Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography with Solutions Set 3 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Set 3 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions
This question paper contains 30 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper is divided into five sections – Sections A. B. C, D, and E.
- Section A – Questions no. 1 to 17 are Multiple Choice (MCQ) Type Questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B – Questions no. 18 and 19 are Source Based Questions carrying 3 marks each.
- Section C – Questions no.20 to 23 are Short Answer (SA) Type Questions carrying 3 marks each. Answer to these questions shall be written in 80 to 100 words.
- Section D – Questions no.24 to 28 are Long Answer (LA) Type Questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to these questions shall be written in 120 to 150 words.
- Section E – Questions no. 29 and 30 are Map-Based Questions.
Section A
Section A consists of 17 questions of 1 mark each
Question 1.
Which of the following is not a major port? (1)
(a) Kandla
(b) Tuticorin
(c) Ennore
(d) Kannur
Answer:
(d) Kannur
Question 2.
Which of the following pairs is correctly matched? (1)
Category of Density of Population States/UTS
(a) State with highest density West Bengal
(b) State with low-density Uttar Pradesh
(c) State with moderate density Assam
(d) UT with highest density Daman and Diu
Answer:
(c) State with moderate density Assam
Question 3.
Gathering is practiced in the …………………. basin. (1)
(a) Amazon
(b) Ganga
(c) Hwang Ho
(d) Nile
Answer:
(a) Amazon
Question 4.
Which of the following is the growth rate of India, according to Census of India, 2011? (1)
(a) 17.64%
(b) 13.31%
(c) 21.54%
(d) 23.85%
Answer:
(a) 17.64%
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following is the largest container port in India? (1)
(a) Mumbai Port
(b) Kolkata Port
(c) Kandla Port
(d) Jawaharlal Nehru Port
Answer:
(d) Jawaharlal Nehru Port
Question 6.
Which of the following parts of a river have the best quality water? (1)
(a) The delta part
(b) The part in the mountains
(c) The plains part
(d) The part in the valleys
Answer:
(b) The part in the mountains
Question 7.
Match the following.
| List I (Act/Policy) | List II (Year) |
| A. Water (Prevention & Control Pollution) Act | 1. 1986 |
| B. Environment Protection Act | 2. 1974 |
| C. The Water Cess Act | 3. 2002 |
| D. National Water Policy | 4. 1977 |
Codes
ABCD
(a) 1 2 3 4
(b) 2 1 4 3
(c) 1 2 3 4
(d) 3 2 4 1
Answer:
(b) 2 1 4 3
Question 8.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct answer with the help of given option.
I. An uneducated child cannot make the choice to be a doctor.
II. His/Her choice has got limited by her lack of education.
Codes
(a) Both the statements are true
(b) Only statement I is true
(c) Only statement II is true
(d) Both the statements arc false
Answer:
(a) Both the statements are true
Question 9.
Arrange the following regions given below, in order of decreasing density of their population. (1)
I. North America
II. Asia
III. Europe
IV. Africa
Codes
(a) 1, II, III, IV
(b) IV, III, II, I
(c) II, IV, III, I
(d) I, III, IV, II
Answer:
(c) II, IV, III, I
Question 10.
Which of the following rivers has the highest replenishable groundwater resource in India? (1)
(a) Indus
(b) Brahmaputra
(c) Ganga
(d) Godavari
Answer:
(c) Ganga
![]()
Question 11.
Which of the following minerals is used in smelting of iron ore?
(a) Mica
(b) Manganese
(c) Copper
(d) Bauxite
Answer:
(b) Manganese
Question 12.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct answer. (1)
I. Rearing is today practiced at the subsistence or commercial levels.
II. Animal rearing depends upon the geographical factors and levels of technological development.
Codes
(a) Only statement I is correct
(b) Only statement Ills correct
(c) Both the statements are correct and statement II correctly explains statement I
(d) Both the statements are incorrect.
Answer:
(c) Both the statements are correct and statement II correctly explains statement I
Question 13.
Which of the following concepts is related to naturalization of humans? (1)
(a) Environmental Determinism
(b) Possiblism
(c) Neo-determinism
(d) Humanism
Answer:
(a) Environmental Determinism
Question 14.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes given below.
Assertion (A) Railways are most suited for large volume bulky materials over long distance.
Reason (R) Railway networks are well-developed and can reach hinterlands. (1)
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Directions Read the following case study and answer the question no. 15 to 17.
Human Settlement means cluster of dwellings of any type or size where human beings live. For this purpose, people may erect houses and other structures and command some area or territory as their economic support base. Thus, the process of settlement inherently involves grouping of people and apportioning of territory as their resource base. Settlements vary in size and
type. They range from a hamlet to metropolitan cities. With size, the economic character and social structure of settlements changes and so do its ecology and technology. Settlements could be small and sparsely spaced; they may also be large
and closely spaced.
The sparsely located small settlements are called villages, specialising in agriculture or other primary activities. On the other hand, there are fewer but larger settlements which are termed as urban settlements specialising in secondary and tertiary activities.
The rural settlements derive their life support or basic economic needs from land-based primary economic activities. whereas, urban settlements, depend on processing of raw materials and manufacturing of finished goods on the one hand and a variety of services on the other.
Cities act as nodes of economic growth, provide goods and services not only to urban dwellers but also to the people of the rural settlements in their hinterlands in return for food and raw materials. This functional relationship between the urban
and rural settlements takes place through transport and communication network.
Rural and urban settlements differ in terms of social relationship, attitude, and outlooks. Rural people are less mobile and therefore, social relations among them are intimate. In urban areas. on the other hand, way of life is complex and fast, and social relations are formal.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 15.
The sparsely located small settlements are (1)
(a) own
(b) villages
(c) hamlet
(d) City
Answer:
(b) villages
Question 16.
Cities provide which of these to the rural areas? (1)
(a) Manufactured goods
(b) Water
(c) Raw materials
(d) Food
Answer:
(a) Manufactured goods
![]()
Question 17.
Rural and urban settlements differ in which of the following terms? (1)
(a) Social relationship
(b) Attitude
(c) Outlook
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Section B
Section B consists of 2 Source based questions of 3 marks each
Question 18.
Read the given passage carefully and answer the questions that follow. Density of population, is expressed as number of persons per unit area. It helps in getting a better understanding of the spatial distribution of population in relation to land. The density of population in India (2011) is 382 persons per sq km. There has been a steady;’ increase of more than 200 persons per sq km over the last 50 years as the density of population increased from 117 persons/sq km in 1951 to 382 persons/sq kin in 2011. The data of census 2011 give an idea of spatial variation of population densities in the country which ranges from as low as 17 persons per sq km in Arunachal Pradesh to 11,297 persons in the National Capital Territory of Delhi. Among the Northern Indian States, Bihar (1102), West Bengal (1029) and Uttar Pradesh (828) have higher densities, while Kerala (859) and Tamil Nadu (555) have higher densities among the peninsular Indian states. States like Assam, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Jharkhand, Odisha have moderate densities.
The hill states of the Himalayan region and North-Eastern states of India (excluding Assam) have relatively low densities while
the Union Territories (excluding Andaman and Nicobar Islands) have very high densities of a population.
(i) What is the defining feature of density of population of a region? (1)
(ii) Which North-Eastern state does not comes under category of low population density? (1)
(iii) Which state among the Southern states is the most densely populated? (1)
Answer:
(i) Human and land relationship is the defining feature of density of population in a region.
(ii) Assam is the only North-Eastern state with moderate density of population.
(iii) Kerala is more densely populated than any other Southern state of India.
Question 19.
Observe the given map and answer the following questions.
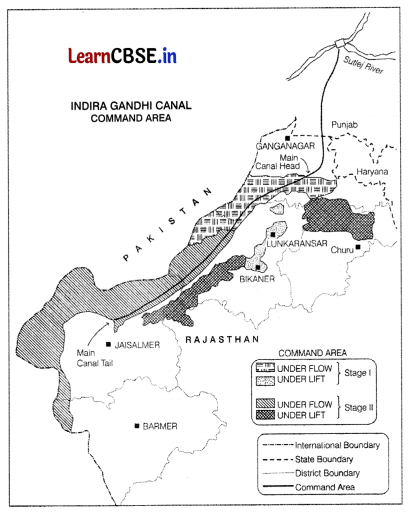
(i) What is the source of origin of this canal? (1)
(ii) What is the economic significance of this canal for the command area? (1)
(iii) Why is the Eastern area of canal under lift irrigation? (1)
Answer:
(i) The source of origin of this canal is the Harike Barrage in Punjab.
(ii) In the command area of the canal, the cultivable area has increased and the intensity of cropping has also increased, this is due to proper and sufficient irrigation provided through canal.
(iii) The area of the East of the Indira Gandhi Canal is under lift irrigation as it comprises of desert land dott with shifting sand dunes. With the help of it irrigation system, the water s lifted up to make it to flow against the slope of the land.
Section C
Section C consists of 4 questions of 3 marks each
Question 20.
Define mining and its various types. (3)
Answer:
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth f rom an ore, lode, vein or placer deposit On the basis of mode of occurrence and the nature of ore, mining is of two types
(i) Surface Mining Surface mining is also known as open-cast mining. It is used to extract minerals occurring closer to the surface. The advantages of this type of mining are It is easy and cheap. Cost of safety precautions and equipment is low in this method. Output is large and rapid.
(ii) Underground Mining It is also known as shaft method, It is the method of mining minerals when the ore lies deep below the surface. This method of mining has following disadvantages It requires specially designed lifts, drills, haulage vehicles, ventilation system for moving people and materials. Poisonous gases. fires, floods and causing can lead to deadly accidents.
Question 21.
Define the nature of human geography. (3)
Answer:
The nature of human geography is very complex It deals with the inter-relationship between the natural physical environment and socio-cultural environment created by human beings through mutual interaction with each other, All the phenomena such as houses, villages, cities, road-rail networks, industries, farms, parks, items of daily use and other elements of material culture have been created by human beings using the natural resources. By creating these phenomena, humans have modified the physical environment and have also been affected by it.
Question 22.
What are reasons behind rise of service sector in the world? (3)
Or
Describe tourism and its place in tertiary sector. (3)
Answer:
Service sector is an important tertiary activity that is used by the households as well as the industry. The service sector has grown enormously over past few decades. This is because of the following reasons Rapid Urbanisation As more people start living in the cities, there is rising demand for various services in urban areas. Increase in Population The necessity for basic services has increased due to increase in the population. These services are hospitals, education, banking, etc.
Increase in Living Standard The increasing living standard of the people has resulted in rising demand for services such as transport, tourism, sports, etc.
Rising income The rising incomes of people have led to increase in the services required by them. These services include retailing, tourist education, etc. Improvement in Technology Improvements in technology have resulted in expansion of service sector in the international markets.
Or
Tourism is the largest sector of tertiary activities in terms of providing employment. Tourism is a travel which is done for the purposes of recreation. It generates the largest revenue among tertiary activities in the world.
Around 40 percent of the world’s total GDP is generated by tourism sector. Tourism not only boosts the infrastructure but also the local as well as global economy. It provides base for making a living for many people residing adjacent to tourist places. Local people are employed to provide variety of services like accommodation, food, transport, special shops and entertainment. It enhances the growth of retail trading, art, and craft business or industries.
![]()
Question 23.
Mention three causes for the deterioration of ‘quality of water’ in India. (3)
Or
Mention any three problems related to water in India. (3)
Answer:
The three causes responsible for the deterioration of quality of water in India are as follows
(i) The foreign substances like micro-organisms, chemicals, industrial and other wastes make water polluted. Because of these substances, quality of water decreases and it becomes unsuitable for the uses of human beings.
(ii) Toxic substances are responsible for water pollution which are dissolved in lakes, streams. rivers, ocean other water sources. It declines the quality of water and harms aquatic life and systems.
(iii) When toxic substances seep down, they pollute groundwater
Or
The three major problems related to water in india are as follows
(i) Insufficient Amount of Freshwater In India, there is insufficient amount of freshwater available to meet the growing demand. Increasing population is also shrinking the per capita availability of water.
(ii) Water Pollution It has increased rapidly after industrialisation- and urbanisation. They have contributed the most in water pollution in India.
(iii) Uneven Distribution of Water Resources Water resources in India are very unevenly distributed. Some regions are facing scarcity of water whereas other areas are facing floods.
Section D
Section D consists of 5 questions of 5 marks each
Question 24.
Give a brief note on diffcrcnt trends of population growth in the world from early period to the present day. (5)
Or
Despite having a magnetic effect, city life is considered very difficult to live. Explain why? (5)
Answer:
The trends of population growth are as follows
- In the early periods of history i.e. 8000 to 12000 years ago the population grew at a slow rate.
- The population of the era was 8 million.
- The count of population in the first century was below 300 million.
- The world population growth rate declined from around 2% per year (50 years ago) to under 1.0% per ‘year.
- By 1600 AD, world population increased to 0.5 billion as expansion in trade and Industrial Revolution increased the population.
World population touched 1 billion in 1830 due to advancements in the field of science and technology. Advancements in healthcare and technology reduced mortality rates and increased life expectancy.
Improved agriculture and better food production and reduced famine contributed to population growth. 20th century shows significant population expansion, especially after Wolrd War II, due to advancements in medical science and public health.
In recent decades, global population growth rate has been declining. Factors contributing to the decline include increased access to contraception women’s empowerment, and urbanisation, As of 2021. the estimated world population is around 7.9 billion.
After 1800. the population was rapidly from around 1 billion to 8 billion at present, 8 times larger. Around 108 billion people have ever lived on our planet. This means that today’s population size makes up 6.5% of the total number of people ever born.
Or
Despite having a magnetic effect, city life is considered very difficult to live, Following are some of the economic, environmental and social reasons that make urban life difficult.
- Environmental reasons
- Increasing pollution of air, water, soil
- Over-exploitation of resources
- Lack of waste management which harms the environment
- Declining green spaces Congestion and small living spaces Economic reasons
- Lack of basic amenities like food, water, housing, etc.
- Unemployment and underemployment
- Low wages and poor working conditions due to surplus ailability of labour
- Overcrowding and growth of slums. Social reasons
- Social vacuum and lack of social interactions among people.
- Increasing crimes and law and order problems in urban areas.
- Lack of community engagement among people.
- Social distress due to a fast urban life.
Question 25.
What are limitations and advantages of air transport? (5)
Or
What is GPS and what are its various uses? (2+3)
Answer:
Following are the limitations of air transport
- It is very costly mode of transport which is out of reach of most of the middle and lower classes of society.
- The manufacturing of aircrafts and their operations require elaborate infrastructure like hangars. landing, fuelling and maintenance facilities for the aircrafts.
- It is also very expensive to construct airports and hence, it is developed more in highly industrialised countries having large volume of traffic.
- Despite having some limitations, air transport is more advantageous in the modern world. The advantages are
Valuable cargo and perishable goods can be moved rapidly on a worldwide scale. - The inaccessible areas have become accessible through this mode of transport. For example, the airplane brings varied articles to the Eskimos in Northern Canada unhindered (freely) by the frozen ground.
Another example, is from the Himalayan region, where the routes are often obstructed due to landslides, avalanches or heavy snowfall. At such times, air travel is the only alternative to reach a place.
Air transport has brought about a connectivity revolution in the world. Because of air transport, the travelling time is reduced to hours and minutes from years and months. Air transport has great strategic advantage as it can be used tor military and tactical operations The air strikes by US. and British forces in Iraq proves this fact.
Or
GPS (full Global Positioning System) is a space-based radio-navigation system that broadcasts highly accurate navigation pulses to users on or near Earth. Originally it was known as Navstar GPS that was developed by USA The GPS provides critical
positioning capabilities to military, civil, and commercial users around the world.
Use of GPS
GPS is a powerful and dependable too for many different organisations in many different ways. Surveyors, scientists, pilots, boat captains, first responders and workers in mining and agriculture, are just some of the people who use GPS on a daily basis
for work. Broadly there are five main uses of GPS.
- Location Determining a position.
- Navigation Getting from one location to another.
- Tracking Monitoring object or personal movement.
- Mapping It creates map of the world.
- Time It made possible to take precise time management.
![]()
Question 26.
What are some of the measures that can be used to reduce air pollution? (5)
Answer:
- Some of the measures to reduce and control air pollution are as follows Old automobiles should be replaced by new ones which should be redesigned in such a way that their emission cause minimum pollution.
- As coal produces poisonous gases that are released into the air, so electric engines should be used instead of steam or diesel engines.
- Industrial areas should be located at a safe distance from the residential areas.
- Newly designed smoke-free furnaces should be used.
- Forest tires should be checked Adequate preventive measures should be adopted to protect the forests.
- In industries, there should be the arrangement for pollution control.
- Replace conventional energy sources with the renewable or non-conventional energy sources. It is due to the reason that, non-conventional energy sources produces less smoke during combustion and are eco-friendly as compared to conventional energy sources.
- Cheap devices for controlling air pollution should be developed.
- Air pollution can be checked only through the joint efforts of the government, non-government organisations and the general public.
Question 27.
What are major characteristics of National Highways in India? (5)
Answer:
- The roads that are constructed and maintained by Central government are known as National Highway.
- The characteristics of National Highways are
- The highways are used for the movement of both passengers as well as goods and commodities across states from one state to another.
- These highways connect state capitals, major cities, important ports railway junctions, etc and help in carrying out trade and commerce across India.
- They carry about 40% of traffic of India but their total road length is only 2% of the total road length of India.
- National Highways Authority of India is the Central organisation that has been entrusted wth the responsibility of construction, maintenance and operation of National Highways in India.
- The responsibility ot improving the quality of National Highways also lies with the National Highways Authority of India.
Question 28.
What is mixed farming? Where is it practiced in the world? Give three characteristics of mixed farming. (1+ 1+3)
Or
State five features of commercial livestock rearing in the world. (5)
Answer:
Mixed farming refers to the practice of raising crops along with animal husbandry. Thus, it involves both growing crops and keeping livestock.
Areas of Practice
Mixed farming is practiced in the developed parts of the world and the temperate parts of the Southern continents It includes countries of North-Western Europe, Eastern-North America and certain parts of Eurasia, The characteristics of mixed farming in the world are
- Mixed farms are smaller in size where crops like wheat, barley, oats, maize, rye, etc are grown. Fodder crops are also grown in these farms to feed the livestock
- The fertility of the soil is maintained by practicing crop rotation and intercropping. Crop rotation means growing different crops at different times whereas intercropping refers to growing different rows of different crops in the same agricultural fields.
- It involves high capital expenditure because agriculture is practiced with the help of farm machinery and buildings are constructed to keep the livestock, It also requires large use of chemical fertilisers and green manures, which involves large costs.
Or
The features of commercial livestock rearing are as follows
Capital Intensive Commercial livestock rearing is more organised and it requires higher amount of capitals.
Permanent Ranches It is practiced on permanent ranches. These ranches cover large areas and are divided into a number of parcels which are fenced to regulate grazing.
Animals Reared It is a specialised activity in which only one type of animal is reared. The number of animals in a pasture are kept according to the carrying capacity of pasture.
Scientific Basis Rearing of animals in ranching is organized on a scientific basis. The main emphasis is on breeding, genetic improvement, disease control, etc.
Diverse Products Products such as meat, wool, hides, skin etc are pocessed and packed for exporting. Commercial livestock ranching is associated with Western cultures. New Zealand. Australia, Argentina, USA, etc are important countries where it is practiced.
Section E
Section E consists of 2 Map based questions of 5 marks each
Question 29.
On the political map of India, locate and label any five of the following with appropriate symbols.
(i) State with highest population density
(ii) A seaport in West Bengal
(iii) A major seaport
(iv) The leading state for wheat production
(v) Khetri copper mine
(vi) An oil refinery in Gujarat
(vii) A coal mine in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
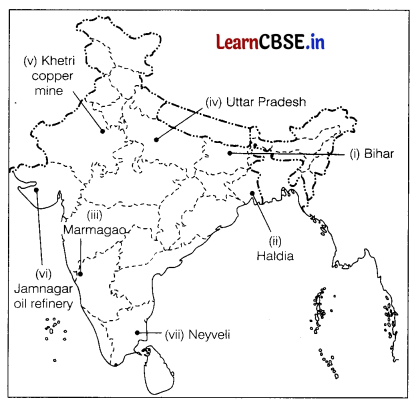
![]()
Question 30.
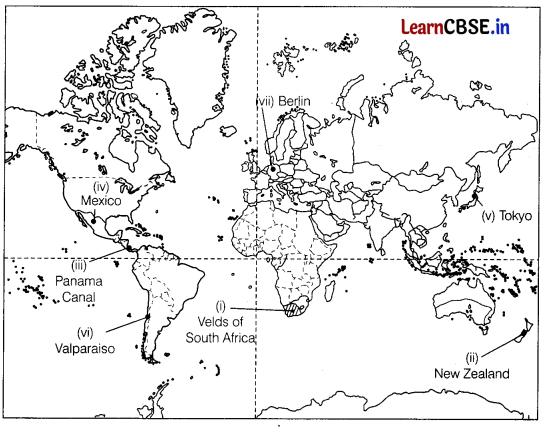
On the given political map of the world, the following seven features are shown. Identify any five of these features and write their correct names on the lines marked near each feature. (5)
(i) Areas of commercial extensive grain farming
(ii) An area of livestock rearing
(iii) An inland waterway
(iv) An area of subsistence agriculture
(v) A major airport in Japan
(vi) A major seaport
(vii) A major airport in Germany.
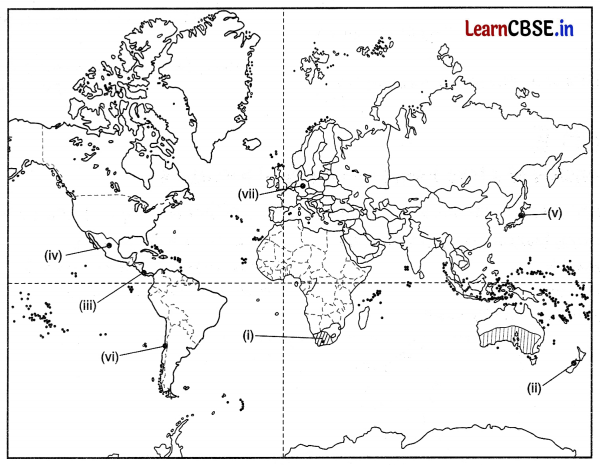
Answer: