Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography with Solutions Set 10 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Set 10 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
General Instructions
The question paper contains 30 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper is divided into five sections — Sections A, B, C, D, and E.
- Section A – Questions no. 1 to 17 are Multiple Choice (MCQ) Type Questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B – Questions no. 18 and 19 are Source Based Questions carrying 3 marks each.
- Section C – Questions no, 20 to 23 are Short Answer (SA) Type Questions carrying 3 marks each. Answer to these questions shall be written in 80 to 100 words.
- Section D – Questions no. 24 to 28 are Long Answer (LA) Type Questions carrying S marks each. Answer to these questions shall be written in 120 to 150 words.
- Section E – Questions no. 29 and 30 are Map-Based Questions.
Section A
Section A consists of 17 questions of 1 mark each
Question 1.
Which of the following is naturalisation of humans? (1)
(a) Artificially heated rooms
(b) Internet networks
(c) Worship of trees
(d) Special Lyres for wet roads
Answer:
(c) Worship of trees
Question 2.
Match the following. (1)
| List I (Crops) | List II (Satellite Port) |
| (a) Mumbai Port | 1. Hugli Port |
| (b) Chennai Port | 2. Jawaharlal Nehru Port |
| (c) Kolkata Port | 3. Ennore Port |
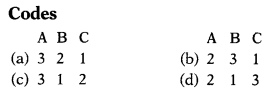
Answer:
(b) 2 3 1
Question 3.
The subject matter of Cultural geography has been taken from which of these fields? (1)
(a) Sociology
(b) Anthropology
(c) Resource Economics
(d) Epidemiology
Answer:
(b) Anthropology
Question 4.
Identify the area which comes under low-density regions of population. (1)
(a) Zaire Basin of Africa
(b) Western China
(c) South-East Asia
(d) East Asia
Answer:
(a) Zaire Basin of Africa
![]()
Question 5.
Identify the feature not associated with mixed farming. (1)
(a) Large farms
(b) Animal husbandry
(c) High capital expenditure
(d) Intercropping
Answer:
(a) Large farms
Question 6.
Eskimos living in Igloos is an example of U)
(a) Possibilism
(b) Neo-determinism
(c) Areal differentiation
(d) Determinism
Answer:
(b) Neo-determinism
Question 7.
Which of the following is main component of population change? (1)
(a) Density of population
(b) Urbanisation
(c) Migration
(d) Industrialisation
Answer:
(c) Migration
Question 8.
Match the following. (1)
List I (Iron & Steel Industry) List II (Country)
A. Port Talbot 1. India
B. Yokohama 2. Japan
C. Tienstein 3. China
D. Durgapur 4. United Kingdom
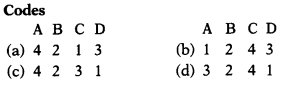
Answer:
(c) 4 2 3 1
Question 9.
Identify a mining town.
(a) Jalandhar
(b) Singrauli
(b) Kolkata
(d) Mhow
Answer:
(b) Singrauli
Question 10.
Which of these is the largest urban agglomeration in India? (1)
(a) Delhi
(b) Ambala
(c) Greater Mumbai
(d) Kolkata
Answer:
(c) Greater Mumbai
Question 11.
Arrange the following in correct sequence of states/UT’s in decreasing order on the basis of urban population.
(i) Delhi
(ii) Maharashtra
(iii) Assam
(iv) Kerala
Codes
(a) Delhi – Maharashtra – Kerala – Assam
(b) Delhi – Kerala – Maharashtra- Assam
(c) Maharashtra – Delhi – Kerala – Assam
(d) Assam- Delhi – Maharashtra – Assam
Answer:
(b) Delhi – Kerala – Maharashtra- Assam
![]()
Question 12.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct option from the given options. (1)
I. The houses in clustered rural settlements generally have no space between houses.
II. These are developed for the defense and security purposes.
Codes
(a) Only statement I is correct
(b) Only statement Il is correct
(c) Both the statements are incorrect
(d) Both statements are correct and statement II correctly explains the statement I
Answer:
(d) Both statements are correct and statement II correctly explains the statement I
Question 13.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes given below.
Assertion (A) Rail transportation is highly cost effective for long distance trade.
Reason (R) Road transport is expensive in long distance trade. (1)
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 14.
Consider the following statements.
I. Tidal energy can be harnessed more than the other renewable energy sources.
II. Tides are more predictable than the wind and solar energy Codes
(a) Only statement I is true
(b) Only statement II is true
(c) Both the statements are true
(d) Both the statements are false
Answer:
(c) Both the statements are true
Directions Observe the given map and answer the question no. 15 to 17.
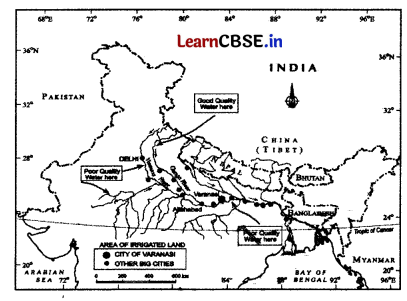
Question 15.
Which river is considered the main tributary of the Ganga river? (1)
(a) Yamuna
(b) Gandak
(c) Son
(d) Ghaghara
Answer:
(a) Yamuna
Question 16.
Which town is situated at the confluence of the Ganga and Yamuna rivers? (1)
(a) Delhi
(b) Varanasi
(c) Allahabad
(d) Kolkata
Answer:
(c) Allahabad
Question 17.
Which river merges with Ganga river near Patna? (1)
(a) Yamuna
(b) Gandak
(c) Son
(d) Kasi
Answer:
(b) Gandak
Section B
Section B consists of 2 Source based questions of 3 marks each
Question 18.
Read the given passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
One of the great advantages of water transportation is that it does not require route construction. The oceans are linked with each
other and are negotiable with ships of various sizes. All that is needed is to provide port facilities at the two ends. It is much cheaper
because the friction of water is far less than that of land. The energy cost of water transportation is lower. Water transport is
divided into sea routes and inland waterways.
Rivers, canals, lakes and coastal areas have been important waterways since time immemorial. Boats and steamers are used as
means of transport for cargo and passengers. The development of inland waterways is dependent on the navigability width and
depth of the channel, continuity in the water flow and transport technology in use. Rivers are the only means of transport in dense forests. Very heavy cargo like coal, cement, timber and metallic ores can be transported through inland waterways.
In ancient times, riverways were the main highways of transportation as in the case of India. But, they lost importance because of competition from railways, lack of water due to diversion for irrigation, and their poor maintenance.
The significance of rivers as in and waterways for domestic and international transport and trade has been recognised throughout the developed world. Despite inherent limitations, many rivers have been modified to enhance their navigability by dredging, stabilising river banks, and building dams and barrages for regulating the flow of water. The following river waterways are some of the world’s important highways of commerce.
(i) What is the major advantage of water transport? (1)
(ii) What led to decline in inland waterway transportation? (1)
(iii) Which transportation is used for navigating in the dense forests? (1)
Answer:
(i) The major advantage of water transport are they does not require route construction.
(ii) The decline is seen due to competitive railways, poor maintenance of waterways, diversion of roads, etc.
(iii) Inland rivers and waterways are used for navigation in dense forests.
![]()
Question 19.
Study the given map and answer the following questions.
(i) What is meant by primitive subsistence agriculture? (1)
(ii) What is used to make the soil fertile? (1)
(iii) In which area in India it is practised and locally known as jhuming cultivation? (1)
Answer:
(i) Primitive subsistence agriculture or shifting cultivation is a primitive type of agriculture in which a patch of forest is burnt and crops are grown in cleared field.
(ii) Ash of trees is used as manure to make the soil fertile.
(iii) In the North-Eastern part of India, shifting cultivation is practiced and is locally known as ‘jumping.
Section C
Section C consists of 4 questions of 3 marks each
Question 20.
What are the major reasons behind the decline of barren and wasteland, cultivable wasteland, area under pastures, tree crops, and fallow lands? (3)
Or
Describe any three characteristics of dryland farming in India. (3)
Answer:
Following reasons are responsible for the decline of barren and wastelands, cultivable wasteland, area under pastures, tree crops and fallow lands Due to increase in pressure on land from agricultural and non-agricultural sectors, wastelands and cultivable wastelands have witnessed decline over time.
Illegal encroachment due to expansion of cultivation on common pasture lands is largely responsible for this decline.
Or
The three features of dryland farming in India are as follows
- It is a type of rainfed farming. Rainfall is the main source of irrigation for this type of farming which provides moisture to the soil to grow crops.
- Dryland farming is done in the areas of rainfall receiving less than 75 cm annually. For example Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh arid Tamil Naclu.
- The major crops which are cultivated in these regions are ragi, bajra, moong, gram, guar, and other drought-resistant crops.
Question 21.
Compare Marmagao and Visakhapatnam sca port on the basis of location, hinterland and significance in world trade. (3)
Answer:
The comparison between Marmagao, and Visakhapatnam seaports can be seen through the following points

Question 22.
Give any four important characteristics of plantation agriculture in the world. (3)
Or
What are the major characteristics of extensive commercial grain cultivation practiced in the world? (3)
Answer:
Plantation agriculture is a type of agriculture in which only a single crop is grown for the whole year and sold in the urban and industrial markets.
The features of this type of agriculture are
(i) Large-Scale Capital Investment Plantation agriculture requires huge amount of capital investment as crops are grown in large estates and high-cost inputs are required.
(ii) Scientific Methods It used scientific methods of growing crops as plantation agriculture requires large-scale machinery and fertilizers. Scientific breeding techniques are also used so that production and productivity can be improved.
(iii) Export-oriented It is export-oriented agriculture as the products such as tea, rubber, coffee, and banana. sugarcane palm oil, pineapple, etc, are sold in the international markets.
Or
- The main characteristics of extensive commercial grain cultivation are as follows
- The interior parts of semi-arid lands of the mid-latitudes are suitable for this cultivation.
- The principal crop in this cultivation is wheat. It is accompanied by other crops like corn, barley, oats and rye.
- Due to larger area of the farm, all the operations from ploughing to harvesting are mechaniseci in this cultivation.
- It is recorded that there is low yield per acre but high yield per person in this cultivation.
- Important areas of this cultivation are European Steppes. the Canadian and American Prairies, the Pampas of Argentina, the Velds of South Africa the Australian Dns and Canterbury Plains of New Zealand.
Question 23.
What is Digital Divide? Explain briefly.
Answer:
Digital divide basically describes the uneven development of Information and Communication Technology industry in the world. There are wide-ranging economic, political, and social differences between developed and developing countries and even among the developing countries.
The main deciding factor of differences in establishment and development of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in countries is that how actively countries can provide ICT access and benefits to its citizens.
In the present modern world, developed countries are showing a positive growth and development in ICT industries, whereas developing countries are showing a steady or declining trend in ICT industry. This major difference between the two region is known as the Digital Divide.
Section D
Section D consists of 5 questions of 5 marks each
Question 24.
“The adolescent population of India is a potential resource for the country. But the adolescent population faces many challenges that make them vulnerable”. Describe. (5)
Or
Describe the regional variation in population growth within a country (5)
Answer:
The adolescent population of India forms a potential human resource. The share of adolescents (10-19 years) is about 20.9% (2011). It is youthful population but it faces many challenges. If their energy is not properly channeled it will make them vulnerable.
These challenges are as follows
- Lower Marriage Age Many adolescents are married off at an early age. This affects their physical as well as mental health. The females are more affected as compared to the males. Their well-being is seriously affected.
- School Dropouts The adolescents drop out of their schools at an early age due to various economic and social reasons. The girls drop out of school to take care of their families, whereas, the boys drop out for carrying out jobs and earning incomes.
- Drug Abuse and Alcoholism Young boys and girls are often vulnerable to drug abuse and alcoholism. It has serious consequences for their physical and mental well-being. Drugs and alcohol induce anxiety and stress, and disturb their social and personal skills.
- Low Level of Nutrition The boys and girls suffer from various deficiencies due to low levels of nutrient intake. This also increases maternal and child mortality rates in young and adolescent mothers.
- Commitment of Crimes The Juvenile population is vulnerable to committing crimes in the society. Poverty, drug abuse, anti-social peer groups, and role of social media results in Juvenile delinquency.
Or
The country has shown wide variations in growth rates from one region to another, The growth rate of population during 1991-2001 in Indian States and Union Territories show very obvious pattern. The states like Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh (undivided), Odisha, Puducherry and Goa shows a low rate of growth. within 20% over the decade. Kerala
registered the lowest growth rate (9.4%) not only this group of states but also in the whole country.
As compared to the Southern states, a continuous belt of states from West to East in the North-West, North and North central parts of the country has relatively high growth rate of population. This belt consists of states of Rajasthan. Gujarat. Maharashtra, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Madhya Pradesh, Sikkim, Assam. West Bengal, Bihar, Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand. The growth rate, on an average here, has remained 20-25%.
During the period 2001-2011, the growth rates of almost all states and UTs have registered a lower figure as compared to 1991-2001. The decadal growth rates (in %) of the six most populous states of Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Bihar, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh have fallen during 2001-2011 as compared to 1991-2001.
The fall in growth rates is lowest for Andhra Pradesh (Undivided) (3.5%) and highest for Maharashtra (6.7%). Tamil Nadu (3.9%) and Puducherry (7.1%) have registered increased growth rates during 2001 -2011 as compared to 1991-2001 period.
![]()
Question 25.
What are the sources of the urban solid waste in India? How does it affect people living in the cities? (2+3)
Or
How trends of urbanisation by 2050 is gaing to pressurise the spatial infrastructure and resources of cities? Explain in brief. (5)
Answer:
Urban solid waste refers to a variety of old and used articles.
The main sources of urban solid waste in India are
(i) Households The waste collected from households is disposed off either on public lands or private contractor sites. It includes organic as well as inorganic waste such as pieces of metal, broken glassware, garbage, plastic, pohene bags. vegetable and fruit waste, polythene bags, used bottles, etc.
(ii) Industrial Units The waste collected from industrial units and commercial establishments are disposed off on public land through municipal facilities into the landfill areas. It includes the ashes, debris from industries, thermal power house waste,
construction and demolition waste, etc.
If the urban solid waste s not treated and disposed, it affects the people living in the cities in following ways
Solid wastes create obnoxious smell and harbouring flies and rodents in the urban houses. These carry diseases and spread them rapidly.
- The dumping of industrial wastes into rivers leads to water pollution, It affects the quality of water and makes it unfit for human use.
- Untreated waste lying in the streets and landfill sites releases toxic biogas into the atmosphere and affects the people living in nearby areas.
- It gives rise to various infectious diseases such as typhoid, diphtheria, diarrhea, malaria, cholera, etc.
- If the solid wastes are not handled properly, it spreads through wind and is sputtered through rainwater. This leads to spread of the waste which causes nuisance in urban areas.
Or
The trends of urbanisation by 2050 is going to pressurise the spatial infrastructure in th following ways Increased demand for housing and infrastructure Urbanisation will lead to a surge in population, requiring additional housing units, transportation networks, water supply systems and other amenities.
Strain on existing Infrastructure The rapid influx of population will put pressure on the spatial infrastructure, which may struggle to accommodate the growing demands,
Resource scarcity and competition Urbanisation escalates the demand for resources such as water, energy, and land, potentially leading to scarcity and competition
Social and environmental challenges Concentration of population in cities can result in issues like traffic congestion, air pollution, waste management problems, and inadequate access to services, impacting the quality of life.
Need for comprehensive urban planning Cities should adopt strategic urban planning to efficiently use land, develop sustainable infrastructure and manage resources effectively.
Question 26.
“A well-developed transport system is essential for modern economic development.” Explain.(5)
Answer:
A modern economy requires a speedy and efficient transportation system to assist in production, distribution and consumption of goods. This is because of the following reasons
(i) Transportation of Raw Materials Transportation system is required for transporting raw material from the mining sites to the industrial regions where they are used to process them into new and useful products. These are sold in the local, regional and national markets and even exported.
(ii) Reduces Regional Disparities Transport system reduces regional disparities as it connects backward areas which were underdeveloped. These areas get connected to the industrial regions and markets develop in these areas which leads to their
economic and social development.
(iii) Generating Employment Transport system helps in solving the problems of unemployment in rural areas by providing transportation facilities to labours so that they can travel easily to the industrial areas. The surplus labour can easily travel to the industries which generates employment.
(iv) Development of Tourism Tourism is an important activity practiced in the developing as well as developed countries. Development of a transport system is essential for developing tourism because transport lines connects tourist places so that, foreign as well as domestic tourists can travel easily to the places of their choice.
(v) Increases Urbanisation Levels A good transportation system leads to increasing levels of urbanisation where a high-income group of people are located. These people have high demand for various products that are transported to the urban areas from the industries. Thus, as well-developed transport system is important for modern economic development.
Question 27.
What do you understand by development? Explain how the people arc at the core of all development process under the concept of Human Development. (1+4)
Answer:
Development refers to a qualitative change which is always valued positively. For any development to take place there must be an or addition to the existing conditions. Thus, development refers to a positive change in the quality.
The concept of Human Development was started by Prof Mahbub-ul-Haq during the 1980s, The people are at the centre of all development activity according to the idea of human development because human development considers enlarging people’s choices and improving their lives very important. The basic goal of human development is to create conditions for the people so that, they can live meaningful lives.
It emphasises that people must be healthy, should be able to develop their talents, participate in the society and they should be free to achieve their goals. This will happen, if they live a life tree of diseases, get knowledge and live a decent life. If the people’s choices are to be enlarged then, they should be free from poverty, social discrimination, unhealthy environment and poor living conditions.
Human development thus focuses upon improving the people’s lives, building their capabilities, improving their education, skills, access to health, empowering people, improving their incomes, reducing discrimination, etc.
This can be done by bringing people-oriented policies and good governance. Thus, people are at the centre of all development under the concept of human development.
Question 28.
Elucidate the concept of ‘trading’ in tertiary sector of economy. (5)
Or
Transport is an important tertiary activity. Explain. (5)
Answer:
Trading is essentially buying and selling of items produced elsewhere and specifically intended for profit. The towns and cities where all these works take place are known as trading centres. The rise of trading from barter at the local level to money exchange of international scale has produced many centres and institutions such as trading centres or collection and distribution points.
The types of trading are
Retail Trading This is the business activity concerned with the sale of goods directly to the consumers, Most of the retail trading takes place in fixed establishments or stores solely devoted to selling. Street peddling, handcarts, trucks, door-to-door, mail-order, telephone, automatic vending machines and internet are examples of non-store retail trading.
Wholesale Trading It constitutes bulk business through numerous intermediary merchants and supply houses and not through retail stores. Some large stores including chain stores are able to buy directly from the manufacturers, However, most retail
stores procure supplies from an intermediary source. Wholesalers often extend credit to retail stores to such an extent that the retailer operates very largely on the wholesaler’s capital.
Or
Transport is a tertiary activity which is important for a nation’s economy. It is a service by which people, materials, and manufactured goods are physically carried from one location to another. It is an organised industry created to satisfy the basic need of mobility.
Speedy and efficient transport systems assist in the production, distribution, and consumption of goods in the modern developing societies, the value of the material is significantly enhanced by transportation. In other words, final sale price of an item depends on the total transportation involved from manufacturing to sale point. Transport distance can be measured as, kilometer distance or actual distance of route length; time distance on the time taken to travel on a particular route; and cost distance or the expense of traveling on a route.
In selecting the mode of transport, distance, in terms of time or cost, is the determining factor. Factors affecting demand for transport is influenced by the size of population. The larger the population size, the greater is the demand for transport. Some of the commonly used form of transport are roadways, railways and airways.
They can vary in distance covered, cost and goods or manpower transported. Railways are the cheapest option to carry large amount of cargo over large distances, whereas airways are the fastest but, usually expensive compared to road and railways transport.
Section E
Section E consists of 2 Map based questions of 5 marks each
Question 29.
On the given political map of India, locate and label any five of the following with appropriate symbols. (5)
(i) State having lowest density of population
(ii) Oil refinery in Uttar Pradesh
(iii) Coal mine in Tamil Nadu
(iv) An iron ore mine
(v) Largest producer of cotton
(vi) A major seaport in Tamil Nadu
(vii) Leading producer of sugarcane
Answer:
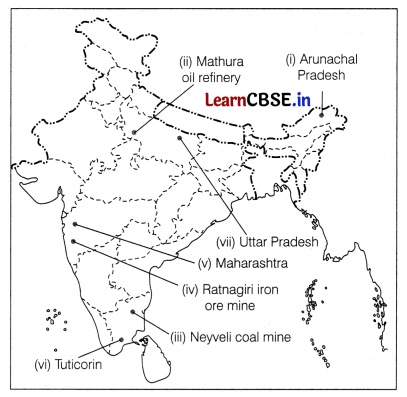
![]()
Question 30.
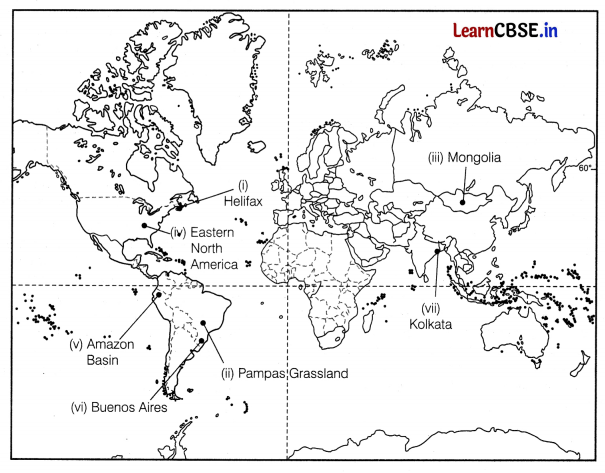
On the given political map of the world, the following seven features are shown. Identify any five of these features and write their correct names on the lines marked near each feature. (5)
(i) East Terminal Stations of Trans-Canadian Railway.
(ii) An area of extensive commercial grain farming in world
(iii) An area of nomadic herding
(iv) An area of mixed farming
(v) An area of subsistence gathering
(vi) A major air port in South America
(vii) A major sea port of Asia
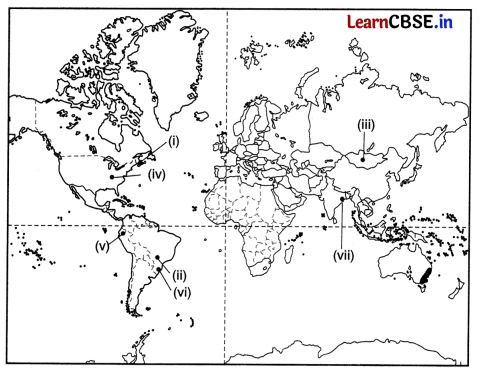
Answer: