Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography with Solutions Set 4 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Set 4 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
General Instructions
This question paper contains 30 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper is divided into five sections – Sections A, B, C, D, and E.
- Section A – Questions no. 1 to 17 are Multiple Choice (MCQ) Type Questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B – Questions no. 18 and 19 are Source Based Questions carrying 3 marks each.
- Section C – Questions no.20 to 23 are Short Answer (SA) Type Questions carrying 3 marks each. Answers to these questions shall be written in 80 to 100 words.
- Section D – Questions no.24 to 28 are long Answer (LA) Type Questions carrying 5 marks each. Answers to these questions shall be written in 120 to 150 words.
- Section E – Questions no. 29 and 30 are Map-Based Questions.
Section A
Section A consists of 17 questions of 1 mark each
Question 1.
Name the serious problem due to the increasing population. (1)
(a) Increased epidemics
(b) Decreased resources
(c) Shortage of education institutions
(d) Shortage of opportunities of employment.
Answer:
(b) Decreased resources
Question 2.
Match the following.
| List I (Industrial Region) | List II (Location) |
| A. Great Lakes Region | 1. Ukraine |
| B. Krivoy Rog | 2. China |
| C. Shanghai | 3. North America |
Codes
ABC
(a) 3 2 1
(b) 3 1 2
(c) 2 1 3
(d) 1 2 3
Answer:
(b) 3 1 2
Question 3.
Which one of the following towns has developed as an 1administrative headquarters’ after Independence? (1)
(a) New Delhi
(b) Chandigarh
(c) Prayagraj
(d) Madurai
Answer:
(b) Chandigarh
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following is not a characteristic of commercial livestock rearing? (1)
(a) It is highly organised and capital intensive.
(b) It is practiced in coastal areas so that the livestock can be easily exported.
(c) Pastures are fenced to regulate grasing.
(d) The number of animals in a pasture are kept according to the pastures capacity.
Answer:
(b) It is practiced in coastal areas so that the livestock can be easily exported.
Question 5.
The natural growth of population can be calculated as (1)
(a) Death rate-Birth rate
(b) Birth rate-In-migration
(c) In-migration-death rate
(d) Birth rate-Death rate
Answer:
(d) Birth rate-Death rate
Question 6.
Which of the following techniques can bring a balance between natural resources and societal needs? (1)
(a) Watershed management
(b) Rainwater harvesting
(c) Resource Recycling
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 7.
Which among the following is a correctly matched pair? (1)
Population-related facts States
(a) State having the highest density of population – Bihar
(b) State with highest literacy – Tripura
(c) State with highest rural population – West Bengal
(d) State with highest urban population – Mizoram
Answer:
(a) State having the highest density of population – Bihar
Question 8.
Name the concept related to Naturalisation of Humans. (1)
(a) Possibilism
(b) Neo-determinism
(c) Humanism
(d) Environment determinism
Answer:
(d) Environment determinism
![]()
Question 9.
Ghaziabad, Rohtak, Gurugram are the examples of ……………………. . (1)
(a) port towns
(b) Garrison towns
(c) satellite towns
(d) transport towns
Answer:
(c) satellite towns
Question 10.
Among the given options, which is the major component of population change? (1)
(a) Migration
(b) Industrialisation
(c) Density of population
(d) Urbanisation
Answer:
(a) Migration
Question 11.
India’ was merged with Air India to form a single airline in which of the following years? (1)
(a) 2009
(b) 2011
(c) 1981
(d) 2010
Answer:
(b) 2011
Question 12.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct option. (1)
I. In India Ganga, Brahmaputra, Barak, and Indus rivers have large catchment areas.
II. Due to high precipitation in the catchments areas of these rivers, they have around 60% of total surface water resources.
Codes
(a) Only statement I is correct
(b) Both statements are correct
(c) Only statement II is correct
(d) Both statements are correct
Answer:
(c) Only statement II is correct
Question 13.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes given below.
Assertion (A) Contribution of tertiary sector is increasing in world’s GD?
Reason (R) People are shifting from agriculture of service sector. (1)
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Answer:
(c) A is true, but R is false
![]()
Question 14.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct answer with the help of given options. (1)
I. An uneducated child cannot make the choice to be a doctor.
II. His/her choice has got limited by her lack of education.
Codes
(a) Only statement I is correct
(b) Only statement ¡lis correct
(c) Both the statements are correct, and statement II correctly explains statement I
(d) Both the statements are true, but not related with each other
Directions Read the following map and answer the following question no. 15 to 17.
Answer:
(c) Both the statements are correct, and statement II correctly explains statement I
Question 15.
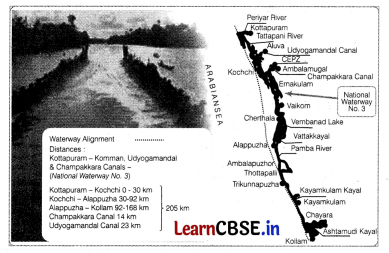
National Waterway-3 (NW 1) stretches from (1)
(a) Allahabad – Haldia
(b) Sadiya – Dhubn
(c) Kottapuram – Kollam
(d) Datra – Allahabad
Answer:
(c) Kottapuram – Kollam
Question 16.
In which state is the Kollam-Kottapuram stretch of the West Canal located? (1)
(a) Gujarat
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Kerala
(d) Andhra Pradesh
Answer:
(c) Kerala
Question 17.
National Waterway-3 in India is also known as (1)
(a) East-West Canal
(b) North-South Canal
(c) West Coast Canal
(d) East Coast Canal
Answer:
(c) West Coast Canal
Section B
Section B consists of 2 Source based questions of 3 marks each
Question 18.
Read the given passage carefully and answer the following questions. The idea of human development is supported by the concepts of equity, sustainability, productivity, and empowerment. Equity refers to making equal access to opportunities available to everybody. The opportunities available to people must be equal irrespective of their gender, race, income, and in the Indian case, caste. Yet this is very often not the case and happens in almost every society in India, a large number of women and persons belonging to socially and economically backward groups drop out of school.
Sustainability means continuity in the availability of opportunities. To have sustainable human development, each generation must have the same opportunities. All environmental, financial, and human resources must be used keeping in mind the future.
Misuse of any of these resources will lead to fewer opportunities for future generations. Productivity means human labour
productivity or productivity in terms of human work. Such productivity must be constantly enriched by building capabilities
in people. Ultimately, it is people who are the real wealth of nations.
Empowerment means to have the power to make choices. Such power comes from increasing freedom and capability. Good governance and people-oriented policies are required to empower people. The empowerment of socially and economically
disadvantaged groups is of special importance.
(i) According to the passage, what is the real wealth of a county? (1)
(ii) What can lead to the empowerment of people? (1)
(iii) After reading this passage, what do you understand by sustainable development? (1)
Answer:
(i) According to the passage, people of a country are the real wealth of that country.
(ii) Good governance and people-oriented policies leads to the empowerment of people.
(iii) Sustainable development is using the resources in such a way that even future generations could use these resources for their welfare.
![]()
Question 19.
Observe the given figure and answer the following questions.
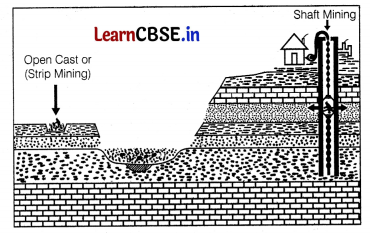
(i) Which of the mining techniques is cheapest? (1)
(ii) Which type of mining is used for extraction of ore deep inside the surface? (1)
(iii) Which of the methods given in picture is more prove to accidents? (1)
Answer:
(i) Open-cast mining is the cheapest mining technique
(ii) Shaft mining method is used for extraction of ore deep inside the surface.
(iii) Shaft mining is more prone to accidents like underground fires, leakage of poisonous gases, flooding, etc.
Section C
Section C consists of 4 questions of 3 marks each
Question 20.
Neo-determinism presents an alternative approach between the two streams of environmental determinism and possibilism. Explain how does it show that human being can live in harmony with their environment. (3)
Answer:
Following points make it clear that neo-determinism believes ¡n harmony between human beings and their environment
The concept of neo-determinism shows that neither is there a situation of absolute necessity (environmental determinism) nor is there a condition of absolute freedom (possibilism). It means that human beings can conquer nature by obeying it.
They can proceed in their pursuits of development when nature permits the modifications. It means that possibilities can be created within the limits which do not damage the environment.
The neo-determinism conceptually attempts to bring a balance nullifying the ‘either ‘or’ dichotomy. In this way, it attempts to enable human beings to live in harmony with their environment by adaptation, adjustment with, and modification of the environment.
Question 21.
Describe any four important characteristics of horticulture and market gardening practiced in the world. (3)
Or
Differentiate between possibilism and determinism. (3)
Answer:
Horticulture and market gardening is specialised agriculture activity in which high-value crops such as vegetable, fruits, flowers, etc are grown.
Characteristics of horticulture and market gardening are There are small farms but they are connected to large urban centers by well-developed transport and communication links, Diverse types of crops are grown in this type of agriculture wtich includes food crops. beverages, flowers, etc having high demand in urban areas.
The products of this type of agricultural activity is sold in the urban markets where high-income group of customers are located. This type of agriculture is both capital-intensive as well as labor-intensive as it lays emphasis on use of extensive irrigation, high-yielding variety seeds, fertilizers, insecticides, greenhouses for artificial heating, etc.
Or
The difference between possibilism and determinism are Possibilism
Possibthsm refers to the idea that human can modify nature by the possibilities provided by it. In this situation, humans understand their environment and create possibilities for their development by resources obtained from nature.
Determinism
Determinism refers to the state of being where human beings are greatly influenced by natural forces and they adopt to the dictates of the nature.
Human activities are dependent upon the natural environment, Humans consider nature as Mother’.
- There is more social and cultural Humans are dictated by development, which leads to natural forces more efficient technology.
- Examples for this approach are agricultural advancement, industrial revolution, etc.
- Example for this approach are primitive tribal societies, Eskimos, etc.
![]()
Question 22.
What are the merits and demerits of air transport? (3)
Answer:
The merits of air transport are
- It has reduced distances by minimising the travel time.
- It is very much essential for a vast country like India, where distances are large and the terrain and climatic conditions are diverse.
- The demerits of air transport are
- It is very costly mode of transportation which is not affordable for everyone.
- It is not suitable for carrying heavy and bulky commodities.
- The air transport is not much in use in the international trade due to its high cost.
Question 23.
What are the major problems associated with water in India? (3)
Or
Describe major features of India’s National Water Policy, 2002. (3)
Answer:
The three major problems related to water in India are as follows
(i) Insufficient Amount of Freshwater In India, there is insufficient amount of freshwater available to meet he growing demand. Increasing population is also shrinking the per capita availability of water.
(ii) Water Pollution It has increased rapidly after industrialisation and urbanisation, They have contributed the most in water pollution in India.
(iii) Uneven Distribution of Water Resources Water resources in India are very unevenly distributed. Some regions are facing scarcity of water whereas other areas are facing floods.
or
The National Water Policy. 2002 explains was allocation priorities in the following order i.e. drinking water, irrigation, hydropower, navigation, industrial and other uses.
The three features of India’s National Water Policy, 2002 are
- When there is no source of drinking water, irrigation and multi-purpose projects or dams should invariably include drinking water components.
- Provide potable water for human beings and animals.
- Exploitation of groundwater should be regulated and limited by adopting suitable measures.
Section D
Section D consists of 5 questions of 5 marks each
Question 24.
Where is intensive subsistence agriculture practiced in the world? What are its two types? Describe any two characteristics of
each type. (1+4)
Or
Explain any five features of nomadic herding in the world. (5)
Answer:
Intensive subsistence agriculture is largely practiced in densely populated regions of monsoon Asia. There are two types of intensive subsistence agriculture which are given below
(i) Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by wet paddy cultivation This type of agriculture is characterised by dominance of the rice crop. Landholdings are very small due to the high density of population. Farmers work with the help of family labour leading to intensive use of land.
Use of machinery is limited and most of the agricultural operations are done by manual labour. Farmyard manure is used to maintain the fertility of the soil. In this type of agriculture, the yield per unit area is high but labour productivity is low.
(ii) Intensive subsistence agriculture dominated by crops other than paddy Due to the difference in relief, climate, soil, and some of the other geographical factors, it is not practical to grow paddy in many parts of monsoon Asia. Wheat, soybean. barley and sorghum are grown in Northern China, Manchuria, North Korea, and North Japan.
Most of the characteristics of this type of agriculture are similar to those dominated by wet paddy except that irrigation is often used.
Or
Features of nomadic herding in the world are as follows
(i) Nomadic herding is also called pastoral nomadism. It is a primitive subsistence activity in which herders depend upon animals for food, clothing, shelter, tools, and transport.
(ii) Herders move from one place to another with their livestock based on the availability and quality of pastures as well as water. Each nomadic community occupies a well-identified territory as a mailer of tradition.
(iii) The variety of animals reared varies from region to region. For instance, in tropical Africa, cattle are the most commonly used livestock, whereas in the hilly areas of Tibet and the Andes mountains, the yak and llama are used.
(iv) Movement in search of pastures is undertaken either over vast grasslands or hilly regions, depending on the season. In the hilly areas, during the winter season the movement is from highlands to lowlands and in the summer season, the movement is
from lowlands to highlands.
(v) Currently, the number of pastoral nomads have reduced considerably due to the imposition of political boundaries of nations and states as well as new settlement plans by various governments.
![]()
Question 25.
Name some sources of population data in India. Explain the distribution of population in India. (1+4)
Or
State the important steps which have been taken by the government of India to solve the problem of adolescence. (5)
Answer:
In India, population data is collected Through Census which held every 10 years in our country. The recent Census was conducted in 2011 In India, spatial pattern of population distribution is very uneven. As some areas are sparsely populated, whereas others are dense. These states can be categorized into three categories:
- States with High Population Uttar Pradesh (highest population), Maharashtra, Bihar, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu together account for 76% of population.
- States with Moderate Populations Assam, Haryana, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Kerala, Punjab and Goa have moderate population.
- States with Low Population Hilly and tribal areas like Jammu and Kashmir (now UT), Uttarakhand, all North-Eastern states (except Assam) and Union Territories excluding Delhi and Chandigarh have low populations.
Population is mainly affected by climate, terrain and availability of water. For example, the North Indian Plains, deltas and coastal plains are densely populated, whereas the mountainous areas and interior areas of Central and Southern India have
relatively low populations. Besides these, evolution of settled agriculture and urbanisation are the socioeconomic and historical factors of distribution of population.
Or
The government of India has undertaken certain policies in this regard to impart proper education to the adolescent group so that their talent are better channelised and properly utilised. These are The programme like SABLA for adolescent girls and SAKSHAM for adolescent boys are being executed by government to improve the nutriention level and provide skills to youth. Various efforts are being taken by central and state governments to empower the youth and to achieve their full potential under the National Youth Policy.
In National Youth Policy 2014, the government defined youth of age group 15-29 years and proposed to empower the youth of country to achieve their full potential.
Kishori Shakti Yojana (KSY) is redesigned version of the already existing Adolescent Girls (AG) Scheme. The objectives of this scheme are to improve the nutritional health and development status of adolescent girls, promote awareness of health and
hygiene, nutrition, and family care help them gain a better understanding of their social environment and take initiatives to become productive members of the society.
Question 26.
What are the sources of water pollution in India? Describe five such sources. (5)
Answer:
The sources of water pollution in India are
(i) Natural Sources Water pollution is caused by natural sources such as land erosion, landslide, decay and decomposition of dead plants and animals, etc. Though naturally water gets polluted but most importantly, it is the man-made sources that pollute the water severely.
(ii) Urbanisation Rapid urbanization in the world has become an important polluter of water. When the household sewage is dumped into the water bodies, it causes the quality of water to decline. The towns that are present at the banks of the rivers pollute rivers, lakes, streams and even the groundwater use of detergents also contribute to the water pollution.
(iii) Industrialisation Industries located along the rivers release toxic wastes into these waters which causes pollution. The life forms in the river water die and river’s water becomes unfit for human use. Both smaller as well as large scale industries cause water pollution due to the use of harmful chemicals and toxic effluents.
(iv) Agricultural Practices Modern agricultural practices requires large-scale use of chemicals such as insecticides and pesticides. The harmful chemicals reach the rivers, ponds, lakes due to irrigation. During rainfall, agricultural runoff causes the water in the fields to diffuse into river basins Due to waterlogging. groundwater is also polluted because the harmful chemicals seep through the soil to reach the groundwater.
(v) Cultural Activities Religious and cultural activities such as idol immersion, pilgrimage, throwing of garlands, animal sacrifice, bathing and drinking, etc makes the river water polluted. Pilgrimage, religious fairs, and tourism activities also cause pollution in the water bodies.
Question 27.
“Trans-Canadian railway line is economic artery of Canada.” Discuss. (5)
Answer:
The longest trans-continental railway line in North America is the Trans-Canadian railway line. It covers a distance of 7050 km, running from Halifax in the East to Vancouver on the Pacific Coast,
The Trans-Canadian Railway tine is considered the economic artery of Canada due to its following importance It connects the important industrial cities of Montreal, Ottawa, Winnipeg, and Calgary Goods and people can be easily transported to and from these economic centres with the railways.
It connects the Quebec-Montreal industrial region with the wheat but of Prairie region. Thus, raw materials and finished products are transported with these railways.
The line also connects the Coniferous forest region in the North to the Quebec Montreal and the Prairies. All these regions have become complementary to each other and they support economic activities.
A loop line from Winnipeg to Thunderbay (Lake Superior) connects this rail line with one of the most important waterways in the world. This is used for exporting various products.
![]()
Question 28.
What are non-conventional sources of energy? Discuss their availability and potential in India. (1+4)
Or
Nuclear energy is replacing the conventional sources of energy in India. Do you think it as variable source of energy in
future? (5)
Answer:
Non- conventional sources of energy such as solar and wind energy are renewable sources, They are equitably distributed and environment friendly as there are no carbon or pollution emissions upon their use. They are not exhaustible as they do not have fixed deposits or reserves.
These sources can provide sustained, cheap, and environment-friendly energy and hence, they are considered as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Some of the commonly used non-conventional sources of energy in India are Solar Energy Sun rays tapped in photovoltaic cells can be converted into energy, known as solar energy. The two effective processes considered to be very effective to tap solar energy are photovoltaics and solar thermal technology. The
Western part of India has greater potential for the development of solar energy in Gujarat and Rajasthan, Wind Energy This form of energy is absolutely pollution-free, inexhaustible source of energy The kinetic energy of wind, through turbines is converted into electrical energy.
The permanent wind systems such the trade winds, westerlies, and seasonal winds like monsoons have been used as sources of energy. Besides these, local winds, land, and sea breezes can also be used to produce electricity. In Rajasthan, Gujarat,
Maharashtra and Karnataka. favourable conditions for wind energy exist.
Tidal and Wave Energy
Ocean currents are the storehouse of infinite energy. Large tidal waves are known to occur along the West Coast of India.
Hence, India has great potential for the development of tidal energy along the coasts but so far these have not yet been utilized.
Geothermal Energy
When the magma from the interior of Earth, comes out on the surface, tremendous heat is released. This heat energy can
successfully be tapped and converted to electrical energy. Apart from this, the hot water that gushes out through the geyser wells is also used in the generation of thermal energy. It is popularly known as geothermal energy. In India, a geothermal energy plant has been commissioned at Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh.
Or
Nuclear energy is replacing the conventional sources of energy in India. Now, nuclear power plants are being constructed to replace thermal power plants in a phase-wise manner. Nuclear energy has multiple benefits over other conventional sources. Country like India, which are deficient in energy resources are promoting nuclear energy to fulfill its demand.
Yes, nuclear energy is a viable source of energy for future keeping in view the availability of nuclear minerals in India, This is due to following reasons
- In nuclear power plant, uranium and thorium are used to generate energy.
- In India, uranium deposits found in the Dharwar rock system. Its main reserves are in Singhbum (Jharkhand), Udaipur, Alwar and Jhunjhunu (Rajasthan), etc.
- India has very rich deposits of the thorium in the World. which is the biggest reason for the viability of nuclear energy in India.
- Thorium is mainly obtained from monazite and ilmenite in the beach sands of India.
- The states which have rich monazite deposits are Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, and Odisha.
- Institutions such as Atomic Energy Commission and Bhabha Atomic Research Centre are working consistently to extract thorium from monazite in efficient manner, so that, India’s dependence on conventional sources can be reduced.
Section E
Section E consists of 2 Map based questions of 5 marks each
Question 29.
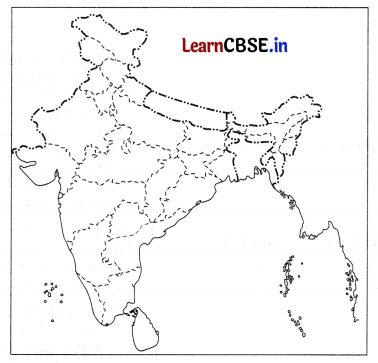
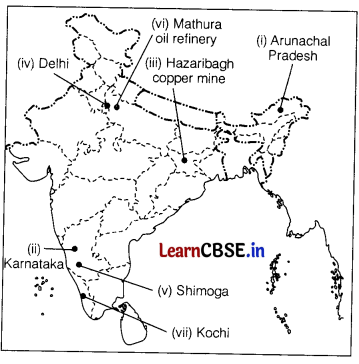
On the political map of India, locate and label any five of the following with appropriate symbols. (5)
(i) The state with the lowest level of population density
(ii) The leading producer state of coffee in India
(iii) Hazaribagh copper mine
(iv) An international airport
(v) A manganese mine in Karnataka
(vi) An oil refinery in Uttar Pradesh
(vii) A major seaport
Answer:
![]()
Question 30.
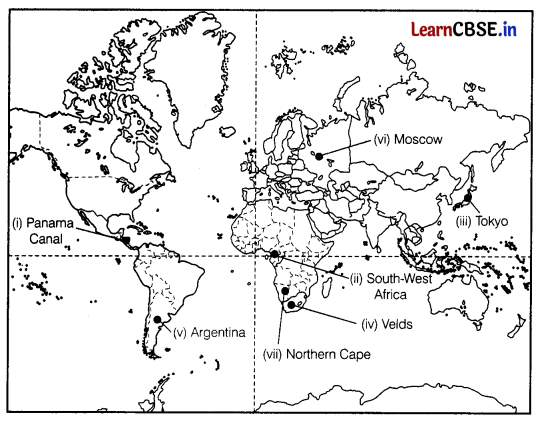
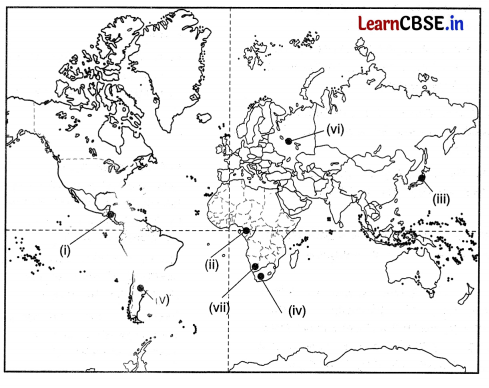
On the given political map of the world, the following seven features are shown. Identify any five of these features and write their correct names on the lines marked near each feature. (5)
(i) An inland waterway
(ii) A major area of nomadic herding
(iii) A major airport in Japan
(iv) A major area of subsistence agriculture
(v) A country in South America where commercial livestock rearing is practiced
(vi) A major airport
(viii) A major seaport in Europe
Answer: