Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography with Solutions Set 5 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Set 5 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
General Instructions
This question paper contains 30 questions. ALL questions are compulsory.
- This question paper is divided into five sections – Sections A, B, C, D and E.
- Section A – Questions no. 1 to 17 are Multiple Choice (MCC) Type Questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section 8 – Questions no. 18 and 19 are Source Based Questions carrying 3 marks each.
- Section C – Questions no. 20 to 23 are Short Answer (SA) Type Questions carrying 3 marks each. Answer to these questions shall be written ir 80 to 100 words.
- Section D – Questions no. 24 to 28 are Long Answer (LA) Type Questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to these questions shall be written in 120 to 150 words.
- Section E – Questions no. 29 and 30 are Map-Based Questions.
Section A.
Section A consists of 17 questions of 1 mark each
Question 1.
Which approach of Human Geography was followed during the later Colonial period? (1)
(a) Area! differentiation
(b) Exploration and description
(c) Regional analysis
(d) Spatial organisation
Answer:
(c) Regional analysis
Question 2.
Match the following. (1)
| List I (States) | List II (Population facts) |
| A. Ratzel | 1. ‘Human geography is the systematic study of relationship between human societies and Earth’s surface.” |
| B. Ellen C Semple | 2. “Human geography is the study of the changing relationship between the unresting man and the unstable Earth.” |
| C. Paul Vidai de la Blache | 3. Conception resulting from a more synthetic knowledge of the physical laws governing our Earth and of the relations between the living beings which inhabit it.” |
| D. Griffith Taylor | 4. Concept of Neo-determinism |
Codes
ABCD
(a) 1 2 3 4
(b) 2 3 4 1
(c) 3 2 1 4
(d) 1 2 4 3
Answer:
(a) 1 2 3 4
Question 3.
Who proposed the concept of stop and go determinism in the interaction of human beings with the environment? (1)
(a) Ellen C Semple
(b) Griffith Taylor
(c) Paul Vidal de la Blache
(d) Ratzel
Answer:
(b) Griffith Taylor
![]()
Question 4.
In which rock system Uranium is found? (1)
(a) Dharwar
(b) Gondwana
(c) Cuddapah
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Dharwar
Question 5.
Which of the following is not a cause of air pollution? (1)
(a) Agricultural runoff
(b) Mining activities
(c) Industries
(d) Combustion of fossil fuels.
Answer:
(a) Agricultural runoff
Question 6.
A land left follow for five years comes under which category of land use? (1)
(a) Culturable wasteland
(b) Net sown area
(c) Season wasteland
(d) Follow land
Answer:
(a) Culturable wasteland
Question 7.
Which of the following pairs is correctly matched? (1)
States Population facts
(a) Kerala – Highest literacy Rate
(b) Goa – Highest rural population
(c) Tamil Nadu – State with highest urban population
(d) Gujarat – Highest density of population
Answer:
(a) Kerala – Highest literacy Rate
Question 8.
Arrange the states as per the decreasing order of their percentage of urban population. (1)
I. Delhi
II. Kerala
III. Maharashtra
IV. Assam
Codes
(a) I, II, III, IV
(b) IV, III, I, II
(c) II, I, III, IV
(d) IV, II, I, III
Answer:
(a) I, II, III, IV
Question 9.
The headquarters of Northern Railway Zone of India is located in ……………………… . (1)
(a) Delhi
(b) Lucknow
(c) Kanpur
(d) Chandigarh
Answer:
(a) Delhi
Question 10.
The largest amount of water resources in India are used for which purpose? (1)
(a) Drinking and domestic purposes
(b) Generating hydroelectric power
(c) Irrigation
(d) Pisciculture.
Answer:
(c) Irrigation
![]()
Question 11.
Respiratory diseases are mainly caused by …………………….. pollution. (1)
(a) land
(b) water
(c) air
(d) noise
Answer:
(c) air
Question 12.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct option from the given options. (1)
I. Nomadic herding is practiced over vast horizontal as well as vertical distances.
II. Nomads migrate from plains to high-altitude pastures during winter season and from high-altitude pastures to plains during summer season.
Codes
(a) Only statement I is correct
(b) Only statement II is correct
(c) Both statements I and II are correct
(d) Both statements I and II are incorrect
Answer:
(a) Only statement I is correct
Question 13.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes given below.
Assertion (A) The contribution of agriculture in economy has declined over time.
Reason (R) People are decreasing in agriculture sector in India.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Answer:
(c) A is true, but R is false
Question 14.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct option from the given options. (1)
I. Water transport is the cheapest of transport.
II. India has 17,500 km of navigable waterways.
Codes
(a) Only statement I is correct
(b) Only statement ¡lis correct
(c) Both the statements are correct and statement I correctly explains statement II
(d) Both the statements are true, but not related with each other
Answer:
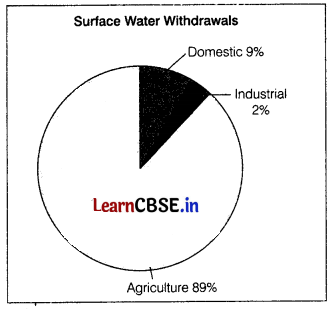
Directions Read the following graph and answer question no. 15-17.
(d) Both the statements arc true, but not related with each other
Question 15.
Which sector alone accounts for most of the surface water utilisation? (1)
(a) Domestic
(b) Agriculture
(c) Industrial
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Agriculture
Question 16.
What percentage of surface water withdrawals is attributed to the industrial sector? (1)
(a) 9%
(b) 2%
(c) 89%
(d) 91%
Answer:
(c) 89%
Question 17.
If the toal surface water withdrawals amount to 100 million cubic meters, how much water is withdrawn by the domestic sector? (1)
(a) 2 million cubic meters
(b) 9 million cubic meters
(c) 89 million cubic meters
(d) 91 million cubic meters
Answer:
(a) 2 million cubic meters
Section B
Section B consists of 2 Source based questions of 3 marks each
Question 18.
Read the given passage carefully and answer the questions that follow. India has traditionally been an agrarian economy and about two-thirds of its population have been dependent on agriculture. Hence, development of irrigation to increase agricultural production has been assigned a very high priority in the Five Year Plans and multipurpose river valleys projects like the Bhakra-Nangal, Hirakud, Damodar Valley, Nagarjuna Sagar, Indira Gandhi Canal Project, etc.. have been taken up.
In fact, India’s water demand at present is dominated by irrigational needs. Agriculture accounts for most of the surface and groundwater utilisation, it accounts for 89 per cent of the surface water and 92 percent of the groundwater utilisation. While
the share of industrial sector is limited to 2 per cent of the surface water utilisation and 5 per cent of the groundwater, the share of domestic sector is higher (9 per cent) in surface water utilisation as compared to groundwater.
The share of agricultural sector in total water utilisation is much higher than other sectors. However, in future with development, the shares of industrial and domestic sectors in the country are likely to increase.
(i) Majority of Indian population is engaged in which type of activity? (1)
(ii) What is the need of irrigation facilities in India? (1)
(iii) What are important ways to conserve groundwater? (1)
Answer:
(i) Majority of Indian population is engaged in agricultural and allied activities. India has traditionally been an agrarian economy.
(ii) India needs better irrigation because of uncertainty in rainfall, over-utilisation of groundwater and high agricultural production due to increasing population.
(iii) Important ways to conserve groundwater are, disposing chemicals properly, limiting the amount of fertilisers used on plants and the use of water harvesting techniques.
Question 19.
Observe the given map and answer the following questions.
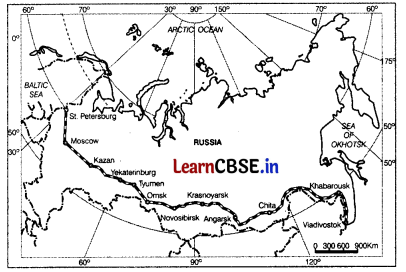
(i) Which railway line is shown on the map? (1)
(ii) Name the Northern and Southernmost point of this railway line. (1)
(iii) Why this railway line is considered lifeline of Russia? (1)
Answer:
(i) The Trans-Siberian railway line is shown on the map.
(ii) The Northernmost point of this railway line is St. Peterburg and Southern point is Vladivostok.
(iii) This railway line is considered lifeline of Russia because it joins most backward and cold regions, to mainland of Russia. It runs through ural mountains and connects agro centres like Chita and lrkutsh.
![]()
Section C
Section C consists of 4 questions of 3 marks each
Question 20.
What are the various sources of noise pollution in urban areas? (3)
Or
“Urban solid waste is a nuisance for metropolitan cities.” Explain briefly. (3)
Answer:
Noise pollution is the state of unbearable and uncomfortable noise levels to human beings caused by different sources.
The main sources of noise pollution are Traffic of vehicles on the roads is the biggest source of noise pollution. Vehicles such as trucks, buses, motorcycles cause varying levels of pollution of noise.
Construction and demolition activities require heavy machinery, which creates large amount of noise in the residential areas.
Industries Industries use large number of moving parts, wtìich leads to more noise pollution. These noises have a significant impact on the workers.
Community Activities Noise from the community activities such as festival celebrations. programmes, loudspeakers create noise. Transport Noise from the transport services such as railways, airways, trucks, etc cause noise pollution.
Or
Urban areas generate a large amount of solid waste, both from the households as well as the industries. In the metropolitan areas where people live in congested places, the problem of solid waste is more serious. It has created multiple problems in the metropolitan regions.
These are Solid waste such as metal pieces, glassware, plastic containers, polythene bags, ashes, floppies are dumped at many places that pollute the land in these areas.
The waste from households and industries is disposed off on private lands or collected and disposed by the municipal facilities in landfill areas. It creates foul smell in these regions.
Ashes and debris from industries, thermal powerhouses and construction of buildings poses serious consequences for the public health, Solid waste acts as carriers of diseases because flies, rodents, etc lives upon the solid waste which spreads diseases such as typhoid, diphtheria, malaria, and cholera, etc.
Question 21.
Growth rate of population in phase IV slow down in India. Why? (3)
Answer:
The decades after 1981 marked the slow growth rate of population due to low birth rate and low death rate. The reasons which are responsible for the slow growth rate of population in phase IV are as follows
The fail in crude birth rate due to family planning is responsible for such slow population growth.
The progressive social development and increase economic progress helped to reduce the growth rate of population.
Question 22.
Differentiate between growth and development. (3)
Or
Discuss importance of human development. (1+4)
Answer:
Differences between growth and development are as follows
| Growth | Development |
| Growth is quantitative and value-neutral. | Development is qualitative approach and it is always value positive. |
| It can be positive or negative. | Development cannot take place unless there is an increment in existing conditions. Hence, it always value positive. |
| For example, it the population of a city grows from one lakh to two lakh over a period of time, we can say that the city has grown. | For example, despite increase in population, if facilities like housing, provision of basic services and other characteristics remain the same, then this growth has not been accompanied by development. |
Or
The importance of human development can understood by the following points
- It improves the quality of life of individuals.
- It provides an individual with various choices.
- It ensures the minimum investment to enhance economic productivity of human beings.
- It makes people aware about their abilities.
- It enhances the conditions of physical environment.
- It provides a stable political system to a country
- It shows the limitations of existing system.
- It works for a long and reasonably healthy human life.
![]()
Question 23.
Describe the development of medieval towns in India during the Mughal period. (3)
Answer:
Medieval towns were developed as headquarters of principalities and kingdoms during the Mughal period. The growth of towns happened at a faster pace in 16th, 17th century which continued upto the middle of 18th century. These were developed as fort towns and came up on the remains of the ancient fort towns.
The basic feature of a town was the presence of a market. The Cuba ¡s defined as the village with a market. There was a hierarchy of towns from the qasba to the district headquarters, to the provincial towns like Agra, Delhi, etc. Examples of these towns are Hyderabad, Jaipur, Lucknow, Nagpur, and so on.
Section D
Section D consists of 5 questions of 5 marks each
Question 24.
Why there is no uniformity in the distribution of roads in India? (5)
Answer:
The distribution of roads is not uniform in India because of the following reasons
- The nature of terrain and level of economic development affects the density of roads in various regions of India.
- Construction of roads in plains in easy and cheap in comparison to hilly areas and mountainous regions.
- Gangetic plains have high-density roads as compared to the North-East region.
- Sandy soil in Rajasthan and parts of (Gujarat is not suitable for construction of roads. Thus, these regions have less density of roads.
Regions which are economically developed have high road density. e.g. Kamataka plateau and Maharashtra have high road density due to high industrialization and economic development.
High density of road network is also found in regions of Punjab, and Haryana because they are agriculturally well developed and there is high level of industrialisation and urbanization.
The regions where there is high rainfall and thick forests have less density of roads. For example, in Meghalaya region, there is very less road density.
Question 25.
What do you mean by Quinary activities? Discuss the new trends in Quinary services. (2 + 3)
Or
What is medical tourism? Explain the scope of medical services in India for overseas patients. How does outsourcing of medical
tests and data interpretation help in this? (1+2+2)
Answer:
Quinary activities are services that focus on the creation, re-arrangement, and interpretation of new and existing ideas, data interpretation, and the use and evaluation of new technologies. Often referred to as gold collar professionals, they represent a sub-division of the tertiary sector representing special and highly paid skills of senior business executives, government officials, research scientists, financial and legal consultants, etc. Their importance in the structure of advanced economies far outweighs their numbers.
New Trends In Quinary Services
New trends in Quinary services include Knowledge Processing Outsourcing (KPO) and home shoring, which an alternative to outsourcing. Knowledge Process Outsourcing It refers to the service industry where there are highly skilled workers. It can also be termed as information-driven knowledge outsourcing, It enables the companies to create additional business opportunities.
The examples of KPO industry are research and development services, intellectual property research, banking sector, and legal profession. Homeshoring It is an operational model in various organisations in which the employees work and perform
all official tasks from a home o external office. The companies hire employees, who work from their domestic location but are connected to the company via Internet. Homeshoring enables a company to reduce infrastructure and maintenance costs of a physical office.
Or
When medical treatment is combined with international tourism activity, it is known as medical tourism. Scope of Medical Tourism in India. The growing medical facilities have made India a favourable destination for the overseas medical tourists. The medical infrastructure in India has developed because of emergence of large number of hospitals, tertiary care clinics which provide highly specialised services at cheaper costs as compared to the developed countries.
Development of advanced transport and communication facilities have also facilitated the flow of tourists for medical purposes. They can now easily visit places which were earlier inaccessible to them due to social, cultural and transport infrastructural issues.
Affordable international fares have contributed to the development of this industry in India. Specialist doctors, nurses and paramedical staff have also emerged in India. They provide quality healthcare to the overseas medical tourists combining the traditional techniques and the modern methods. Thus, medical tourism can emerge as a huge industry in India.
Role of Outsouring of Medical Tests and Data Interpretation
Outsouring of medical tests and data interpretation can help in improving the quality of healthcare for the overseas medical tourists. It results in higher levels of specialised healthcare because the reading of medical tests such as radiology images, ultrasound tests, and MRIs becomes more accurate, It leads to better diagnosis and gives utmost quality healthcare to the
people of overseas country.
![]()
Question 26.
State the global distribution of railways in the continents of the world. (5)
Answer:
The global distribution of railways in the world are Europe has one of the most dense rail networks in the world. There are about 4,40,000 km of railways, most of which is double or multiple-tracked. The important rail heads are London. Paris, Brussels, Milan, Berlin, and Warsaw. Passenger transport is more important than freight in many of these countries.
In Russia, railways account for about 90 percent of the country’s total transport with a very dense network West of the Urals. Moscow is the most important railhead with major lines radiating to different parts of the country’s vast geographical area.
North America has one of the most extensive rail networks accounting for nearly 40 percent of the world’s total. The railways are used more for long-distance bulky freight like ores, grains, timber, and machinery than for passengers. The most dense rail network is found in the highly industrialised and urbanised region of East Central USA and adjoining Canada.
Australia has about 40,000 km of railways, of which 25 percent are found in New South Wales alone. The West-East Australian National Railway line runs across the country from Perth to Sydney. New Zealand’s railways are mainly in the North Island o
serve the farming areas.
In South America, the rail network is the most dense in two regions, namely, the Pampas of Argentina and the coffee-growing region of Brazil which together account for 40 percent of South America’s total route length. Only Chile, among the remaining countries, has a considerable route length linking coastal centers with the mining sites in the interior.
Question 27.
What are three components of population change in the world Analyse the impacts of population change. (5)
Or
Explain, why the population growth has been rapid in last few hundred years. (5)
Answer:
The three components of population change in the world are Crude Birth Rate (CBR), Crude Death Rate (CDR), and Migration.
(i) Crude Birth Rate is referred to as a number of live births in a year per thousand of population It is calculated as:
CBR = \(\frac{B i}{P}\) x 1000
Here, CBR = Crude Birth Rate
Bi = Live births during the year
P = Mid-year population of the year
(ii) Crude Death Rate is referred to as number of deaths in a particular year per thousand of population in a particular region. It is calculated as:
CBR = \(\frac{D}{P} \times 1000 \)
Here, CDR = Crude Death Rate
D = Number of deaths
P = Estimated mid-year population of that year
(iii) Migration is the displacement of people from place of origin to place of destination. In migration increases the population and out migration decreases the population of the region.
Impacts of population change are as follows If the population change results in high population growth, then it puts pressure on the resources leading to scarcity and other problems.
Population change results in decline of population which shows that the available resources are not sufficient to maintain the population
Or
The last few hundred years witnessed the rapid population growth due to following reasons
Life-saving drugs are one of the reasons of population growth.
Improvement in medical facilities and sanitation changed global population dynamics.
Immunization against epidemics and other communicable diseases, suppression or elimination of many disease vectors.
Expansion in international trade in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries set the stage for rapid population growth.
Scientific and technological advancements improved the quality of life. A series of dramatic technological change rapidly expanded the resource base and provided a foundation for accelerated population growth.
![]()
Question 28.
What is commercial livestock rearing and how is it a specialised activity? (1+4)
Or
What is pastoral nomadism? Name three regions where it is practiced? Why is it declining? (1+2+2)
Answer:
Commercial livestock rearing is a modern agricultural or primary activity where only one type of animal is reared to get products such as meat, wool, hides, which are processed, packed and exported. It is a specialized activity because
It is organised and capital-intensive activity. For example, it involves constructing large ranches that require huge capital.
To improve the production, animals are kept in ranches which are divided into parcels. These ranches are fenced in a systematic way which improves the overall efficiency. For example, when one parcel in ranches is grazed, animais are moved to another parcel.
The products of this type of activity are scientifically packed and processed. They are also exported to world markets. For example, wool, hides, skin, etc exported in international markets.
The ranches in this type of activity are managed on scientific basis. For example, special emphasis is laid on breeding, genetic improvement, disease control and health care of livestock.
This type of activity involves processing units that are involved in processing of the obtained products and diversifying the production. For example, processing of milk is done to make curd, cream, cheese, etc.
Pastoral nomadism or nomadic herding is a primitive subsistence activity in which the herders rely on animals for food,
clothing, shelter, tools, and transport. They move from one place to another along with their livestock, depending on the
amount of quality of pastures and water.
Pastoral nomadism is associated with three regions
- Region extending from Atlantic shores of North Africa Eastwards across the Arabian Peninsula into Mongolia and Central China.
- Tundra region in Eurasia The region in Southern Hemisphere in South West Africa and the Island of Madagascar.
- Pastoral nomadism is declining in the world because the number of pastoral nomads have been decreasing and areas operated by them is declining because
- Imposibon of political boundaries by countries.
- New settlement plans by different countries.
Section E
Section E consists of 2 Map based questions of 5 marks each
Question 29.
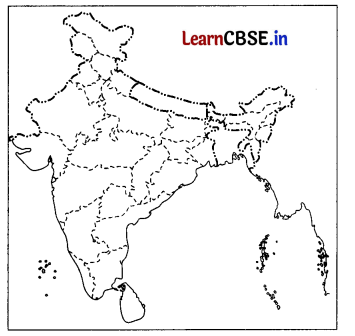
On the political map of India, locate and label any five of the following with appropriate symbols. (5)
(i) State with lowest population density.
(ii) An International airport
(iii) The leading producer state of rice in Eastern India
(iv) Shimoga Manganese mine
(v) Barauni oil refinery
(vi) Hyderabad International Airport
(vii) A coal mine in West Bengal
Answer:
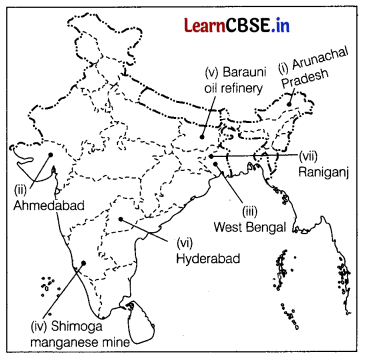
![]()
Question 30.
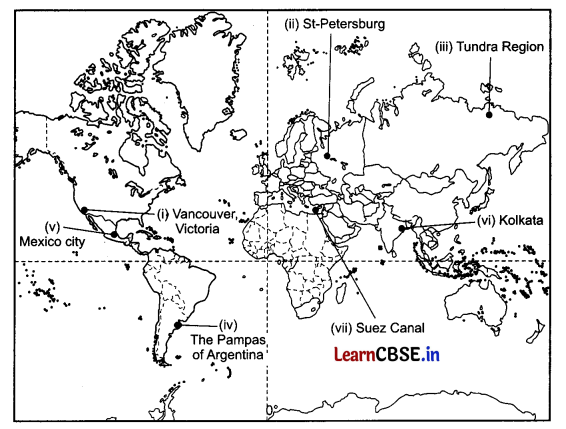
On the given political map of the world, the following seven features are shown. Identify any five of these features and write their correct names on the lines as marked near each feature. (5)
(i) West Terminal Station of Trans-Canadian Railway
(ii) A Terminal Station of Trans-Continental Railway
(iii) An area of nomadic herding
(iv) An area of extensive commercial grain farming
(v) An major airport
(vi) A major seaport
(vii) An inland waterway
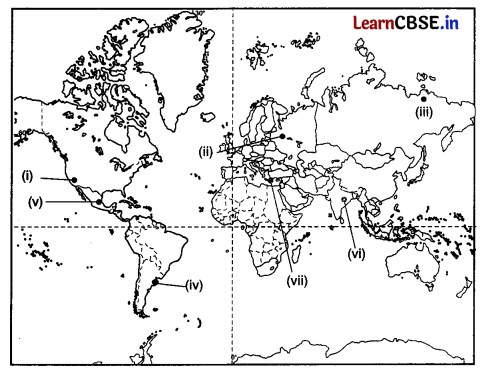
Answer: