Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography with Solutions Set 1 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Set 1 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
General Instructions
- This question paper contains 30 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper is divided into five sections – Sections A, B, C, D and E.
- Section A – Questions no. 1 to 17 are Multiple Choice (MCQ) Type Questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B – Questions no. 18 and 19 are Source Based Questions carrying 3 marks each.
- Section C – Questions no. 20 to 23 are Short Answer (SA) Type Questions carrying 3 marks each. Answer to these questions shall be written in 80 to 100 words.
- Section D – Questions no. 24 to 28 are l..ong Answer (LA.) Type Questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to these questions shall be written in 120 to 150 words.
- Section E – Questions no.29 and 30 are Map-Based Questions.
Section A
Section A consists of 17 questions of 1 mark each
Question 1.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct answer with the help of given options. (1)
Assertion (A) High level of human development group has 53 countries.
Reason (R) A higher investment in people and good governance has set this group apart from others.
Codes
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of A.
(c) Both (A) and (R) are false.
(d) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of A.
Question 2.
Consider the following and choose the correct answer with the help of given codes (1)
| List I (Stages of Population) | List II (Growth Features) |
| A. Period between 1901 to 1921 | 1. Period of steady growth |
| B. Period between 1921 to 1951 | 2. Phase of stagnant growth of Population |
| C. Period between 1951 to 1981 | 3. High but decreasing growth rate |
| D. After 1981 till present | 4. Period of population explosion |
Codes
A B C D
(a) 1 2 3 4
(b) 2 1 4 3
(c) 4 3 2 1
(d) 2 1 3 4
Answer:
(b) 2 1 4 3
Question 3.
Maracaibo, Esskhira and Tripoli ports are classffied as ……………………… . (1)
(a) Ports of call
(b) Naval ports
(c) Oil ports
(d) Entrepot ports
Answer:
(c) Oil ports
Question 4.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct answer with the help of given option. (1)
I. The resource-intensive approach of modern expensive agriculture has become unmanageable for marginal and small farmers due to very meager or no savings to invest in agriculture.
II. Most of such farmers have resorted to availing credit from various institutions and money lenders but crop failures and
low returns from agriculture have forced them to fall in the trap of indebtedness.
Options
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Only statement I is true.
(c) Only statement II is true.
(d) Both the statements are false.
Answer:
(a) Both the statements are true.
![]()
Question 5.
Given below is a list of pillars of human development and its indicators. Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched? (1)
(a) Equity – Making equal access to opportunities available to everybody.
(b) Sustainability – Continuity in the availability of opportunities.
(c) Productivity – Resources must be used keeping in mind the future.
(d) Empowerment – To have the power to make choices
Answer:
(c) Productivity – Resources must be used keeping in mind the future.
Question 6.
Which one of the following is the largest linguistic group of India? (1)
(a) Sino-Tibetan
(b) Austric
(c) Indo – Aryan
(d) Dravidian
Answer:
(c) Indo – Aryan
Question 7.
When was the GATT transformed into World Trade Organisation (WTO)? (1)
(a) 1st Januar3 1994
(b) 1st July, 1994
(c) 1st January, 1995
(d) 1st July, 1995
Answer:
(c) 1st January, 1995
Question 8.
Which of the following is an example of low-order service? (1)
(a) Teacher
(b) Gardener
(c) Lawyer
(d) Musician
Answer:
(b) Gardener
Question 9.
In which of the following group of countries of the world, HYV of wheat and rice were developed? (1)
(a) Japan and Australia
(b) Mexico and Philippines
(c) USA and Japan
(d) Mexico and Singapore
Answer:
(b) Mexico and Philippines
Question 10.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct answer with the help of given options. (1)
Statement I In recent years- ropeways, cableways and pipelines were developed as a means of transport.
Statement II They were developed to cater to the demands of transporting specific goods under special circumstances.
(a) Only statement I is correct.
(b) Only statement II is correct.
(c) Both the statements are correct, and statement II correctly explains statement I.
(d) Both the statements are true, but not related with each other.
Answer:
(c) Both the statements are correct, and statement II correctly explains statement I.
Question 11.
Given below are the steps to generate geothermal energy. Arrange the following in correct sequence (1)
I. It is so hot that when it rises to the Earth’s surface, it turns into steam.
II. Groundwater in such areas (where the geothermal gradient is high) absorbs heat from the rocks and becomes hot.
III. This steam is used to drive turbines and generate electricity.
IV. Geothermal energy exists because the Earth grows progressively hotter with increasing depth.
(a) IV II III I
(b) II I IV III
(c) I IV III II
(d) III II IV I
Answer:
(a) IV II III I
![]()
Question 12.
Which of the following is not the benefit of rainwater harvesting? (1)
(a) It increases water availability.
(b) It checks the declining groundwater table.
(c) It improves the quality of groundwater through dilution of contaminants like fluoride and nitrates.
(d) Helpful in production of hydroelectricity.
Answer:
(d) Helpful in production of hydroelectricity.
Question 13.
Which of the following plans was introduced to improve the conditions of roads in India after independence? (1)
(a) Five-Year Road Plan
(b) Nagpur Plan
(c) Ten Years Road Plan
(d) Twenty Years Road Plan
Answer:
(d) Twenty Years Road Plan
Question 14.
If you are asked to formulate the National Water Policy, what will be the utmost important priority for you? (1)
(a) To provide water for generation of hydroelectricity.
(b) Availability of water for industries.
(c) To provide drinking water.
(d) Availability of water for navigation.
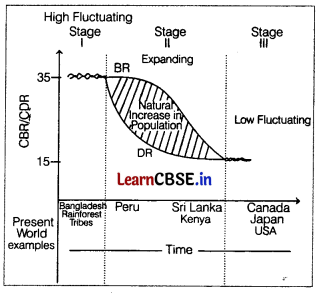
Directions Read the following graph and answer questions no 15 to 17.
Answer:
(c) To provide drinking water.
Question 15.
How does the natural increase in population occur, as per the graph? (1)
(a) Birth Rate – Death Rate
(b) Death Rate + Birth Rate
(c) Growth Rate – Birth Rate
(d) Birth Rate + Migration
Answer:
(a) Birth Rate – Death Rate
Question 16.
What does the transition from high fluctuating stage to low fluctuating stage indicate? (1)
(a) Shift from urban industrial economy to rural agrarian economy.
(b) Shift from rural agrarian economy to urban industrial economy.
(c) Low birth and death rate to high birth and death rate.
(d) Migration from urban to rural areas.
Answer:
(b) Shift from rural agrarian economy to urban industrial economy.
![]()
Question 17.
From the given graph, what condition can you infer about the least developed countries? (1)
(a) High birth rate and high death rate
(b) Low birth rate and low death rate
(c) High birth rate and low death rate
(d) Low birth rate and high death rate
Answer:
(a) High birth rate and high death rate
Section B
Section B consists of 2 Source based questions of 3 marks each
Question 18.
Read the given passage carefully and answer the questions that follow. Settlements vary in size and type. They range from a hamlet to metropolitan cities. With size, the economic character and social structure of settlements changes and so do its ecology and technology. Settlements could be small and sparsely spaced, they may also be large and closely spaced.
The sparsely located small settlements are called villages, specializing in agriculture or other primary activities. On the other
hand, there are fewer but larger settlements which are termed as urban settlements specialising in secondary and tertiary
activities.
The basic differences between rural and urban settlements are as follows:
The rural settlements derive their life support or basic economic needs from land-based primary economic activities, whereas,
urban settlements depend on processing of raw materials and manufacturing of finished goods on the one hand and a variety
of services on the other.
Cities act as nodes of economic growth, provide goods and services not only to urban dwellers but also to the people of the rural settlements in their hinterlands in return for food and raw materials. This functional relationship between the urban and rural settlements takes place through transport and communication networks.
Rural and urban settlements differ in terms of social relationship, attitude and outlook. Rural people are less mobile and therefore, social relations among them are intimate. In urban areas, on the other hand, way of life is complex and fast, and social relations are formal.
(a) On what basis rural and urban settlements can differ from each other. (1)
(b) ‘Towns act as nodes of economic growth.’ How? (1)
(c) Social relationships are more intimate in rural areas in comparison to urban areas. Justify. (1)
Answer:
(a) Rural and urban settlements are differ from each other in terms of social relationships, attitude, and outlook.
(b) Towns act as nodes of economic growth because they provide goods and services not only to urban dwellers but also to the people of the rural settlements in their hinterlands in return for food and raw materials.
(c) Rural people are less mobile and therefore, social relationships are more intimate in rural areas. In urban areas, on the other hand, of life is complex and fast, and social relations are formal.
Question 19.
observe the given map and answer the following questions.
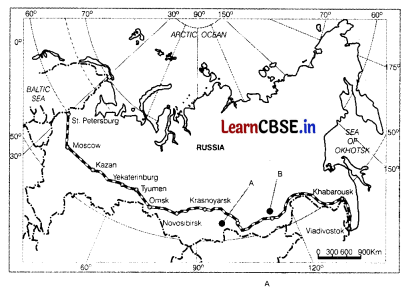
(a) Name the Railway line and the country where it lies. (1)
(b) Name the stations marked as A and B. (1)
(c) State two reasons why it is the most important route in Asia? (1)
Answer:
(a) Trans-Siberian Railway, Russia
(b) A-Angarsk, B-Chita
(c) It is the most important route in Asia because it runs through the Chita, which is an important agro-center, and Irkutsk, a fur Centre. It also connects links to the Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Mongolia, and China.
Section C
Section C consists of 4 questions of 3 marks each
Question 20.
‘The basic goal of development is to create conditions where the people can live a meaningful life’. What do you mean by meaningful life? (3)
Or
How do people’s choices get affected in different aspects of life due to lack of human development? (3)
Answer:
Meaningful life means the life which include the following
- Healthy life
- Purposeful life
- Free to achieve their goal
- Able to develop their talent
Or
The lack of human development can limit individual’s choices in education, health, economic opportunities, and social and cultural factors. It can result in poor health outcomes, limited access to education and job training, discrimination and exclusion from certain groups, and reduced options for improving financial situations. To ensure individuals have the knowledge, skills, and resources to make informed decisions, it is essential to invest in human development. This will enable people to lead fulfilling lives and contribute to their communities.
![]()
Question 21.
What are the features of National Youth Policy? (3)
Answer:
The National Youth Policy 2014 of India launched in February 2014 proposes a holistic ‘vision’ for the youth of India.
The following are the features of National Youth Policy
- It aims to provide a framework for the holistic development of young people in the country and emphasizes the need for youth empowerment, participation, and inclusion.
- The policy focuses on five key areas that are education and skill development, health and well-being, employment and entrepreneurship, civic engagement and youth leadership, and social inclusion.
- It also recognises the importance of digital literacy and the need to address emerging challenges facing youth such as substance abuse, mental health issues, and violence.
- It seeks to promote the overall development of young people and enable them to contribute positively to society.
Question 22.
How is ‘Naturalisation of Humans’ different from ‘Humanisation of Nature’? (3)
Or
‘Geography got subjected to dualism and the wide-ranging debates started with regard to the subject matter of geography as a
discipline.’ Mention any three dualisms that exist in Geography. (3)
Answer:
Naturalisation of Humans are different from Humanisation of Nature in the following ways
Naturalisation of Humans
- It refers to the point of view supporting environmental control on human action.
- Human listened to nature, was afraid of its fury, and worshipped the natural forces,
- Many of primitive societies live in complete harmony with their natural environment.
- The physical environment for such societies becomes the Mother Nature Humanisation of Nature With social and cultural development, humans develop better and more efficient technology.
- They move from a state of Necessity to a state of freedom.
- People create possibilities with the resources obtained from the environment.
- Human has modified their surroundings according to their needs,
- Imprints of human may be seen everywhere on the Earth.
Or
- The three dualism in geography which started wide-ranging debates in the discipline of geography are
- Whether geography as a discipline should be a law making! the arising (nomothetic) or descriptive (idiographic),
- Whether the approach of the study should be regional or systematic.
- Whether geographical phenomena can be interpreted theoretically or through a historic-institutional approach?
Question 23.
“Quaternary activities centre around research and development.” Examine the statement. (3)
Answer:
Quaternary activities centre around research and development, due to the following reasons
- It is an advanced form of services.
- It involves specialised knowledge and technical skill.
- It involves, collection, production and dissemination of information
Section D
Section D consists of 5 questions of 5 marks each
Question 24.
“There is low yield per acre but high yield per person in the interior parts of semi-arid lands of the mid-latitudes in the world.”
Support the statement with suitable examples from different parts of the world. (5)
Answer:
The interior parts of semi-arid lands of the mid-latitudes in the world are the areas where extensive commercial grain cultivation takes place. Here the size of farms is very large and population is in small number Operations of cultivation, right from ploughing to harvesting is mechanised.
Yield per person is high as the number of people working in farms is less and lot of machines is used. The size of the farms is very large due to which per acre production or yield is low even though the total production is high. This type of agriculture is practiced in Eurasian Steppes, Canadian and American Prairies, Pampas of Argentina, Velds of South Africa, Australian Downs, and the Canterbury Plains of New Zealand.
Question 25.
Formulate the guidelines to promote sustainability in the Indira Gandhi Canal Command Area. (5)
Answer:
The guidelines to promote sustainability in the India Gandhi Canal Command Area are as follows
There is an urgent need to strictly implement the water management policy.
Water-intensive crops should be avoided and instead plantation crops such as Citrus fruits should be encouraged.
The Command Area Development programmes such as lining of water courses, land development. and levelling and warbands system (equal distribution of canal water in the command area of outlet) shall be effectively implemented to reduce the conveyance loss of water. Efforts should be made to reclaim areas affected by water logging and soil salinity, Afforestation, shelter belt plantation and pasture development are necessary for eco-development.
![]()
Question 26.
Land degradation in India is caused by human-made processes that are more harmful than natural processes. Explain the
statement with suitable examples. (5)
Or
How has noise pollution become a serious problem in recent years in India Explain. (5)
Answer:
Land degradation is generally understood either as a temporary or a permanent decline in productive capacity of the land.
The causes or factors responsible for ‘and degradation in India are given below
- Soil erosion
- Waterlogging
- Salinization
- Alkalinisation of land
Land is constantly used without managing its fertility, it is degraded, and its productivity declines. Deforestation, overgrazing, mining, and quarrying too are responsible for land degradation in India. Thus, land degradation caused by human processes s more harmful than natural processes in India.
Man-made degraded wastelands such as degraded shifting cultivation areas, degraded land under plantation crops, degraded forest, mining, and industrial wastelands are 5.8% of the total geographical area of the country.
In states such as Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, and Odisha, deforestation due to mining has caused severe land degradation.
In states such as Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra overgrazing is one of the main reasons for land degradation.
Or
Noise pollution has became a serious problem in recent years due to a variety of technological innovations which are as follows
The biggest nuisance is the noise produced by traffic, because its intensity and nature depend upon factors, such as the type of aircraft, vehicle, train and the condition of road, as well as that of vehicle (in case of automobiles).
In sea traffic, the noise pollution is confined to the harbour due to loading and unloading activities being carried. Industries cause noise pollution but with varying intensity depending upon the type of industry. Ocean noise is due to the vast increase in global shipping trade, the number of ships plying the oceans and higher speed of vessels.
Question 27.
How technological innovations are important aspect of modern manufacturing industries? Explain any five aspects. (5)
Or
“High technology, or simply high-tech, is the latest generation of manufacturing activities.” Justify the statement with suitable arguments. (5)
Answer:
Technological innovations through research and development strategies are an important aspect of modern manufacturing for quality control, eliminating waste and inefficiency, and combating pollution.
Five aspects in this regard are as follows
- Complex machine technology is needed so that high-quality goods are produced at less time.
- It requires vast capital so that machines with the latest technology can be used in manufacturing.
- Extreme specialisation and division of labour is required, that can work efficiently on the machines.
Supply chain management technologies such as Radio-frequency Identification (RAD) and GPS tracking help manufacturers optimise their supply chain by providing real-time visibility and improving coordination.
The manufacturers use data analytics tools to analyse large volumes of data generated by their operations, enabling them to identity patterns, optimize production processes, and make data-driven decisions.
Or
High technology or high-tech is the latest generation of industries manufacturing industries due to the following reasons
High-tech industries require great deal of Scientific Research and Development (R&D) and produce highly sophisticated products.
These Industries improve their products very fast to meet the growing market demands.
As their products are highly sophisticated therefore it requires highly skilled labour.
Professional (White Collar) workers are main workforce.
Robotics on the assembly line, computer-aided design (CAD) and manufacturing, electronic controls of smelting and refining process are notable examples of high-tech industry. Neatly spaced, low, modern, dispersed, office-plant-lab buildings rather than massive assembly structures, factories and storage are mark the high-tech industrial landscape.
Question 28.
What are the advantages of sea ports for India? (5)
Or
Why is seaport termed as gateway of international trade?
Answer:
Seaports play a vital role in the economic development of India. The advantages of seaports for India are as follows
Trade Facilitation It provide an efficient and cost-effective mode of transportation, facilitating international trade and commerce. It helps in boosting the country’s economy and increasing its competitiveness in the global market.
Employment Generation It provide direct and indirect employment opportunities to a large number of people, including cargo handlers, port operators, customs officials, and other support staff.
Regional Development It act as a catalyst for the development of the surrounding regions, stimulating economic activity and encouraging the growth of related industries such as logistics and manufacturing.
Revenue Generation It generate significant revenue for the government through customs duties, port charges, and other fees.
Infrastructure Development The development of sea ports requires the creation of supporting infrastructure such as roads, railways, and warehousing facilities, which can have a positive impact on the overall development of the country.
Seaports are termed as gateways of international trade due to the following reasons
- The ports act as suction points of the resources from their hinterlands.
- The extension of railways and roadways towards the interior facilitates the linking of the local markets to regional markets, regional markets to national markets and national markets to the international market.
- Cargoes and travellers pass from one part of the world to another through these ports.
- The ports provide facilities of docking, loading, unloading, and the storage facilities for cargo.
Section E
Section E consists of 2 Map based questions of 5 marks each
Question 29.
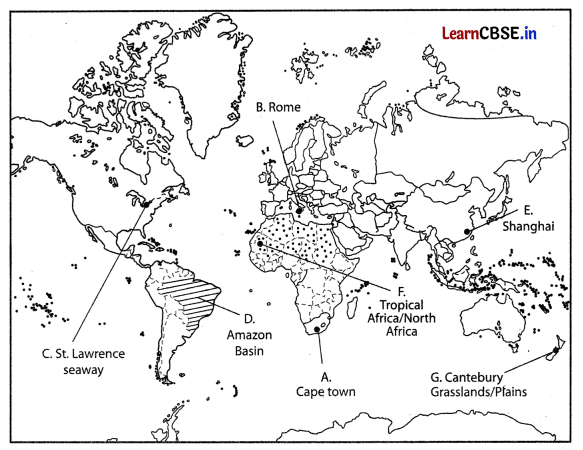
On the given political map of the World, seven geographical features have been marked as A, B, C, D, E, F and G. Identify any five with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines drawn near each feature. (5)
(i) A major seaport
(ii) An international airport
(iii) An important Seaway
(iv) An area of subsistence gathering in South America
(v) An important seaport of Asia
(vi) An area of Nomadic Herding
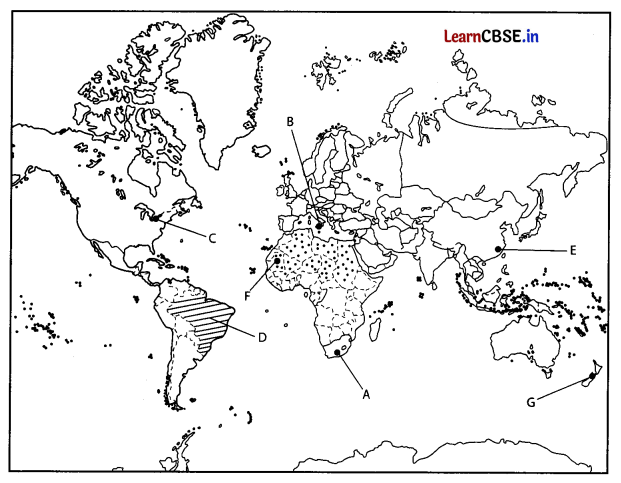
Answer:
![]()
Question 30.
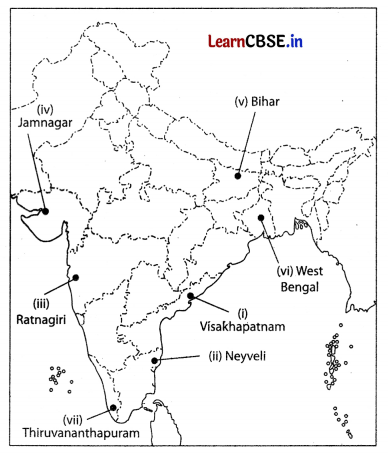
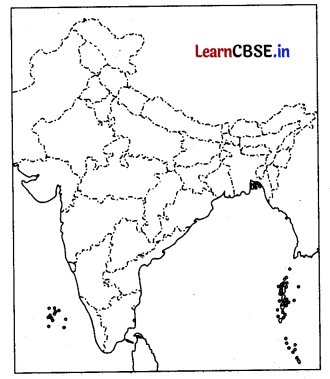
Locate and label any five of the following geographical features on the Political Outline map of India with appropriate symbols. (5)
(i) An important seaport in Andhra Pradesh.
(ii) An important coal mine in Tamil Nadu.
(iii) Ratnagiri – iron ore mines.
(iv) An oil refinery in Gujarat.
(v) The state with highest population density.
(vi) The state leading in the production of jute.
(vii) An international airport in Kerala.
Answer: