1985 | 19,54,000 | 20,15,000 |
| 1995 | 51,62,000 | 52,92,000 |
| 2005 | 1,03,93,000 | 1,07,53,000 |
| 2015 | 1,55,83,232 | 1,56,28,204 |
(i) Which aspect of trade has shown rapid growth? (1)
(ii) Has the total volume of trade increased or decreased? (1)
(iii) Why does import take place? Write any two reasons. (1)
Answer:
(i) The imports of total merchandise has shown a rapid growth from 1955 to 2015.
(ii) The given table shows that the total volume of world trade has been steadily rising over the past decades.
(iii) Import takes place due to the following reasons:
When there is lack of some resources or services in a country then import takes place.
When there is a demand of good quality foreign products then import takes place
Section C
Section C consists of 4 questions of 3 marks each
Question 20.
Mention some of the characteristics of border roads. (3)
Or
Mention some of the major problems of road transport in the world. (3)
Answer:
The important characteristics of border roads are as follows
(i)These roads are constructed on the international borders by some specialised agency in a country.
(ii) These roads are important for strategic as well as defence purposes as they help in providing access to strategically important areas along the borders.
(iii) These roads are important for the economy of the people living along the border areas as these are used to supply goods and connect the border areas with major cities.
(iv) It helps in providing security to the country as in case of any conflict at the borders. sufficient action can be taken early.
(v) These roads also provide a good transport system to the people living in the border areas of a country.
Or
Road transport plays an important role in the economy of a country. But it faces various problems, which include
(i) During rainy days, the roads which are unmetalled are damaged seriously. Even unmettled roads are washed away by floods, which results in breaking up the road network.
(ii) The road transport system records heavy traffic. When roads cannot cope up with the demands of traffic on the road, roads are heavily congested.
(iii) Huge amounts of money is required for construction and maintenance of roads which affects the quality of roads, mainly in developing countries. Road networks of the world are not fully developed.
![]()
Question 21.
Write any three differences between mixed farming with dairy farming. (3)
Answer:
Mixed farming and dairy farming are compared in the points given below
(i) Mixed farming is found in the highly developed parts of the world, e.g. North-Western Europe. Eastern-North America. parts of Eurasia and the temperate latitudes of Southern continents, but there are three main regions of commercial dairy fan-fling. The largest is North-Western Europe, the second is Canada and the third belt includes South-Eastern Australia, New Zealand, and Tasmania.
(ii) Mixed farming is characterised by high capital expenditure on farm machinery and building, extensive use of chemical fertilizers and green manures, and also by the skill and expertise of the farmers. In dairy farming, animal sheds. storage facilities for fodder, feeding, and maching machines add to the cost of dairy farming. Special emphasis is laid on cattle breeding. healthcare and veterinary services.
(iii) In mixed farming, equal emphasis is laid on crop cultivation and animal husbandry. Animals like cattle, sheep, pigs, and poultry provide the main income along with crops, but dairy farming involves rigorous care in feeding and matching. There is no off-season during the year as in the case of crop raising.
Question 22.
List the primary contaminants that cause water pollution. (3)
Answer:
Main pollutants which are involved in water pollution are as follows
- Odour, dissolved and suspended solids discharged by industries.
- Ammonia and urea discharged by agricultural activities
- Nitrate and nitrites caused by industrial activities.
- Chloride, fluoride, carbonates oil and grease discharged by industries.
- Insecticide and pesticide residue discharged by agricultural activities.
- Tannin, coliform MPM (bacterial count) sulphates, and sulpbides.
- Heavy metals, e.g. lead, arsenic, mercury, and manganese discharged by industries which disturbs aquatic life badly.
- Radioactive substances discharged by thermal and atomic power plants.
Question 23.
What is World Trade Organisation? Discuss its major functions. (1+ 2)
Or
Describe balance of trade. When does it became favourable or unfavorable for a country? (1+2)
Answer:
World Trade Organisation (WTO) is an international organisation associated with the free and liberal trade in the world. General Agreement for Tariffs and Trade (GATT) was formed in 1948 to make the world tree from tariffs as well as non-tariff barriers.
The main functions of WTO are
- Setting up global rules of trade between nations.
- Resolve disputes between its member states.
- Overseeing the trade in services such as telecommunication and banking.
- Resolve issues related to the intellectual property rights.
Or
The volume of goods and services imported and exported by a country to other countries is known as balance of trade. A country’s economy is affected by its balance of trade. Balance of trade can either be favourable or even unfavourable. It is discussed below
- Negative or Unfavourable Balance of Trade When the value of a country’s imports is more than the value of that country’s exports, then there is a negative or unfavorable balance of trade.
- Positive or Favourable Balance of Trade When the value of a country’s exports is more than the value of that country’s imports, then there is a positive or favourable balance of trade.
Section D
Section D consists of 5 questions of 5 marks each
Question 24.
“The depleting water resources may lead to social conflicts and disputes.” Elaborate it with suitable examples. (5)
Or
What is rainwater harvesting? Discuss its scope and benefits in India to preserve the precious water resources. (1+2+2)
Answer:
Water is a cyclic resource with abundant supplies on the globe. It plays a vital role in the economy of a country. The tensions and disputes on sharing and control of this scarce resource are becoming contested issues among communities, regions and states. In India, the overuse of groundwater resources has led to decline in groundwater table in some states.
Over withdrawal in many states such as Haryana, Punjab, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, etc has led to increase in the concentration fluoride in groundwater. Arsenic concentration has increased in parts of West Bengal. This has led to declining levels of usable and potable groundwater as well as surface water resources.
In states such as Punjab, over-irrigation by tubewells has resulted in soil salinity and depletion of water at a very fast pace. These conditions have caused an artificial scarcity of water because the water resources are present in adequate amount but they cannot be used because of the rate at which they are declining.
Besides this, the rivers in India flow through multiple states due to which these states have to chart a plan for sharing of water resources with each other. The depletion of water resources in one state affects the resources of water in other states. This leads to serious inter-state water disputes and conflicts among the states.
Various states already having disputes among themselves include
- The sharing of water of rivers within the different states such as Himachal Pradesh, Haryana and Punjab is a contesting issue.
- A dispute is going on between Tamil Nadu and Karnataka regarding the water of Kaveri.
- Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat are facing a dispute over the sharing of water of Narmada basin.
Or
Rainwater Harvesting Rainwater harvesting is a method to capture and store rainwater locally for various uses and to recharge groundwater. Scope of Rainwater Harvesting in India
There is a wide scope to use the rainwater harvesting technique to conserve the precious water resources. It can be done by harvesting rainwater on rooftops and open spaces. Traditional rainwater harvesting in rural areas is done by using surface storage bodies such as lakes, ponds, irrigation tanks, etc. In Rajasthan and Gujarat, rainwater harvesting structures locally known as kund or tanka (a covered underground tank) are constructed iri residential areas to store harvested rain water.
At present, rainwater harvesting has been taken up in most of the rural areas of the country. The urban areas present an opportunity for the construction of rainwater harvesting structures on a huge scale The residential, as well as commercial buildings, can be used to tap the rainwater and store and use according to the needs.
The depletion of groundwater resources has made rainwater harvesting much more important in the present time.
Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting
- It will balance the huge gap in the demand and supply of water in urban as well as rural areas.
- It will replenish the groundwater table that has declined in various regions of the country.
- It will reduce the community’s dependence on groundwater as well’ as surface water resources.
- It will result in curtailing the pollution in groundwater as well as surface water resources.
![]()
Question 25.
Discuss the four approaches of human development. (5)
Answer:
There are a number of ways to look at the issues of Human Development. There are four approaches to Human Development. These are
(i) Welfare Approach This approach puts human beings at a central position where he/she is the beneficiary of all the developmental activities. Here people do not participate in the process of development but they are Only passive recipients.
The government is responsible for providing health, education, and social services.
(ii) Income Approach In this approach, human development is linked to income. The level of income decides the level of freedom an individual enjoys. It is believed that if a nation has higher level of income, it leads to higher level of human development.
(iii) Minimum Needs Approach It was proposed by the International Labour Organisation. It considers six basic needs as most important for development of human beings-health, education, food, water supply, sanitation, and housing.
(iv) Capabilities approach This approach emphasises upon building human capabilities in areas of health, education, and access to resources for their human development.
Question 26.
Why is there decline in pasture land in India? How does the change in economy affect the land use? (1+4)
Answer:
Increasing population pressure on land is one of the major reasons which is responsible for the decline in land under pasture and grazing areas. The economic changes that affected the land use in India are When composition of an economy changes, it also changes the land uses because different sectors use land for different purposes. For example, when agricultural area decreases, The area under other categories like area under non-agriculture use increases. With the compositional change in economy and change in land use, area under agriculture declines, but it does not reduce the population pressure on agricultural land.
As land is fixed in s size or area and due to intensive cultivation, the soil fertility is declined, it is very difficult to produce more from the same piece of land. So, more land is needed for agricultural practices and higher production for the growing population. Thus. pasture land is decreasing in India.
![]()
Question 27.
Elucidate the concept of ‘trading’ in tertiary sector of economy. (5)
Or
Transport is an important tertiary activity. Explain. (5)
Answer:
Trading is essentially buying and selling of items produced elsewhere and specifically intended for profit. The towns and cities where all these works take place are known as trading centers. The rise of trading from barter at the local level to money exchange of international scale has produced many centers and institutions such as trading centers or collection and distribution points.
The types of trading are Retail Trading This is the business activity concerned with the sale of goods directly to the consumers. Most of the retail trading takes place in fixed establishments or stores solely devoted to selling and street peddling. handcarts. trucks, door-to-door, mail-order, telephone. automatic vending machines and Internet are examples of non-store retail trading.
Wholesale Trading It constitutes bulk business through numerous intermediary merchants and supply houses and not through retail stores. Some large stores including chain stores are able to buy directly from the manufacturers. However, most retail stores procure supplies from an intermediary source.
Wholesalers often extend credit to retail stores to such an extent that the retailer operates very largely on The wholesaler’s capital.
Or
Transport is a tertiary activity which is essential for a ‘nation’s economy. It is a service by which people, materials, and manufactured goods are physically carried from one location to another. It is an organised industry created to satisfy the basic need of mobility.
Speedy and efficient transport systems assist in the production. distribution and consumption of goods in the modern developing societies, the value of the material is significantly enhanced by transportation. In other words, final sale price of an item depends on the total transportation involved from manufacturing to sale point. Transport distance can be measured as kilometer distance or actual distance of route length; time distance or the time taken to travel on a particular route, and cost distance or the expense of traveling on a route. In selecting the mode of transport, distance, in terms of time or cost, is the determining factor.
Factors affecting demand for transport is influenced by the size of population. The larger the population size, the greater is the demand for transport. Some of the commonly used form of transport are roadways. railways and airways. They can vary in distance covered, cost, and goods or manpower transported. Railways are the cheapest option to carry large amounts of cargo over large distances, whereas airways are the fastest but usually expensive compared to road and railways transport.
Question 28.
What is the basic principle on which collective farming was based? Describe how it was implemented in the erstwhile USSR. (2+3)
Or
Explain market gardening and horticulture. Describe any four characteristics of this type of agriculture of the world. (1+4)
Answer:
The basic principle on which collective farming was based is social ownership of the means of agricultural production and collective labour. According to this principle, the farmers had to collectively pool their resources and sell their produce to the state at remunerative prices offered by the government.
It was implemented in the erstwhile USSR from 1929 onwards during the regime of Joseph Stalin as Kolkhoz model. Kolkhoz was a term used for a collective farm. The purpose was to improve upon the inefficiency of the previous methods of agriculture and to boost agricultural production for self-sufficiency.
According to this model, the farmers used to pool in all their resources such as land, livestock, and labour to practice agriculture and produce crops in the agricultural fields, They were allowed to retain very small plots to grow crops in order to meet their daily requirements.
Annual targets were set by the government and the produce was sold to the state at fixed prices. Production in excess ot the target was distributed among the members of the group or sold in the market.
The farmers had to pay taxes on the farm produce, hired machinery, etc. Members of each Kolkhoz were paid according to the nature of the work allotted to them by the farm management. Exceptional work was rewarded in cash or kind. After the collapse of the USSR, this model no longer being followed.
Or
Market Gardening and horticulture specialises in the production of high-value crops such as vegetables, fruits, and flowers, mainly for the urban markets. These farms are located near urban areas.
Features characteristics of market gardening and horticulture are as follows:
- Farms are small in size and located near urban centers where good transportation facilities are available.
- It is both labour and capital intensive and lays emphasis on the use of irrigation. HYV seeds, fertilizers, insecticides, greenhouses, and artificial heating systems in colder regions.
- The regions where farmers specialize in cultivation of vegetables only is known as truck farming.
- This type of agriculture is practiced in well-developed and densely populated regions of North-West Europe. North Eastern USA and the Mediterranean regions. The Netherlands specializes in growing flower and horticultural crops, especially Tulips.
Section E
Section E consists of 2 Map based questions of 5 marks each
Question 29.
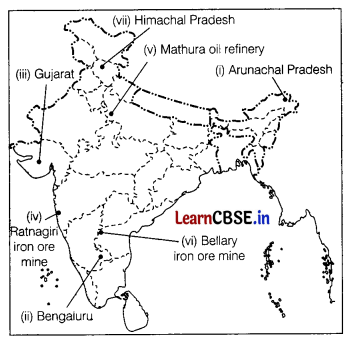
On the political map of India, locate and label any five of the following with appropriate symbols. (5)
(i) The state with the low population density
(ii) The city in Karnataka with more than 10 million population
(iii) The leading producer state of cotton in India
(iv) Ratnagiri iron ore mine
(v) Mathura oil refinery
(vi) Iron ore mine in Karnataka
(vii) A state with lowest level of urbanisation
Answer:
![]()
Question 30.
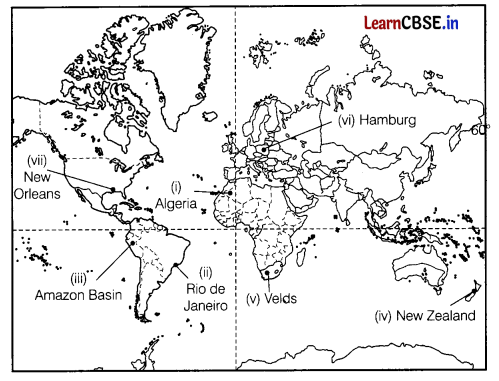
On the given political map of the world, the following seven features are shown. Identify any five of these features and write their correct names on the lines marked near each feature. (5)
(i) The largest country in Africa in terms of area
(ii) A major seaport
(iii) An area of subsistence gathering
(iv) A country where commercial livestock rearing is practiced
(v) Commercial grain cultivation in South Africa
(vi) A major seaport in Europe
(vii) A major airport
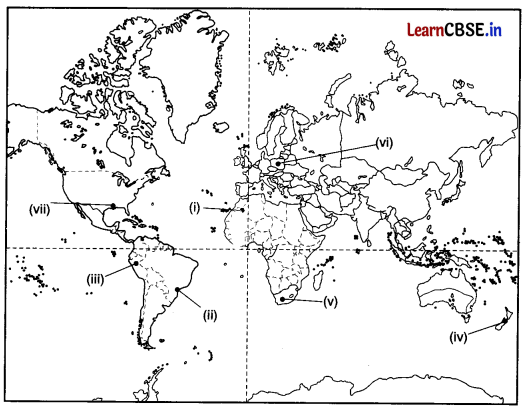
Answer: