Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography with Solutions Set 6 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Set 6 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
General Instructions
This question paper contains 30 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper is divided into five sections – Sections A, B, C, D, and E.
- Section A – Questions no. 1 to 17 are Multiple Choice (MCQ) Type Questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B – Questions no. 18 and 19 are Source Based Questions carrying 3 marks each.
- Section C – Questions no. 20 to 23 are Short Answer (SA) Type Questions carrying 3 marks each. Answer to these questions shall be written in 80 to 100 words.
- Section D – Questions no.24 to 28 are Long Answer (L.A) Type Questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to these questions shall be written in 120 to 150 words.
- Section E – Questions no.29 and 30 are Map-Based Questions.
SectionA
Section A consists of 17 questions of 1 mark each
Question 1.
Which of the following best signifies the nature of Human Geography? (1)
(a) It covers all the elements created by men only.
(b) It covers all the elements created by nature only.
(c) It covers all the elements created by nature as well as men.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) It covers all the elements created by nature as well as men.
Question 2.
With reference to Malthusjan’s theory, what is preventive check for population control? (1)
(a) Famine
(b) Disease
(c) War
(d) Late marriage
Answer:
(d) Late marriage
Question 3.
Which of the following states has a high demand of groundwater? (1)
(a) Arunachal Pradesh
(b) Punjab
(c) Gujarat
(d) Kerala
Answer:
(b) Punjab
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following is not a feature of plantation agriculture? (j)
(a) Large estates
(b) Crop specialisation
(c) Heavy capital investment
(d) Highly skilled labour.
Answer:
(d) Highly skilled labour.
Question 5.
Human beings interact with the physical environment with which of the following? (1)
(a) Tools
(b) Technology
(c) Skills
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Technology
Question 6.
Match the following. (1)
| List I (Phase of Population growth) | List II (Characteristics) |
| A. Phase I | 1. Steady population growth |
| B. Phase II | 2. Population explosion |
| C. Phase III | 3. Negative growth rate |
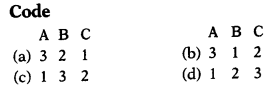
Answer:
(b) 3 1 2
Question 7.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct answer with the help of given codes. (1)
I. The tribe to-Himalayan group of languages is mainly spoken in Sikkim.
II. Indo-Axyan is the largest linguistic group of India.
Codes
(a) Both the statements are true
(b) Only statement I is true
(c) Only statement II is true
(d) Both the statements are false
Answer:
(a) Both the statements are true
Question 8.
Which of the following is the best example of tertiary activities? (1)
(a) Trade and Commerce
(b) Transport
(c) Communication
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 9.
The important mineral available in the North-Eastern plateau region mineral belt is (1)
(a) Iron ore
(b) Coal
(c) Manganese
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
![]()
Question 10.
Arrange the following features of Human Geography as per their period of origin. (1)
I. Emergence of three new schools of thought.
II. Use of sophisticated statistical tools.
III. Universal theories to explain the human conditions were questioned.
IV. Elaborate descriptions of all aspects of a region were undertaken.
Codes
(a) I, II, III, IV
(b) II, III, IV, I
(c) IV, II, I, III
(d) I, IV, II, III
Answer:
(c) IV, II, I, III
Question 11.
Match the following. (1)
| List I | List II |
| A. Population Density | 1. \(\frac{B_i}{P} \times 100\) |
| B. Crude Birth Rate | 2. \(\frac{D}{P} \times 100 \) |
| C. Crude Death Rate | 3. \(\frac{\text { Population }}{\text { Area }} \) |
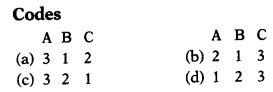
Answer:
(a) 3 1 2
Question 12.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct options from given below. (1)
I. Road transport is cheap and faster mode of transport.
II. It is highly preferred for long-distance trade of goods.
Codes
(a) Only statement I is correct
(b) Only statement II is correct
(c) Both the statements are correct and statement II correctly explains statement I
(d) Both the statements are true, but not related with each other.
Answer:
(a) Only statement I is correct
Question 13.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes given below.
Assertion (A) Many industries benefit from nearness to a leader Industry.
Reason (R) Linkages between industries increases savings and profits for all the industries.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is false, but R is true
(d) A is true, but R is false
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
Question 14.
Which of the following have very high density of population in the world?
(a) North-East USA
(b) Norway
(c) Arabian Desert
(d) Amazon Basin
Answer:
(a) North-East USA
Directions Read the following graph and answer question no. 15 to 17.
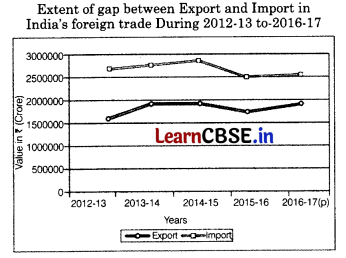
Question 15.
The difference between exports and imports of a country is known as (1)
(a) Balance of Trade
(b) Balance of Payment
(c) Composition of Trade
(d) Terms of Trade
Answer:
(a) Balance of Trade
![]()
Question 16.
In which year both exports and imports started declining? (1)
(a) 2013-14
(b) 2014-15
(c) 2015-16
(d) 2012-13
Answer:
(b) 2014-15
Question 17.
Which year represent the maximum difference between import and export? (1)
(a) 2012-13
(b) 2013-14
(c) 2014-15
(d) 2015-16
Answer:
(a) 2012-13
Section B
Section B consists of 2 Source based questions of 3 marks each
Question 18.
Read the given passage carefully and answer the questions that follow. India is endowed with fairly abundant resources of iron ore. It has the largest reserve of iron ore in Asia. The two main types of ore found in our country are haematite and magnetite. It has great demand in international market due to its superior quality. The iron-ore mines occur in close proximity to the coal fields in the North-Eastern plateau region of the country which adds to their advantage.
About 95 percent of total reserves of iron ore is located in the States of Odisha, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Karnataka, Goa, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu. In Odisha, iron ore occurs in a series of hill ranges in Sundergarh, Mayurbhanj, and Jhar.
The important mines are Gurumahisani, Sulaipet, Badampahar (Mayurbhaj), Kiruburu (Kendujhar) and Bonai (Sundergarh). Similar hill ranges, Jharkhand has some of the oldest iron-ore mines and most of the iron and steel plants are located around them.
Most of the important mines such as Noamundi and Gua are located in Poorbi and Pashchimi Singhbhum districts. This
belt further extends to Durg, Dantewara and Bailadila. Dalli, and Rajhara in Durg are the important mines of iron-ore in the country.
In Karnataka, iron-ore deposits occur in the Sandur-Hospet area of Bailan district, Baba Budan hills and Kudremukh in Chikkamagaluru district and parts of Shivamogga, Chitradurg, and Tumakuru districts. The districts of Chandrapur, Bhandara, and Ratnagiri in Maharashtra, Karimnagar and Warangal districts of Telangana, Kurnool, Cuddapah and Anantapur districts of Andhra Pradesh, Salem and Nilginis districts of Tamil Nadu are other iron mining regions. Goa has also emerged as an important producer of iron ore.
(i) Which areas are sources of iron-ore mineral? (1)
(ii) Which mineral is found in Dharwar rocks? (1)
(iii) Where is Baba Budan hills are located? (1)
Answer:
(i) Mayurbhanj Hills. Sundergarh and Jhar hills are sources of iron-ore minerals.
(ii) Manganese is found in Dharwar rocks.
(iii) Baba Budan hills are located on state of Karnataka.
Question 19.
Observe the given map of the Suez Canal and answer the following questions.
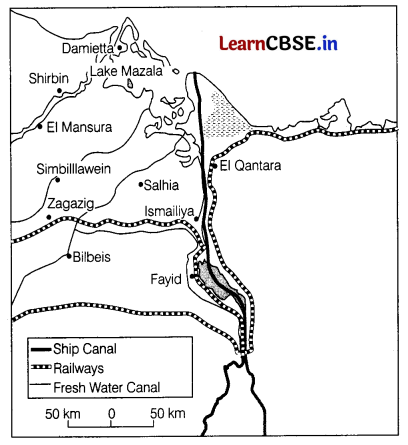
(i) From which country is the given canal passing? (1)
(ii) Which sea is connected. by this canal? (1)
(iii) Why is this canal considered a Gateway of Europe to the Indian Ocean? (1)
Answer:
(i) This canal passes through Egypt.
(ii) This canal connects Mediterranean sea and Red Sea.
(iii) This canal is considered as a Gateway of Europe to the Indian Ocean because the canal cut short the thousands of miles of distance if the trade happen from Europe to the Indian Ocean countries via Suez Canal.
Section C
Section C consists of 4 questions of 3 marks each
Question 20.
how is the service sector important for the economy of a country? (3)
Or
“Transport and communication services are important for a country’s development”. Describe. (3)
Answer:
The growth of service sector has been an important source of prosperity for the economy of various countries. It is important for economy of a country in the following ways Creation of Infrastructure Service sector growth has resulted in creation of infrastructure such as IT and Telecommunications transport lines, communication lines, which provides a strong base for the economy to grow further.
More Employment Opportunities Service sector has contributed to growth of more employment opportunities for the people. Service sector has provided employment to people from the Tier-II and Tier-III towns who used to migrate to large urban
centres in search of job opportunities.
Skilling ol People Growth of service sector has led to skilling of more number of people. The levels of education has also increased as now there are more number of teachers, doctors, lawyers, physicians, etc.
Source of Foreign Income Service sector is also the source of foreign income for the economy as more services are now outsourced to other countries.
Or
Transport and communication services are important for the development of a country. It can be seen with the following points
The transport and communication lines connect one region of a country with the other. It results in transfer of ideas and resources from one region to another.
Means of communication helps in linking various traders across the country and providing essential products to the population of the country. Transport links manufacturing centers and industries with the markets.
Means of transportation also carry people from one place to another and help in fulfilling their basic needs of commuting leisure, etc. Transport and communication services also play an important role in the defense and security of a country, The lines of communication are vital to quickly send army, navy, etc in case of any calamity.
![]()
Question 21.
What are the key features of semi-clustered rural settlements of India? (3)
Answer:
The characteristics of semi-clustered rural settlements in India are as follows
(i) These are developed by the concentration of houses in a restricted area of a dispersed settlement. These settlements are also developed due to fragmentation of a large compact village.
(ii) In the case of fragmentation, a particular group is forced to live far from the center or main village. In this condition, the dominant community or land-owning community captures the most important part in the main village and may force people of
lower strata (level) to live away.
(iii) In India, these types of settlements are mostly found in the plains of Gujarat and Rajasthan.
Question 22.
Satellites and computers have brought revolutionary changes in the present life of the people. Elaborate the statement with three suitable examples. (3)
Or
Evaluate the role and importance of roads in the economic development of India. (3)
Answer:
Satellites and computers have brought revolutionary changes in the present lite of people. It can be elaborated with the help of following examples
(i) Satellites are a part of human lives in many ways. Every time we use a cell phone to call a friend, send SMS, or watch a popular programme on cable television, we are using satellite communication.
(ii) Today weather forecasting through television is helpful in saving the loss of life and property. It is possible through artificial satellites which are successfully installed in the Earth’s orbit and these can connect even the remote corners of the globe
with limited on-site verification.
(iii) As many people use of the internet via computers each year, cyberspace will expand the contemporary economic and social space of humans through e-mail, e-commerce, e-learning, and e-governance.
Or
Importance and role of roadways in the economic development in India are
- Roads provides better connectivity between rural and urban areas, and hence advancement of rural India occurs.
- Road connectivity is very important in linking intra-state urban areas and inter-states for better transportation of various goods and services, and hence for overall development in terms of saving time, money, etc, and reduction in pollution and CO2 emission levels.
- Rural economy would be connected with urban economy through a dense road network.
- A good road network helps to improve import and export in the country.
Question 23.
Discuss how growth in population influences the economic development. (3)
Answer:
The growth in population influences the economic development in the following ways
- Rapid growth of population creates pressure on available resources id hence it causes loss of foreign currency due to import of food and other products.
- Population growth leads to poor living conditions of people in over-populated areas due to low per capital income.
- High percentage of dependent population puts pressure on economy.
Section D
Section D consists of 5 questions of 5 marks each
Question 24.
What is commercial livestock rearing? What are its major characteristics? (1+4)
Answer:
Commercial livestock rearing is a specialised activity in which only one type of animal is reared for products such as meat, wool, hides, which are processed, packed, and exported.
- The major characteristics of commercial livestock rearing are as follows
- Commercial livestock rearing is more organised and capital-intensive.
- Commercial livestock rearing is practised on permanent ranches. These ranches are of large size and are divided into parcels which are fenced to regulate the grazing. When one parcel is grazed, then animals are moved to another parcel.
- All animals are kept according to the carrying capacity of pasture.
- Only one type of animals are reared in commercial livestock rearing. Sorne important animals are sheep, goats, horses, etc. They produce meat, wool hides and skin.
- These products are processed and packed scientifically and exported to different world markets.
- Ranches are managed scientifically and they emphasize on breeding, genetic improvement, disease control, and health care of the livestock.
- USA, Argentina, New Zealand, Australia, and Uruguay are important countries where commercial livestock rearing is practiced.
Question 25.
Explain how water quality has deteriorated in India over the past few decades. (5)
Or
The problem of water pollution has become peculiar in India. What steps can be taken to improve the deteriorating quality of
water? (5)
Answer:
Water quality has deteriorated over the past few decades in India. The causes of degradation in water quality in India are
Rapid Urbanisation Rapid urbanisation in India during the recent decades has given rise to a number of environmental problems such as water supply, waste water generation, collection and disposal of waste. The wastewater discharged from households is untreated and contains harmful elements that cause surface water pollution.
Industries Many freshwater bodies are polluted by industrial wastes or effluents. These are toxic wastes that destroy the natural life forms living in water bodies. It seriously affects the quality of water and increases the level of pollution. Large-scale as well as Small-scale industries contribute to the pollution of water.
Agricultural Runoff Fertilisers and pesticides are carried over by agricultural runoff due to monsoon rainfall or means of irrigation. These harmful chemicals are washed away into the river and pollute the river water. This polluted river water is
consumed by the people and used in agriculture fields again.
Overexploitation of Water Overexploitation of water in the form of irrigation, canals, household use groundwater extraction has resulted in shortage of water in many urban areas and has led to increasing concentrations of harmful elements such as fluorides and arsenic.
Social and Cultural Practices Social and cultural practices such as mass bathing, idol immersion, etc. have, also led to declining quality of river water that is used for drinking, and household activities.
Or
The quality of water has been deteriorating at a very fast place in India, Many large water bodies have deteriorated and their water has become unfit for human use.
Following steps can be taken to improve quality of water Treatment Plants Water treatment plants and sewage treatment plants should be established near the industries so that polluted water is not discharged into the water bodies without treating it properly. This will reduce the harmful level of pollutants present in water and improve its quality.
Waste Reduction and Recycling Instead of generating large quantities of wastewater from households as well as industries, waste generated can be reduced by recycling and reusing the waste material into useful energy or other things. Plastic pollution needs to be stopped at an urgent pace because plastics can be easily recycled and reused without discharging them into the water bodies.
Safe Agricultural Practices Safe and green agricultural practices should be started so that crops that do not pollute water bodies can be grown These is a need to use organic fertilisers instead of harmful chemical fertilizers so that pollution of water can be
prevented.
Watershed Management Watershed management can be used to conserve groundwater and surface water resources. It involves preventing the runoff of water and recharging groundwater bodies through percolation tanks, recharge wells, etc. It also involves conservation and judicious use of all types of resources along with the water resources.
Rainwater Harvesting Rainwater harvesting is used to capture and store rainwater for various purposes, water is stored in pits, wells, and storage tanks. It increases water availability and improves the groundwater quality.
![]()
Question 26.
What is noise pollution? Describe major sources and consequences of noise pollution. (1 + 2+2)
Or
The disposal of urban waste has become a serious concern for the local authorities. Analyse the statement with suitable
examples. (5)
Answer:
Noise pollution is the harmful level of noise that creates an unbearable and uncomfortable state of sound. It is growing as a major problem in urban localities. With increase in technology and transportation. noise pollution is also increasing.
Major sources of noise pollution are various factories. mechanised construction and demolition works. automobiles, aircrafts, etc. Besides these, there are also some periodic but polluting sources of noise like sirens, loudspeakers, etc which are used in various festivals, programmes associated with community activities. The level of noise is measured by sound level expressed in terms of decibels (dB). The biggest nuisance of noise pollution is the noise produced by traffic.
The intensity and nature of noise produced by traffic depends upon factors such as the type of aircrafts, vehicles, trains, etc. In the case of automobiles, it depends upon the quality and condition of road and the automobile. In sea traffic, the noise pollution is confined to the harbour due to loading and unloading activities Intensity of noise pollution from industries depends upon the type of industry. Noise pollution is location-specific and its intensity declines with increase in distance from the source of pollution that is industrial areas, arteries of transportation, airports, etc.
Consequences of noise pollution are of de spectrum. Noise pollution is hazardous in many big cities and metropolitan regions in India. An increase in environmental noise pollution can cause hearing impairment, hypertension, annoyance, mental problems or disorders, sleep disturbance. etc.
Or
The disposal of urban waste has become a serious concern for the local authorities in the following ways Tons of waste come out daily in metropolitan cities and are burnt. The smoke released from the waste pollutes the air. Lack of sewers or other means to dispose of human excretes safely and the inadequacy of garbage collection sources adds to water pollution.
The concentration of industrial units in and around urban centres gives rise to a series of environmental problems. Dumping of industrial waste into rivers is the major cause of water pollution. The solid waste generation continues to increase in both absolute and per capital in cities.
The improper disposal of solid waste attracts rodents and flies which spread diseases The thermal plants release a lot of smoke and ash in the air. For example, a plant producing 500 MW electricity releases 2000 tons of ash which is difficult to manage.
Question 27.
What are the merits and demerits of road transport in the world? (5)
Answer:
Merits of road transport are
Economical Road transport is cheap and most economical mode of transport for short-distance travel and freight movement.
Connectivity Road transport offers the best connectivity among all the means of transport as it offers door to door services,
Transporting Perishable Goods Perishable goods such as milk, vegetables, etc are transported by road transport. It is best suited for transporting these items.
Trade and Commerce Road transport plays an important role in promoting trade and commerce in the country. It also promotes tourism and other economic activities. Flexible Road transport is flexible in nature as multiple routes can be travelled to reach a particular place.
Demerits of road transport are
- Heavy Expenditures The construction and maintenance of roads require heavy expenditures.
- This affects road quality.
- Traffic Road transport is severely affected by traffic and congestion. When roads are not able to cope up with the demands of the traffic, then congestion occurs.
- Not Sustainable for All Seasons During the rainy period, the unmetalled roads are damaged. Even the metalled roads are washed away during floods.
- Difficulty in Construction Roads are difficult to construct in various areas such as mountains. Here, specialised agencies are required to construct roads.
Question 28.
How does countries are classified different categories under the HDI?
Or
Explain the three main areas of measuring human development. (5)
Answer:
According to the human development scores earned by countries, these are classified into four categories.
(i) Countries with very High HDI These are the countries that have a score of more than 0.800 according to the Human Development Report, 2018. This group includes 54 countries according to HDR, 2018.
(ii) Countries with High HDI These are the countries that have a score between 0.701 upto 0.799. These countries invest a lot in social sectors like education, health, etc. They are characterised by good governance and welfare of the people. These
include 53 countries according to HDR, 2018.
(iii) Countries with Moderate HDI These countries have a score between 0.550 upto 0.700. Many of these countries are trying improve their human development score by adopting more people-oriented policies and reducing social discrimination. These countries have higher social diversity and have faced political instability and social uprisings in recent parts. They include 39 countries according to HDR, 2018.
(iv) Countries with Low HDI These countries have score below 0.549. These countries face political turmoil, social instability, civil war famines, wars and high incidence of diseases. These include 38 countries according to HDR, 2018.
Or
The key areas of human development are health, education, and access to resources, They are explained as follows
(i) Health Indicator of health is measured through life expectancy at birth. It shows whether people have longer and healthier lives.
(ii) Education Level of education is measured through gross enrollment ratio and adult literacy rate that represent access to knowledge.
(iii) Access to Resources The indicator of access to resources is purchasing power in terms of US dollars, Building people’s capabilities in areas of health, education, and access to resources is important in enlarging their choices.
Section E
Section E consists of 2 Map based questions of 5 marks each
Question 29.
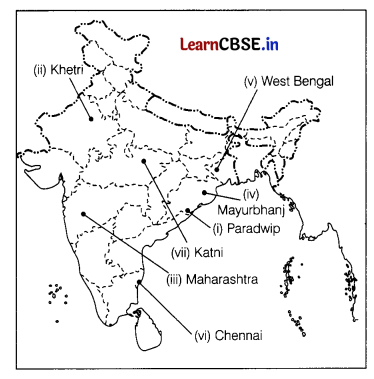
On the given political map of India, locate and label any five of the following with appropriate symbols. (5)
(i) A major seaport in Odisha
(ii) A copper mine in Gujarat
(iii) Leading producer of cotton
(iv) An iron ore mine in Odisha
(v) Leading producer of jute
(vi) An international airport in Tamil Nadu
(vii) A bauxite mine in Madhya Pradesh
Answer:
![]()
Question 30.
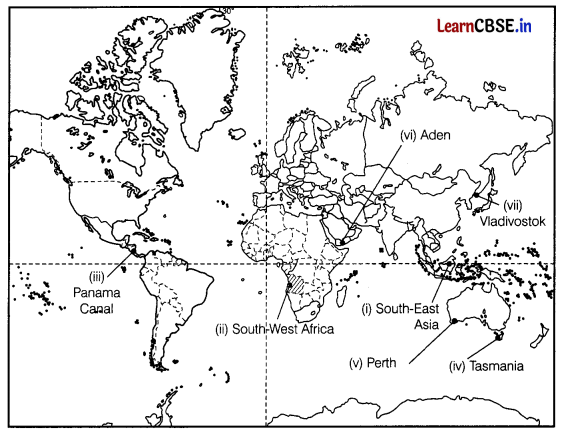
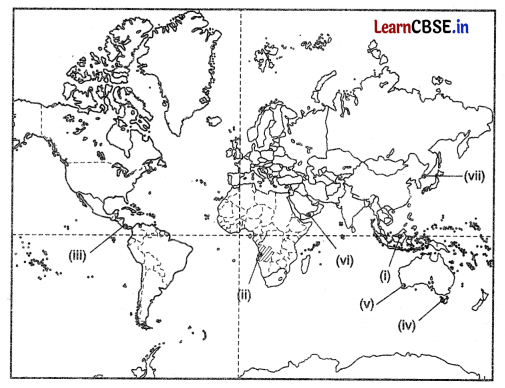
On the given political map of the world, the following seven features are shown. Identify any five of these features and write their
correct names of the lines marked near each feature. (5)
(i) Area of subsistence gathering
(ii) An area of nomadic herding
(iii) An inland waterway
(iv) An area of mixed farming in Australia
(v) A major seaport
(vi) A major airport
(vii) Eastern Terminal Station of Trans-Siberian.
Answer: